Magnetism and Matter
Class 12th Physics Chapter Important Questions
Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 Important Extra Questions Magnetism and Matter
Very Short Answer
Question 1.
A small magnetic needle pivoted at the center is free to
rotate In a magnetic meridian. At what place will the needle
be vertical?
Answer:
At the potes
Question 2.
What is the angle of dip at a place where the horizontal and
vertical components of the earth’s magnetic field are equal?
Answer:
450
Question 3.
How does the intensity of a paramagnetic sample vary with
temperature?
Answer:
it decreases with the increase in temperature.
Question 4.
What should be the orientation of a magnetic dipole in a
uniform magnetic field so that its potential energy is maximum?
Answer:
It
should be anti-parallel to the applied magnetic field.
Question 5.
What is the value of angle of dip at a place on the surface of
the earth where the ratio of the vertical component to the horizontal component
of the earth’s magnetic field is 1/\(\sqrt{3}\)?
Answer:
Using the
expression tan δ = \(\frac{B_{V}}{B_{H}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
Therefore, δ =
30°
Question 6.
Where on the surface of the earth is the angle of dip 90°?
(CBSE Al 2011)
Answer:
Poles.
Question 7.
Where on the surface of the earth is the angle dip zero? (CBSE
Al 2011)
Answer:
Magnetic equator
Question 8.
What are permanent magnets? Give one example. (CBSE Delhi
2013)
Answer:
It is an arrangement that has a permanent dipole moment,
e.g. bar magnet.
Question 9.
At a place, the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic
field is B, and the angle of dip is 60°. What is the value of the horizontal
component of the earth’s magnetic field at the equator? (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Zero.
Question 10.
Is the steady electric current the only source of the
magnetic field? Justify your answer. (CBSE Delhi 2013C)
Answer:
No, the
magnetic field is also produced by alternating current.
Questions 11.
The permeability of a magnetic material is 0.9983. Name the
type of magnetic materials it represents. (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
It
represents diamagnetic materials.
Question 12.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 1.9 ×
10-5. Name the type of magnetic materials it represents. (Delhi
2011)
Answer:
It represents Paramagnetic substance.
Question 13.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is – 4.2 ×
10-6. Name the type of magnetic materials it represents. (Delhi
2011)
Answer:
It represents diamagnetic substances.
Question 14.
Where on the surface of Earth is the angle of dip 90°? (All
India 2011)
Answer:
At the magnetic poles, the angle of dip is 90° on the
surface of Earth.
Question 15.
Where on the surface of Earth is the angle of dip zero? (All
India 2011)
Answer:
At the magnetic equator, the angle of dip is 0°.
Question 16.
Where on the surface of Earth is the vertical component of
Earth’s magnetic field zero? (All India 2011)
Answer:
At the Magnetic
equator the vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field is zero.
Question 17.
The horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at a
place is B and angle of dip is 60°. What is the value of vertical component of
earth’s magnetic field at equator? (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
BH = B
cos δ
BV = BH tan δ = B tan 60° = B × √3 = √3B
∴ At
equator, BV = 0 (zero).
Question 18.
Current flows through a circular loop. Depict the north and
south pole of its equivalent magnetic dipole. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Direction of the magnetic field lines is given by right hand thumb
rule.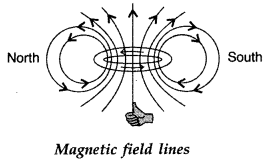
Question 19.
A straight wire extending from east to west falls with a speed
v at right angles to the horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field.
Which end of the wire would be at the higher electrical potential and why?
(Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
West end of the wire must be at higher
electric potential. According to Fleming’s Right Hand rule, “the direction of
induced emf is from West to East”.
Question 20.
What are permanent magnets? Give one example. (Delhi
2013)
Answer:
Substances which at room temperature retain their
ferromagnetic property for a long period of time are called permanent
magnets.
Example: Steel, alinco
Question 21.
Which of the following substances are diamagnetic?
Bi, Al,
Na, Cu, Ca and Ni (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Bi and Cu
Question 22.
Which of the following substances are para-magnetic ?
Bi,
Al, Cu, Ca, Pb, Ni (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Al and Ca are para-magnetic.
Question 23.
Is the steady electric current the only source of magnetic
field? Justify your answer. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
No. Steady
current is not the only source of magnetic field. Magnets are also source of
magnetic field. Unsteady current will also be source of varying magnetic
field.
Question 24.
Where on the surface of Earth is the vertical com-ponent of
Earth’s magnetic field zero? (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
At the Equator
the vertical component of the Earth’s magnetic field is zero.
