Electromagnetic Waves
Class 12th Physics Chapter Important Questions
Class 12 Physics Chapter 8 Important Extra Questions Electromagnetic Waves
Very Short Answer
Question 1.
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which has the
longest wavelength and write its one use. (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
- In the electromagnetic spectrum, long radio waves have the longest wavelength.
- Radio waves are used in communication systems.
Question 2.
The small ozone layer on the top of the stratosphere is
crucial for human survival. Why?
Answer:
The ozone layer absorbs the
ultraviolet rays, emitted by the sun, which are harmful to the living tissues of
human beings.
Question 3.
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is used in
the “greenhouse” to keep plants warm.
Answer:
Infrared rays.
Question 4.
How are radio waves produced? (CBSE AI 2011)
Answer:
They are produced by rapid acceleration and decelerations of electrons in
aerials.
Question 5.
How are X-rays produced? (CBSE Al 2011)
Answer:
By the
transition of inner-shell electrons.
Question 6.
How are microwaves produced? (CBSE AI 2011)
Answer:
By
using a magnetron.
Question 7.
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in a vacuum along the
z-direction. What can you say about the direction of electric and magnetic field
vectors? (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
The electric and magnetic field vectors
will be along the x and y directions.
Question 8.
What is the frequency of electromagnetic waves produced by the
oscillating charge of frequency v? (CBSE Delhi 2011C)
Answer:
The
frequency of electromagnetic waves produced by the oscillating charge of
frequency v is also v.
Question 9.
What are the directions of electric and magnetic field vectors
relative to each other and relative to the direction of propagation of
electromagnetic waves? (CBSE AI 2012)
Answer:
The three are mutually
perpendicular to one other.
Question 10.
Welders wear special goggles or face masks with glass windows
to protect their eyes from electromagnetic radiation. Name the radiations and
write the range of their frequency. (CBSE Al 2013)
Answer:
UV radiations,
1015 to 1017 Hz
Question 11.
To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of
frequency 5 × 1019 Hz belong? (CBSEAI 2014)
Answer:
X –
rays
Question 12.
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum of wavelength
10-2 m and mention its one application. (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
Name of the part: Microwave
Applications :
- It is used in radar communication.
- It is used in microwave ovens.
- It is also used in analysis of fine details of molecular and atomic structure.
Question 13.
Write the following radiations in ascending order in respect
of their frequencies ;
X-rays, Microwaves, UV rays and radiowaves. (Delhi
2009)
Answer:
Radiowaves, microwaves, UV-rays and X-rays.
Question 14.
Name the electromagnetic radiation to which waves of
wavelength in the range of 10-2 m belong. Give one use of this part
of EM spectrum. (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Name : Microwave, Range 0.1 to 1
mm
Uses : Microwaves are used in aircraft navigation.
Question 15.
Name the part of electromagnetic spectrum which is suitable
for
- radar systems used in aircraft navigation
- treatment of cancer tumours. (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
- Micro-waves
- Gamma-rays.
Question 16.
Name the EM waves used for studying crystal structure of
solids. What is its frequency range? (All India 2009)
Answer:
X-rays
frequency range : 1017 Hz to 1020 Hz
Question 17.
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum has largest penetrating
power? (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
γ-rays are the electromagnetic waves of
frequency range 3 × 1018 Hz to 5 × 1022 Hz and have the
highest penetrating power.
Question 18.
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is absorbed from
sunlight by ozone layer? (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Ultraviolet rays are
absorbed from sunlight by ozone layers.
Question 19.
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in radar
systems? (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Microwave region of electromagnetic spectrum
is used in radar systems.
Question 20.
Name the part of electromagnetic spectrum whose wavelength
lies in the range of 10-10 m. Give its one use. (All India 2010)
Answer:
Name : X-rays
Use : In medical diagnosis to look for broken bones;
treatment study of crystal structure.
Question 22.
Which of the following has the shortest wavelength :
Microwaves, Ultraviolet rays, X-rays. (All India 2010)
Answer:
X-rays have
the shortest wavelength.
Question 23.
Arrange the following in descending order of wavelength :
X-rays, Radio waves, Blue light, Infrared light. (All India 2010)
Answer:
Decreasing order ➝ Radio waves, Infrared light, Blue light, X-rays.
Question 24.
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along
z-direction. What can you say about the direction of electric and magnetic field
vectors? (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
The direction of electric field vector is
along X-axis. Magnetic field vector is along Y-axis.
Question 25.
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along
x-direction. What can you say about the direction of electric and magnetic field
vectors? (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
The electric field and magnetic field
vectors are in YZ-plane in the Y-direction and Z-direction respectively.
Question 26.
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along
y-direction. What can you say about the direction of electric and magnetic field
vectors? (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
The electric field and magnetic field vector
are in ZX-plane in the X-direction and Z-direction respectively.
Question 27.
How are radio waves produced? (All India 2011)
Answer:
Radio waves are produced by the accelerated motion of charges in conducting
wires.
Question 28.
How are X-rays produced? (All India 2011)
Answer:
X-rays are produced by sudden deceleration or acceleration of electrons in an
X-ray tube.
Question 29.
How are microwaves produced? (All India 2011)
Answer:
Microwaves are produced by Klystron valve or magnetron valve.
Question 30.
Name the physical quantity which remains same for microwaves
of wavelength 1 mm and UV radiations of 1600 Å in vacuum. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Speed/Velocity of light remains the same.
Question 31.
What are the directions of electric and magnetic field
vectors relative to each other and relative to the direction of propagation of
electromagnetic waves? (All India 2012)
Answer:
The oscillations of
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}\) fields are
perpendicular to each other as well as to the direction of propagation of the
wave.
Question 32.
The speed of an electromagnetic wave in a material medium is
given by \(v=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu \varepsilon}}, \mu\) the permeability of the
medium and ε its permittivity. How does its frequency change? (All India
2012)
Answer:
Frequency remains unchanged.
Question 33.
A capacitor has been charged by a dc source. What are the
magnitudes of conduction and displacement currents, when it is fully charged?
(Delhi 2013)
Answer:
On full charging, the source will maintain the
potential across the plates. The magnitudes of displacement current and
conduction current will be zero.
Question 34.
Welders wear special goggles or face masks with glass windows
to protect their eyes from electromagnetic radiations. Name the radiations and
write the range of their frequency. (All India 2013)
Answer:
The name of
radiations is ultraviolet radiation. Its frequency range is 1015 to
1017 Hz.
Question 35.
To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of
frequency 5 × 1019 Hz belong? (All India 2013)
Answer:
A wave
of frequency 5 × 1019 Hz belongs to γ-rays region of electromagnetic
spectrum.
Question 36.
To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of
frequency 3 × 1013 Hz belong? (All India 2014)
Answer:
Infra-red region of electromagnetic spectrum.
Question 37.
Why are microwaves considered suitable for radar systems used
in aircraft navigation? (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Due to their short
wavelengths, microwaves are considered suitable for radar systems in aircraft
navigation.
Question 38.
How is the speed of em-waves in vacuum determined by the
electric and magnetic fields? (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Speed of em-waves in
vacuum is determined by the ratio of the peak values of electric and magnetic
field vectors.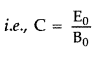
Question 39.
Do electromagnetic waves carry energy and momentum? (All
India 2017)
Answer:
Yes, they do, because of change of magnetic flux
associated with circular loop.
Question 40.
Write the relation for the speed for electromagnetic waves in
terms of the amplitudes of electric and magnetic fields. (All India 2017)
Answer: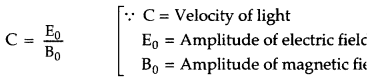
Question 41.
In which directions do the electric and magnetic field
vectors oscillate in an electromagnetic wave propagating along the x-axis? (All
India 2017)
Answer:
Electric field (\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}\))
oscillates along y-axis and magnetic field ( \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}\) )
oscillates along z-axis;in an electromagnetic wave propagating along the
x-axis.
Question 42.
