Current Electricity
Class 12th Physics Chapter MCQs
Current Electricity Class 12 Physics MCQs
1. An electric heater is connected to the voltage supply. After few seconds,
current gets its steady value then its initial current will be
(a) equal to
its steady current
(b) slightly higher than its steady current
(c)
slightly less than its steady current
(d) zero
Answer
Answer: b
2. In the series combination of two or more than two resistances
(a) the
current through each resistance is same.
(b) the voltage through each
resistance is same.
(c) neither current nor voltage through each re-sistance
is same.
(d) both current and voltage through each resis¬tance are
same.
Answer
Answer: a
3. Combine three resistors 5 Q, 4.5 Q and 3 Q in such a way that the total
resistance of this combination is maximum
(a) 12.5 Q
(b) 13.5 Q
(c)
14.5 Q
(d) 16.5 Q
Answer
Answer: a
4. A cell having an emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a
variable external resistance R. As the resistance R is increased, the plot of
potential difference V across R is given by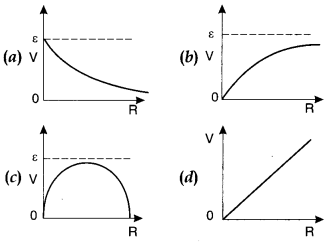
Answer
Answer: b
5. In parallel combination of n cells, we obtain
(a) more voltage
(b)
more current
(c) less voltage
(d) less current
Answer
Answer: b
6. If n cells each of emf e and internal resistance r are connected in
parallel, then the total emf and internal resistance will be
Answer
Answer: a
7. In a Wheatstone bridge if the battery and galvanometer are interchanged
then the deflection in galvanometer will
(a) change in previous direction
(b) not change
(c) change in opposite direction
(d) none of these.
Answer
Answer: b
8. When a metal conductor connected to left gap of a meter bridge is heated,
the balancing point
(a) shifts towards right
(b) shifts towards left
(c) remains unchanged
(d) remains at zero
Answer
Answer: a
9. In a potentiometer of 10 wires, the balance point is obtained on the
7th wire. To shift the balance point to 9th wire, we should
(a)
decrease resistance in the main circuit.
(b) increase resistance in the main
circuit.
(c) decrease resistance in series with the cell whose emf is to be
measured.
(d) increase resistance in series with the cell whose emf is to be
determined.
Answer
Answer: d
10. AB is a wire of potentiometer with the increase in the value of
resistance R, the shift in the balance point J will be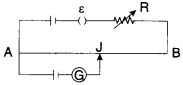
(a) towards B
(b) towards A
(c) remains constant
(d)
first towards B then back towards A.
Answer
Answer: a
11. A charge is moving across a junction, then
(a) momentum will be
conserved.
(b) momentum will not be conserved.
(c) at some places
momenturii will be conserved and at some other places momentum will not be
conserved.
(d) none of these.
Answer
Answer: d
12. Which of the following I-V graph represents ohmic conductors?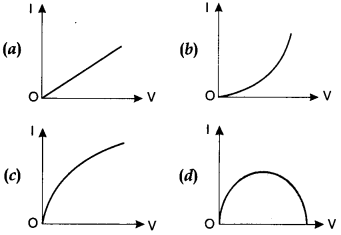
Answer
Answer: a
13. The I-V characteristics shown in figure represents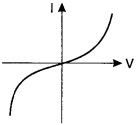
(a) ohmic conductors
(b) non-ohmic conductors
(c)
insulators
(d) superconductors
Answer
Answer: b
14. Which of the following is correct for V-I graph of a good
conductor?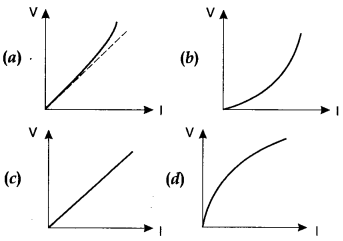
Answer
Answer: a
15. The resistivity of alloy manganin is
(a) Nearly independent of
temperature
(b) Increases rapidly with increase in temperature
(c)
Decreases with increase in temperature
(d) Increases rapidly with decrease in
temperature
Answer
Answer: a
Question 16.
The speed at which tjie current travels in a conductor is
nearly:
(a) 3 × 104 ms-1
(b) 3 × 106
ms-1
(c) 3 × 108 ms-1
(d) 3 ×
1010 ms-1
Answer
Answer: (a) 3 × 104 ms-1
Question 17.
The resistance of a human body is about:
(a) 12 Ω
(b)
120 Ω
(c) 12 KΩ
(d) 120 MΩ
Answer
Answer: (c) 12 KΩ
Question 18.
