Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Class 12th Physics Chapter MCQs
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Photoelectrons are being obtained by irradiating zinc by a
radiation of 3100 Å. In order to increase the kinetic energy of ejected
photoelectrons.
(a) the intensity of radiation should be increased.
(b)
the wave length of radiation should be increased.
(c) the wavelength of
radiation should be decreased.
(d) both wavelength and intesity of radiation
should be increased.
Answer
Answer: (c) the wavelength of radiation should be decreased.
Question 2.
The de-Broglie wavelength of an electron moving with a speed
of 6.6 × 1015 ms-1 is nearly equal to
(a)
10-11m
(b) 10-9 m
(c) 10-7 m
(d)
10-5 m
Answer
Answer: (b) 10-9 m
Question 3.
An electron accelerated through a potential difference of V
volt has a wavelength λ associated with it, Mass of proton is nearly 2000 times
that of an electron. In order to have the same λ for proton, it must be
accelerated through a potential difference (in volt) of
(a) V
(b)
\(\sqrt{2000}\) V
(c) 2000V V
(d) \(\frac{V}{2000}\)
Answer
Answer: (d) \(\frac{V}{2000}\)
Question 4.
An electron of mass m, when accelerated through a potential
difference V, has de-Broglie wavelength λ. The de-Broglie wavelength associated
with a proton of mass M and accelerated through the same potential difference
will be
(a) λ\(\sqrt{\frac{m}{M}}\)
(b) λ\(\frac{m}{M}\)
(c)
λ\(\sqrt{\frac{M}{m}}\)
(d)
λ\(\sqrt{\frac{m}{m}}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) λ\(\sqrt{\frac{m}{M}}\)
Question 5.
The energy E and momentum p of a photon is given by E = hv h
and p = \(\frac{h}{λ}\). The velocity of photon will be
(a)
\(\frac{E}{P}\)
(b) (\(\frac{E}{P}\))²
(c) \(\sqrt{\frac{E}{P}}\)
(d)
(EP)³
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{E}{P}\)
Question 6.
Ultra-violet radiation of 6.2 eV falls on an aluminium surface
having work-function 4.2 eV. The kinetic energy (in J) of the fastest electron
emitted is nearly.
(a) 3 × 10-19
(b) 3 × 10-15
(c) 3 × 10-17
(d) 3 × 10-21
Answer
Answer: (a) 3 × 10-19
Question 7.
For light of wavelength 5000 Å, the photon energy is nearly
2.5 eV. For X-rays of wavelength 1 Å, the photon energy will be close to:
(a)
2.5 × 5000 eV
(b) 2.5 ÷ 5000 eV
(c) 2.5 × (5000)² eV
(d) 2.5 ÷ (5000)²
eV
Answer
Answer: (a) 2.5 × 5000 eV
Question 8.
A photocell is illuminated by a small bright source placed 1
metre away. When the same source of light is placed 2 m away, the electrons
emitted per sec. (i.e. saturation current in the photo cell is) are
(a) I ∝
2²
(b) I × \(\frac {1}{4}\)
(c) I ∝ 4
(d) I ∝ \(\frac
{1}{2}\)
Answer
Answer: (b) I × \(\frac {1}{4}\)
Question 9.
Which one of the following graph represent correctly the
variation of maximum kinetic energy Emax with the intensity of
incident radiations having a constant frequency.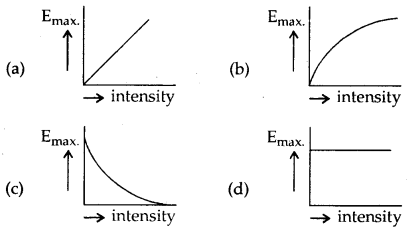
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 10.
The best metal to be used for photoemission is:
(a)
Potassium
(b) Lithium
(c) Sodium
(d) Cesium
Answer
Answer: (d) Cesium
Question 11.
The threshold frequency for a certain metal is v0.
When light of frequency v = 2v0 is incident on it, the maximum
velocity of photo electrons is 4 × 106 ms-1. If the
frequency of incident radiation is increased to 5 v0, then the
maximum velocity of photo electrons (m/s) is
(a) 8 × 105
(b) 2
× 106
(c) 2 × 107
(d) 8 ×
106
Answer
Answer: (d) 8 × 106
Question 12.
