CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Set-8
Class 12thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Set-8
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Set 8 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section-B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section-C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section-D has 2 case-based questions of 4 marks each; and Section-E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided
in some questions.
A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions. - Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section A
Question 1.
Among the following crosses, which cross will yield recessive
progeny in Frgeneration?
(a) IT × tt
(b) Tt × tt
(c) tt × tt
(d) TT
× TT
Answer:
(c) A cross between homozygous recessive parents, i.e. tt xtt
will yield F1 recessive progeny.
Parents → tt × tt
Gametes → t
× t
F1 → tt (Recessive homozygous trait)
Question 2.
Cranial capacity of approx. f650cc is associated with which
man during human evolution?
(a) Cro-Magnon man
(b) Neanderthal man
(c)
Homo erectus
(d) Homo habilis
Answer:
(a) The Cro-Magnon man is
considered the closest evolutionary form of living modern man, Its cranial
capacity was about 1650cc and they were intelligent, hard working, cave
dwellers.
Question 3.
Given below are the modes of pollination with their
pollinating agents.
| Methods | Agent required | ||
| A. | Anemophily | 1. | Pollination takes place via the winds |
| B. | Hydrophily | 2. | Pollination by hydrocarbons |
| C. | Ornithophily | 3. | Pollination is performed by birds |
| D. | Entomophily | 4. | Insects carry out pollination |
Methods Agent required
A. Anemophily 1. Pollination takes place via the
winds
B. Hydrophily 2. Pollination by hydrocarbons
C. Ornithophily 3.
Pollination is performed by birds
D. Entomophily 4. Insects carry out
pollination
Select how many pollinating agents are perfectly matched with
their methods?
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
The correct option is ‘b’ as anemophily, ornithophily and entomophily are
correctly matched with their pollinating agents, while in hydrophily water is
the medium for pollination.
Question 4.
On what basis an area would be classified as a hotspot?
(a)
Disrupted network of interaction
(b) Number of endemic species and degree of
threat
(c) Habitat destruction
(d) Presence of alien species
Answer:
(b) An area is considered as a hotspot when it is extremely rich in
species diversity, have high endemisim and are under constant threat of
extinction.
Question 5.
A patient is admitted for myocardial infarction. Which of the
following bioactive molecule can improve his condition?
(a) Cyclosporin-A
(b) Statins
(c) Protease and pectinase
(d) Streptokinase
Answer:
(d)
Streptokinase is derived from the bacteria, Streptococcus. It is used to remove
blood clots from the vessels of patients suffering from myocardial
infarction.
Question 6.
Stability of DNA is impacted by
(a) deoxyribose sugar
(b) presence of thymine in place of uracil
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None
of the above
Answer:
(c) DNA contains deoxyribose sugar and thymine
instead of uracil. These two factors along with the double helical structure
impacts the stability to a DNA molecules.
Question 7.
Which of the following is false regarding gene therapy?
(a)
Gene therapy may be effective in the treatment of cancer
(b) It could be used
to treat genetic diseases caused by single gene effect
(c) Gene therapy
replaces faulty genes with functional genes
(d) It is widely used everywhere
with great success
Answer:
(d) Gene therapy is not widely used everywhere
with great success because, it is still in trial and tested stages for many
diseases.
Question 8.
The cycle of events shown below highlights in vitro
replication of DNA.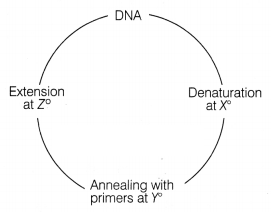
X, Y, Z represents specific temperature for each step. Choose
the correct option which allows in vitro replication of DNA correctly?
| X | Y | Z | |
| (a) | 98°C | 105°C | 25°C |
| (b) | 100°C | > 25°C | < 80°C |
| (c) | 95°C | 50°C | 72°C |
| (d) | 72°C | <25°C | > 80°C |
Answer:
(c) tn vitro replication of DNA is called PCR (Polymerase Chain
Reaction). The first step of PCR is denaturation, i.e. separation of dsDNA which
occurs at 95°C (X). The next step is annealing of RNA primer with separated
strands, for which temperature is lowered to 50°C (Y) followed by extension at
72°C (Z).
Question 9.
Having become an expert on gel electrophoresis, you are asked
to examine a gel for a colleague. Where would you find the smallest fragments of
DNA?