The available frequency AC source is connected to a
capacitor. Will the displacement current change if the frequency of the AC
source is decreased? (CBSE Al 2015C)
Answer:
No
Question 42 a.
Why microwaves are considered suitable for radar systems used
in aircraft navigation? (CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
They have a small
wavelength and travel along a straight line with deflecting.
Question 43.
Do electromagnetic waves carry energy and momentum? (CBSE AI
2017)
Answer:
Yes.
Question 44.
How is the speed of em-waves in vacuum – determined by the
electric and magnetic field? (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
c =
\(\frac{E_{0}}{B_{0}}\)
Question 45.
Why is skywave propagation of signals restricted to a
frequency of 30 MHz? (CBSE Al 2017 C)
Answer:
The atmosphere is
transparent to frequencies higher than 30 MHz.
Question 46.
Name the electromagnetic radiations used for
(a) water
purification
Answer:
UV radiation
(b) eye surgery. (CBSEAI 2018, Delhi 2018)
Answer:
Visible light
Question 47.
Write the range of frequencies of electromagnetic waves which
propagate through sky wave mode. (CBSE Al 2018 C)
Answer:
A few MHz up to
30 to 40 MHz.
Question 48.
Optical and radio telescopes are built on the ground but
X-ray astronomy is possible only from satellites orbiting the earth. Why?
Answer:
This is because of the fact that X-rays are absorbed by the
atmosphere, whereas light and radio waves penetrate through it.
Question 49.
A charged particle oscillates about its mean equilibrium
position with a frequency of 109 Hz. What is the frequency of
the electromagnetic wave produced by the oscillator?
Answer:
Same as that
of the oscillating charged particle, i. e. 109 Hz.
Question 50.
Why are infrared radiations referred to as heat waves also?
Name the radiations which are next to these radiations in the electromagnetic
spectrum having
(a) Shorter wavelength and
(b) Longer wavelength.
Answer:
This is because they produce a heating effect.
(a) Visible light
and
(b) Microwaves.
Question 51.
What physical quantity are the same for X-rays of wavelength
10-10 m, the red light of wavelength 680 nm, and radio waves of
wavelength 500 m?
Answer:
Since all of them are electromagnetic waves,
their speed in a vacuum will be the same, i.e. 3 × 108 m
s-1.
Question 52.
A charged particle oscillates about its mean equilibrium
position with a frequency of 109 Hz. What is the frequency of the
electromagnetic waves produced by the oscillator?
Answer:
The frequency of
the electromagnetic waves produced by the oscillator is the same as its
frequency of vibration, i.e. 109 Hz.
Question 53.
The amplitude of the magnetic field part of a harmonic
electromagnetic wave in a vacuum is B0 = 510 nT. What is the
amplitude of the electric field part of the wave?
Answer:
Given
B0 = 510 nT = 510 × 10-9 T, E0 = ?
Using the relation E0 = c × B0, we have
E0 = 3 × 108 × 510 × 10-9 = 153 N C-1
Question 54.
Why does a microwave oven heat up a food item containing
water molecules most efficiently?
Answer:
It is because the frequency of
the microwave matches the resonant frequency of water molecules. This makes the
molecules vibrate with maximum amplitude thereby producing heat.
Question 55.
Name the most energetic electromagnetic radiation and write
its frequency range. (CBSE AI 2019 C)
Answer:
The most energetic
radiations are Gamma Rays Frequency range of gamma rays is: 1018 Hz
to 1023 Hz
Or
Name the electromagnetic radiations used in eye
surgery or to kill germs in water purifiers. Write its frequency, range.
Answer:
- Radiations used for eye surgery or to kill germs are Ultraviolet Rays.
- The frequency range of ultraviolet rays: 105 Hz to 1017 Hz.
Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Radio waves and gamma rays both are transverse in nature and
electromagnetic in character and have the same speed in a vacuum. In what
respect are they different?
Answer:
The radio waves have an atomic origin,
while gamma rays have a nuclear origin. Further owing to their very small
wavelength, gamma rays are highly penetrating in comparison to radio waves.
Question 2.
Show that the average energy density of the electric field
equals the average density of the magnetic field.
Answer:
The average
density of the electric field is given by
Ue =
\(\frac{1}{2}\)ε0E2 and the average energy density of the
magnetic field is given by UB = \(\frac{B^{2}}{2 \mu_{0}}\).
But B = \(\frac{E}{c}\) and c = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu_{0} \varepsilon_{0}}}\) , hence the above equation becomes UB = \(\frac{B^{2}}{2 \mu_{0}}=\frac{E^{2}}{2 \mu_{0} c^{2}}\)
UB = \(\frac{E^{2}}{2 \mu_{0} \times \frac{1}{\mu_{0} \varepsilon_{0}}}=\frac{1}{2} \varepsilon_{0} E^{2}\). Hence the result.
Question 3.
State four properties of electromagnetic waves.
Answer:
(a) They do not require any material medium to travel.
(b) They are
transverse in nature, i.e. electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to
each other and also to the direction of the propagation of the wave.
(c) The
energy of the wave is divided equally amongst the electric and the magnetic
field.
(d) They travel, in free space, with a velocity of 3 × 108
m s-1.
Question 4.
The oscillating magnetic field in a plane electromagnetic
wave is given by
By = (8 × 10-6) sin [2 × 10-11 t + 300
π x] T
(i) Calculate the wavelength of the electo-magnetic wave.
(ii)
Write down the expression for the oscillating electric field. (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
Given: By = 8 × 10-6 sin [2 × 1011 t
+ 300 π x] T
(i) Standard equation is,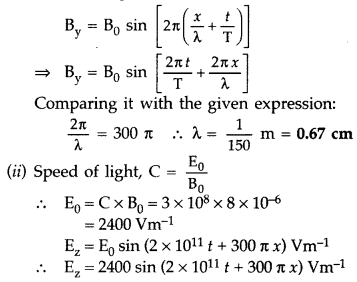
The oscillations of \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}\) fields are perpendicular to each other as well as to the direction of propagation of the wave. So we take electric field in z-direction because oscillating magnetic field is in y-di recti on and propagation of the wave is in x-direction.
Question 5.
The oscillating electric field of an electromagnetic wave is
given by :
E = 30 sin [2 × 1011 t + 300 π x] Vm-1
(a) Obtain the value of the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave.
(b) Write
down the expression for the oscillating magnetic field. (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
(a) We compare the given expression with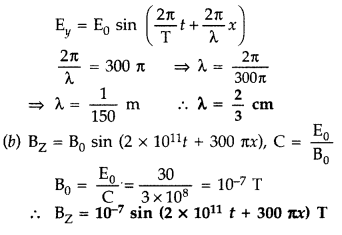
Question 6.
How does a charge q oscillating at certain frequency produce
electromagnetic waves? Sketch a schematic diagram depicting electric and
magnetic fields for an electromagnetic wave propagating along the Z-direction.
(Delhi 2009)
Answer:
As the charge q moves accelerating, the electric
field and magnetic field produced will change the space and time E and B varying
with time produced the other field B and E respectively and sustain the E.M.
pattern.
This is from the interpretation of Maxwell supported by
Question 7.
Arrange the following electromagnetic radiations in ascending
order of their frequencies:
(i) Microwave
(ii) Radiowave
(iii)
X-rays
(iv) Gamma rays
Write two uses of any one of these. (Delhi
2009)
Answer:
In ascending order of their frequencies :
Radiowave <
Microwave < X-rays < Gamma rays.
Two uses of microwaves are :
1. In
microwave ovens.
2. In aircraft navigation.
Question 8.
Draw a sketch of a plane electromagnetic wave propagating
along the z-direction. Depict clearly the directions of electric and magnetic
fields varying sinusoidally with z. (All India 2009)
Answer:
Sketch of a
plane electromagnetic wave propagating along the z-direction with oscillating
electric field E along the x-direction and the oscillating magnetic field B
along the y-direction.
Question 9.