The frequency and the intensity of a beam of light falling on
the surface of photoelectric material are increased by a factor of two. This
will:
(a) increase the maximum K.E. of photo-electron as well as
photoelectric current by a factor of two.
(b) increase maximum K.E. of
photoelectrons and would increase the photo current by a factor of two.
(c)
increase the maximum K.E. of photo electrons by a factor of two and will no
affect photoelectric current.
(d) No effect on both maximum K.E. and
photoelectric current.
Answer
Answer: (b) increase maximum K.E. of photoelectrons and would increase the photo current by a factor of two.
Question 13.
Which of the following is not the property of photons
(a)
charge
(b) rest mass
(c) energy
(d) momentum
Answer
Answer: (a) & (b)
Question 14.
Dynamic mass of photon of wavelength k is
(a) Zero
(b)
\(\frac {hc}{λ}\)
(c) \(\frac {h}{cλ}\)
(d) \(\frac
{h}{2λ}\)
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac {h}{cλ}\)
Question 15.
The time required in emitting photo electrons is
(a)
10-8 s
(b) 10-4 s
(c) Zero
(d) 1
sec
Answer
Answer: (c) Zero
Question 16.
When light is directed at the metal surface, the emitted
electrons:
(a) are called photons
(b) have energies that depend upon the
intensity of light.
(c) have random energies.
(d) have energies that
depend upon the frequency of light.
Answer
Answer: (d) have energies that depend upon the frequency of light.
Question 17.
The wavelength associated with n electron is 1Å. The
potential difference required for accelerating it is
(a) 100 V
(b) 150
V
(c) 250 V
(d) 10³ V
Answer
Answer: (b) 150 V
Question 18.
The momentum of a photon is 10-27 kg
ms-1. Its energy will be:
(a) 3 × 10-19 J
(b) 3 ×
10-34 j
(c) 3 × 10-27 J
(d) none of
these
Answer
Answer: (a) 3 × 10-19 J
Question 19.
With which of the following particles moving with same
velocity de-Broglie wave length will be maximum?
(a) ß-particle
(b) ∝
particle
(c) electron
(d) proton
Answer
Answer: (a) & (c)
Question 20.
The magnification produced by electron microscope is of the
order of:
(a) 10
(b) 105
(c) 10³
(d)
107
Answer
Answer: (b) 105
Question 21.
De-Broglie equation states the:
(a) dual nature
(b)
particle nature
(c) wave nature
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a) dual nature
Question 22.
Protons and alpha particles have the same de-Broglie
wavelength. What is same for both of them ?
(a) Energy
(b) Time period
(c) Frequency
(d) Momentum
Answer
Answer: (d) Momentum
Question 23.
Kinetic energy of emitted electrons depends upon :
(a)
frequency
(b) intensity
(c) nature of atmosphere surrounding the
electrons
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a) frequency
Question 24.
De-Broglie wavelength of a body of mass m and kinetic energy E
is given by (symbols have their usual meanings):
(a)
\(\frac{h}{\sqrt{2mE}}\)
(b) \(\frac{h}{2mE}\)
(c)
\(\frac{\sqrt{2mE}}{h}\)
(d) \(\frac{h}{mE}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{h}{\sqrt{2mE}}\)
Question 25.
The ratio of specific charge of an alpha particle to the
proton is:
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 2 : 1
(c) 4 : 1
(d) 1 : 4
Answer
Answer: (a) 1 : 2
Question 26.
In Thomson’s experiment number of parabola gives :
(a) the
no. of electrons present in element
(b) the no. of proton present in
element
(c) the no. of neutrons present in element
(d) the no. of isotopes
of the element present
Answer
Answer: (d) the no. of isotopes of the element present
Question 27.
The work function of photoelectric material is 3.3 eV. The
threshold frequency will be equal to:
(a) 8 × 1014 Hz
(b) 8 ×
1010 Hz
(c) 5 × 1010 Hz
(d) 4 × 1014
Hz
Answer
Answer: (a) 8 × 1014 Hz
Question 28.