Question 25.
Where on the surface of Earth is the horizontal component of
Earth’s magnetic field zero? (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
At poles of
Earth the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field is zero.
Question 26.
Where on the surface of Earth is the Earth’s magnetic field
perpendicular to the surface of the Earth? (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
At
poles of the Earth. The Earth’s magnetic field is perpendicular to the surface
of the Earth.
Question 27.
The motion of copper plate is damped when it is allowed to
oscillate between the two poles of a magnet. What is the cause of this damping?
(All India 2013)
Answer:
The cause of this damping is eddy current.
Question 28.
Relative permeability of a material, µr = 0.5.
Identify the nature of the magnetic material and write its relation to magnetic
susceptibility. (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
- Diamagnetic material
- µr = 1 + Xm
Question 29.
Relative permeability of a material µr = 400.
Identify the nature of the magnetic material (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
It is Ferromagnetic.
Question 30.
Relative permeability (µr) of a material has a
value lying 1 < µr < 1 + ε (where ε is a small quantity).
Identify the nature of the magnetic material. (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Substance : Paramagnetic
Question 31.
In what way is the behaviour of a diamagnetic material
different from that of a paramagnetic, when kept in an external magnetic field?
(All India 2016)
Answer:
- A diamagnetic specimen would move towards the weaker region of the field; while a paramagnetic specimen would move towards the stronger region.
- A diamagnetic specimen is repelled by a magnet while a paramagnetic specimen moves towards the magnet.
- The paramagnetic gets aligned along the field and the diamagnetic perpendicular to the field.
Question 32.
At a place, the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic
field is B and angle of dip is 60°. What is the value of horizontal component of
the earth’s magnetic field at the equator? (Delhi 2017)
Answer: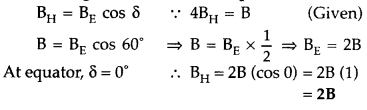
Question 33.
Write one important property of a paramagnetic material.
(CBSEAI2019)
OR
Do the diamagnetic substances have a resultant magnetic
moment in an atom in the absence of an external magnetic field?
Answer:
It
moves from the weaker to the stronger regions of the magnetic field.
OR
No
Question 34.
Steel is preferred for making permanent magnets, whereas soft
iron is preferred for making electromagnets. Give one reason.
Answer:
- The Retentivity of steel is more than that of soft iron.
- Soft iron has a smaller value of coercivity than steel.
Question 35.
Define angle of inclination at a given place due to the
earth’s magnetic field. (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
The angle of inclination is
the angle at which the earth’s magnetic field at a given place makes with the
horizontal line in the magnetic meridian.
Question 36.
Relative permeability of a material p = 0.5. Identify the
nature of the magnetic material and write its relation to magnetic
susceptibility. (CBSE Delhi 2014C)
Answer:
Paramagnetic.
Susceptibility
is small and greater than one.
Short Answer Type
Question 37.
Define magnetic susceptibility of a material. Name two
elements, one having positive susceptibility and the other having negative
susceptibility. What does negative susceptibility signify? (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
(i) Magnetic susceptibility \(\left(\chi_{m}\right)\) : It is the
property of a material which determines how easily it can be magnetised when
kept in a magnetising field.
Also, it is the ratio of intensity of magnetisation (I) produced in the
material to the intensity of magnetising field (H)![]()
(ii) Positive susceptibility : para-magnetic material
Example: Al, Ca.
Negative susceptibility : diamagnetic material
Example: Bi, Cu.
(iii) Negative susceptibility signifies that the material is diamagnetic in nature.
Question 38.
The figure shows the variation of intensity of magnetisation
versus the applied magnetic field intensity, H, for two magnetic materials A and
B :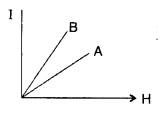
(a) Identify the materials A and B.
(b) Why does the
material B, has a larger susceptibility than A, for a given field at constant
temperature? (All India 2008)
Answer:![]()
Slope of the line gives magnetic susce¬ptibilities.
For
magnetic material B, it is giving higher +ve value.
So material is
‘ferromagnetic’.
For magnetic material A, it is giving lesser +ve value than
‘B’.
So material is ‘paramagnetic’.
(b) Larger susceptibility is due to characteristic ‘domain structure’. More number of mag¬netic moments get aligned in the direction of magnetising field in comparision to that for paramagnetic materials for the same value of magnetising field.
Question 39.
(i) Write two characteristics of a material used for making
permanent magnets.