How are infrared waves produced? Why are these referred to as
‘heat waves’? Write their one important use. (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Infrared
rays are produced by hot bodies and molecules. This may involve vibration and
bending of molecules. Infrared band lies adjacent to low-frequency or
long-wavelength end of the visible spectrum. Infrared waves are sometimes
referred to as heat waves.
Use: Infrared rays are used to take photographs in darkness. These are also used to study secret writing. They are also used in physical therapy.
Question 10.
A parallel plate capacitor is being charged by a time varying
current. Explain briefly how Ampere’s circuital law is generalized to
incorporate the effect due to the displacement current. (All India 2011)
Answer:
Maxwell’s displacement current : According to Ampere’s circuital law,
the magnetic field B is related to steady current I as
Maxwell showed that this relation is logically in-consistent. He accounted
this inconsistency as follows :
Ampere’s circuital law for loop C1
gives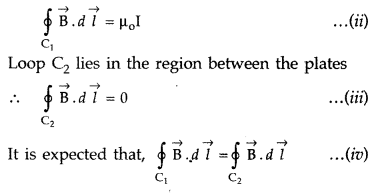
which is logically inconsistent. So, Maxwell gave idea of displacement
current.
Thus displacement current is that current which comes into play in the region
in which the electric field and hence the electric flux is changing with
time.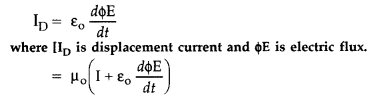
It is now called Ampere-Maxwell law. This is the generalization of Ampere’s
circuital law.
Question 11.
When an ideal capacitor is charged by a dc battery, no
current flows. However, when an ac source is used, the current flows
continuously. How does one explain this, based on the concept of displacement
current?
Answer:
A dc battery connected to an ideal capacitor
‘ provides only a momentarily charge, whereas an ac battery allows a continuous
flow of current![]()
As charge on capacitor plates changes, electric field
associated with that also changes and hence giving rise to a displacement
current according to![]()
Question 12.
A capacitor of capacitance ‘C is being charged by connecting
it across a dc source along with an ammeter. Will the ammeter show a momentary
deflection during the process of charging? If so, how would you explain this
momentary deflection and the resulting continuity of current in the circuit?
Write the expression for the current inside the capacitor. (All India 2012)
Answer:
Ammeter will definitely show a momentary deflection, which is due to
the flow of electron produced in the charging process. As the capacitor plates
get charging, the displacement current start flowing in the gap and thus shows a
continuity of current.![]()
Question 13.
(a) An em wave is travelling in a medium with a velocity
\(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}=\mathbf{v} \hat{i}\). Draw a sketch showing the
propagation of the em wave, indicating the direction of the oscillating electric
and magnetic fields.
(b) How are the magnitudes of the electric and magnetic
fields related to the velocity of the em wave?
Answer: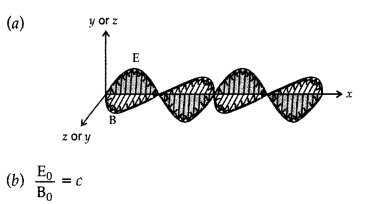
Question 14.
A capacitor, made of two parallel plates each of plate area A
and separation d, is being charged by an external ac source. Show that the
displacement current inside the capacitor is the same as the current charging
the capacitor. (All India 2012)
Answer:
The displacement current arises
due to varying electric field![]()
If q be instantaneous charge, then E is electric field between the plates of
capacitor at that time and A is area of plate; then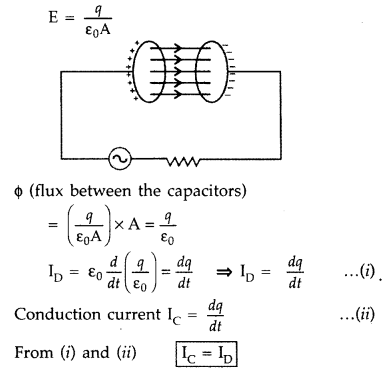
Question 15.
(a) How are electromagnetic waves produced?
(b) How do you
convince yourself that electromagnetic waves carry energy and momentum? (Comptt.
Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(a) Electromagnetic Waves : Accelerating electric
charge produces electromagnetic waves.
(b) Einstein’s explanation of photoelectric effect led de Broglie to the wave-particle duality, i.e., matter exhibits wave as well as particle properties. Electromagnetic waves are characterised by wave properties, such as periodicity in space-time, wavelength, amplitude, frequency, wave velocity etc. It transports energy but no matter.
The term wave-particle duality refers to the behaviour where both wave-like
and particle-like properties are exhibited under different conditions by the
same entity. Hence electromagnetic waves show particle properties such as
definite position, size, mass, velocity, momentum, energy etc.
For a photon
of momentum (p), an associated wavelength is given by
\(\lambda=\frac{h}{p}\).
Question 16.
(a) Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in the
descending order of their wavelengths :
- Microwaves
- Infra-red rays
- Ultra-violet radiation
- Gamma rays
(b) Write one use each of any two of them. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Arrangement:
- Microwaves
- Infra-red rays
- Ultra-violet radiation
- Gamma rays
(b) Uses :
- Microwaves are used in radar system.
- Infra-red rays are used for protecting dehydrated fruits.
- Ultra-violet rays are used in the study of molecular structure.
- Gamma rays are used to kill micro-organisms in food industry.
Question 17.
Considering the case of a parallel plate capacitor being
charged, show how one is required to generalize Ampere’s circuital law to
include the term due to displacement current. (All India 2014)
Answer:
Maxwell’s displacement current : According to Ampere’s circuital law, the
magnetic field B is related to steady current I as
Maxwell showed that this relation is logically in-consistent. He accounted
this inconsistency as follows :
Ampere’s circuital law for loop C1
gives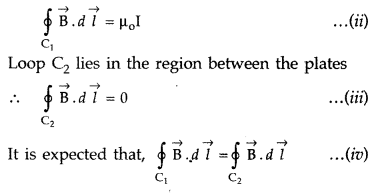
which is logically inconsistent. So, Maxwell gave idea of displacement
current.
Thus displacement current is that current which comes into play in the region
in which the electric field and hence the electric flux is changing with
time.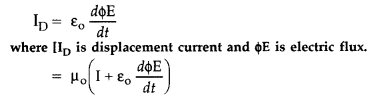
It is now called Ampere-Maxwell law. This is the generalization of Ampere’s
circuital law.
Question 18.
A capacitor is connected in series to an ammeter across a
d.c. source. Why does the ammeter show a momentary deflection during the
charging of the capacitor? What would be the deflection when it is fully
charged? (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
The momentary deflection is due
to the transient current flowing through the circuit when the capacitor is
getting charged.
The deflection would be zero when the capacitor gets fully
charged.
Question 19.
Name the types of e.m. radiations which
- are used in destroying cancer cells,
- cause tanning of the skin and
- maintain the earth’s warmth.
Write briefly a method of producing any one of these waves. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
- γ-rays
- Ultraviolet rays
- Infrared rays
Mode of production
- γ-rays are produced by radioactive decay of nucleus.
- Ultraviolet rays are produced when inner shell electrons in atoms move from one energy level to an other energy level.
- Infrared rays are produced due to vibration of atoms and molecules.
Question 20.
For a plane electromagnetic wave, propagating along the
Z-axis, write the two (possible) pairs of expression for its oscillating
electric and magnetic fields. How are the peak values of these (oscillating)
fields related to each other? (Comptt. All India 2016)
Answer:
For the
e.m. wave, propagating along the z-axis, we have![]()
The two possible forms for electric and magnetic fields are :![]()
The peak values of these two fields are related by![]()
Question 21.
An e.m. wave, Y1, has a wavelength of 1 cm while
another e.m. wave, Y2, has a frequency of 1015 Hz. Name
these two types of waves and write one useful application for each. (Comptt. All
India 2014)
Answer:
(i) Y1 ➝ Microwaves
Applications :
Microwaves are used in Microwave ovens, Aircraft Navigators etc.
(ii) Y2 ➝ Ultraviolet waves
Applications : Ultraviolet rays are
used in sterilizing surgical instruments, food preservation etc.