The number of electrons that constitute 1 A of current is:
(a) 6.25 × 1016
(b) 6.25 × 1017
(c) 6.25 ×
1018
(d) 6.25 × 1019
Answer
Answer: (c) 6.25 × 1018
Question 19.
How many different resistances are possible with two equal
resistors?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer
Answer: (b) 3
Question 20.
Given three equal resistors, how many different combinations
(taken all of them together) can be made?
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d)
6
Answer
Answer: (b) 4
Question 21.
Specific resistance of ali metals is mostly affected by:
(a) temperature
(b) pressure
(c) magnetic field
(d) volume
Answer
Answer: (a) temperature
Question 22.
The example of a non-ohmic resistance is:
(a) copper
wire
(b) fi lament lamp
(c) carbon resistor
(d) diode
Answer
Answer: (d) diode
Question 23.
If a certain piece of copper is to be shaped into a conductor
of minimum resistance, its length (L) and cross-sectional area (a) shall
respectively be :
(a) L, 2A
(b) \(\frac{L}{2}\), 2A
(c) 2L, 2A
(d)
2l, \(\frac{A}{2}\)
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\frac{L}{2}\), 2A
Question 24.
The specific resistance of a rod of copper as compared to that
of thin wire of copper is :
(a) less
(b) more
(c) same
(d) depends
upon the length and area of cross-section of the wire
Answer
Answer: (c) same
Question 25.
A wire of resistance 3 Ω is cut into three pieces, which are
then joined to form a triangle. The equivalent resistance between any corners of
the triangle is :
(a) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Ω
(b) \(\frac{3}{2}\) Ω
(c)
\(\frac{1}{2}\) Ω
(d) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Ω
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Ω
Question 26.
The length of a conductor is halved. Its resistance will be
:
(a) halved
(b) doubled
(c) unchanged
(d)
quadrupled
Answer
Answer: (a) halved
Question 27.
In the above question, the conductance:
(a) halved
(b)
doubled
(c) unchanged
(d) quadrupled
Answer
Answer: (b) doubled
Question 28.
Siemen is the unit of:
(a) resistance
(b)
conductance
(c) specific conductance
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (b) conductance
Question 29.
How much electric energy is consumed by a 100 W lamp used for
6 hours everyday for 30 days?
(a) 18 kJ
(b) 18 kWh
(c) 1.8 J
(d)
None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) 18 kWh
Question 30.
Suppose H1 is the heat generated per second in the
filament of a 100 W, 250 V lamp and H2 is the heat generated in the
filament of a 200 W, 250 V lamp. Then H1/H2 is equal
to:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(d)
\(\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 31.
Two wires of copper are of the same length but’have different
diameters. When they are connected in series across a battery, the heat
generated is H1 When connected in parallel across the same battery,
the heat generated during the same time is H2 Then :
(a)
H1 = H2
(b) H1 < H2
(c)
H1 > H2
(d) H1 >
H2
Answer
Answer: (b) H1 < H2
Question 32.
In questions 135, w hen the wires are connected in series,
the heat produced in the thinner wire is H1 and that in the thicker
wire is H2. Then :
(a) H1 = H2
(b)H1 < H2
(c) H1 > H2
(d) H1 > H2
Answer
Answer: (c) H1 > H2
Question 33.
Kirchhoffs first and second laws for electrical circuits are
consequences of:
(a) conservation of energy
(b) conservation of electrical
charge and energy respectively
(c) conservation of electric charge
(d)
neither conservation of energy nor electric charge
Answer
Answer: (b) conservation of electrical charge and energy respectively
Question 34.
A 5 A fuse wire can with stand a maximum power of 1 W in
circuit. The resistance of the fuse wire is:
(a) 0.2 Ω
(b) 5 Ω
(c) 0.4
Ω
(d) 0.04 Ω
Answer
Answer: (d) 0.04 Ω
Question 35.
The length and radius of an electric resistance of a certain
wire are doubled simultaneously, then the:
(a) resistance will be doubled and
specific resistance will be halved
(b) resistance will be halved and specific
resistance will remain uncharged
(c) resistance will be halved and the
specific resistance will be doubled
(d) resistance and specific resistance
will both remain uncharged
Answer
Answer: (b) resistance will be halved and specific resistance will remain uncharged
Question 36.
A galvanometer acting as a volt meter will have with its
coil.
(a) a high resistance in parallel
(b) a high resistance in
series
(c) a low resistance in parallel
(d) a low resistance in
series
Answer
Answer: (b) a high resistance in series
Question 37.