(ii) Why is core of an electromagnet made of ferromagnetic
materials? (Delhi)
Answer:
(i) Two characteristics of a material used for
making permanent magnets are :
(a) High retentivity so that it produces a
strong magnetic field.
(b) High coercivity so that its magnetisation is not
destroyed by strong magnetic fields, temperature variations or minor mechanical
damage.
(ii) The core of electromagnet is made of ferromagnetic materials because
they have
high initial permeability so that magnetisation is large even for a
small magnetising field and low resistivity to reduce losses due to eddy
currents.
Question 40.
Draw magnetic field lines when a
(i) diamagnetic,
(ii)
paramagnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field.
Which
magnetic property distinguishes this behaviour of the field lines due to the two
substances?
Answer:
(i) When a diamagnetic material is placed in an
external magnetic field.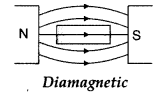
(ii) When a paramagnetic material is placed in an external magnetic
field.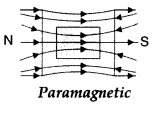
Magnetic susceptibility distinguishes this behaviour of the
field lines due to the two substances.
Question 41.
A magnetic needle free to rotate in a vertical plane parallel
to the magnetic meridian has its north tip down at 60° with the horizontal. The
horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at the place is known to be
0.4 G. Determine the magnitude of the earth’s magnetic field at the place.
(Delhi 2011)
Answer: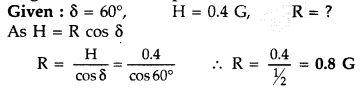
Question 42.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is – 2.6 ×
10-5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two
properties. (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Magnetic material is diamagnetic, because
susceptibility of a magnetic material is in negative.
Properties are :
- In a non-uniform magnetic field, it tends to move slowly from stronger to weaker parts of the field.
- A freely suspended diamagnetic rod aligns itself perpendicular to the field.
- They expel magnetic field lines.
- Such substances are repelled by a magnet. [any two]
Question 43.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 2.6 ×
10-5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two
properties. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The material is paramagnetic.
Its two
properties are :
- They are feebly attracted by magnets.
- In a non-uniform magnetic field, they tend to move slowly from weaker to stronger parts of the field.
Question 44.
The relative magnetic permeability of a magnetic material is
800. Identify the nature of magnetic material and state its two properties.
(Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Substance is ferromagnetic.
Its properties are
:
- They are strongly attracted by magnets.
- In a non-uniform magnetic field, they tend to move quickly from weaker to stronger parts of the field.
Question 45.
A circular coil of N turns and radius R carries a current I.
It is unwound and rewound to make another coil of radius R/2, current I
remaining the same. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic moments of the new coil
and the original coil. (All India 2012)
Answer: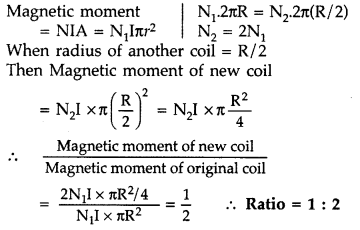
Question 46.
A circular coil of N turns and diameter ‘d’ carries a current
‘I’. It is unwound and rewound to make another coil of diameter ‘2d’, current T
remaining the same. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic moments of the new coil
and the original coil. (All India 2012)
Answer:
Magnetic moment of the
coil is given by M = NIA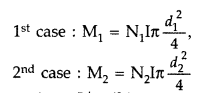
But as given, Ist coil is rewound to make new
coil.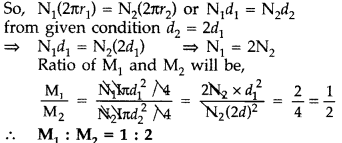
Question 47.
(a) How does a diamagnetic material behave when it is cooled
to very low temperatures?
(b) Why does a paramagnetic sample display greater
magnetisation when cooled? Explain. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(a) When
diamagnetic material is cooled to very low temperature then it exhibits both
perfect conductivity and perfect diamagnetism.
(b) This is because at lower
temperature, the tendency to disrupt the alignment of dipoles (due to
magnetising field) decreases on account of reduced random thermal motion.
Question 48.
State two characteristic properties distinguishing the
behaviour of paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials. (Comptt. All India
2012)
Answer:
| Paramagnetic | Diamagnetic | |
| (i) | Susceptibility is small and positive, i.e., 0 < \(\chi_{m}\) < ε (where e is a small number) for paramagnetic | Susceptibility is small and negative, i.e., -1 ≤ \(\chi_{m}\) for diamagnetic. |
| (ii) | Paramagnetic materials are feebly attracted by magnets | Diamagnetic materials are feebly repelled by magnets |
Question 49.