Question 22.
How does Ampere-Maxwell law explain the flow of current
through a capacitor when it is being charged by a battery? Write the expression
for the displacement current in terms of the rate of change of electric flux.
(Delhi 2017)
Answer:
During charging, the electric flux between the plates
of a capacitor keeps on changing; this results in the production of a
displacement current between the plates.
Question 23.
Identify the electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths vary
as
(a) 10-12 < λ < 10-8 m
(b) 10-3
m < X < 10-1 m
Write one use for each. (All India 2017)
Answer:
(a) X-rays—Used in medical science for the purpose of detection of
fractures, stones in gall bladder, stones in kidney etc.
(b) Microwaves—Used in radar systems for aircraft navigation.
Question 24.
Identify the electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths lie in
the range
(a) 10-11 m < λ < 10-8 m
(b)
10-4 m < λ < 10-6 m Write one use of each. (All
India 2017)
Answer:
(a) Uses of X-Rays and Gamma rays :
X-rays are used
as a diagnostic tool in medicine and as a treatment for certain forms of cancer.
Gamma rays are used in medicine to destroy cancer cells.
(b) Uses of Infrared, visible and microwaves :
- Infrared waves are widely used in remote switches of household electronic systems such as remotes for TVs, video recorders etc.
- Visible rays provide us information about the world.
- Microwaves are used in the radar systems in aircraft navigation.
Question 25.
How is electromagnetic wave produced? Draw a sketch of a
plane e.m. wave propagating along X-axis depicting the directions of the
oscillating electric and magnetic fields. (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Electromagnetic waves are produced due to oscillating/accelerating charged
particles.
Sketch of e.m. wave :
Question 26.
Electromagnetic radiations with wavelength
(a)
λ1 are used to kill germs in water purifiers.
(b) λ2
are used in TV communication systems.
(c) λ3 plays an important
role in maintaining the earth’s warmth.
Name the part of the electromagnetic
spectrum to which these radiations belong. Arrange these wavelengths in
decreasing order of their magnitude.
Answer:
(a) λ1 –
Ultraviolet radiations.
(b) λ2 – Microwaves
(c) λ3 –
Infrared rays
Their order is λ1 < λ3 <
λ2.
Question 27.
Name the constituent radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum
which
(a) is used in satellite communication.
Answer:
Microwaves.
(b) is used for studying crystal structure.
Answer:
X-rays
(c) is similar to the radiations emitted during the decay of a radioactive
nucleus.
Answer:
Gamma rays
(d) is absorbed from sunlight by the ozone layer.
Answer:
UV rays
(e) produces an intense heating effect.
Answer:
Infrared rays
(f) has its wavelength range between 390 nm and 770 nm.
Answer:
Visible
light.
Question 28.
Name the radiations of the electromagnetic spectrum which are
used in
(a) warfare to look through the haze.
Answer:
Infrared rays
(b) radar and geostationary satellites
Answer:
Microwaves.
(c) studying the structure and properties of atoms and molecules.
Answer:
Gamma rays.
Question 29.
Why are microwaves used in RADAR?
Answer:
Microwaves are
electromagnetic waves of very short wavelength. Such waves are used in RADAR due
to the reason that they can travel in a particular direction in the form of a
beam without being deflected.
Question 30.
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
(a) λ1 are
used to treat muscular strain.
(b) λ2 are used by an FM radio
station for broadcasting.
(c) λ3 are used to detect fractures in
bones.
(d) λ4 are absorbed by the ozone layer of the
atmosphere.
Identify and name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to
which these radiations belong. Arrange
these wavelengths in decreasing order
of magnitude.
Answer:
(a) Infrared radiations are used to treat muscular
strain.
(b) Radio and microwave radiations are used for FM transmission.
(c) X-rays are used to detect fractures in bones.
(d) Ultraviolet radiation
is absorbed by the ozone layer of the atmosphere.
The decreasing order of
their wavelength is
λ2 > λ1 > λ4 >
λ3.
Question 31.
(a) Draw a graph of a linearly polarised em wave propagating
in the Z-direction showing the directions of the oscillating electric and
magnetic fields.
Answer:
Graph of linearly polarised em wave propagating
in the Z-axis.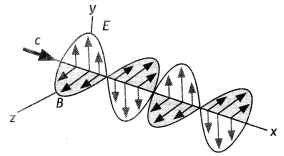
(b) Write the relations (i) between the speed of light and the amplitudes of
electric and magnetic fields, (ii) for the speed of em wave in terms of a
permittivity e0, and magnetic permeability p0, of the medium. (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
(i) Relation between speed of light and amplitudes of electric and
magnetic field c = \(\frac{E_{0}}{B_{0}}\)
(ii) Speed of light in terms of ε<sub>0</sub> and μ0,
c =
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu_{0} \varepsilon_{0}}}\)
Question 32.
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in the order of
their increasing wavelength:
(a) Gamma rays
(b) Microwaves
(c)
X-rays
(d) Radio waves
How are infrared waves produced? What role does
infrared radiation play in
(a) maintaining the Earth’s warmth and
(b)
physical therapy? (CBSE Al 2015)
Answer:
Gamma(γ) rays, X-rays,
Microwaves, Radio waves:
Infrared rays are produced by hot bodies/ vibration
of atoms and molecules Infrared rays: (a) Maintain the earth’s warmth through
the greenhouse effect, (b) produce heat
Question 33.
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is
(a) suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation.
Answer:
Microwave: They are produced by oscillating circuits.
(b) used to treat muscular strain.
Answer:
Infrared rays: They are
produced by the vibration of atoms and molecules.
(c) used as a diagnostic tool in medicine. Write in brief, how these waves
can be produced. (CBSE Delhi 2015)
Answer:
X-rays: They are produced by
bombarding high atomic number targets with electrons.
Question 34.
An e.m wave Y1 has a wavelength of 1 cm while
another e.m wave, Y2 has a frequency of 1015 Hz. Name
these two types of waves and write one useful application for each. (CBSE AI
2016 C)
Answer:
Y1 – Microwaves and
Y2 –
Ultraviolet waves.
- Microwaves: used for communication.
- Ultraviolet waves: used for sterilization.
Question 35.
Identify the electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths vary
as
(a) 10-12 m < λ < 10-8 m
Answer:
X –
rays: a study of crystal structure
(b) 10-3 m < λ < 10-1 m. Write one of their uses.
(CBSE Al 2017)
Answer:
Microwaves: radar and communication
Question 36.
Name the type of e.m waves having a wavelength range of 0.1 m
to 1 mm. How are these waves generated? Write their two uses. (CBSE Al 2017
C)
Answer:
- Microwaves: These are generated with the help of special vacuum tubes (called klystrons, magnetrons, and Gunn diodes).
- Uses: Cooking, radar, and communication
Question 37.
Identify the following electromagnetic radiations as per the
wavelengths given below. Write one application of each. (All India 2008)
(a)
10-3 nm
(b) 10-3 m
(c) 1 nm
Answer:
(a)
10-3 nm : γ-rays
Application :
- γ-rays are used in the treatment of cancer and tumour.
- γ-rays are used in radiation therapy. (any one)
(b) 10-3m : Microwave
Application : Microwaves are used in
Radar systems for aircraft navigation.
(c) 1 nm : X-rays Application :
- Infra-red waves are used for taking photographs during the conditions of fog, smoke etc.
- These are also used as a diagonostic tool for the detection of fractures, (any one)
Question 38.
Identify the following electromagnetic radiations as per the
wavelengths given below. Write one application of each.
(a) 1 mm
(b)
10-12 m
(c) 10-8 m (All India 2008)
Answer:
(a) 1
mm : Microwaves
Application : In aircraft navigation for the radar system.
Also used in microwave ovens.
(b) 10-12 m : Gamma rays
Application : Gamma rays are used as
medicine to destroy cancer cells
(c) 10-8 m : Ultraviolet rays
Application : Ultraviolet rays
are used in LASIK eye surgery.