(a) Near the positive electrode, farthest away from the wells
(b)
Near the negative electrode, close to the wells
(c) Near the top, near the
negative pole
(d) Near the middle they tend to slow-down after the first few
minutes
Answer:
(a) The smallest fragments of DNA are found near the
positive electrodes as DNA is negatively charged. These fragments travel towards
the anode (farthest away from the leading wells).
Question 10.
In a grassland ecosystem, a food chain comprising of four
trophic level exists. Identify the amount of correct energy that will be
conserved at each of its trophic level.
| Levels of food chain | Energy conserved | |
| (a) | Primary consumer | 30% of second level |
| (b) | Tertiary consumer | 20% of third level |
| (c) | Producer | 40% of first level |
| (d) | Secondary consumer | 10% of second level |
Levels of food chain Energy conserved
(a) Primary consumer 30% of second
level
(b) Tertiary consumer 20% of third level
(c) Producer 40% of first
level
(d) Secondary consumer 10% of second level
Answer:
(d) According
to the Lindemann’s law of energy transfer, only 10% of energy is conserved at
each level.
So, at all levels, 10% of their previous trophic level’s energy
will get conserved. Secondary consumer conserved 10% energy of second trophic
level, i.e. primary consumer. Hence, option (d) is the correct one.
Question 11.
Bacteria possessing restriction endonuclease enzyme
remain
(a) affected by bacteriophages
(b) unaffected by bacteriophages
(c) resistant to drugs and heat
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) The
bacteria possessing restriction endonucleases remains unaffected by
bacteriophages because DNA of bacteria is methylated when compared to that of a
bacteriophage.
Question 12.
The diagram given below show the inheritance of haemophilia
in a family. What will be the genotype of the individual marked M?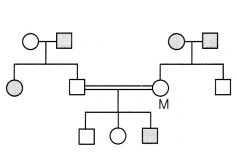
(a) M – XY
(b) M – XX
(c) M –
XhXh
(d) M – XhX
Answer:
(d) The
genotype of the individual marked ‘M’ has to be XhX, i.e. she has to
be the carrier, so as to produce an individual who is affected, in the last
generation.
Question Nos. 13 to 16 consist of two statements, Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below.
(a)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of
Assertion
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the
correct explanation of Assertion
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is
false
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true
Question 13.
Assertion (A) : An infected mother can pass syphilis to her
developing foetus.
Reason (R) : Some pathogens can cross the placental
barrier.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the
correct explanation of Assertion.
During parturition, some pathogen from infected mother’s blood can enter the newborn through placental blood. This transmission would result in congenital syphilis.
Question 14.
Assertion (A) : Mutation, genetic recombination, natural
selection and isolation form the most essential process for evolution.
Reason
(R) : All new traits arise from these processes.
Answer:
(a) Both
Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of
Assertion.
For evolution to occur, changes in gene frequency is essential. These changes are brought about by mutation, natural selection, isolation (reproductive as well as geographic) resulting in the formation of new species over a longer span of time.
Question 15.
Assertion (A) : In a monohybrid cross,
F2-genotypic ratio is 1 : 2 : 1.
Reason (R) : It gives phenotypic
ratio 3 : 1.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is
not the correct explanation of Assertion.
A monohybrid cross involves the
crossing of single pair of contrasting traits such as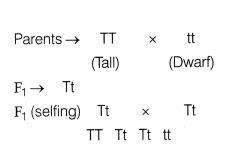
Genotypic ratio is 1 : 2 : 1
Phenotypic ratio is 3 :
1.
Question 16.
Assertion (A) : Menstrual phase is also compared to shedding
tears for the lost ovum.
Reason (R) : In the menstrual phase, loss of
endometrial lining takes place due to reduced titre of progesterone.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct
explanation of Assertion.
Menstrual phase is the phase of menstrual flow/ menses which continues for 3 – 5 days and involves discharge of blood (a total of 50 – 100 mL) along with shedding off endometrial lining (uterus, Fallopian tube and vagina) due to reduced levels of both oestrogen and progesterone hormones. As such menstrual phase is also called funeral of unfertilised egg of shedding tears of lost ovum.
Section B
Question 17.
The daughter born to a couple where father is haemophilic and
mother is normal, could be a carrier/normal. Show with the help of a Punnett
cross. Give reason for your answer.
