Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Class 12th Physics Chapter Important Questions
Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 Important Questions Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Very Short Answer
Question 1.
Express dielectric constant in terms of the capacitance of a
capacitor.
Answer:
It is given by the expression K = \(\frac{c}{c_{0}}\)
where C is the capacitance of the capacitor with dielectric and C0 is
the capacitance without the dielectric.
Question 2.
On what factors does the capacitance of a parallel plate
capacitor depend?
Answer:
- Area of plates,
- The separation between the plates and
- Nature of dielectric medium between the plates.
Question 3.
What is the ratio of electric field intensities at any two
points between the plates of a capacitor?
Answer:
The ratio is one, as the
electric field is the same at all points between the plates of a capacitor.
Question 4.
A 500 µC charge is at the centre of a square of side 10 cm.
Find the work done in moving a charge of 10 µC between two diagonally opposite
points on the square. (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
The work done in moving a
charge of 10 µC between two diagonally opposite points on the square will be
zero because these two points will be at equipotential.
Question 5.
What is the electrostatic potential due to an electric dipole
at an equatorial point? (All India 2009)
Answer:
Electric potential at any
point in the equatorial plane of dipole is Zero.
Question 6.
What is the work done in moving a test charge q through a
distance of 1 cm along the equatorial axis of an electric dipole? (All India
2009)
Answer:
Since potential for equatorial axis
V = 0
∴ W = qV =
0
Question 7.
Define the term ‘potential energy’ of charge ‘q’ at a distance
V in an external electric field. (All India 2009)
Answer:
It is defined as
the amount of work done in bringing the charge from infinity to its position in
the system in the electric field of another charge without acceleration.
V =
Er.
Question 8.
A point charge Q is placed at point O as shown in the figure.
Is the potential difference VA – VB positive, negative or
zero, if Q is
(i) positive
(ii) negative? (Delhi 2011)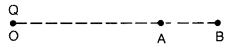
Answer:
Clearly,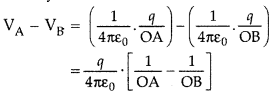
As OA < OB, so the quantity within bracket is
negative.
(i) If q is positive charge, VA – VB =
negative
(ii) If q is negative charge, VA – VB =
positive
Question 9.
A hollow metal sphere of radius 5 cm is charged such that the
potential on its surface is 10 V. What is the potential at the centre of the
sphere?
(All India 2011)
Answer:
The electric field inside the shell is
zero. This implies that potential is constant inside the shell (as no work is
done in moving a charge inside the shell) and, therefore, equals its value at
the surface, which is 10 V.
Question 10.
Write a relation between electric displacement vector D and
electric field E.
Answer:
\(\vec{D}\) = ε0 \(\vec{E}\) +
\(\vec{P}\)
Question 5.
Write the relation between dielectric constant (K) and
electric susceptibility χe
Answer:
K = 1 + χe
Question 11.
A hollow metal sphere c radius 5 cm is charged such that the
potential on its surface is 10 V. What is the potential at the center of the
sphere? (CDSE AI 2011)
Answer:
10 V
Question 12.
What is the geometrical shape of equipotential surfaces due to
a single isolated charge? (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Concentric
circles.
Question 13.
Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an isolated point
charge. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
These areas are shown.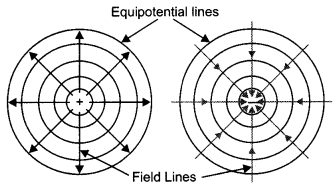
Question 14.
‘For any charge configuration, equipotential surface through a
point is normal to the electric field’. Justify. (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
This is because work done in moving a charge on an equipotential
surface is zero. This is possible only if the equipotential surface is
perpendicular to the electric field.
Question 15.
The given graph shows the variation of charge ‘q’ versus
potential difference ‘V for two capacitors C1 and C2. Both
the capacitors have the same plate separation but the plate area of
C2 is greater than that of Cy Which line (A or B)
corresponds to C1 and why? (CBSEAI 2014C)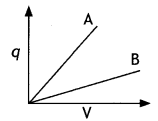
Answer:
Since C = ε0 A/d, since the area for C2 is
more, therefore capacitance of C2 is more. From the graph greater the
slope greater is than the capacitance, therefore, graph A belongs to capacitor
C2. While graph B belongs to capacitance Cv
Question 16.
Write a relation for polarisation P of dielectric material in
the presence of an external electric field E . (CBSE AI 2015)
Answer:
P =
χe ε0 \(\vec{E}\).
Question 17.