Question 39.
(a) How does an oscillating charge produce electromagnetic
wave? Explain.
(b) Draw a sketch showing the propagation of a plane em wave
along the Z-direction, clearly depicting the directions of oscillating electric
and magnetic field vectors. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(a) Consider a
charge oscillating with same frequency. This produces an oscillating electric
field in space, which produces an oscillating magnetic field which in turn is a
source of oscillating electric field and so on. The oscillating electric and
magnetic fields thus regenerate each other, as the waves propagate through the
space. The frequency of the electromagnetic wave naturally equals the frequency
of the oscillation of the charge.
(b)
Sketch of a plane electromagnetic wave propagating along the
z-direction with oscillating electric field E along the x-direction and the
oscillating magnetic field B along the y-direction.
Question 40.
When an ac source is connected across a capacitor, current
starts flowing through the circuit. Show how Ampere’s circuital law is
generalized to explain the flow of current through the capacitor. Hence obtain
the expression for the displacement current inside the capacitor. (Comptt. All
India 2012)
Answer:
When an ‘ac’ source is connected across a capacitor,
the charge on the capacitor also becomes time dependent. It gives rise to a time
dependent electric field between the plates of capacitor. As a result the
electric flux changes.
It was suggested that we need to regard this changing electric flux, between
the plates of capacitor, as equivalent to a current which is called the
displacement current.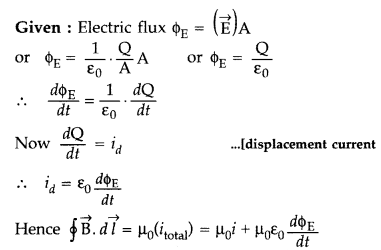
which is generalised form of an Ampere’s circuital law. .
Question 41.
(a) When the oscillating electric and magnetic fields are
along the x- and indirection respectively
- point out the direction of propagation . of electromagnetic wave.
- express the velocity of propagation in terms of the amplitudes of the oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
(b) How do you show that the em wave carries energy and momentum?(Comptt. All
India)
Answer:
(a)
- Along z-direction.
- Velocity of propogation will be, \(\mathbf{C}=\frac{\mathbf{E}_{0}}{\mathbf{B}_{0}}\)
(b) Photoelectric effect shows the particle nature of electromagnetic waves.
As such the photons carry energy and momentum. The energy is given by![]()
Question 42.
Answer the following :
(a) Name the em waves which are
suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation. Write the range of
frequency of these waves.
(b) If the. earth did not have atmosphere, would
its average surface temperature be higher or lower than what it is now?
Explain.
(c) An em wave exerts pressure on the surface on which it is
incident. Justify. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a) Microwaves are used in radar
systems. Its frequency range : 1010 to 1012 Hz
(b) In the absence of earth’s atmosphere, there would have no ozone layer to prevent ultraviolet radiations reaching the earth, the temperature on earth’s surface would have been lower due to green house effect, making it difficult for human survival.
(c) Since em wave carries both energy and momentum, hence exerts pressure on the surface on which it is incident.
An em wave exerts negligibly very small pressure on the surface on which it is incident.
It is due to the fact that momentum of the photon is extremely small, which
can be
calculated by de-Broglie relation
\(\left(\lambda=\frac{h}{p}\right)\)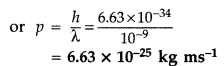
Question 43.
Answer the following :
(a) Name the em waves which are
used for the treatment of certain forms of cancer. Write their frequency
range.
(b) Thin ozone layer on top of stratosphere is crucial for human
survival. Why?
(c) Why is the amount of the momentum transferred by the em
waves incident on the surfrace so small? (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a) Gamma
(γ) rays are used for the treatment of certain forms of cancer. Their frequency
range is 1018 Hz to 1022 Hz.
(b) The thin ozone layer on top of stratosphere absorbs most of the harmful
ultraviolet rays coming from the Sun towards the Earth. They include UVA, UVB
and UVC radiations, which can destroy the life system on the Earth.
Hence,
this layer is crucial for human survival.
(c) Thus, the amount of the momentum transferred by the em waves incident on
the surface is very small, because of small value of planks constant. For
example, an electromagnetic wave of wavelength 1.00 nm will provide momentum (p)
according to de-Broglie’s relation,![]()
It is extremely small value of the momentum.
Question 44.
Answer the following questions :
(a) Name the em waves
which are produced during radioactive decay of a nucleus. Write their frequency
range.
(b) Welders wear special glass goggles while working. Why?
Explain.
(c) Why are infrared waves often called as heat waves? Give their
one application. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a) γ-rays; Frequency range :
1018 Hz to 1022 Hz
(b) Because to protect eyes from intense ultra-violet radiations produced during welding; and also to protect from glare and flying sparks.
(c) Because infrared waves are em waves of higher wavelength (less frequency)
and are produced by highly vibrating molecules of hot bodies.
Applications
:
- used in the remote switches of household electronic systems.
- used for protecting dehydrated fruits.
- used in solar water heaters and cookers. (Any one)
Question 45.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Show, by giving a
simple example, how em waves carry energy and momentum.
(i) How are
microwaves produced? Why is it necessary in microwave ovens to select the
frequency of microwaves to match the resonant frequency of water molecules?
(iii) Write two important uses of infrared waves. (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Consider a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation of
the wave. An electric charge, on the plane, will be set in motion by the
electric and magnetic fields of em wave, incident on this plane. This
illustrates that em waves carry energy and momentum.
(ii) Microwaves are produced by special vacuum tubes like the
Klystron/Magnetron/Gunn diode.
In microwave ovens, the frequency of
microwaves is selected to match the resonant frequency of water molecules, so
that energy is transferred efficiently to the kinetic energy of the
molecules.
(iii) Important uses of infra-red waves :
1. These are associated with the
green house effect.
2. These are used in remote switches of household
electrical appliances.
Question 46.
(a) A capacitor is connected in series to an ammeter across a
d.c. source. Why does the ammeter show a momentary deflection during the
charging of the capacitor? What would be the deflection when it is fully
charged?
(b) How is the generalized form of Ampere’s circuital law obtained
to include the term due to displacement current? (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
(a) The momentary deflection is due to the transient current flowing
through the circuit when the capacitor is getting charged.
The deflection
would be zero when the capacitor gets fully charged.
(b)
Maxwell’s displacement current : According to Ampere’s circuital law,
the magnetic field B is related to steady current I as
Maxwell showed that this relation is logically in-consistent. He accounted
this inconsistency as follows :
Ampere’s circuital law for loop C1
gives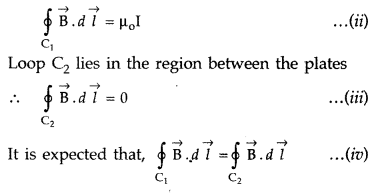
which is logically inconsistent. So, Maxwell gave idea of displacement
current.
Thus displacement current is that current which comes into play in the region
in which the electric field and hence the electric flux is changing with
time.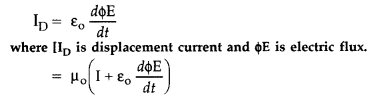
It is now called Ampere-Maxwell law. This is the generalization of Ampere’s
circuital law
Question 47.
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is
(a) suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation.
(b) used to treat
muscular strain.
(c) used as a diagnostic tool in medicine.
Write in
brief, how these waves can be produced. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a)
Microwaves
Production : Klystron/magnetron
(b) Infrared Radiations
Production ; Hot bodies/vibrations of atoms and
molecules.
(c) X-Rays
Production : Bombarding high energy electrons on a metal
target.
Question 48.
