Atoms
Class 12th Physics Chapter MCQs
Atoms Class 12 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
A spectral line is emitted when an electron
(a) jumps from
lover orbit to higher orbit.
(b) jumps from higher orbit to lower orbit.
(c) rotates in a circular orbit.
(d) rotates in an elliptical orbit.
Answer
Answer: (b) jumps from higher orbit to lower orbit.
Question 2.
The ionisation potential of hydrogen is 13.6 V. The energy of
the atom in n = 2 state will be
(a) -10.2 eV
(b) -6.4eV
(c) – 3.4
eV
(d) – 4.4 eV
Answer
Answer: (c) – 3.4 eV
Question 3.
At the time of total solar eclipse, the spectrum of solar
radiation would be
(a) a large number of dark Fraunhoffer lines
(b) a
small number of dark Fraunhofer lines.
(c) All Fraunhofer lines changed into
brilliant colours.
(d) None of these.
Answer
Answer: (c) All Fraunhofer lines changed into brilliant colours.
Question 4.
The adjoining figure indicates the energy levels of a certain
atom when the system moves from 2 E to E level, a photon of wavelength λ is
emitted. The wavelength of photon produced during its transition from \(\frac
{4E}{3}\) to E is
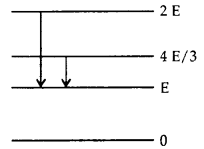
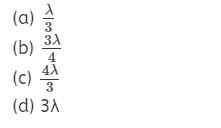
Question 5.
A hydrogen atom is in the p-state. For this, values of J
are
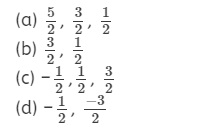
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 6.
Energy levels A, B, C of a certain atom correspond to
increasing value of energy i.e., EA > EB >
EC. If λ1, λ2 and λ3 are the
wavelengths of radiation corresponding to transition C to B, B to A and C to A
respectively, which of these of the following is correct?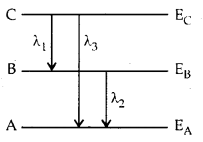
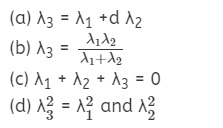
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 7.
In Rutherford’s scattering experiment with gold foil, 232
counts per minute are observed at an angle of 60°. The number of counts/min. at
an angle of 120° will be
(A) 232
(b) 116
(c) 26
(d) 52
Answer
Answer: (c) 26
Question 8.
In an atom, the two electrons move round the nucleus in
circular orbits of radii R and 4R. The ratio of the times taken by them to
complete one revolution is

Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 9.
The ratio of the energies of the hydrogen atom in its first to
second excited state is :

Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 10.
In Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom, the ratio between the
period of revolution of an electron in the orbit n = 1 to the period of
revolution of electron in the orbit n = 2 is

Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 11.
According to Bohr’s theory, the radius of electron in an
orbit described by the principal quantum number n and the atomic number Z is
propotional to :
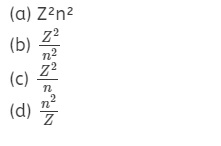
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 12.
The electron in hydrogen atom jumps from the 3rd orbit to
second orbit. The wavelength X of the emitted radiations is

Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 13.
To explain fine structure of spectrum of hydrogen atom, we
must consider.
(a) a finite size of nucleus.
(b) the presence of neutrons
in the nucleus.
(c) spin angular momentum.
(d) orbital angular
momentum.
Answer
Answer: (b) the presence of neutrons in the nucleus.
Question 14.
The ratio of the energy of the electron in first orbit to
that in the second orbit is