Why are electric field lines perpendicular at a point on an
equipotential surface of a conductor? (CBSE AI 2015C)
Answer:
So that no
net force acts on the charge on the equipotential surface and it remains
stationary.
Question 18.
A hollow metal sphere of radius 10 cm is charged such that the
potential on its surface is 5 V. What is the potential at the centre of the
sphere? (All India 2011)
Answer:
Hollow metal sphere behaves as an
equipotential surface, so the potential at its centre will be 5 V.
Question 19.
Why is electrostatic potential constant throughout the volume
of the conductor and has the same value (as inside) on its surface? (Delhi
2012)
Answer:
Electric field inside the conductor = 0![]()
Question 20.
Distinguish between tor. dielectric and a conductor (Comptt.
Delhi 2012)
Answer:
| Dielectric | Conductor |
| Dielectrics are the insulating materials which transmit electric effects without conducting. | Conductors are the substances which can be used to carry or conduct electric charge from one place to the other. |
Question 21.
Why must the electrostatic potential inside a hollow charged
conductor be the same at every point? (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Inside the hollow charged conductor, electric field is zero therefore no work is
done in moving a small test charge within the conductor. Hence electrostatic
potential inside a hollow charged conductor is same at every point.
Question 22.
What is the geometrical shape of equipotential surfaces due
to a single isolated charge? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Concentric spheres with
a gap between them not being uniform as V \(\propto \frac{1}{r}\)
Question 23.
Two charges 2µC and – 2µC are placed at points A and B 5 cm
apart. Depict an equipotential surface of the system. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer: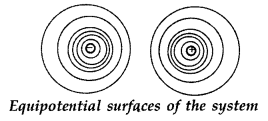
Question 24.
What is the amount of work done in moving a point charge
around a circular arc of radius r at the centre of which another point charge is
located? (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
Being an equipotential surface,
work done will be zero.
Question 25.
Two charges 4µC and -4µC are placed at points A and B 3 cm
apart. Depict an equipotential surface of the system. (Comptt. All India
2013)
Answer: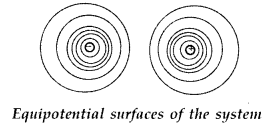
Question 26.
“For any charge configuration, equipotential surface through
a point is normal to the electric field.” Justify. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Work done in moving a charge over an equipotential surface is zero, hence a
point on it will be normal to the electric field.
W = FS cos θ ∴ cos θ = 0 or
θ = 90o
Question 27.
Two equal balls having equal positive charge ‘q’ coulumbs are
suspended by two insulating strings of equal length. What would be the effect on
the force when a plastic sheet is inserted between the two ? (All India
2014)
Answer:
The force would be reduced by a factor ‘K’ (equal to the
value of dielectric constant of plastic sheet)![]()
Question 28.
The given graph shows variation of charge ‘q’ versus
potential difference ‘V’ for two capacitors C1 and C2.
Both the capacitors have same plate seperation but plate area of C2
is greater than that of C1. Which line (A or B) corresponds to
C1 and why? (Comptt. All India 2014)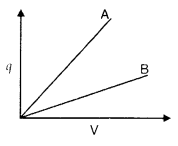
Answer:
Line B corresponds to C1
Reason:
Since slope \(\left(\frac{q}{v}\right)\) of ‘B’ is less than that of ‘A’
Question 29.
A charge ‘q’ is moved from a point A above a dipole of dipole
movement ‘p’ to a point B below the dipole in equitorial plane without
acceleration. Find the work done in the process. (All India 2016)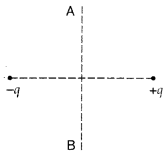
Answer:
No work is done
[W = q VAB = q × 0 =
0, since potential remains constant]
Question 30.
Why does a given capacitor store more charge at a given
potential difference when a dielectric is filled in between the plates?
Answer:
Because the capacitance of the capacitor increases on filling the
dielectric medium in between the plates.
Question 31.
Why is the electrostatic potential inside a charged
conducting shell constant throughout the volume of the conductor? (CBSE AI
2019)
Answer:
We know that E = – \(\frac{d V}{d r}\)
Inside a
conductor, the electric field is zero and no work is done in moving a charge
inside a conductor. Therefore, V is constant.
Question 32.
Does the charge given to a metallic sphere depend on whether
it is hollow or solid? (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
If the capacitance of the
two spheres, solid and hollow, is the same, then they will hold the same
quantity of charge.
Question 33.
Is the electric potential necessarily zero at a place where
the electric field is zero?