Write the expression for the generalized form of Ampere’s
circuital law. Discuss its significance and describe briefly how the concept of
displacement current is explained through charging/discharging of a capacitor in
an electric circuit. (All India 2014)
Answer:
Maxwell’s displacement
current : According to Ampere’s circuital law, the magnetic field B is related
to steady current I as![]()
Maxwell showed that this relation is logically inconsistent. He accounted this
inconsistency as follows :
Ampere’s circuital law for loop C1
gives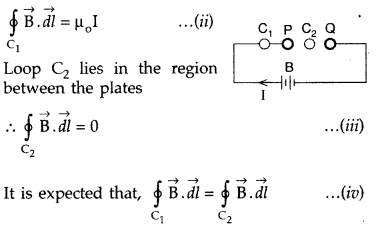
which is logically inconsistent. So, Maxwell gave idea of displacement
current.
Thus displacement current is that current which comes into play in
the region in which the electric field and hence the electric flux is changing
with time.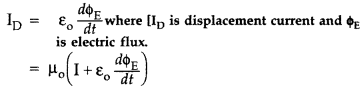
It is now called Ampere-Maxwell law. This is the generalization of Ampere’s
Circuital law.
Question 49.
How are em waves produced by oscillating charges?
Draw a
sketch of linearly polarized em waves propagating in the Z-direction. Indicate
the directions of the oscillating electric and magnetic fields. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
em waves by oscillating charges.
(a) Consider a charge oscillating with same frequency. This produces an oscillating electric field in space, which produces an oscillating magnetic field which in turn is a source of oscillating electric field and so on. The oscillating electric and magnetic fields thus regenerate each other, as the waves propagate through the space. The frequency of the electromagnetic wave naturally equals the frequency of the oscillation of the charge.
(b)
Sketch of a plane electromagnetic wave propagating along the
z-direction with oscillating electric field E along the x-direction and the
oscillating magnetic field B along the y-direction.
Sketch of em waves.
Sketch of a plane electromagnetic wave propagating
along the z-direction with oscillating electric field E along the x-direction
and the oscillating magnetic field B along the y-direction.
Question 50.
Write Maxwell’s generalization of Ampere’s Circuital Law.
Show that in the process of charging a capacitor, the current produced within
the plates of the capacitor is![]()
where ϕ E is electric flux produced during charging of the
capacitor plates. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Maxwell’s displacement current : According to Ampere’s circuital law, the
magnetic field B is related to steady current I as
Maxwell showed that this relation is logically in-consistent. He accounted
this inconsistency as follows :
Ampere’s circuital law for loop C1
gives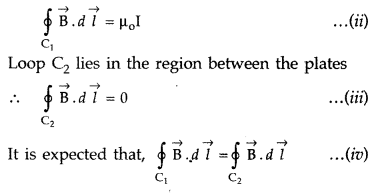
which is logically inconsistent. So, Maxwell gave idea of displacement
current.
Thus displacement current is that current which comes into play in the region
in which the electric field and hence the electric flux is changing with
time.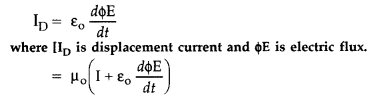
It is now called Ampere-Maxwell law. This is the generalization of Ampere’s
circuital law.
Question 51.
(i) Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which
is :
(a) suitable for radar system used in aircraft navigation,
(b)
produced by bombarding a metal target by high speed electrons.
(ii) Why does
a galvanometer show a momentary deflection at the time of charging or
discharging a capacitor? Write the necessary expression to explain this
observation. (All India 2016)
Answer:
(i)
(a) Microwaves
(b)
X-rays
(ii) The total current
(i) is the sum of conduction current
(ic) and displacement current (id), so we have![]()
This means that outside the capacitor plates in connecting
wires, we have only conduction current ic = i and no displacement
current (id = 0). On the other hand, inside the capacitor, there is
no conduction current (ic = 0) and there is only displacement current
hence i = id.
It is why there is momentary deflection in the
galvanometer at the time of charging or discharging a capacitor.
Question 52.
Name the e.m. waves in the wavelength range 10 nm to
10-3 nm. How are these waves generated? Write their two uses.
Answer:
- e.m. waves in the wavelength range 10 nm to 10-3 nm are X-rays.
- X-rays are generated by bombarding a metal target with high energy electrons.
• Uses :
- Diagnosis of bone fractures.
- Treatment of some forms of cancer.
Question 53.
Name the type of e.m. waves having a wavelength range of 0.1
m to 1 mm. How are these waves generated? Write their two uses. (Comptt. All
India 2017)
Answer:
- e.m. waves having a wavelength range 0.1 m to 1 mm are MICROWAVES.
- Microwaves are generated by special vacuum tubes such as klystron, magnetron and gunn diodes.
- Microwaves are used in :
- Radar system in aircraft navigation
- Ovens for heating and cooking.
Question 54.
Name the type of e.m. waves having a wavelength range
10-7 m to 10-9 m. How are these waves generated? Write
their two uses. (Comptt. All India 2017)
Answer:
- e.m. waves having a wavelength range 10-7 m to 10-9 m are ultra violet rays.
- Sun is an important source of UV rays. Some special lamps and very hot bodies also produce UV rays.
• Uses :
- UV rays are used in lasik eye surgery.
- UV lamps are being used to kill germs in water purifiers.
Question 55.
(a) Give one use of electromagnetic radiations obtained in
nuclear disintegrations.
Answer:
Treating cancer.
(b) Give one example each to illustrate the situation where there is
(i)
displacement current but no conduction current and
Answer:
Between the
plates of a capacitor
(ii) only conduction current but no displacement current.(CBSE Al 2018 C)
Answer:
Outside the plates of a capacitor
Question 56.
Scientists predict that a global nuclear war on the earth
will be followed by a severe nuclear winter, with devastating effects on the
earth. What is the basis of this prediction?
Answer:
The explosions will
produce so much dust, which will cover the whole atmosphere, thereby blocking
the sun’s rays from reaching the earth. This will cause the setting in of a long
winter, which is called nuclear winter.
Question 57.
If the earth did not have an atmosphere, would its average
surface temperature be higher or lower than what it is now?
Answer:
Due to
the Greenhouse effect, the temperature of the earth’s surface is raised in the
presence of the atmosphere. In the absence of the atmosphere, the heat received
by the earth during the day is completely lost during the night. Hence the
average surface temperature will be lower than the preset temperature.
Question 58.
A capacitor of capacitance ‘C is being charged by connecting
it across a dc source along with an ammeter. Will the ammeter show a momentary
deflection during the process of charging? If so, how would you explain this
momentary deflection and the resulting continuity of current in the circuit?
Write the expression for the current inside the capacitor. (CBSE AI 2012)
Answer:
Yes, this is due to the rate of change of electric flux inside the
capacitor due to the production of displacement current. The expression for the
current inside the capacitor is lD = εo \(\frac{d
\phi_{E}}{d t}\)
Question 59.
Define displacement current. What role does it play while
charging a capacitor by dc source? Is the value of displacement current the same
as that of the conduction current? Explain. (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
- Displacement current is the current due to the change of electric flux.
- It provides continuity of current in circuits containing capacitors.
- Yes, the value of displacement current is equal to the conduction current.
- ld = εo \(\frac{d \phi_{e}}{d t}\)
Question 60.
Why is the orientation of the portable radio with respect to
the broadcasting station important? (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
This is
because the electromagnetic waves are plane polarised; hence the receiving
antenna should be parallel to the electric/magnetic part of the wave.
Question 61.
(a) Give one use of electromagnetic radiations obtained in
nuclear disintegrations.
Answer:
used to destroy cancer cells
(b) Give one example each to illustrate the situation where there is
(i)
displacement current but no conduction current and
Answer:
The region,
between the plates of a capacitor, connected to a time-varying voltage source,
has a displacement current but no conduction current.
(ii) only conduction current but no displacement current. (CBSE Delhi
2018C)
Answer:
The wires, connected to the plates of a capacitor, joined
to a time-varying or steady voltage source, carry a conduction current but no
displacement current. (Alternatively, A circuit, having no capacitor in it, and
carrying a current has conduction current but no displacement current.)
Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Answer the following:
(a) Name the em waves which are used
for the treatment of certain forms of cancer. Write their frequency range.
Answer:
Gamma rays.
Frequency range > 3 × 1020 Hz
(b) Thin ozone layer on top of the stratosphere is crucial for human
survival. Why?