State two characteristic properties distinguish¬ing the
behaviour of diamagnetic and ferromagnetic materials. (Comptt. All India
2013)
Answer:
| Diamagnetic material | Ferromagnetic material |
| (i) Relative magnetic permeability of
dia-magnetic substances is always less than unity, i.e.,\(\mu_{r}\) <
1.
(ii) The susceptibility of diamagnetic substances has a small -ve value : \(\mu_{r}\) < 1 ⇒ -1 ≤ \(\chi_{m}\) ≤ 0 |
Relative magnetic permeability of ferromagnetic
materials is very large (= 103 to 105).The susceptibility of ferromagnetic materials is very large. \(\chi_{m}\) > 1 |
Question 50.
Write two characteristic properties each to select materials
suitable for
(i) permanent magnets and
(ii) electromagnets. (Comptt. All
India 2013)
Answer:
Properties of a material—
(a) For making a
permanent magnet:
- High retentivity
- High coercivity
- High permeability
(b) For making an electromagnet:
- High permeability .
- Low retentivity
- Low coercivity
Question 51.
A coil of ‘N’ turns and radius ‘R’ carries a current ‘I’. It
is unwound and rewound to make a square coil of side ‘a’ having same number of
turns (N). Keeping the current ‘I’ same, find the ratio of the magnetic moments
of the square coil and the circular coil. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer: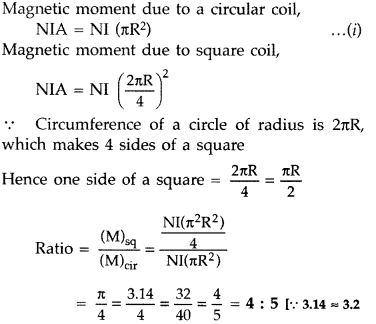
Question 52.
Depict the behaviour of magnetic field lines when
(i) a
diamagnetic material and
(ii) a paramagnetic material is placed in an
external magnetic field. Mention briefly the properties of these materials which
explain this distinguishing behaviour. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
Diamagnetic materials. Diamagnetic materials are those which have tendency to
move from stronger to the weaker part of the external magnetic field.
Examples. Bismuth, copper, lead and silicon.
Properties:
(i) When a rod of
diamagnetic material is sus-pended inside a magnetic field, it slowly sets
itself at right angles to the direction of field.
(ii) When a diamagnetic
material is placed inside a magnetic field, the magnetic field lines become
slightly less dense in the diamagnetic material.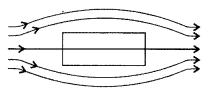
(iii) For diamagnetic material :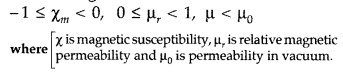
Paramagnetic materials. Paramagnetic materials are those which get weakly
magnetised when placed in an external magnetic field. They have tendency to move
from a region of weak magnetic field to strong magnetic field.
Examples.
Aluminium, sodium, calcium and oxygen.
Properties :
(i) When a rod of paramagnetic material is suspended inside a
magnetic field, it slowly sets itself parallel to the direction of the magnetic
field.
(ii) When a paramagnetic material is placed inside a magnetic field, the
magnetic field lines become slightly more dense in the paramagnetic
material.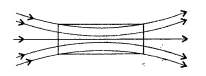
(iii) The magnetic susceptability ‘\(\chi_{m}\)‘ of a paramagnetic material has a small positive value, ie. 0 < \(\chi_{m}\) < ε
Question 53.
Out of the two magnetic materials, ‘A’ has relative
permeability slightly greater than unity while ‘B’ has less than unity. Identify
the nature of the materials ‘A’ and ‘B’. Will their susceptibilities be positive
or negative? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
‘A’ is paramagnetic
‘B’ is
diamagnetic
The susceptibility of material ‘A’ is positive while of ‘B’ is
negative.
Question 54.
Show diagrammmatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines
in the presence of
(i) paramagnetic and
(ii) diamagnetic substances.
How does one explain this distinguishing feature? (All India 2013)
Answer:
(i) Paramagnetic substance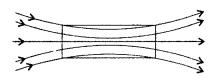
(ii) Diamagnetic substance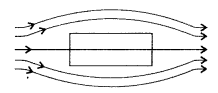
The range of relative magnetic permeability (µr)
of paramagnetic substance is µr > 1 . while for diamagnetic
substance, it is µr < 1.
Question 55.
(a) How is an electromagnet different from a permanent
magnet?