Answer:
No, it is not necessary. The electric
field inside a hollow metallic conductor is zero but the electric potential is
not zero.
Question 34.
In a parallel plate capacitor, the potential difference of
102 V is maintained between the plates. What will be the electric
field at points A and B as shown in the figure below?
Answer:
The electric
field between the plates of a capacitor is uniform; therefore the electric field
at points A and B will be the same.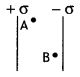
Question 35.
If the plates of a charged capacitor are suddenly connected to
each other by a wire, what will happen?
Answer:
The capacitor is
discharged immediately.
Question 36.
Can you place a parallel plate capacitor of one farad
capacity in your house?
Answer:
Ordinarily, it is not possible because the
surface area of such a capacitor will be extra-large.
Question 37.
Is there any conductor which can be given almost unlimited
charge?
Answer:
Yes, the earth.
Question 38.
What would be the work done if a point charge + q is taken
from a point A to a point B on the circumference of a circle drawn with another
point charge + q at the center?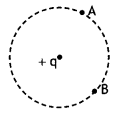
Answer:
Zero.
Question 39.
Sketch a graph to show how a charge Q, acquired by a
capacitor of capacitance, C, varies with the increase in the potential
difference between the plates.
Answer: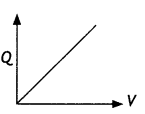
Question 40.
In a parallel plate capacitor, the capacitance increases from 4
μF to 80 μF, introducing a dielectric medium between the plates. What is the
dielectric constant of the medium?
Answer:
The dielectric constant is
given by
K = \(\frac{80}{4}\) = 20
Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Derive the expression for the electric potential at any point
along the axial line of an electric dipole (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
Consider
an electric dipole consisting of two points charged -q and +q and seperated by
distance 2a. Let P be a point on the axis of the dipole at a distance r from its
centre O.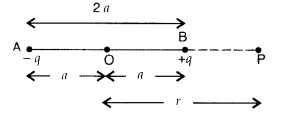
Electric potential at point P due to dipole is,
V =
V1 + V2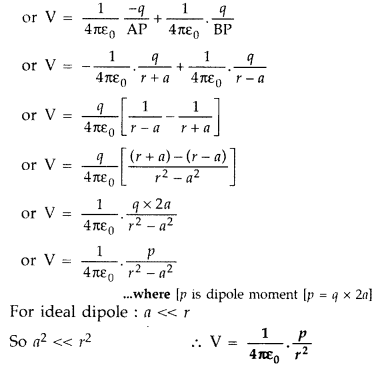
Question 2.
Derive an expression for the potential energy of an electric
dipole of dipole movement \(\vec{p}\) in the electric field \(\vec{E}\)
(Delhi 2008)
Answer:
Consider a dipole with charges +q and -q placed in a
uniform electric field \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}\) such that AB = 2a as
shown in the figure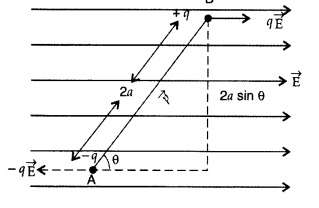
Since the dipole experiences no net force in a uniform electric field but
experiences a torque (τ) is given by![]()
It tends to rotate the dipole in clockwise direction. To
rotate the dipole anti-clock wise has to be done on the dipole.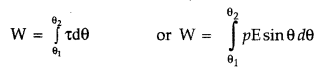
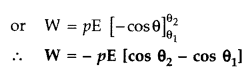
Question 3.
Two point charges, q1 = 10 × 10-8C,
q2 = -2 × 10-8C are seperated by a distance of 60 cm in
air.
(i) Find at what distance from the 1st charge, q1
would the electric potential be zero.
(ii) Also calculate the electrostatic
potential energy of the system. (All India 2008)
Answer:
(i) Given :
q1 = 10 × 10-8C, q2 = -2 × 10-8C
AB = 60 cm = 0.60 = 0.6m
Let AP = x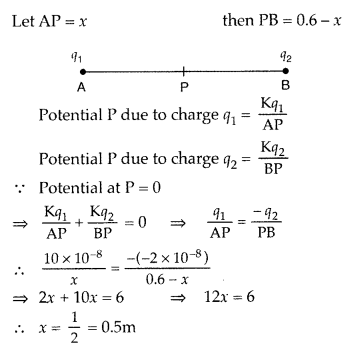
∴ Distance from first charge = 0.5 m = 50 cm.
(ii) Electrostatic energy of
the system is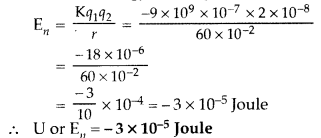
Question 4.