Answer:
The thin ozone layer on top of the stratosphere is
crucial for human survival because it absorbs most of the ultraviolet rays
coming from the sun. If the ozone layer had not been there, then ultraviolet
rays would have entered the earth and caused danger to the survival of the human
race.
(c) An em wave exerts pressure on the surface on which it is incident.
Justify. (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
An em wave carries a linear momentum
with it. The linear momentum carried by a portion of a wave having energy U is
given by p = U/c.
Thus, if the wave incident on a material surface is completely absorbed, it delivers energy U and momentum p = U/c to the surface. If the wave is totally reflected, the momentum delivered is p = 2U/c because the momentum of the wave changes from p to – p. Therefore, it follows that an em wave incident on a surface exerts a force and hence a pressure on the surface.
Question 2.
Answer the following questions:
(a) Why is the thin ozone
layer at the top of the stratosphere crucial for human survival? Identify to
which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does this radiation belongs and write
one important application of the radiation.
Answer:
The thin ozone layer
on top of the stratosphere is crucial for human survival because it absorbs most
of the ultraviolet rays coming from the sun. If the ozone layer had not been
there, then ultraviolet rays would have entered the earth and caused danger to
the survival of the human race. This radiation is UV radiation. It is used in
sterilization.
(b) Why are infrared waves referred to as heat rays? How are they produced?
What role do they play in maintaining the earth’s warmth through the greenhouse
effect? (CBSE Delhi 2015C)
Answer:
Infrared radiations heat up the
material on which they fall, hence they are also called heat rays. They are
produced by the vibration of atoms and molecules. After falling on the earth,
they are reflected back into the earth’s atmosphere. The earth’s atmosphere does
not allow these radiations to pass through as such they heat up the earth’s
atmosphere.
Question 3.
How are electromagnetic waves produced? What is the source of
energy of these waves? Write mathematical expressions for electric and magnetic
fields of an electromagnetic wave propagating along the z-axis. Write any two
important properties of electromagnetic waves. (CBSE AI 2016)
Answer:
Electromagnetic waves are produced by accelerated charges which produce an
oscillating electric field and magnetic field (which regenerate each other).
- Source of the Energy: Energy of the accelerated charge or the source that accelerates the charges.
- Expression: Ex = Eo sin (kz – ωt) and By
= Bo sin (kz – ωt)
(a) They are transverse in nature.
(b) They don’t require a medium to propagate.
Question 4.
How are em waves produced by oscillating charges?
Draw a
sketch of linearly polarised em waves propagating in the Z-direction. Indicate
the directions of the oscillating electric and magnetic fields. (CBSE Delhi
2016)
Answer:
(a) An oscillating charge produces an oscillating electric
field in space, which produces an oscillating magnetic field. The oscillating
electric and magnetic fields regenerate each other, and this results in the
production of em waves in space.
(b) See Figure.
Question 5.
Write Maxwell’s generalization of Ampere’s Circuital Law. Show
that in the process of charging a capacitor, the current produced within the
plates of the capacitor is i = εo\(\frac{d \phi_{E}}{d t}\) where ΦE
is the electric flux produced during charging of the capacitor plates. (CBSE
Delhi 2016)
Answer:
The generalized form of Maxwell ampere law is
\(\oint \vec{B} \cdot \overrightarrow{d l}\)= μo(l + lD)
where lD = εo\(\frac{d \phi_{E}}{d t}=\frac{d q}{d
t}\)
The electric flux Φ between the plates of the parallel plate capacitor
through which a time-dependent current flow is given by:
ΦE = E A,
but E = σ/εo
Therefore we have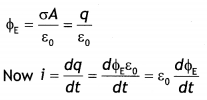
Question 6.
(a) Why are Infrared waves often called heatwaves? Explain.
Answer:
Infrared waves have frequencies lower than those of visibLe Light;
they have the ability to vibrate not only the electrons but the entire atoms or
molecules of a body. This vibration increases the internal energy and
temperature of the body. That is why infrared waves are often called heat
waves.
(b) What do you understand by the statement, “Electromagnetic waves transport
momentum”? (CBSE AI, Delhi 2018)
Answer:
If we consider a plane
perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave, then
electric charges present on the plane will be set and sustained in motion by the
electric and magnetic fields of the electromagnetic wave. The charges present on
the surface thus acquire energy and momentum from the waves. This just
illustrates the fact that an electromagnetic wave (like other waves) transfers
energy and momentum.
Question 7.
(a) When the oscillating electric and magnetic fields are
along the x- and y-direction respectively
(i) point out the direction of
propagation of the electromagnetic wave,
Answer:
Z-axis
(ii) express the velocity of propagation in terms of the amplitudes of the
oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
Answer:
c = Eo /
Bo
(b) How do you show that the em wave carries energy and momentum? (CBSE A!
2013C)
Answer:
Consider a plane perpendicular to the direction of
propagation of the electromagnetic wave. If there are, on this plane, electric
charges, they will be set and sustained in motion by the electric and magnetic
fields of the electromagnetic wave. The charges thus acquire energy and momentum
from the waves. This illustrates the fact that an electromagnetic wave carries
energy and momentum.
Question 8.
Answer the following questions:
(a) Show, by giving a
simple example, how em waves carry energy and momentum.
Answer:
Consider a
plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave.
If there are, on this plane, electric charges, they will be set and sustained in
motion by the electric and magnetic fields of the electromagnetic wave. The
charges thus acquire energy and momentum from the waves. This just illustrates
the fact that an electromagnetic wave (like other waves) carries energy and
momentum.
(b) How are microwaves produced? Why is it necessary in microwave ovens to
select the frequency of microwaves to match the resonance frequency of water
molecules?
Answer:
Microwaves (short-wavelength radio waves), with
frequencies in the gigahertz (GHz) range, are produced by special vacuum tubes
(called klystrons, magnetrons, and Gunn diodes). In such ovens, the frequency of
the microwaves is selected to match the resonant frequency of water molecules so
that energy from the waves is transferred efficiently to the kinetic energy of
the molecules. This raises the temperature of any food containing water.
(c) Write two important uses of infrared waves. (CBSE Delhi 2014C)
Answer:
Remote control of electronic devices, heating
Question 9.
A parallel plate capacitor is being charged by a time-varying
current. Explain briefly how Ampere’s circuital law is generalized to
incorporate the effect due to the displacement current. (CBSE AI 2011)
Answer:
Consider the curve C bounding two surfaces S1 and
S2. For the bound surface S1; the current passes through it, as such,
we can write Ampere’s circuital law as
\(\oint_{s_{1}} \vec{\phi} \cdot
\vec{d}\) = μol …(1)
If however, we choose the bound surface S2 that passes through the plates of
the capacitor and is not pierced by a current-carrying conductor, then Ampere’s
circuital law is written as
\(\oint_{s_{2}} \vec{\phi} \cdot \vec{d}\) = 0
….(2)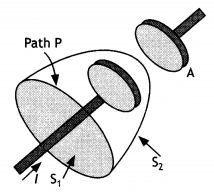
The above two equations contradict each other. To resolve this contradiction,
Maxwell showed that this inconsistency is due to the assumed discontinuity of
the current. According to Maxwell a current called displacement current “flows”
between the plates of the capacitor, where there is no conduction current.
Therefore Ampere’s circuital law takes the generalised expression \(\oint \vec{B} \cdot d \vec{l}\) = μo (l + lD),
here l is the conduction current and lD is the displacement current given
by
lD = εo \(\frac{d \phi_{E}}{d t}=\frac{d q}{d
t}\).
Outside the plates of the capacitor, conduction current flows and displacement current is zero, whereas inside the plates of the capacitor, displacement current exists and there is no conduction current.
Question 10.