(b) Write tivo properties of a material which make it suitable for
making electromagnets. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
(a) A permanent
magnet is prepared from a ferromagnetic material, which retains magnetic
properties for a long time at room temperature while
- an electromagnet consists of a core made of a ferromagnetic material placed inside a solenoid. It behaves like a permanent magnet as long as a current flows through it.
(b) Properties of material :
- high permeability
- low retentivity
- low coercivity (any two)
Question 56.
Write two properties of a material suitable for making
(a)
a permanent magnet, and
(b) an electromagnet. (All India 2017)
Answer:
Properties of a material—
(a) For making a permanent magnet:
- High retentivity
- High coercivity
- High permeability
(b) For making an electromagnet:
- High permeability .
- Low retentivity
- Low coercivity
Question 57.
Depict the behaviour of magnetic field lines near
(i)
diamagnetic and
(ii) paramagnetic substances. Justify, giving reasons.
Answer:
Behaviour of magnetic lines of force near
(i) diamagnetic substances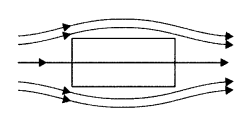
(ii) paramagnetic substances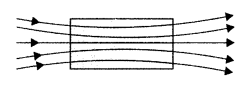
Justification : The field lines are repelled or expelled and
the field inside the material is reduced near diamagnetic substances.
In the presence of magnetic field, the individual atomic dipoles can get aligned in the direction of the applied magnetic field. Therefore, field lines get concentrated inside the material and the field inside is enhanced near paramagnetic substances.
Question 58.
Define the following using suitable diagrams :
(i)
magnetic declination and
(ii) angle of dip. In what direction will a compass
needle point when kept at the
(i) poles and
(ii) equator? (Comptt. Delhi
2015)
Answer:
Magnetic declination:
Angle between magnetic meridian and
geographical meridian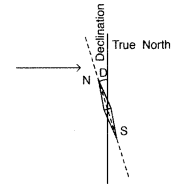
Angle of dip : It is the angle which the magnetic needle makes with the
horizontal in the magnetic meridian.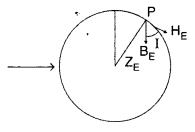
- Direction of compass needle is vertical to the earth’s surface at poles.
- Parallel to the earth’s surface at equator.
Question 59.
(a) Define the term magnetic susceptibility and write its
relation in terms of relative magnetic permeability.
Answer:
It refers to
the ease with which a substance can be magnetized. It is defined as the ratio of
the intensity of magnetization to the magnetizing field. The required relation
is µr = 1 + χm
(b) Two magnetic materials A and B have relative magnetic permeabilities of
0. 96 and 500. Identify the magnetic materials A and B. (CBSE Al, Delhi
2018C)
Answer:
A: Paramagnetic,
B: Ferromagnetic
Question 60.
A magnetic needle free to rotate in a vertical position
orients itself with its axis vertical at a certain place on the earth. What are
the values of
(a) the angle of dip and
(b) the horizontal component of the
earth’s magnetic field at this place? Where will this place be on the earth?
Answer:
The angle of dip is 90° and the horizontal component of the earth’s
magnetic field is zero. This place is the magnetic pole of the earth.
Question 61.
Out of the two magnetic materials ‘A’ has relative
permeability slightly greater than unity while ‘B’ has less than unity. Identify
the nature of the materials ‘A’ and ‘B’. Will their susceptibilities be positive
or negative? (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
- ‘A’ is paramagnetic and ‘B’ is diamagnetic.
- ‘A’ will have positive susceptibility while
- ‘B’ will have negative susceptibility.
Question 62.
A magnetic needle free to rotate in a vertical plane parallel
to the magnetic meridian has its northern tip down at 60° with the horizontal.
The horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at the place is known to
be 0.4 G. Determine the magnitude of the earth’s magnetic field at the place.
(CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Given δ = 30°, BH = 0.4 G, B = ?
Using the expression
BH = Bcos δ we have
B =
\(\frac{B_{H}}{\cos \delta}=\frac{0.4}{\cos 30^{\circ}}=\frac{0.4}{\sqrt{3} /
2}=\frac{0.8}{\sqrt{3}}\) G
Question 63.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is -0.085. Identify
the type of magnetic material. A specimen of this material is kept in a
non-uniform magnetic field. Draw the modified field pattern.
Answer:
The
material is a diamagnetic material as diamagnetic materials have negative
susceptibility. The modified field pattern is as shown below.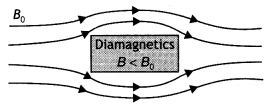
Question 64.