When three identical bulbs of 60 W, 200 V rating are
connected in series to a 200 V supply, the power drawn by them will be:
(a)
20 W
(b) 60 W
(c) 180 W
(d) 10 W
Answer
Answer: (a) 20 W
Question 38.
n resistances, each of R Ω, are connected in parallel gives
an equivalent resistance of R Ω. If these resistances were , connected in
series, the combination would have a resistance in Ω is equal to
(a) n²R
(b) R/n²
(c) R/n
(d) nR
Answer
Answer: (a) n²R
Question 39.
Why is the Wheatstone bridge more accurate than other methods
of measuring resistances: ‘
(a) It is a null method
(b) It is based on
Kirchhoffs laws
(c) It has four resistances
(d) It does not involve ohm’s
law
Answer
Answer: (a) It is a null method
Question 40.
A potential difference of 10 V is applied across a
conductance of 2 S. The current in the conductor will be :
(a) 20 A
(b) 5
A
(c) 0.2 A
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) 20 A
Question 41.
Ohm’s law is valid when the temperature of conductor is :
(a) very low
(b) very high
(c) varying
(d)
constant
Answer
Answer: (d) constant
Question 42.
The emf of a car battery is about:
(a) 2.5 V
(b) 4.5
V
(c) 8.6 V
(d) 12 V
Answer
Answer: (d) 12 V
Question 43.
Emf is measured in :
(a) joule
(b) joule/coulomb
(c)
joule-coulombs
(d) joule/coulomb/metre
Answer
Answer: (b) joule/coulomb
Question 44.
1 kilowatt hour is commonly known as :
(a) unit
(b) 1
faraday
(c) 1 curie
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) unit
Question 45.
How many joules are equal to I kWh ?
(a) 3.6 ×
104
(b) 3.6 × 105
(c) 3.6 × 106
(d)
None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) 3.6 × 106
Question 46.
The temperature coefficient of resistance is expressed in
:
(a) °C
(b) °C-1
(c) m°C-1
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (b) °C-1
Question 47.
Copper wire is used as connecting wire because :
(a)
copper has high electrical resistivity
(b) copper has low electrical
resistivity
(c) copper has low electrical conductivity
(d) copper has high
value of elasticity
Answer
Answer: (b) copper has low electrical resistivity
Question 48.
The heat sensitive device whose resistivity changes very
rapidly with change of temperature is called a :
(a) resistor
(b)
super-conductor
(c) thermocouple
(d) thermistor
Answer
Answer: (d) thermistor
Question 49.
The phenomenon of super-conductivity was discovered by :
(a) Ohm
(b) Onnes
(c) Edison
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (b) Onnes
Question 50.
The specific resistance of a conductor increases with :
(a) increase in temperature
(b) increase in cross-sectional area
(c)
decrease in length
(d) decrease in cross-sectional
area
Answer
Answer: (a) increase in temperature
Question 51.
In an experiment with potentiometer, null point with a cell
is found at 240 cm. When the cell is shunted with a resistance 2 Ω, the null
point becomes 120 cm internal resistance of cell is :
(a) 4 Ω
(b) 2 Ω
(c) 1 Ω
(d) \(\frac{1}{2}\) Ω
Answer
Answer: (b) 2Ω
Question 52.
Two conductors of equal length and radii the ratio of 2 : 3
are; connected in parallel the source of electricity. The ratio of the velocity
of electrons in the conductor be :
(a) 2 : 3
(b) 4 : 9
(c) 1 : 1
(d)
3 : 2
Answer
Answer: (c) 1 : 1
Question 53.
The charge flowing in a conductor varies with time as :
q
= αt \(\frac{1}{2}\) βt² + \(\frac{1}{6}\) γt³
Where α, β, γ are positive
constants. Then the initial current (l) is given by the condition :
(a) l =
α
(b) l = α²
(c) l = α-1
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (a) l = α
Question 54.
In questions 38, the maximum value of current
(lmax) is given by the condition :
(a) lmax = α –
\(\frac{β^2}{2γ}\)
(b) lmax = α – \(\frac{β^2}{2α}\)
(c)
lmax = α – \(\frac{γ^2}{2β}\)
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (a) lmax = α – \(\frac{β^2}{2γ}\)
Question 55.
In questions 38, the line (t) after which the value of
current reaches a maximum values given by :
(a) t = \(\frac{α}{β}\)
(b) t
= \(\frac{β}{α}\)
(c) t = \(\frac{β}{γ}\)
(d) t =
\(\frac{γ}{β}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) t = \(\frac{α}{β}\)
Question 56.