(a) Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in
(i) radar and (ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
Answer:
Microwaves:
Frequency range (1010 to 1012 Hz)
Ultraviolet rays:
Frequency range (1015 to 1017 Hz)
(b) Prove that the average energy density of the oscillating electric field
is equal to that of the oscillating magnetic field. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
The average density of the electric field is
uE =
\(\frac{1}{2}\)εo E2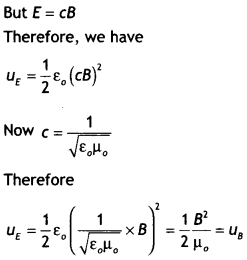
Question 11.
Answer the following questions:
(a) Long-distance radio
broadcasts use short-wave bands. Why?
Answer:
The long-distance radio
broadcast is not possible using long or medium wave bands because these waves,
traveling as ground waves, can cover a maximum distance of 200 km. When used as
sky waves, the short waves pass through the lower portion of the atmosphere but
are reflected back from the ionosphere. In this way, short waves can travel very
large distances and can even travel around the earth.
(b) It is necessary to use satellites for long-distance TV transmission.
Why?
Answer:
TV waves have a frequency range of 47 MHz to 940 MHz. These
frequencies are not reflected by the ionosphere. As space waves, they can cover
a distance of 50-60 km only. Therefore, for long-distance TV transmission, we
make use of satellites that reflect the TV signal wave back towards the
earth.
(c) Optical and radio telescopes are built on the ground but X-ray astronomy
is possible only from satellites orbiting the earth. Why?
Answer:
In
optical and radio-telescopes we use visible light and radio waves, respectively,
which can pass through the atmosphere. Hence, such telescopes are built on the
ground. However, X-rays have extremely small wavelengths and are absorbed by the
atmosphere. Hence, X-ray astronomy is not possible from ground stations. X-ray
astronomy is possible only from satellites orbiting the earth at a height of 500
km or more.
(d) The small ozone layer on top of the stratosphere is crucial for human
survival. Why?
Answer:
The thin ozone layer on top of the stratosphere is
crucial for human survival because it absorbs most of the ultraviolet rays
coming from the sun. If the ozone layer had not been there, then ultraviolet
rays would have entered the earth and caused danger to the survival of the human
race.
(e) If the earth did not have an atmosphere, would its average surface
temperature be higher or lower than what it is now?
Answer:
If the earth
did not have an atmosphere, then its average surface temperature would be lesser
than what it is now because in that case greenhouse effect will be absent.
(f) Some scientists have predicted that a global nuclear war on the earth
would be followed by a severe nuclear winter’ with a devastating effect on life
on the earth. What might be the basis of this prediction?
Answer:
The
prediction is based on the assumption that the large dust clouds produced by
global nuclear war would perhaps cover a substantial part of the sky and solar
radiations will not be able to reach the earth. It may cause a severe winter on
the earth with a devastating effect on life on the earth.
Numerical Problems
Question 1.
The frequency values v1 and v2, for two
spectral lines of the e.m. spectrum are found to be 5 × 1020 Hz and
2.5 × 1011 Hz respectively. Find the ratio,
λ1/λ2 of their wavelengths.
Answer: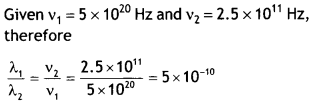
Question 2.
In a plane electromagnetic wave, the electric field oscillates
with a frequency of 2 × 1010 Hz and an amplitude of 40 VM.
(i)
What is the wavelength of the wave and
(ii) what is the energy density due to
the field?
Answer: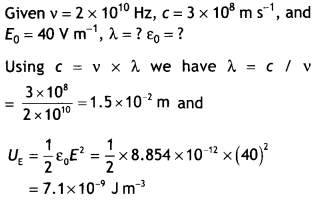
Question 3.
A plane electromagnetic wave of frequency 25 MHz travels In free
space along the x-direction. At a particular point In space and time, the
electric vector is \(\vec{E}\) = 6.3 Vm-1 ĵ. Calculate \(\vec{B}\) at
this point. (NCERT)
Answer:
The magnitude of B and E are related as c =
\(\frac{E}{B}\), therefore B = \(\frac{E}{c}=\frac{6.3}{3 \times 10^{8}}\) = 2.1
× 10-8. This field is along the z-axis, i.e. perpendicular to both
the propagation of the wave and the electric field.
Question 4.
The magnetic field in a plane electromagnetic wave Is given by
B = 2 × sin (0.5 × 10-3 x + 1.5 × 1011 t) T
(a) What
are the wavelength and frequency of the wave?
Answer:
(a) Comparing the
given equation with the equation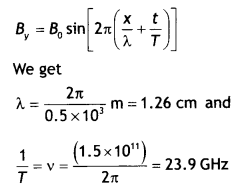
(b) Write an expression for the electric field. (NCERT)
Answer:
Eo = cBo = 2 × 107 × 3 × 108 = 60
Vm-1
The electric field component is perpendicular to the direction of propagation
and the direction of the magnetic field. Therefore, the electric field component
aLong the z-axis is obtained as
Ez = 60 sin(0.5 × 103
× + 1.5 × 1011 t)Vm-1
Question 5.
A radio can tune In to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz
bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band? (NCERT)
Answer: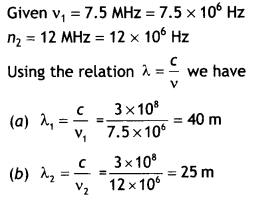
Thus the wavelength band is 40 m to 25m.
Question 6.
Suppose that the electric field amplitude of an
electromagnetic wave E0 = 120 N C-1 and that Its frequency
is v = 50.0 MHz. (a) Determine, B0, ω k, and λ. (b) Find expressions for E and
B. (NCERT)
Answer: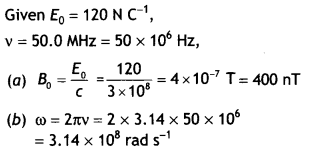
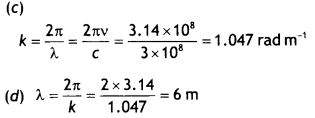
Question 7.
In a plane electromagnetic wave, the electric field oscillates
sinusoidally at a frequency of 2.0 × 1010 Hz and amplitude 48 V
m-1.
(a) What is the wavelength of the wave?
(b) What is the
amplitude of the oscillating magnetic field?
(c) Show that the average energy
density of the E field equals the average energy density of the 8 fields. [c = 3
× 108ms-1.] (NCERT)
Answer: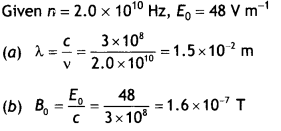
(c) The average density of electric field is
given by Ue =
\(\frac{1}{2}\)ε0E2 and the average energy density of the
magnetic field is given by UB = \(\frac{B^{2}}{2 \mu_{0}}\). But B =
\(\frac{E}{c}\) and C = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu_{0} \varepsilon_{0}}}\) , hence the
above equation becomes UB = \(\frac{B^{2}}{2 \mu_{0}}=\frac{E^{2}}{2 \mu_{0}
c^{2}}\),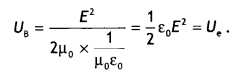
Question 8.
Suppose that the electric field part of an electromagnetic wave
in a vacuum is
E = {(3.1 NC-1>)cos(1.8 rad m-1)y +
(5.4 × 106 rad s-1)t}î
(a) What is the direction of
propagation?
(b) What is the wavelength?
(c) What is the frequency v?
(d) What is the amplitude of the magnetic field part of the wave?
(e) Write
an expression for the magnetic field part of the wave. (NCERT)
Answer:
The
electric field is of the form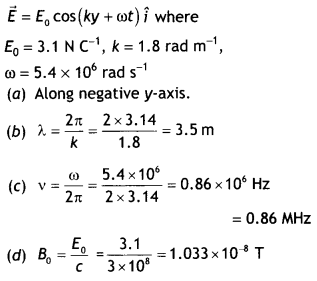
(e) Expression for magnetic field part of the wave
\(\vec{B}\) =
Bo cos (ky + ωt) k̂
or
\(\vec{E}\) = {(10.3 n T)cos[(1.8 rad
m-1)y + (5.4 × 106 rad s-1)t} î