A uniform magnetic field gets modified as shown below when two
specimens X and Y are placed in it.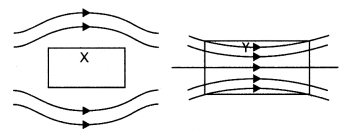
(a) Identify the two specimens X and Y.
Answer:
X is a diamagnetic
substance and Y is a paramagnetic substance.
(b) State the reason for the behavior of the field lines in X and Y.
Answer:
This is because the permeability of a diamagnetic substance is less
than one and that of a paramagnetic substance is greater than one.
Question 65.
Three identical specimens of magnetic materials nickel,
antimony, and aluminum are kept in a non-uniform magnetic field. Draw the
modification in the field lines in each case. Justify your answer.
Answer:
Nickel is ferromagnetic, antimony is diamagnetic and aluminium is
paramagnetic. Therefore, they will show the behavior as shown in the following
figures.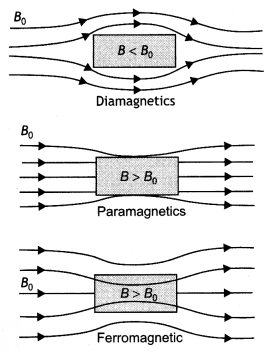
Question 66.
Define neutral point. Draw lines of force when two identical
magnets are placed at a finite distance apart with their N-poles facing each
other. Locate the neutral points.
Answer:
It is a point near a magnet
where the magnetic field of the earth is completely balanced by the magnetic
field of the magnet. The figure is as shown below.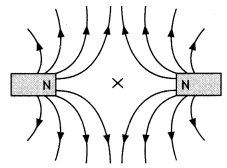
The cross indicates the neutral point.
Question 67.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is -2.6 x
10-5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two
properties. (CBSE Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Diamagnetic:
- Very small and negative susceptibility
- Permeability is less than one.
Long Answer Type
Question 68.
(a) A small compass needle of magnetic moment ‘m’ is free to
turn about an axis perpendicular to the direction of uniform magnetic field ‘B’.
The moment of inertia of the needle about the axis is ‘I’. The needle is
slightly disturbed from its stable position and then released. Prove that it
executes simple harmonic motion. Hence deduce the expression for its time
period.
(b) A compass needle, free to turn in a vertical plane orients itself with its axis vertical at a certain place on the earth. Find out the values of
- horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field and
- angle of dip at the place. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) This is done by placing a small compass needle of known
magnetic moment m and moment of inertia I and allowing it to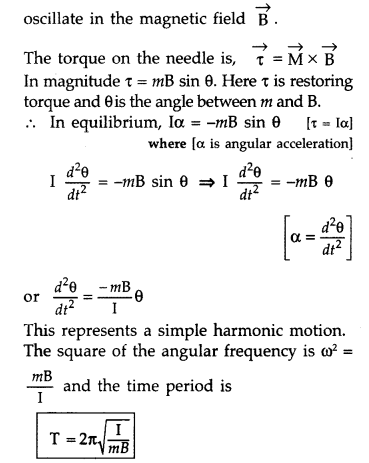
(b) Since, the compass needle is oriented vertically
- Horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field will be zero.
- The value of angle of dip at that place will be 90°.
Question 69.
Write the expression for the magnetic dipole moment for a
closed current loop. Give its SI unit. Derive an expression for the torque
experienced by a magnetic dipole in a uniform magnetic field.
Answer:
The
required expression is m = nIA.
It is measured in A m².
Consider a uniform magnetic field of strength B. Let a magnetic dipole be
suspended in it such that its axis makes an angle 6 with the field as shown in
the figure below. If ‘m’ is the strength of each pole, the two poles experience
two equal and opposite force ‘B’ each. These forces constitute a couple that
tends to rotate the dipole. Suppose the couple exerts a torque of magnitude
τ.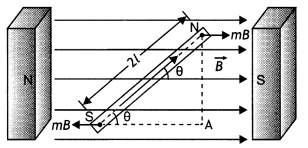
Then
τ = either force × arm of the couple
= mB × AN = mB × 2 L sin θ
or
Since m × 2L is the magnetic dipole moment of the magnet.
Therefore τ = MB
sin θ in vector form
we have \(\vec{τ}\) = \(\vec{M}\) × \(\vec{B}\)
Question 70.
(a) State Gauss’s law for magnetism. Explain Its
significance.
Answer:
(a) Gauss’s Law for magnetism states that “The total
flux of the magnetic field, through any closed surface, is aLways
zero, i.e.
∮\(\vec{B}\).\(\vec{dL}\) = 0
This law implies that magnetic monopoles do not exist” or magnetic field lines form closed loops.