Answer:
The daughter born to a
haemophilic father and normal mother would be a carrier. This is because
haemophilia is sex linked (X-linked) recessive disorder which follows
criss-cross inheritance, (i.e. it gets transmitted) as shown below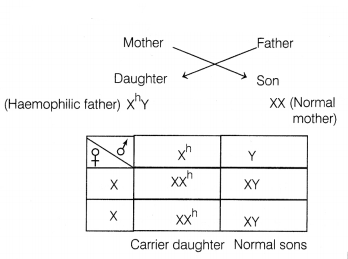
Question 18.
Refer to the following diagram of the side view of the male
reproductive system to answer the following questions.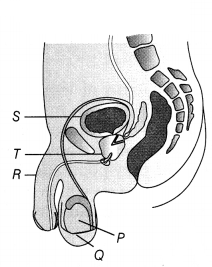
(i) Name the organs labelled as P, Q and R.
(ii) State the
function of parts labelled S and T.
Answer:
(i) The organs labelled P, Q
and R are identified as testis, scrotum and penis, respectively.
(ii) Part S is urinary bladder which is meant to temporarily store urine.
While, part T is the prostate gland, which is an accessory gland of male
reproductive system. It produces nutrients and enzymes required for sperm
activation.
Question 19.
Observe the graph given below and answer the following
question.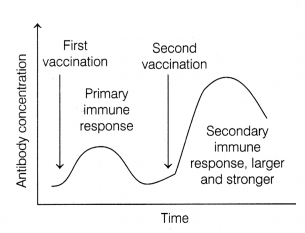
Explain the response initiated in the body after first and second
vaccination.
Answer:
After the first vaccination the primary immune
response is generated. It is of low intensity and after every primary response
cell memory store details of the encounter.
After second vaccination the secondary anamnestic response is generated, it is of high intensity. It has the capacity to distinguish between self and foreign cells.
Question 20.
The image below shows type of bioreactor.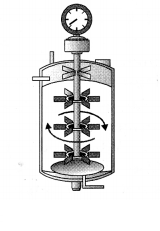
(i) Give the name of the type of bioreactor shown.
(ii)
List five growth conditions that a bioreactor should provide for obtaining the
desired product.
Answer:
(i) The bioreactor shown in the figure is the
simple stirred-tank type bioreactor.
(ii) A bioreactor provides optimum growth conditions like temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins and oxygen to get desired products.
Question 21.
For a species-area relationship, Z
(indicates species
richness), is calculated as
· 0.7 for area P
· 0.16 for area Q
Which
area has higher species richness and steeper slope? What is the significance of
species-area relationship?
Or
The following graph shows the species-area
relationship. Answer the following , questions as directed.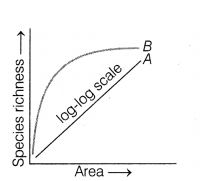
(i) Name the naturalist who studied the kind of relationship
shown in the graph. Write the observations made by him.
(ii) Write the
situations as discovered by the ecologists when the value of Z (slope of the
line) lies between (a) 0.1 and 0.2 (b) 0.6 and 1.2. What does Z stand for?
Answer:
According to Alexander van Humboldt, species richness increases with
explored area.
Thus, area P with species richness (Z), 0.7 will have more
species and steeper slope.
Species-area relationship helps in understanding
the structure of a habitat and study of factors which impact the survival of a
species.
Or
(i) Alexander von Humboldt studied the relationship shown in
the graph. He observed that species richness increased within an explored area,
but only upto a limit.
(ii) (a) Value of Z lies between 0.1 – 0.2, when area is small to normal.
(b) Value of Z lies between 0.6-1.2, when area is very large.
Z is slope of
the line, which is regression coefficient.
Section C
Question 22.
Carefully observe the pyramid of number shown below.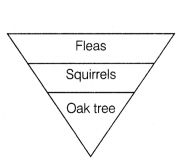
(i) Why is this pyramid inverted?
(ii) How much energy is
being transferred at each level? Will the pyramid of energy if drawn for this
food chain also be inverted? Give reason.
Answer:
(i) The pyramid of
number is inverted because the oak tree is only one in number as compared to the
squirrels and fleas. Pyramid of number does not account for the relative size of
organisms present at each trophic level.
(ii) Total 10% of the energy is transferred to each level from the lower trophic level. No, pyramid of energy will not be inverted because the producers always have more energy than other level which continuously decreases as it passes from one trophic level to next.