In following figure shows currents in a part of electrical
circuit, then the value of/(in ampere) is given by :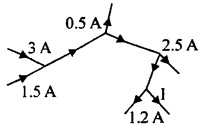
(a) 0.3 A
(b) 0.5 A
(c) 1.3 A
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (a) 0.3 A
Question 57.
The smallest resistance that can be obtained by the
combination of n resistors each resistance r is :
(a) \(\frac{r}{n}\)
(b)
nr
(c) \(\frac{n}{r}\)
(d) n²r
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{r}{n}\)
Question 58.
Which of the following has a negative temperature coefficient
of resistance ?
(a) Tungsten
(b) Carbon
(c) Nichrome
(d)
Platinum
Answer
Answer: (b) Carbon
Question 59.
An electric heating element consumes 500 W, when connected to
a 100 V line. If the line voltage becomes 150 V, the power consumed Will be:
(a) 500 W
(b) 750 W
(c) 1000 W
(d) 1125 W
Answer
Answer: (b) 750 W
Question 60.
A uniform w ire connected across a supply produces heat H per
second. If wire is cut into three equal parts and all the parts are connected in
parallel across the same supply, the heat produced per second will be :
(a)
\(\frac{H}{9}\)
(b) 9 H
(c) 3 H
(d)
\(\frac{H}{3}\)
Answer
Answer: (d) \(\frac{H}{3}\)
Question 61.
In India electricity is supplied fordomestic use at 220 V. It
is supplied at 110 V in U.S.A. If the resistance of a 60 W bulb use in India is
R. the resistance of a 60 W bulb for use in USA will be:
(a) 2 R
(b) R
(c) R/2
(d) R/4
Answer
Answer: (d) R/4
Question 62.
In the following figure represents a balanced Wheatstone
bridge circuit. What is the value of X ?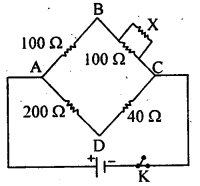
(a) 15 Ω
(b) 20 Ω
(c) 25 Ω
(d) 30 Ω
Answer
Answer: (c) 25 Ω
Question 63.
Two bulbs 25 W, 220 V and 100 W, 220 V are given. Which has
higher resistance?
(a) 25 W
(b) 100 W
(c) both bulbs have equal
resistance
(d) resistance of bulbs can not be
compared
Answer
Answer: (a) 25 W
Question 64.
Potentiometer measures the potential difference more
accurately than a voltmeter because:
(a) It has a wire of high resistance
(b) It has a wire of low resistance
(c) It does not draw current from
external circuit
(d) It draws heavy current from external
circuit
Answer
Answer: (c) It does not draw current from external circuit
Question 65.
In a Wheatstone bridge, the resistance each arm is 10 Ω. If
the resistance galvanometers is also 10 Ω, then effective resistance of the
bridge will be :
(a) 40 Ω
(b) 20 Ω
(c) 10 Ω
(d) 5
Ω
Answer
Answer: (c) 10 Ω
Question 66.
The resistance of an aluminium wire is/i. It is stretched to
/i times its original length. Its new resistance will be :
(a) nr
(b)
n²r
(c) \(\frac{n^2}{r}\)
(d) \(\frac{r}{n^2}\)
Answer
Answer: (b) n²r
Question 67.
A wire P is half the diameter and half the length of a wire Q
of similar material. The ratio of resistances of P to that 0 is:
(a) 4 :
1
(b) 8 : 1
(c) 2 : 1
(d) 1 : 2
Answer
Answer: (c) 2 : 1
Question 68.
What is the resistance across A and B in the network in
Fig.?
(a) R
(b) 2 R
(c) \(\frac{R}{2}\)
(d) 6
R
Answer
Answer: (a) R
Question 69.
When the wires are connected in parallel, the heat produced
in the thinner wire is H1 and that in the thicker wire is
H2 Then:
(a) H1 = H2
(b) H1
< H2
(c) H1 > H2
(d) H1
≥ H2
Answer
Answer: (b) H1 < H2
Question 70.
Two equal resistors are connected in series across a battery
and consume a power of P. If these are connected in parallel, then the’ power
consumed will be:
(a) 2P
(b) 4P
(c) \(\frac{p}{4}\)
(d)
P
Answer
Answer: (b) 4P
Question 71.
Thermo electricity was discovered by:
(a) Joule
(b)
Peitier
(c) Thomson
(d) Seebeck
Answer
Answer: (d) Seebeck
Question 72.
Thermo emf is the order of:
(a) 10 V
(b)
10-3 V
(c) 10-6 V
(d) 10-12
V
Answer
Answer: (c) 10-6 V