Electromagnetic Induction
Class 12th Physics Chapter MCQs
Electromagnetic Induction Class 12 Physics MCQs
1. The north pole of a long bar magnet was pushed slowly into a short
solenoid connected to a short galvanometer. The magnet was held stationary for a
few seconds with the north pole in the middle of the solenoid and then withdrawn
rapidly. The maximum deflection of the galvanometer was observed when the magnet
was
(a) moving towards the solenoid
(b) moving into the solenoid
(c) at
rest inside the solenoid
(d) moving out of the solenoid
Answer
Answer: d
2. The magnetic flux linked with a coil of N turns of area of cross section A
held with its plane parallel to the field B is![]()
Answer
Answer: d
3. Faraday’s laws are consequence of the conservation of
(a) charge
(b)
energy
(c) magnetic field
(d) both (b) and (c)
Answer
Answer: b
4. Two identical coaxial coils P and Q carrying equal amount of current in
the same direction are brought nearer. The current in
(a) P increases while
in Q decreases
(b) Q increases while in P decreases
(c) both P and Q
increases
(d) both P and Q decreases
Answer
Answer: d
5. Direction of current induced in a wire moving in a magnetic field is found
using
(a) Fleming’s left hand rule
(b) Fleming’s right hand rule
(c)
Ampere’s rule
(d) Right hand clasp rule
Answer
Answer: b
6. Lenz’s law is a consequence of the law of conservation of
(a)
charge
(b) energy
(c) induced emf
(d) induced current
Answer
Answer: b
7. A solenoid is connected to a battery so that a steady current flows
through it. If an iron core is inserted into the solenoid, the current will
(a) increase
(b) decrease
(c) remain same
(d) first increase then
decrease
Answer
Answer: b
8. Which of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Whenever the
amount of magnetic flux linked with a circuit changes, an emf is induced in
circuit.
(b) The induced emf lasts so long as the change in magnetic flux
continues.
(c) The direction of induced emf is given by Lenz’s law.
(d)
Lenz’s law is a consequence of the law of conservation of
momentum.
Answer
Answer: d
9. There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the
plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into
a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then
(a) current is induced in the
loop in the anti-clockwise direction.
(b) current is induced in the loop in
the clockwise direction.
(c) ac is induced in the loop.
(d) no current is
induced in the loop.
Answer
Answer: a
10. In the given figure current from A to B in the straight wire is
decreasing. The direction of induced current in the loop is A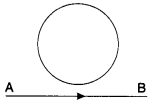
(a) clockwise
(b) anticlockwise
(c) changing
(d) nothing can be said
Answer
Answer: b
11. The north pole of a bar magnet is rapidly introduced into a solenoid at
one end (say A). Which of the following statements correctly depicts the
phenomenon taking place?
(a) No induced emf is developed.
(b) The end A of
the solenoid behaves like a south pole.
(c) The end A of the solenoid behaves
like north pole.
(d) The end A of the solenoid acquires positive
potential.
Answer
Answer: c
12. A metal plate can be heated by
(a) passing either a direct or
alternating current through the plate.
(b) placing in a time varying magnetic
field.
(c) placing in a space varying magnetic field, but does not vary with
time.
(d) both (a) and (b) are correct.
Answer
Answer: d
13. Identify the wrong statement.
(a) Eddy currents are produced in a
steady magnetic field.
(b) Eddy currents can be minimized by using laminated
core.
(c) Induction furnace uses eddy current to produce heat.
(d) Eddy
current can be used to produce braking force in moving
trains.
Answer
Answer: a
14. Which of the following does not use the application of eddy current?
(a) Electric power meters
(b) Induction furnace
(c) LED lights
(d)
Magnetic brakes in trains
Answer
Answer: c
15. If number of turns in primary and secondary coils is increased to two
times each, the mutual inductance
(a) becomes 4 times
(b) becomes 2
times
(c) becomes A times
(d) remains unchanged
4
Answer
Answer: a
16. When the rate of change oic current is unity, the induced emf is equal
to
(a) thickness of coil
(b) number of turns in coil
(c) coefficient of
self inductance
(d) total flux linked with coil
Answer
Answer: c
17. Two inductors of inductance .L each are connected in series with
opposite? magnetic fluxes. The resultant inductance is
(Ignore mutual
inductance)
(a) zero
(b) L
(c) 2L
(d) 3L
Answer
Answer: c
Question 18.
The coupling co-efficient of the perfectly coupled coils
is:
(a) Zero
(b) 1
(c) slightly more than 1
(d) infinite
Answer
Answer: (b) 1
Question 19.
1 henry is equal to :
(a) \(\frac{weber}{ampere}\)
(b)
\(\frac{weber}{Volt}\)
(c) weber ampere
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{weber}{ampere}\)
Question 20.
The magnetic field is parallel to a surface, then the magnetic
flux through the surface is :
(a) zero
(b) small but not zero
(c)
infinite
(d) large but not infinite
Answer
Answer: (b) small but not zero
Question 21.
In the expression e = –\(\frac{d∅}{dt}\), the -ve sign
signifies:
(a) The induced emf is produced only when magnetic flux
decreases
(b) The induced emf opposes the change in the magnetic flux
(c)
The induced emf is opposite to the direction of the flux
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (b) The induced emf opposes the change in the magnetic flux
Question 22.
An e– and a p– are moving parallel to
each other in a magnetic field. The magnetic force acting on the p+
is:
(a) 1840 times that on e–
(b) less than that of
e–
(c) same as that of e–
(d) slightly more than
that of e–
Answer
Answer: (c) same as that of e–
Question 23.