(b) Write the four Important properties of the magnetic field lines due to a
bar magnet. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Four properties of magnetic field
lines are as follows:
- Magnetic field lines always form continuous closed loops.
- The tangent to the magnetic field line at a given point represents the direction of the net magnetic field at that point.
- The larger the number of field lines crossing per unit area, the stronger is the magnitude of the magnetic field.
- Magnetic field lines do not intersect.
Question 71.
A short bar magnet placed with its axis at 30° with an
external field of 800 G experiences a torque of 0.016 Nm.
(a) What is the
magnetic moment of the magnet?
Answer:
(a) From equation τ = mB sin
θ,
For θ = 30°, sin θ = 0.5
Thus, 0.016 = m × 800 × 10-4 × 0.5 or m = 160 × 2/800 = 0.40 Am²
(b) What is the work done in moving it from its most stable to a most
unstable position?
Answer:
From equation U= -mB cos θ, the most stable
position is for θ = 0° and the most unstable position is for θ = 180°.
Work done is given by
W = Um (θ = 180°) – Um for (θ = 0°)
=
2 mB = 2 × 0.40 × 800 × 10-4
= 0.064 J
(c) The bar magnet is replaced by a solenoid of cross-sectional area 2 ×
10-4 m² and 1000 turns but of the same magnetic moment. Determine the
current flowing through the solenoid. (NCERT Delhi 2005C)
Answer:
From
part (i), m = 0.40 Am² Using equation m = NIA.
0.40 = 1000 × l × 2 ×
10-4
l = 2 A
Question 72.
(a) What happens if a bar magnet is cut into two pieces: (i)
transverse to its length and (ii) along its length?
Answer:
(a) In either
case one gets two magnets each with a north pole and a south pole.
(b) A magnetized needle in a uniform magnetic field experiences a torque but
no net force. An iron nail near a bar magnet, however, experiences a force of
attraction in addition to torque. Why?
Answer:
The needle experiences no
net force because the field is uniform.
The iron nail experiences a non¬uniform field due to the bar magnet. There is an induced magnetic moment in the nail; therefore, it experiences both force and torque.
The net force is attractive because the induced south pole (say) in the nail is closer to the north pole of the magnet than the induced north pole.
Question 73.
Name the elements of the earth’s magnetic field at a place.
Explain their meaning.
Answer:
The elements required to completely specify
the earth’s magnetic field are called magnetic elements. These elements are:
(a) Declination (θ)
(b) Dip or inclination (δ)
(c) Horizontal component of
the earth’s magnetic field (BH).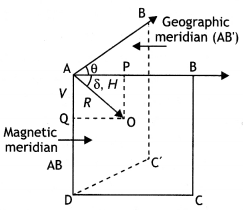
(a) Declination (θ): Declination at a place is defined as the acute angle
between the magnetic meridian and the geographic meridian.
In the figure
above ∠BAB’ = θ is called the angle of declination. There are several periodic
variations in the value of declination for a given location.
(b) Dip (δ): Dip at a place is defined as the angle between the direction of the total intensity of the earth’s magnetic field and a horizontal line in the magnetic meridian at that place. It is denoted by 8.
Suppose a freely suspended magnet aligns itself along the direction AB as shown in the figure, then this gives the direction of the earth’s total magnetic field at that place. Then the angle ∠BAO = δ is called the angle of dip or simply dip at that point.
(c) Horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field (BH): It is the component of the total intensity of the earth’s magnetic field along a horizontal line in the magnetic meridian. It is denoted by BH or H.
Question 74.
Name the three types of magnetic materials which behave
differently when placed in a non-uniform magnetic field. Give two properties for
each of them.
Answer:
The three types of magnetic materials are
(a)
Diamagnetic
(b) Paramagnetic and
(c) Ferromagnetic
| Diamagnetic | Paramagnetic | Ferromagnetic |
| These are the substances that are feebly repelled by a magnet, e.g., Bi, Zn, Cu, Ag, Au, diamond, C, NaCI, H20, Hg, N2, H2, etc. Exhibited by solids, liquids, and gases. | These are the substances that are feebly attracted by a magnet, e.g., AL, Na, Pt, Mn, CuCL2, O2, etc. Exhibited by solids, liquids, and gases. | These are the substances that are strongly attracted by a magnet, e.g., Fe, Ni, Co, Fe304, etc. Exhibited by solids only, that too crystalline. |
| When a diamagnetic substance is placed in a magnetizing field, the Lines of force prefer not to pass through the substance. | When a paramagnetic substance is placed in a magnetizing field, the Lines of force prefer to pass through the substance. | When a ferromagnetic substance is placed in a magnetizing field, the Lines of force prefer to pass through the substance. |
Question 75.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 0-9853. Identify
the type of magnetic material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on
keeping a piece of this material in a uniform magnetic field. (CBSEAI, Delhi
2018)
Answer:
We know that the susceptibility of a paramagnetic substance
is positive but small. Hence, the given magnetic material is paramagnetic in
nature.