Answer
Answer: (d) 4
Question 15.
When an electron jumps from some outer orb it to the
innermost orbit in the hydrogen atom, the spectral line belongs to
(a) Lyman
series
(b) Balmer series
(c) Paschen series
(d) Pfund
series
Answer
Answer: (a) Lyman series
Question 16.
How does the energy difference between two consecutive energy
levels vary on the quantum number n increases?
(a) does not change
(b)
decrases
(c) increases
(d) may increase or
decrease.
Answer
Answer: (b) decrases
Question 17.
According to classical theory, Rutherford atom is
(a)
stable
(b) unstable
(c) metastable
(d)
semistable
Answer
Answer: (b) unstable
Question 18.
For an electron orbit to be non-radiating, it should be
(a) such that the angular momentum should be integral multiple of h.
(b)
circular in nature
(c) elliptical in nature
(d) none of
these
Answer
Answer: (a) such that the angular momentum should be integral multiple of h.
Question 19.
Which of the following type ot radiation is not emitted by
the electronic structure of atoms :
(a) X-rays
(b) Visible light
(c)
γ-rays
(d) Ultraviolet light.
Answer
Answer: (c) γ-rays
Question 20.
If the electron in hydrogen atoms is excited to n = 5 state,
the number of different frequencies of radiation which may be emitted is:
(a)
4
(b) 10
(c) 8
(d) 5
Answer
Answer: (b) 10
Question 21.
The ratio of the angular momentum of an electron in first
orbit to that in the second orbit is
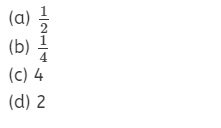
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 22.
An atom stays in an excited state for about:
(a) 10 micro
seconds
(b) 10 milli seconds
(c) 10 nano seconds
(d) 10 seconds
Answer
Answer: (c) 10 nano seconds
Question 23.
The energy equivalent to one atomic mass unit is :
(a) 1.6
× 10-19 J
(b) 6.02 × 1023 J
(c) 9.31 MeV
(d) 931
MeV
Answer
Answer: (d) 931 MeV
Question 24.
Who explained the splitting of special lines in magnetic
field?
(a) Zeeman
(b) Bohr
(c) Summerfield
(d) Einstein
Answer
Answer: (a) Zeeman
Question 25.
The mass of a neutron is:
(a) 1.00866 u
(b) 1.0866 u
(c) 1.866 u
(d) 0.1866 u
Answer
Answer: (a) 1.00866 u
Question 26.
Isobars have the same:
(a) A
(b) Z
(c) N
(d) All
the above
Answer
Answer: (a) A
Question 27.
Isotones have the same:
(a) A
(b) Z
(c) N
(d) All
the above
Answer
Answer: (c) N
Question 28.
Half-life of a substance depends on:
(a) pressure
(b)
temperature
(c) density
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these
Question 29.
The concept of electron spin was introduced by:
(a)
Becquerel
(b) Goudsmit
(c) Millikan
(d) Uhlenbeek and
Goudsmit
Answer
Answer: (d) Uhlenbeek and Goudsmit
Question 30.
The principle that a quantum orbital cannot be occupied by
more than two electrons was given by:
(a) Pauli
(b) Millikan
(c)
Hund
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Pauli
Question 31.
For ionization of excited Hydrogen atom, the, required energy
is:
(a) a little less than 13.6
(b) equal to 13.6
(c) more than
13.6
(d) 3.4 or less
Answer
Answer: (d) 3.4 or less
Question 32.
According to Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom, the radius r of
stationary orbit are related to principal quantum number n as:
(a)
rg ∝ \(\frac{1}{n^2}\)
(b) rg ∝ \(\frac{1}{n}\)
(c)
rg ∝ n
(d) rg ∝ n²
Answer
Answer: (d) rg ∝ n²
Question 33.
Fg and Fe represents the gravitational
and electrostatic force respectively between two electrons situated at some
distance the ratio \(\frac{F_g}{F_e}\) is if the order of:
(a) 9.8
(b)
109
(c) 1042
(d)
10-42
Answer
Answer: (d) 10-42
Question 34.
Artificial radioactivity was discovered by:
(a) Joliot
(b) Becquerel
(c) Pauli
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Joliot
Question 35.
P-decay produces:
(a) isobars
(b) isotopes
(c)
isotones
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (a) isobars
Question 36.
Natural radioactivity was discovered by:
(a) Joliot
(b)
Becquerel
(c) Pauli
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Becquerel
Question 37.
Transmutation of nuclei was discovered by:
(a)
Rutherford
(b) Becquerel
(c) Pauli
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (a) Rutherford
Question 38.
The energy equivalent to mass defect is called :
(a)
binding energy
(b) internal energy
(c) external energy
(d)
enthalpy
Answer
Answer: (a) binding energy
Question 39.
The total energy that will be released if a nucleus is built
from its constituents is called the:
(a) binding energy of the nucleus
(b)
binding energy of the solid
(c) binding energy of the atom
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (a) binding energy of the nucleus
Question 40.
The binding energy of \(_{2}^{4}\)He is about:
(a) 28.3
eV
(b) 28.3 MeV
(c) 28.3 J
(d) 2.83 MeV
Answer
Answer: (b) 28.3 MeV
Question 41.
The binding energy of a deuteron is about:
(a) 2.22
MeV
(b) 2.22 J
(c) 2.22 eV
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) 2.22 MeV
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1
………………… of the electron in the orbit signifies that the
electron and nucleus is a bound system.
Answer
Answer: Negative energy.
Question 2.
The ………………… lies in the infrared region of the
spectrum.
Answer
Answer: Paschen series.
Question 3.
Lyman series lies in the ………………… region of spectrum and Balmer
series lies in the ………………… of the spectrum.
Answer
Answer: Ultraviolet, visible region.
Question 4.
The difference of energy levels goes on ………………… as we move
towards higher energy levels.
Answer
Answer: decreasing.
Question 5.
Separation between the orbits goes on ………………… as we move
towards higher orbits.
Answer
Answer: increasing.
Question 6.
The radius of the first orbit of hydrogen atom is …………………
times the radius of first orbit of a H-like helium
atom.
Answer
Answer: two.
Question 7.
The minimum energy required to excite a hydrogen atom from its
ground state is …………………
Answer
Answer: 10.2 eV.
Question 8.
In a hydrogen atom, the electron moves in an orbit of radius
0.5 Å making 1016 revolutions per second. The magnetic dipole moment
associated with the orbital motion of the electron is
…………………
Answer
Answer: 256 × 10-23 Am².
Question 9.
Band spectrum is produced by the substance in …………………
state.
Answer
Answer: molecular.
Question 10,
Rutherford’s a-particle scattering experiment shows the
existence of a ………………… charged nucleus of ………………… size located at the
…………………
Answer
Answer: Positively, very small, centre of the atom.
Question 11.
The maximum number of photons emitted when an electron jumps
from an energy level n = 4 to n = 1 is …………………
Answer
Answer: 6.
Question 12.
The radius of Bohr’s first orbit is a0. The
electron in nth orbit has a radius …………………
Answer
Answer: n² a0
Question 13.
The kinetic energy associated with an electron decreases with
an ………………… in the radii of the orbits.
Answer
Answer: increase.
Question 14.
For a given projectile and target, the distance of closest
approach ………………… with increase in K.E. of the
projectile.
Answer
Answer: decreases.
Question 15.
In scattering of α-particles by nucleus, the distance of
closest approach depends upon the charges of ………………… and ………………… as well as
………………… of α-particle.
Answer
Answer: Projectile, target nucleus, kinetic-energy.
Question 16.
The ionisation energy of hydrogen atom is E. When the
electron in a hydrogen atom jumps from the state n = 1 to the state n = 2, the
energy absorbed by it is …………………
Answer
Answer: \(\frac {3E}{4}\)
Question 17.
The energy of the atom goes on ………………… as we go to higher
excited states.
Answer
Answer: increasing.
Question 18.
From Bohr’s theory, when an electron jumps from higher energy
orbit to second orbit, the spectral lines that occur belong to …………………
series.
Answer
Answer: Balmer.
Question 19.
When a hydrogen atom is raised from the ground state to an
excited state, them P.E ………………… and Kinetic energy
…………………
Answer
Answer: increases, decreases.
Question 20.
If elements with principal quantum number n > 4 were not
existed in nature then the number of possible electrons would be
…………………
Answer
Answer: 60.