The strength of photoelectric current depends upon :
(a)
angle of incident radiation
(b) frequency of incident radiation
(c)
intensity of incident radiation
(d) distance between anode and
cathode
Answer
Answer: (b) frequency of incident radiation
Question 29.
The momentum of an electron that emits a wavelength of 2 Å.
will be:
(a) 6.4 × 10-36 kgms-1
(b) 3.3 ×
10-24 kgms-1
(c) 3.3 × 10-34
kgms-1
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (b) 3.3 × 10-24 kgms-1
Question 30.
Name the scientists who first studied the passage of
electricity through fluids to establish the electrical nature of matter:
(a)Millikan
(b) Planck
(c) Faraday
(d) Boyle
Answer
Answer: (c) Faraday
Question 31.
Millikan’s oil drop experiment makes use of:
(a) Stokes’
law
(b) Boyle’s law
(c) Gas equation
(d) Bernoulli’s
theorem
Answer
Answer: (a) Stokes’ law
Question 32.
X-rays are:
(a) deflected by an electric field
(b)
deflected by a magnetic field
(c) deflected by both electric and magnetic
fields
(d) not deflected by electric and magnetic
fields
Answer
Answer: (d) not deflected by electric and magnetic fields
Question 33.
In photo electric emission, for alkali metals the threshold
frequency lies in the:
(a) visible region
(b) ultraviolet region
(c)
infrared region
(d) far end of the infrared region
Answer
Answer: (a) visible region
Question 34.
Which of the following radiations cannot eject photo
electrons?
(a) ultraviolet
(b) infrared
(c) visible
(d)
X-rays
Answer
Answer: (b) infrared
Question 35.
What is the de-Broglie wavelength of an electron accelerated
from rest through a potential difference of V volts?
(a) \(\frac{12.3}{V^2}\)
Å
(b) \(\frac{12.3}{V}\) Å
(c) \(\frac{12.2}{V^2}\) Å
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{12.3}{V^2}\) Å
Question 36.
What is the de-Broglie wavelength of an electron accelerated
from rest through a potential difference of 100 volts?
(a) 12.3 Å
(b) 1.23
Å
(c) 0.123 Å
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) 1.23 Å
Question 37.
What is the de-Broglie wavelength of a proton accelerated
from rest through a potential difference of V volts?
(a) \(\frac{12.3}{√V}\)
Å
(b) \(\frac{12.3}{V}\) Å
(c) \(\frac{12.2}{V^2}\) Å
(d) None of
these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these
Question 38.
When a yellow light is incident on a surface, no electrons
are emitted while green light can emit electrons. If the red light is incident
on the surface then:
(a) no electrons are emitted
(b) photons are
emitted
(c) electrons of higher energy are emitted
(d) electrons of lower
energy are emitted
Answer
Answer: (a) no electrons are emitted
Question 39.
The de-Broglie wavelength of particle of mass 1 mg moving
with a velocity of 1 ms-1, in terms of Planck’s constant h, is given
by (in metre):
(a) 105 h
(b) 106 h
(c)
10-3 h
(d) 103 h
Answer
Answer: (b) 106 h
Question 40.
Evidence of the wave nature of light cannot be obtained
from:
(a) diffraction
(b) interference
(c) doppler effect
(d)
reflection
Answer
Answer: (d) reflection
Question 41.
which Characteristic of a target does the Mosley’s law relate
the frequency of X-rays?
(a) density
(b) atomic number
(c) atomic
weight
(d) interatomic space
Answer
Answer: (b) atomic number
Question 42.
The charge of a photo electron is :
(a) 9.1 ×
10-31 C
(b) 9.1 × 10-27 C
(c) 9.1 × 10-24
C
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (d) none of these
Question 43.
The number of photons of frequency n present in energy E, in
terms of Planck’s constant h:
(a) \(\frac{E}{nh}\)
(b) nhE
(c)
\(\frac{nh}{E}\)
(d) \(\frac{nE}{h}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{E}{nh}\)
Question 44.
Compared to liquids and solids, gases are:
(a) good
conductors of electricity
(b) best conductors of electricity
(c) very poor
conductors of electricity
(d) good or bad conductors of electricity depending
upon the nature of the gas
Answer
Answer: (c) very poor conductors of electricity
Question 45.