Question 23.
‘Transcription is considered more complex in eukaryotes’.
Elaborate.
Answer:
Transcription is considered to be more complex in
eukaryotes because it has additional complexities.
(i) The three types of RNA
polymerases in the nucleus show division of labour.
RNA polymerase-I
transcribes rRNAs (28S, 18S and 5.8S).
RNA polymerase-II transcribes the
precursor of mRNA, called hnRNA.
RNA polymerase-III transcribes tRNA, 5s rRNA
and snRNA.
(ii) hnRNA contains both coding sequences called exons and non-coding sequences called introns. Hence, it undergoes a process called splicing, in which the non-coding sequences (introns) are removed and the coding sequences (exons) are joined together in a defined order.
(iii) In capping, unusual nucleotide, methyl guanosine triphosphate residues are added at the 5’ end of the hnRNA.
(iv) In tailing, 200-300 adenylate residues are added at the 3’end of the hnRNA.
Question 24.
The ability of the body (host) to fight against the disease
causing agents is called immunity. It is of two types, i.e. innate immunity and
acquired immunity.
(i) Describe any two situations in which preformed
antibodies are given to a person. What kind of immunisation is it? Also, discuss
its advantages.
(ii) Describe autoimmunity.
Answer:
(i) Immunisation is
of two kind-active and passive. Active immunity results when exposure to a
disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that
disease. It can be acquired through the natural immunity or vaccine-induced
immunity.
Passive immunisation is the introduction of preformed (or readymade) antibodies for an immediate immune response. It is given in the following situations
- In the case of snake bites, an antitoxin against venom is directly given.
- In case of injury, tetanus injection is given to avoid muscle spasms.
Advantage These preformed antibodies develop quick immune response in the recipient against the infective agents.
(ii) Autoimmunity is the state in which the body loses its ability of distinguishing between self and non-self cells.
The body’s immune system starts destroying its own cells which leads to fatal malfunctions called as autoimmune diseases, e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, Grave’s disease, haemolytic anaemia, etc.
![]()
Question 25.
Study the graph given below and answer the questions that
follows.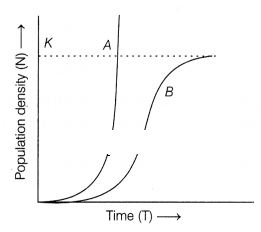
(i) Write the status of food and space in the curves A and B.
In the absence of predators, which one of the two curves or growth models would
appropriately depict the prey population?
(ii) According to you which growth
curve is more realistic and why?
Answer:
(i) The status of food and space
resources in curve A is unlimited, while in curve B, the sources of food and
space are limited.
In the absence of predators, the curve 6 would
appropriately depict the competition for limited food and shelter resources
within the prey population.
(ii) Since, resources for growth of most animal populations are finite and become limiting sooner or later, the logistic growth model, i.e. curve B for population is considered a more realistic one.
Question 26.
Human insulin can be produced in bacterial cells using
biotechnology. List any two applications of recombinant DNA technology, each in
medical diagnosis and agriculture.
Answer:
Transgenic bacteria have been
produced that translate the constituting polypeptide chains of human insulin.
These polypeptides can be extracted from the bacterial cells and combined by
creating disulphide bonds to produce human insulin.
In humans, insulin is produced as a prohormone with three polypeptides A, B and C. After processing, the C-peptide is removed and mature insulin is formed. When transgenic bacteria are used, instead of producing extra stretch of C-peptide, only A and B polypeptides are produced and then linked to produce mature insulin directly.
Various applications of recombinant DNA technology are as follows
(i)
Medical diagnosis It is used to detect HIV infection using ELISA.
(ii)
Agricultures It is used in agriculture to produce genetically modified organisms
such as FlavrSavr tomatoes, Golden rice, Bt cotton, etc. These are either
nutritionally enriched or resistant to pests, worms, etc.
Question 27.
A newly married couple was afraid of using contraceptive and
IUDs. So, they opted for natural methods of contraception. During a random
councelling session, the couple found that natural contraception is not
reliable, instead they can use barrier contraceptives.
(i) Name two barrier
methods of contraception that could be used by this couple.
(ii) Give an
example each of hormonal IUDs, Cu-IUDs and non-medicated IUDs.
(iii) What
does the contraceptive pill ; Saheli contains?
