Magnetism and Matter
Class 12th Physics Chapter MCQs
Magnetism and Matter Class 12 Physics MCQs
1. The earth behaves as a magnet with magnetic field pointing approximately
from the geographic
(a) North to South
(b) South to North
(c) East to
West
(d) West to East
Answer
Answer: b
2. The strength of the earth’s magnetic field is
(a) constant
everywhere.
(b) zero everywhere.
(c) having very high value.
(d) vary
from place to place on the earths surface.
Answer
Answer: d
3. Which of the following is responsible for the earth’s magnetic field?
(а) Convective currents in earth’s core
(б) Diversive current in earth’s
core.
(c) Rotational motion of earth.
(d) Translational motion of
earth.
Answer
Answer: a
4. Which of the following independent quantities is not used to specify the
earth’s magnetic field?
(a) Magnetic declination (θ).
(b) Magnetic dip
(δ).
(c) Horizontal component of earth’s field (BH).
(d)
Vertical component of earth’s field (BV).
Answer
Answer: d
5. Let the magnetic field on earth be modelled by that of a point magnetic
dipole at the centre of earth. The angle of dip at a point on the geographical
equator is
(a) always zero
(b) positive, negative or zero
(c)
unbounded
(d) always negative
Answer
Answer: b
6. The angle of dip at a certain place where the horizontal and vertical
components of the earth’s magnetic field are equal is
(a) 30°
(b) 75°
(c) 60°
(d) 45°
Answer
Answer: d
7. The vertical component of earth’s magnetic field . at a place is √3 times
the horizontal component
the value of angle of dip at this place is
(a)
30°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°
Answer
Answer: c
8. At a given place on earth’s surface the horizontal component of earth’s
magnetic field is 2 × 103-5 T and resultant magnetic field is 4 ×
103-5 T. The angle of dip at this place is
(a) 30°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 45°
Answer
Answer: b
9. Which of the following property shows the property of ferromagnetic
substances?
(a) The ferromagnetic property depends on tem-perature. ‘
(b)
The ferromagnetic property does not depend on temperature.
(c) At high enough
temperature ferromagnet becomes a diamagnet.
(d) At low temperature
ferromagnet becomes a paramagnet.
Answer
Answer: a
10. The primary origin of magnetism lies in
(a) atomic current and
intrinsic spin of electrons.
(b) polar and non polar nature of molecules.
(c) pauli exclusion principle.
(d) electronegative nature of
materials.
Answer
Answer: a
11. Magnetic moment for solenoid and corresponding bar magnet is
(a) equal
for both
(b) more for solenoid
(c) more for bar magnet
(d) none of
these
Answer
Answer: a
12. Which of the following is correct about magnetic monopole?
(a)
Magnetic monopole exist.
(b) Magnetic monopole does not exist.
(c)
Magnetic monopole have constant value of monopole momentum.
(d) The monopole
momentum increase due to increase at its distance from the
field.
Answer
Answer: b
13. Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d
apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two
magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on
the charge Q is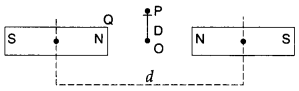
(a) zero
(b) directed along OP
(c)
directed along PO
(d) directed perpendicular to the plane of
paper
Answer
Answer: a
14. A current carrying loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field in four
different orientations as shown in figure. Arrange them in the decreasing order
of potential energy.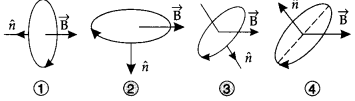
(a) 4, 2, 3,1
(b) 1, 4, 2, 3
(c)
4, 3, 2,1
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4
Answer
Answer: b
15. Which of the following is not showing the essential difference between
electrostatic shielding by a conducting shell and magnetostatic shielding?
(a) Electrostatic field lines can end on charges and conductors have free
charges.
(b) Magnetic field lines can end but conductors cannot end them.