The different stages of discharge in a discharge tube can be
explained on the basis of:
(a) the wave nature of light
(b) the dual
nature of light
(c) wave nature of electrons
(d) the collision between the
charged particles emitted from the cathode the atoms of the gas in the
tube
Answer
Answer: (d) the collision between the charged particles emitted from the cathode the atoms of the gas in the tube
Question 46.
When an electron jumps across a potential difference of 1 V,
it gains energy equal to :
(a) 1.602 × 10-19 J
(b) 1.602 ×
1019 J
(c) 1.602 × 1024 J
(d) 1
J
Answer
Answer: (a) 1.602 × 10-19 J
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
Stopping potential is the measure of the ………………… of the
photoelectrons and does not depend upon …………………
Answer
Answer: Maximum kinetic energy, intensity of incident light.
Question 2.
In photoelectric effect experiment, photo electric current
does not depend upon ………………… but depends only on the ………………… of incident
reduction.
Answer
Answer: Frequency, intesity.
Question 3.
The threshold wavelength of a photo cathode to emit
photoelectrons is λ0. When a radiation of wavelength λ is incident on
it, the average K.E. of the photoelectron is …………………
Answer
Answer: h(\(\frac {1}{λ}\) – \(\frac {1}{λ_0}\))
Question 4.
The stopping potential depends upon ………………… of incident light
and ………………… of metal.
Answer
Answer: freqeuncy, work function.
Question 5.
The maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in
photoelectric effect is linearly dependent on the ………………… of the incident
radiation.
Answer
Answer: freqeuncy.
Question 6.
The mass of a moving photon is
…………………
Answer
Answer: \(\frac {h}{cλ}\)
Question 7.
The photoelectric threshold frequency of a metal is
v0. When light of frequency uv0 is incident on the metal,
the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron is
…………………
Answer
Answer: 3hv0
Question 8.
An electron beam passes at right angles to a magnetic field of
2 × 10-3 Wb m-2. The speed of the electron is 3 ×
107 ms-1 An electric field of ………………… intensity should be
applied along with the magnetic field so that the path of the electron beam
remains indeviated.
Answer
Answer: 6 × 10-4 NC-1.
Question 9.
An electron, photon, a neutron are accelerated through the
same potential difference. The kinetic energies acquired by them will be in the
ratio …………………
Answer
Answer: 1 : 1 : 1.
Question 10.
Light of frequency 1.5 times the threshold frequency is
incident on a photo sensitive material. If the frequency of incident light is
halved and the intensity is doubled, the photo current becomes
…………………
Answer
Answer: Zero.
Question 11.
A photon behaves as if it had a mass equal to ………………… and
momentum equal to …………………
Answer
Answer: \(\frac {hv}{c^2}\), \(\frac {hv}{c}\)
Question 12.
An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of
100 V. The wavelength associated with it is …………………
Answer
Answer: 1.23 Å.
Question 13.
An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of
104 V. The energy acquired by the electron is
…………………
Answer
Answer: 1.6 × 10-15 J
Question 14. Out of proton, neutron, ß-particle and a-particle ………………… will have the maximum de-Broglie wavelength.
Answer
Answer: ß particle.
Question 15.
If electrons photons are considered to be of same de- Broglie
wavelength, then they will have the same …………………
Answer
Answer: momentum
Question 16.
If a photon and an electron ate considered to be of same
de-Broglie wavelength, then the velocity of photon is
…………………
Answer
Answer: greater than that of the electron.
Question 17.
An electron of mass m and charge e is accelerated from rest
through a potential difference of V in vacuum. Its final velocity will be
…………………
Answer
Answer: \(\sqrt{\frac {2eV}{m}}\)
Question 18.
The mass of a photon at rest is
…………………
Answer
Answer: zero.
Question 19.
When a proton is accelerated through a potential difference
of one volt, the kinetic energy gained by it is roughly equal to
…………………
Answer
Answer: 1 eV.
Question 20.
Einstein’s photoelectric equation is expressed as
…………………
Answer
Answer: hv = ω0 + \(\frac {1}{2}\) mv².