Two point charges 4Q, Q are separated by lm in air. At what
point on the line joining the charges is the electric field intensity zero?
Also calculate the electrostatic potential energy of the system of charges,
taking the value of charge, Q = 2 × 10-7C
Answer: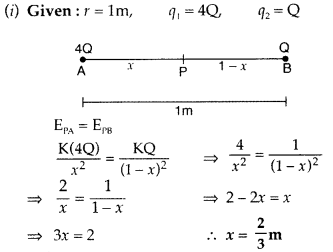
(ii) Electrostatic potential energy of the system is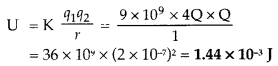
Question 5.
Two point charges 20 x 10-6 C and -4 X 10-6 C are separated
by a distance of 50 cm in air.
(i) Find the point on the line joining the
charges, where the electric potential is zero.
(ii) Also find the
electrostatic potential energy of the system. (All India 2008)
Answer:
(i)
Here q1 = 20 × 10-6C, q2 = -4 ×
10-6C
and AB = 50 cm = 0.50 m = 0.5 m Let AP = x then PB = 0.5 –
x
Potential at P due to charge q1 = \(\frac{\mathrm{K}
q_{1}}{\mathrm{AP}}\)
Potential at P due to charge q2 =
\(\frac{\mathrm{K} q_{2}}{\mathrm{PB}}\)
Potential at P = 0 \(\Rightarrow
\frac{\mathrm{K} q_{1}}{\mathrm{AP}}+\frac{\mathrm{K}
q_{2}}{\mathrm{PB}}=0\)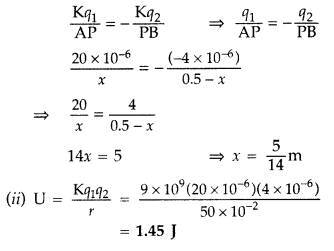
Question 6.
Calculate the work done to dissociate the system of three
charges placed on the vertices of a triangle as shown. (Delhi 2008)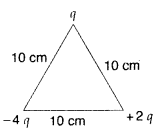
Answer:
Initial P.E. of the three charges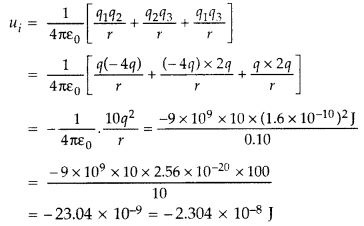
Final P.E, uf = 0
∴ Work required to dissociate the system of
three charges,
W = uf – ui = -2.304 × 10-8
J
Question 7.
(i) Can two equipotential surfaces intersect each other? Give
reasons.
(ii) Two charges -q and + q are located at points A (0, 0, – a) and
B (0, 0, +a) respectively. How much work is done in moving a test charge from
point P (7, 0, 0) to Q (-3,0,0)? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
(i) No, if they
intersect, there will be two different directions of electric field at that
point which is not correct. If they intersect, then at the same point of
intersection, there will be two values of potential. This is not possible and
hence two equipotential surfaces cannot intersect.
(ii) Since both the points
P and Q are on the equatorial line of the dipole and V = 0 at every point on it,
work done will be zero. Also the force on any charge is perpendicular to the
equatorial line, so work done is zero.
Question 8.
Draw 3 equipotential surfaces corresponding to a field that
uniformly increases in magnitude but remains constant along Z-direction. How are
these surfaces different from that of a constant electric field along
Z-direction? (All India 2009)
Answer:
d2 < d1 for
increasing field
and d2 = d1 for uniform field.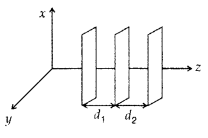
Question 9.
Two uniformly large parallel thin plates having charge
densities + σ and – σ are kept in the X-Z plane at a distance ‘d’ apart. Sketch
an equipotential surface due to electric field between the plates. If a particle
of mass m and charge q’ remains stationary between the plates, what is the
magnitude and direction of this field? (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
The
equipotential surface is at a distance d/2 from either plate in X-Z plane. For a
particle of charge (- q) at rest between the plates, then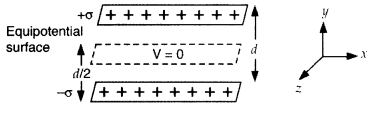
(i) weight mg acts, vertically downward
(ii) electric force qE acts
vertically upward
so mg = qE
E = \(\frac{m g}{q}\) vertically
downward,
i.e., along (-) Y-axis.