(c) Lines of magentic field cannot end on any material and perfect shielding is
not possible.
(d) Shells of high permeability materials can be used to divert
lines of magnetic field from the interior region.
Answer
Answer: b
16. The net magnetic flux through any closed surface, kept in a magnetic
field is
(a) zero
(b) \(\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi}\)
(c) 4πμ0
(d) \(\frac{4 \mu_{0}}{\pi}\)
Answer
Answer: a
17. Point out the correct direction of magnetic field in the given
figures.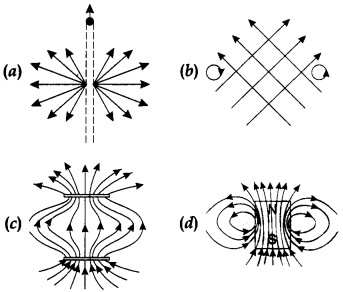
Answer
Answer: d
Question 18.
S.I. unit of flux is :
(a) Ohm
(b) Weber
(c)
Tesla
(d) None
Answer
Answer: (b) Weber
Question 19.
What is the angle of dip at a place where the horizontal
component of earth’s magnetic field is equal to the vertical component?
(a)
0°
(b) 30°
(c) 45°
(d) 90°
Answer
Answer: (c) 45°
Question 20.
Which of the following has a low value in ferrites?
(a)
Conductivity
(b) Permeability
(c) Magnetic susceptibility
(d) All the
above
Answer
Answer: (a) Conductivity
Question 21.
The dimensional representation of magnetic flux density is
:
(a) [MLT-2]
(b) [MLT-2A-1]
(c)
[MLT-2A-2]
(d)
[MT-2A-1]
Answer
Answer: (d) [MT-2A-1]
Question 22.
Tangent law is applicable only when:
(a) two uniform and
mutually perpendicular magnetic fields exist
(b) two magnetic fields
exist
(c) horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is present
(d)
uniform magnetic field are used
Answer
Answer: (a) two uniform and mutually perpendicular magnetic fields exist
Question 23.
Ferrites may be:
(a) ant. ferromagnetic
(b)
ferromagnetic
(c) ferrimagnetic
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) ferromagnetic
Question 24.
A magnetic bar of M magnetic moment is placed m the field of
magnetic strength B, the torque acting on it is :
(a) \(\vec{M} \).\(\vec{B}
\)
(b) –\(\vec{M} \).\(\vec{B} \)
(c) \(\vec{M} \) × \(\vec{B} \).
(d)
\(\vec{B} \) × \(\vec{M} \)
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\vec{M} \) × \(\vec{B} \).
Question 25.
The magnetic lines of force inside a bar magnet:
(a) do not
exist
(b) depends on area of cross-section of bar magnet
(c) are from
N-pole to S-pole of the magnet
(d) are from S-pole to N-pole of the
magnet.
Answer
Answer: (d) are from S-pole to N-pole of the magnet.
Question 26.
A magnetic dipole moment is a vector quantity directed
from:
(a) S to N
(b) N to S
(c) E to W
(d) W to
E
Answer
Answer: (a) S to N
Question 27.
What is the magnetic field in the empty space enclosed by the
toroidal solenoid of radius ‘R’? ,
(a) Infinity
(b)
\(\frac{µ_0}{4π}\).\(\frac{2πl}{R}\)
(c)
\(\frac{µ_0}{4π}\).(\(\frac{πl}{R}\))
(d) zero
Answer
Answer: (d) zero
Question 28.
A current carrying power line carries current from west to
east. What will be direction of magnetic field 1 meter above it?
(a) N to
S
(b) S to N
(c) E to W
(d) W to E
Answer
Answer: (a) N to S
Question 29.
The dimensional representation of \(\sqrt{l/MB}\) is similar
to that of:
(a) frequency
(b) time
(c) distance
(d)
speed
Answer
Answer: (b) time
Question 30.