Or
Neha, a NGO worker is
given the responsibility to educate the sex workers about sexually transmitted
diseases. While the sex workers were initially hesitant and reluctant to attend
Neha’s session. Neha was patient and convinced them by explaining the importance
of understanding STD so that they can protect themselves and lead healthy
reproductive lives. The workers agreed and were happy to attend the session.
(i) Specify any two ways of prevention from such diseases.
(ii) What are
STDs?
(iii) What are the symptoms of STDs?
Answer:
(i) Condoms and
cervical caps are the two barrier methods of contraception that could be used
by
this couple.
(ii) Hormonal IUD — Progestasert and LNG-20 Cu-IUDs –
Multiload-375 and Cu-T. Non-medicated lUDs – Lippes loop.
(iii) Saheli is
once a week contraceptive pill, which contain a non-steroidal preparation,
centchroman.
Or
(i) STD’s can be prevented by the following measures.
(a) Avoid sex with unknown/multiple partners,
(b) Always use condoms during
coitus.
(ii) The diseases that are mainly passed from one person to another during sexual intercourse are known as Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs). These are also known as Venereal Diseases (VD).
(iii) The early symptoms of STDs are minor and include itching, fluid discharge, slight pain, swelling, etc. in the genital region.
Question 28.
What is GMO? List any five possible advantages of a GMO to a
farmer.
Answer:
The plants, bacteria, fungi and animals whose genes have
been altered are called Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs).
Advantages of
GMOs to a Farmer
(i) Crops become more tolerant to abiotic stresses like
cold, drought, salt and heat.
(ii) Dependence on chemical pesticides has
reduced, i.e. pest-resistant crops.
(iii) Helped to reduce post-harvest
losses.
(iv) Efficiency of mineral usage increased in plants, preventing
early exhaustion of fertility of soil.
(v) Enhanced nutritional value of
food, e.g. vitamin-A
enriched rice.
Section D
Q. Nos. 29 and 30 are case-based questions. Each question has 3 subparts with internal choice in one subpart.
Question 29.
Study the given diagrams and answer the questions that
follows.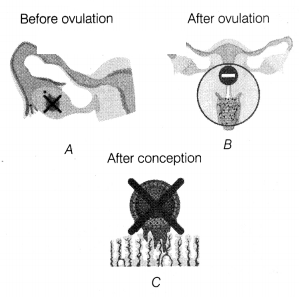
(i) Identify A, B and C with reference to the mechanism of action of themorning
after pill. [1]
(ii) On the basis of the above diagrams, explain the effects
of pills on menstrual cycle. [2]
(iii) Mention the side effects of emergency
pill. [1]
Or
(iii) What are the contents of Saheli pills? [1]
Answer:
(i) A-Block ovulation
B-Prevents sperm from advancing
C-Blocks
implantation
(ii) Pills cause alterations in the menstrual cycle. These alterations depends on the time of the menstrual cycle at which it is taken.
Before ovulation : The dose of pill will induce deprivation bleeding, usually within a few days of taking the pill.
After ovulation : It is possible that due to the dose of pill the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle will lengthen, with the consequent delay of menstruation.
(iii) Side effects of emergency pill
(a) Nausea
(b) Vomiting
(c)
Sensitive breasts
(d) Abdominal pain
Or
(iii) Saheli contains progestin
with no oestrogen and a non-steroidal preparation called centrochroman.
Question 30.
The cross below shows the blood group phenotypes for mother
and her two children. Observe the same carefully and answer the questions that
follow.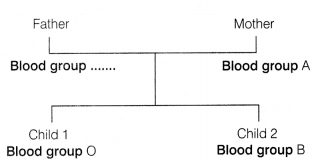
(i) Analyse the cross and predict the blood group genotype of the father.
[1]
(ii) Explain the phenomenon of codominance in regard of the above given
cross. [1]
(iii) State the basis behind the occurrence of
different
genotypes of blood types in human beings. [2]
Or
(iii) Prepare a cross to
show the genotypes of children born to the parents where father has blood group
A and mother has B blood group. [2]
Answer:
(i) In the cross given, the
child 1 has blood group O, i.e. is recessive in nature. Thus, father needs to
have allele i, while, child 2 has blood group B, so father need to have
IB. Hence, the blood group of father would be B and the genotype is
IBi.
(ii) Codominance is the phenomenon in which two alleles expresses themselves independently when present together in an organism.
(iii) The gene I responsible for ABO blood group in humans have three
alleles, i.e. IA,IB,i.