Question 10.
Two small identical electrical dipoles AB and CD, each of
dipole moment ‘p’ are kept at an angle of 120° as shown in the figure. What X’
is the resultant dipole moment of this combination? If this system is subjected
to electric field (\(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{E}}\)) directed along + X
direction, what will be the magnitude and direction of the torque acting on
this? (Delhi 2011)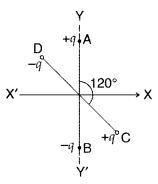
Answer:
Resultant dipole moment of both dipoles is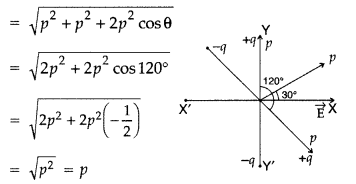
Resultant dipole moment (p) makes an angle of 60° with each dipole and 30° with
x-axis as shown in the figure.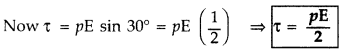
Question 11.
Figure shows two identical capacitors C1 and
C2, each of 2 µF capacitance, connected to a battery of 5 V.
Initially switch ‘S’ is left open and dielectric slabs of dielectric constant K
= 5 are inserted to fill completely the space between the plates of the two
capacitors. How will the charge and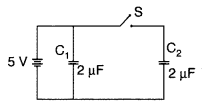
(ii) potential difference between the plates of the
capacitors be affected after the slabs are inserted? (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
(i) When switch S is open and dielectric is introduced, charge on each capacitor
will be q1 = C1 V, q2 = C2V
q1 = 5CV
= 5 × 2 × 5 = 50 µC, q2 = 50 µC
Charge on
each capacitor will become 5 times
(ii) P.d. across C1 is still 5V
and across C2,
q = (5C) V![]()
Question 12.
Figure shows two identical capacitors C1 and
C2 each of 1.5 µF capacitance, connected to a battery of 2 V.
Initially switch ‘S’ is closed. After sometime ‘S’ is left open and dielectric
slabs of dielectric constant K = 2 are inserted to fill completely the space
between the plates of the two capacitors. How will the
(i) charge and
(ii)
potential difference between the plates of the capacitors be affected after the
slabs are inserted? (Delhi)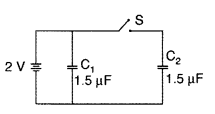
Answer:
(i) When switch S is open and dielectric is
introduced, charge on each capacitor, will be
q1 =
C1V,
q2 = C2V,
q1 = 2CV = 2 ×
1.5 × 2 = 6 µC, q2 = 6 µC
Charge on each capacitor will become
twice.
(ii) P.d. across C1 is still 2V and across
C2,
q = (2C) V’![]()
Question 13.
Net capacitance of three identical capacitors in series is 1
pF. What will be their net capacitance if connected in parallel?
Find the
ratio of energy stored in the two configurations if they are both connected to
the same source. (All India 2011)
Answer:
Let C be the capacitance of a
capacitor
Given : C1 = C2 = C3 = C When
connected in series: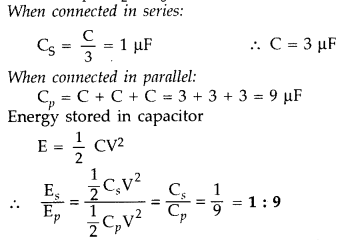
Question 14.
Net capacitance of three identical capacitors in series is 3
pF. What will be their net capacitance if connected in parallel?
Find the
ratio of energy stored in the two configurations if they are both connected to
the same source. (All India 2011)
Answer:
Let C1, C2
and C3 be the capacitances of three capacitors. But these three
capacitors are of same capacitance, so C is the capacitance of each
capacitor.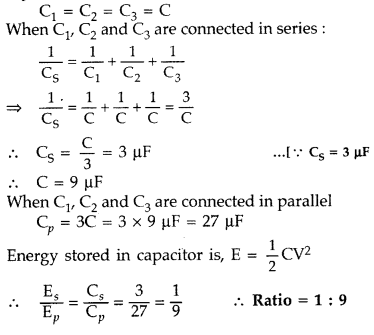
Question 15.
Draw a plot showing the variation of
(i) electric field
(E) and
(ii) electric potential
(iii) with distance r due to a point
charge Q. (Delhi 2012)
Answer: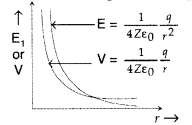
Question 16.