Which of the following is not equal to a henry?
(a)
\(\frac{Volt second}{ampere}\)
(b) \(\frac{Volt second^2}{Coulomb}\)
(c)
\(\frac{Volt^2 second}{Coulomb}\)
(d) \(\frac{Jole second}{Coulomb^2}\)
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac{Volt^2 second}{Coulomb}\)
Question 24.
A transformer is used to light 100 W and 110 V lamp from a 220
V mains. If the main current is 0.5 A. Then the efficiency of the transformer
is:
(a) 11%
(b) 50%
(c) 80%
(d) 90%
Answer
Answer: (d) 90%
Question 25.
The magnetic flux (∅) linked with a coil is related to the
number of turns (N) ofthe coil as:
(a) f ∝ N
(b) f ∝ N-1
(c)
f ∝ N2
(d) f ∝ N-2
Answer
Answer: (a) f ∝ N
Question 26.
The magnetic flux (∅) lined with a coil is related to its area
(s) as:
(a) ∅ ∝ s
(b) ∅ ∝ s²
(c) ∅ ∝ s1/2
(d) ∅ ∝
s-1/2
Answer
Answer: (a) ∅ ∝ s
Question 27.
If the magnetic flux linked with a coil through which a
current off ampere is set up is ∅, then the coefficient of self-inductance of
the coil is:
(a) \(\frac{l}{∅}\)
(b) \(\frac{∅}{l}\)
(c) ∅l
(d) None
of these
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\frac{∅}{l}\)
Question 28.
In a uniform magnetic field B, a wire in the form of a
semicircle of radius r rotated about the diameter of the circle with angular
frequency ‘ω’. The axis of rotation is perpendicular to the field. If the total
resistance of the circuit is R the mean power generated per period of rotation
is :
(a) \(\frac{Bπr^2ω}{2R}\)
(b) \(\frac{(Bπr^2ω)^2}{8R}\)
(c)
\(\frac{(Bπrω)^2}{2R}\)
(d)
\(\frac{(Bπrω^2)^2}{8R}\)
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\frac{(Bπr^2ω)^2}{8R}\)
Question 29.
The role of inductance is equivalent to:
(a) inertia
(b) force
(c) energy
(d) momentum
Answer
Answer: (a) inertia
Question 30.
A metal conductor of length 1 m rotates vertically about one
of its ends at angular velocity 5 rad s-1 . If the horizontal
component of earth’s magnetism is 2 × 10-5 T, then e.m.f. developed
between the two ends of the conductor is:
(a) 5 µV
(b) 50 µV
(c) 5
mV
(d) 50 mV
Answer
Answer: (a) 5 µV
Question 31.
coil of L = 8.4 mH and R = 6 Ω is connected to a 12 V
battery. The current in the coil is 1.0 A at approx’time of:
(a) 500 s
(b)
20 s
(c) 35 ms
(d) 1 ms
Answer
Answer: (d) 1 ms
Question 32.
If I current is flowing inductance L, then the dimension of
\(\frac{3}{2}\) LI² is equivalent to:
(a) charge
(b) force
(c)
momentum
(d) energy
Answer
Answer: (c) momentum
Question 33.
The phase difference between the flux linkage and the emf in
a rotating coil in a uniform magnetic field is:
(a) zero
(b)
\(\frac{π}{2}\)
(c) \(\frac{π}{4}\)
(d) π
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac{π}{4}\)
Question 34.
A choke is used as a resistance in :
(a) dc circuits
(b) ac circuits
(c) both ac and dc circuits
(d) neither (a) nor
(b)
Answer
Answer: (b) ac circuits
Question 35.
The SI unit of magnetic flux is:
(a) T
(b)
Tn-2
(c) Wb
(d) Wb m-2
Answer
Answer: (c) Wb
Question 36.
For purely capacitive circuits, power factor is:
(a) 0
(b) -1
(c) 1
(d) infinity
Answer
Answer: (a) 0
Question 37.
The magnetic flux linked with a coil is inversely
proportional to the?
(a) magnetic field
(b) area of cross section
(c)
number of turns
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a) magnetic field
Question 38.
When the magnetic field is parallel to a surface, then the
magnetic flux through the surface is:
(a) infinite
(b) zero
(c) small
but not zero
(d) large but not infinite.
Answer
Answer: (b) zero
Question 39.
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4
A is:
(a) 0.1 J
(b) 0.4 J
(c) 0.04 J
(d) 0.01
J
Answer
Answer: (b) 0.4 J
Question 40.
The flux linked with a coif at any instant t is given by ∅ =
10t² – 50t + 250. The induced emf at t = 35 is:
(a) 10 V
(b) 190 V
(c)
-190 V
(d) -10 V
Answer
Answer: (d) -10 V
Question 41.
Two coils of self inductance 2 mil and 8 mil are placed so
close together that the effective flux in one coil is completely linked with
other. The mutual inductance between these coils is :
(a) 4 mH
(b) 16
mH
(c) 10 mH
(d) 6 mH
Answer
Answer: (c) 10 mH
Question 42.
The core of a transformer is laminated because:
(a)
rusting of core may be prevented
(b) ratio of voltage in primary and
secondary may be increased.
(c) energy losses due to eddy current may be
minimised
(d) The weight of transformer may be
reduced
Answer
Answer: (c) energy losses due to eddy current may be minimised