In this, the alleles
IA and IB are dominant over i and produce slightly
different sugar in comparison to i which does not produces any sugar.
Therefore, IAIB when present together in single organism expresses their own genotypes due to codominance. Hence, persons can have both A and B types of sugars.
Hence, total different six genotypes are present in human beings.
Or
(iii)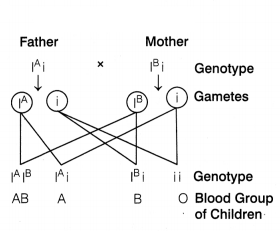
Section E
Question 31.
Three different type of crosses were made between plants
P1 and P2 for different characters. The
F1-generation obtained is tabulated below. Mention the various laws
of inheritance associated with them.
Also find the phenotypic ratio of
F2– generation of each cross.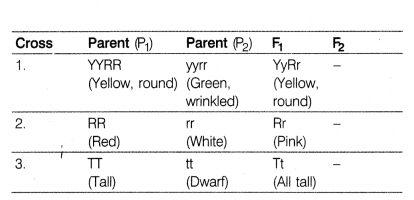
Or
Study the schematic representation of DNA fingerprinting.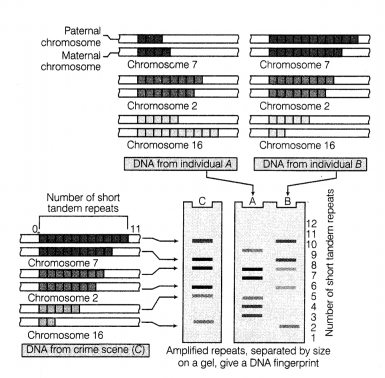
(i) Explain the methodology included in the above figure.
(ii) Mention the
cause of DNA polymorphism.
Answer:
Cross 1 is associated with law of
independent assortment.
According to this law when two pairs of traits are
combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of character is independent of
other pair of characters. In dihybrld cross the phenotype of
F2-generation is round yellow, wrinkled yellow, round green and
wrinkled green appear in the ration of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
Cross 2 is associated with law of incomplete dominance.
Incomplete
dominance is a form of gene interaction in which both alleles of a gene at a
locus are partially expressed, often resulting in an intermediate or different
phenotype. It is also known as partial dominance.
For example, in roses, the allele for red colour is dominant over the allele for white colour. But the heterozygous flower with both the alleles are pink in colour.
The F2-generation obtained by self-crossing the
F1-generation are as follows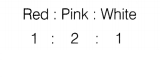
Cross 3 is associated with law of dominance.
This law states that when
parents with pure, contrasting traits are crossed together, only one allele
express itself in next generation. The allele which express itself is called
dominant allele and which do not express is called recessive allele.
The F2-generation obtained by selfing F1 hybrids are as
follows :
Or
(i) The methodology includes
(a) DNA is isolated and
digested by the restriction endonucleases.
(b) DNA fragments are separated by
gel electrophoresis.
(c) Separated DNA fragments are transferred to synthetic
membranes like nitrocellulose or nylon.
(d) Hybridisation using labelled VNTR
probe.
(e) Hybridised DNA fragments are detected by autoradiography.
The
sensitivity has been increased by the use of polymerase chain reaction.
(ii) DNA polymorphism occurs due to mutation. The mutations keep on accumulating generation after generation and form one of the basis of variability/ polymorphism.
Question 32.
Antibiotic production by microorganisms is one of their more
interesting features, particularly from a medical and commercial point of view.
More than 10,000 antibiotics and similar bioactive metabolites have been
isolated from microbes, with approximately 500 new classes of low molecular
weight compounds published every year.
(i) What is antibiotic and give one
example?
(ii) How antibiotics are produced?
(iii) What is an issue with
overuse of antibiotics?
Or
The bar chart shows the percentage of women who
gave birth to babies of low weight, amongst smokers and non-smokers.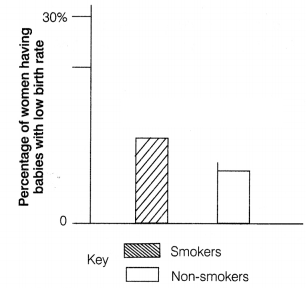
(i) What is shown by the bar chart?
(ii) Explain the harmful effects of
cigarette smoking.
(iii) Explain how smoking may affect the health of the
mother and the development of her foetus.