On quadrupling the moment of inertia of a magnet, its
frequency of oscillation will become:
(a) half
(b) double
(c) four
times
(d) one-fourth
Answer
Answer: (a) half
Question 31.
The magnetic field strength due to a short bar magnet
directed along its axial line at a distance r is B. What is its value at the
same distance along the equatorial line?
(a) B
(b) 2B
(c)
\(\frac{B}{2}\)
(d) \(\frac{B}{4}\)
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac{B}{2}\)
Question 32.
The neutral point in the magnetic field of a horizontally
placed bar magnet is a point where the magnetic field due to that bar magnet
is:
(a) zero
(b) more than that of earth
(c) less than that of
earth
(d) equal to that of earth
Answer
Answer: (d) equal to that of earth
Question 33.
In a moving coil galvanometer, we use a radial magnetic field
so that the galvanometer scale is :
(a) exponential
(b) linear
(c)
algebraic
(d) logarithmic
Answer
Answer: (b) linear
Question 34.
The force between two parallel wire 2 × 10-7
Nm-1, placed 1 m apart to each other in vacuum. The electric current
flowing through the wires is:
(a) 1 A
(b) zero
(c) 5 × 106
A
(d) 2 × 10-7 A
Answer
Answer: (a) 1 A
Question 35.
The force acting per unit length of a semi circular wire of
radius R carrying a current I is:
(a) \(\frac{µ_0l^2}{4R}\)
(b)
\(\frac{µ_0l^2}{2R}\)
(c) \(\frac{µ_0l^2}{R}\)
(d)
\(\frac{2µ_0l^2}{R}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{µ_0l^2}{4R}\)
Question 36.
Which of the following has higher magnetic
susceptibility?
(a) diamagnetic
(b) paramagnetic
(c) ferromagnetic
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) ferromagnetic
Question 37.
The magnetic field of earth is due to:
(a) induction
effect of the sun
(b) the presence of a large magnet at the centre of the
earth
(c) interaction of cosmic rays with the current of earth
(d) motion
and distribution of some material in an outside the
earth
Answer
Answer: (d) motion and distribution of some material in an outside the earth
Question 38.
In a bar magnet, magnetic lines of force z :
(a) are
produced only at north pole like rays of light from a bulb
(b) starts from
north pole and ends at the south pole
(c) emerge in circular paths from the
middle of the bar
(d) run continuously through the bar and
outside
Answer
Answer: (b) starts from north pole and ends at the south pole
Question 39.
The Mariner’s compass is provided with Gimbals arrangement so
as to :
(a) keep the needle always horizontal
(b) give a direct reading of
declination
(c) give the direct value of dip
(d) all of the
above
Answer
Answer: (c) give the direct value of dip
Question 40.
A wire of length I has a magnetic moment M. It is then bent
into a semi-circular arc. The neyv magnetic moment is :
(a) M
(b) M.l.
(c) \(\frac{2M}{π}\)
(d) \(\frac{M}{π}\)
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac{2M}{π}\)
Question 41.
The relation between geometric length (L) and magnetic length
(Lm) is:
(a) Lm = \(\frac{5}{6}\) Lg
(b)
Lm = \(\frac{6}{5}\) Lg
(c) (a) Lm =
Lg
(d) Lm = 2RY;UL
Lg
Answer
Answer: (a) Lm = \(\frac{5}{6}\) Lg
Question 42.
The radius of curvature of the path of charged particle in a
uniform magnetic file is directly proportional to the
(a) charge on fie
particle
(b) Momentum of particle
(c) energy of particle
(d) Strength
of field
Answer
Answer: (b) Momentum of particle
Question 43.
The magnetic field at the centre of a current carrying
circular loop is B. If the radius of the loop is doubled keeping the current
unchanged, the magnetic field at the centre of loop will become:
(a)
\(\frac{B}{2}\)
(b) \(\frac{B}{4}\)
(c) 2B
(d)
4B
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\frac{B}{4}\)