A test charge ‘q’ is moved without acceleration from A to C
along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in
the figure.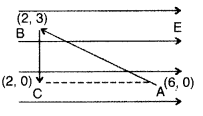
(i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C.
(ii) At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why? (All
India)
Answer:
(i) P.D does not depend upon the path along which the test
charge q moves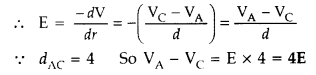
(ii) At point C, electric potential will be more as potential decreases in the
direction of electric field.
Question 17.
An electric dipole is held in a uniform electric field.
(i) Show that the net force acting on it is zero.
(ii) The dipole is alligned
parallel to the field.
Find the work done in rotating it through the angle of
180°. (All India 2012)
Answer:
(i) Force acting on point A due to charge
-q is -qE
Force acting on point B due to charge +q. is + qE
Net force
acting on
= -qE + qE = 0 (zero)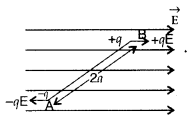
Hence, the net force acting on electric dipole held in a
uniform electric field is zero.
(ii) W = -pE(cos 02 — cos
θ2)
W = -pE(cos 180° – cos 0°)
=> W = -pE(-1 – (1)) =
+2pE
Question 18.
Determine the potential difference across the plates of the
capacitor ‘C1‘ of the network shown in the figure.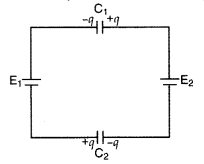
[Assume E2 > E1] (Comptt. Delhi
2012)
Answer:
Net E = E2 – E1
Both capacitors are
in series![]()
∴ V1, (Potential difference across the plates of
the capacitor C1) = \(\frac{q}{C_{1}}\)
Question 19.
A network of four capacitors, each of capacitance 15 µF, is
connected across a battery of 100 V, as shown in the figure. Find the net
capacitance and the charge on the capacitor C4. (Comptt. Delhi &
All India 2012)
Answer:
C1, C2 and C3 are
in series as shown in the figure, we have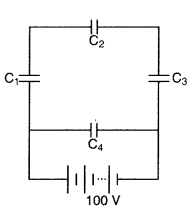
Question 20.
A network of four capacitors, each of capacitance 30 pF, is
connected across a battery of 60 V as shown in the figure.
Find the net
capacitance and the energy stored in each capacitor. (Comptt. All India
2012)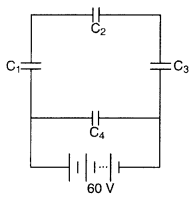
Answer: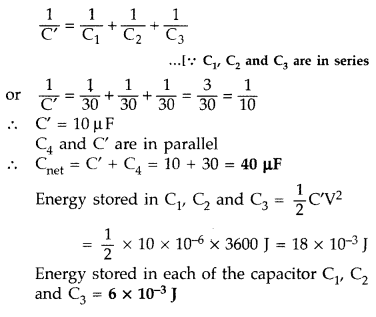
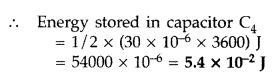
Question 21.
An electric dipole of length 4 cm, when placed with its axis
making an angle of 60° with a uniform electric field, experiences a torque of
4√3 Nm. Calculate the potential energy of the dipole, if it has charge ± 8 nC.
(Delhi 2014)
Answer:
1st method Given : 2a = 4 cm = 4 ×
10-2 m, θ = 60°
τ = 4 × √3 Nm, q = ±8 nC = ±8 x 10-9
C
P.E. = |p| |E| cos θ, τ = |p| |E| sin θ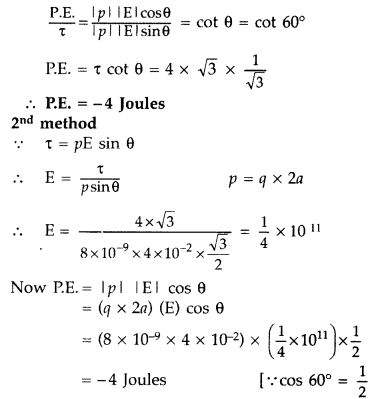
(Note:
However, the first method is preferred because it saves a lot of time for
unnecessary calculations)
Question 22.