Answer:
(i) Antibiotics are
substances produced by bacteria or fungi which can kill other microorganisms,
especially bacteria. One of the well-known antibiotic is penicillin.
(ii) Antibiotics are produced on a large scale by the
fermentation
process. This is a chemical process which is induced by the microorganisms in a
large tank. A large tank contains the growth medium that provides nutrition for
the microorganism’s growth. Optimisation of temperature, pH levels, oxygen and
nutrient in the fermentation tank is very crucial to produce antibiotic
production, they are extracted and purified through multiple physical processes.
Finally, the purified antibiotics are converted into crystal form.
(iii) Taking antibiotics too often or for the wrong reasons can change
bacteria, so much that antibiotics do not work against them. This is called
bacterial resistance or antibiotic resistance. Some bacteria are now resistant
to even the most powerful antibiotics available. Antibiotic resistance is a
growing problem,
Or
(i) Bar chart simply shows, the percentage of women
having babies with low birth weight increases in smokers, thus the risk
increases by smoking during pregnancy.
(ii) The cigarette smoke contains nicotine which causes addiction. Nicotine causes clotting of RBC in blood and raises blood pressure. It also contains tar which constitutes many carcinogen chemicals which may cause lung cancer. Carbon monoxide is also found in cigarette smoke which can cause blockage in the coronary artery resulting in a heart attack.
(iii) Nicotine in cigarette smoke increases fatty deposits on the inner layers of blood vessels, this would reduce the diameter of lumen of blood vessels, including those that bring blood to the placenta, over time less food molecules would reach the placenta from maternal blood to foetal blood, for the growth and development of foetus.
Question 33.
Trace the events of the implantation of zygote in uterus.
Or
Describe the embryonic development in humans.
Answer:
The
implantation of zygote in uterus occurs in the following steps
- (i) The mitotic division within the zygote termed cleavage starts as the zygote moves towards the uterus through the isthmus of the oviduct.
- (ii) It forms 2, 4, 8 and 16 daughter cells called blastomeres.
- (iii) The embryo with 8-16 blastomeres is called a morula.
- (iv) Morula continues to divide and transforms into blastocyst as it moves further into the uterus.
- Blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into an outer layer called trophoblast.
- The inner group of cells attached to trophoblast constitute the inner cell mass.
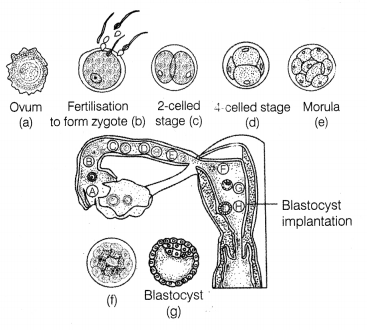
- Trophoblast layer then gets attached to the endometrium and the inner cell mass gets differentiated as the embryo.
- After attachment, the uterine cells divide rapidly and cover the blastocyst. This leads to embedding of blastocyst in the endometrium of the uterus. This is called implantation.
Or
It starts after pregnancy and involves the following changes
(i) The inner cell mass (embryo) differentiates into an outer layer called
ectoderm and an inner layer called endoderm.
(ii) Middle layer called
mesoderm appears between the ectoderm and endoderm. These three layers are
called primary germ layers.
(iii) Primary germ layers give rise to all the
tissues and organs of the adult. The inner cell mass contains certain cells
called stem cells, which have the potency to give rise to all the tissues and
organs.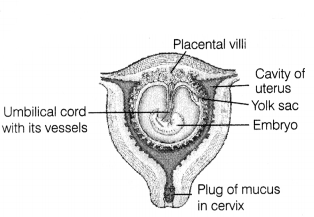
(iv) In humans, after one month of pregnancy, the embryo’s heart is formed. The
sign of growing foetus can be ensured by listening to the heartbeat after 5-7
week of pregnancy.
(v) By the end of second month, limbs and digits
develop.
(vi) By the end of third month (first trimester), most of the major
organ systems are formed.
(vii) During the fifth month, the first movement of
foetus and appearance of hair on the head are observed.
(viii) By the end of
sixth month (second trimester), the body gets covered with fine hair, eyelids
separate and eyelashes are formed.
(ix) By the end of eight months, the
testes in male foetus descend into the scrotum.
(x) By the end of nine
months, the foetus is fully
developed and ready for the birth.