When a specimen of a paramagnetic substance is placed in a magnetizing field,
the magnetic field lines prefer to pass through the specimen rather than through
air. Thus, magnetic induction 6 inside the sample is more than the magnetic
induction B0 outside the sample.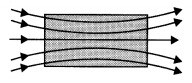
Question 76.
(a) Draw the magnetic field lines due to a circular loop of
area \(\vec{A}\) carrying current l. Show that it acts as a bar magnet of
magnetic moment \(\vec{m}\) = I \(\vec{A}\).
Answer:
(a) The magnetic
field lines are as shown.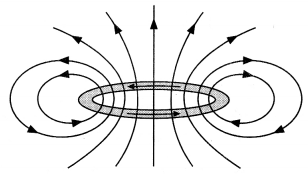
Magnetic field due to circular loop on its axis at far off points B =
\(\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi} \frac{2 l A}{x^{3}}\)
Magnetic field due to a bar magnet at its axial point is B =
\(\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi} \frac{2 m}{x^{3}}\)
Comparing the above two we have m
= IA
(b) Derive the expression for the magnetic field due to a solenoid of length
‘21’, radius ‘a’ having ‘n’ number of turns per unit length and carrying a
steady current T at a point on the axial line, distant ‘r’ from the center of
the solenoid. How does this expression compare with the axial magnetic field due
to a bar magnet of the magnetic moment ‘m’? (CBSEAI 2015)
Answer:
(b) By
the-Biot-Savarts law, the magnetic field at point P on the axis of the solenoid
due to a small element of length dx at a distance ‘x’ from the center of the
solenoid is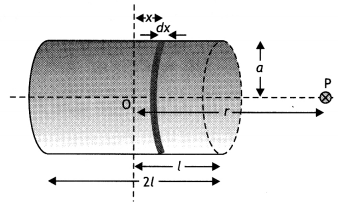
dB = \(\frac{\mu_{0} n d x / a^{2}}{2\left[(r-x)^{2}+a^{2}\right]^{3 / 2}}\)
Hence total magnetic field is given by
B = ∫dB = \(\frac{\mu_{0} / a^{2}
n^{+L}}{2} \int_{-L}^{d x} \frac{d x}{\left[(r-x)^{2}+a^{2}\right]^{3 /
2}}\)
For r >> a (R >> L)
We have
B = ∫dB = \(\frac{\mu_{0} /
a^{2} n^{+L}}{2 r^{3}} \int_{-L}^{+L} d x=\frac{\mu_{0} \ln }{2} \frac{2 L
a^{2}}{r^{3}}\)
Magnetic moment of a solenoid
m = (n × 2L) I (πa²)
Therefore,
B = \(\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi} \frac{2 m}{r^{3}}\) as that of a
bar magnet.
Numerical Problems :
- Torque on a magnetic dipole τ = MB sin θ
- Potential energy of a magnetic dipole U = – MB cos θ
- \(B_{H}^{2}+B_{v}^{2}=B^{2}\)
- tan θ = \(\frac{B_{V}}{B_{H}}\)
- H = B cos δ
- V = B sin δ
Question 1.
A bar magnet of the magnetic moment 6 J T1 is
aligned at 60° with a uniform external magnetic field of 0 – 44 T. Calculate
(a) the work is done in turning the magnet to align its magnetic moment (i)
normal to the magnetic field and (ii) opposite to the magnetic field and
Answer:
(b) the torque on the magnet in the final orientation in case (ii). (CBSEAI,
Delhi 2018)
Answer:
τ = M × B sin θ2
= 6 × 0.44 × sin 180° =
0
Question 2.
A short bar magnet placed with its axis at 30° with a uniform
external magnetic field of 0.25 T experiences a torque of magnitude equal to 4.5
x 10-2 J. What is the magnitude of the magnetic moment of the
magnet?
Answer:
Given θ = 30°, B = 0.25 T, τ = 4.5 × 10-2 J,M =
?
Using the expression τ = MB sin θ we have
M = \(\frac{\tau}{B \sin
\theta}=\frac{4.5 \times 10^{-2}}{0.25 \times \sin 30^{\circ}}\) = 0.36 J
T-1