An electric dipole of length 2 cm, when placed with its axis
making an angle of 60° with a uniform electric field, experiences a torque
of
8 √3 Nm. Calculate the potential energy of the dipole, if it has a charge
of ± 4 nC. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
1st method Given : 2a = 4 cm =
4 × 10-2 m, θ = 60°
τ = 4 × √3 Nm, q = ±8 nC = ±8 x
10-9 C
P.E. = |p| |E| cos θ, τ = |p| |E| sin θ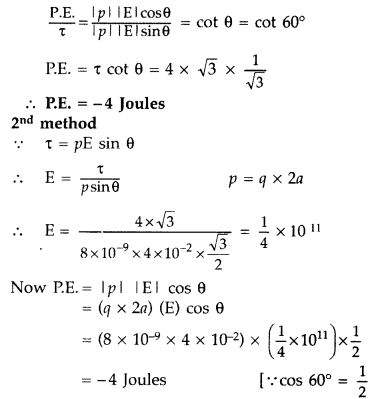
(Note:
However, the first method is preferred because it saves a lot of time for
unnecessary calculations)
Answer:
8 Joules
Question 23.
An electric dipole of length 1 cm, which placed with its axis
making an angle of 60° with uniform electric field, experiences a torque of
6√3 Nm. Calculate the potential energy of the dipole, if it has a charge of ± 2
nC. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
1st method Given : 2a = 4 cm = 4 ×
10-2 m, θ = 60°
τ = 4 × √3 Nm, q = ±8 nC = ±8 x 10-9
C
P.E. = |p| |E| cos θ, τ = |p| |E| sin θ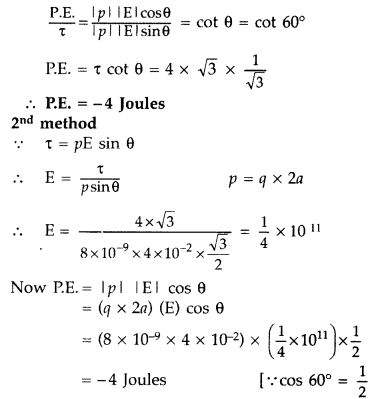
(Note:
However, the first method is preferred because it saves a lot of time for
unnecessary calculations)
Answer: 6 Joules
Question 24.
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a
potential V. It is then connected to another uncharged capacitor having the same
capacitance. Find out the ratio of the energy stored in the combined system to
that stored initially in the single capacitor. (All India 2014)
Answer:
Let us say that capacitor has an initial energy![]()
When the first capacitor is connected across the second
capacitor, let the common potential be V’
Then charge on each capacitor q’ = CV’
By charge
conservation
q’ = \(\frac{q}{2}\)
Hence total energy stored in the
capacitors,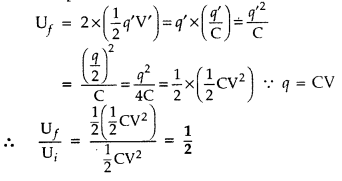
Question 25.
Draw a plot showing the variation of (i) electric field (E)
and (ii) electric potential (V) with distance r due to a point charge Q. (CBSE
Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The plot is as shown.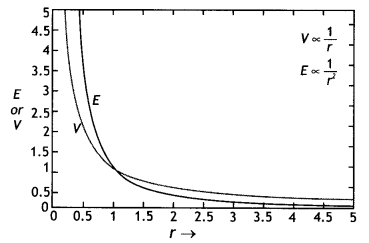
Question 26.
Two identical capacitors of 10 pF each are connected in turn (i)
in series and (ii) in parallel across a 20 V battery. Calculate the potential
difference across each capacitor in the first case and the charge acquired by
each capacitor in the second case. (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
(i) Since the
two capacitors have the same capacitance, therefore, the potential will be
divided amongst them. Hence V = 10 V each
(ii) Since the capacitors are
connected in parallel, therefore, potential difference = 20 V
Hence charge Q
= CV = 10 × 20 = 200 pC
Question 27.
A point charge ‘q’ is placed at O as shown in the figure. Is
VA – VB positive, negative, or zero, if ‘q’ is an (i)
positive, (ii) negative charge? (CBSE Delhi 2011, 2016)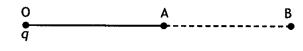
Answer:
If VA – VB = \(\frac{q}{4 \pi
\varepsilon_{0}}\left(\frac{1}{\mathrm{OA}}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{OB}}\right)\)
As OA < OB
∴ If q is positive then VA– VB is
positive and
if q is negative VA – VB is also
negative.
Question 28.
The graph shows the variation of voltage V across the plates
of two capacitors A and B versus charge Q stored on them. Which of the two
capacitors has higher capacitance? Give a reason for your answer.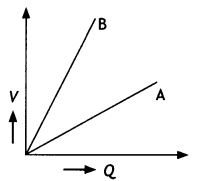
Answer:
Capacitor A has higher capacitance. We know that capacitance C =
Q/V.
For capacitor A
\(c_{A}=\frac{Q}{V_{A}}\)
For capacitor B
\(c_{B}=\frac{Q}{V_{B}}\)
As VB > VA
∴ CB < CA
Thus capacitance of A is higher.
Question 29.
A test charge ‘q’ is moved without acceleration from A to C
along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in
the figure,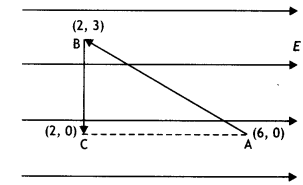
(i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C
Answer:
(i) dV = –
E dr = – E (6 – 2) = – 4E
(ii) At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why?
(CBSE AI 2012)
Answer:
Electric potential is more at point C as dV = –
Edr, i.e. the electric potential decreases in the direction of the electric
field.
Question 30.
A slab of material of dielectric constant K has the same area
as that of the plates of a parallel plate capacitor but has the thickness d/2,
where d is the separation between the plates. Find out the expression for its
capacitance when the slab is inserted between the plates of the capacitor. (CBSE
AI 2013)
Answer:
Given t = d/2, C = ?
We know that when a dielectric of
thickness ‘t’ is inserted between the plates of a capacitor, its capacitance is
given by
C = \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d-t+\frac{t}{K}}\)
Hence we have
C = \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d-\frac{d}{2}+\frac{d}{2
K}}=\frac{2 K \varepsilon_{0} A}{d(1+K)}\)
Question 31.
Two-point charges q and -2q are kept ‘d’ distance apart. Find
the location of the point relative to charge ‘q’ at which potential due to this
system of charges is zero. (CBSE Al 2014C)
Answer:
Let the potential be
zero at point P at a distance x from charge q as shown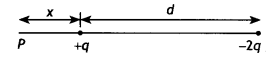
Now potential at point P is
V = \(\frac{k q}{x}+\frac{k(-2 q)}{d+x}\) =
0
Solving for x we have
x = d
Question 32.
Four-point charges Q, q, Q., and q are placed at the corners
of a square of side ‘a’ as shown in the figure.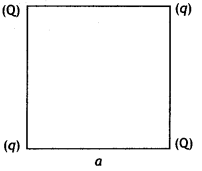
Find the potential energy of this system. (CBSEAI, Delhi 2018)
Answer:
The
potential energy of the system
U = \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}}\left(4
\frac{q Q}{a}+\frac{q^{2}}{a \sqrt{2}}+\frac{Q^{2}}{a \sqrt{2}}\right)\)
U = \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0} a}\left(4 q Q+\frac{q^{2}}{\sqrt{2}}+\frac{Q^{2}}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\)
Question 33.
Three-point charges q, -4q, and 2q are placed at the vertices
of an equilateral triangle ABC of side T as shown in the figure. (CBSE Delhi
2018)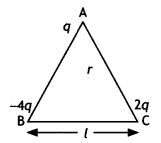
Find out the amount of the work done to separate the charges at infinite
distance. (CBSE AI, Delhi 2018)
Answer:
Net potential energy of the
system
= \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \frac{q^{2}}{l}[-4+2-8]=\frac{5
q^{2}}{2 \pi \varepsilon_{0} l}\)
Question 34.
Two point charges q1 and q2 are located
at \(\overrightarrow{r_{1}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{r_{2}}\) respectively in an
external electric field \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{E}}\) .
Obtain the
expression for the total work done in assembling this configuration. (Comptt.
Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Work done in bringing the charge q1 from
infinity to position r1
W1 =
q1V(r1)
Work done in bringing charge q2 to
the position r2![]()
Hence, total work done in assembling the two charges
w =
W1 + W2![]()
Question 35.
Two point charges q and -2q are kept ‘d’ distance apart. Find
the location of the point relative to charge ‘q’ at which potential due to this
system of charges is zero. (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer: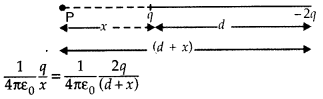
At distance’d’ towards left of charge ‘q’
Question 36.
Two closely spaced equipotential surfaces A and B with
potentials V and V + δV, (where δV is the change in V), are kept δl distance
apart as shown in the figure.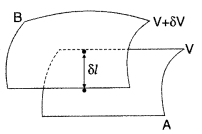
Deduce the relation between the electric field and the
potential gradient between them. Write the two important conclusions concerning
the relation between the electric field and electric potentials.
(Comptt.
Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Work done in moving a unit positive charge along
distance δl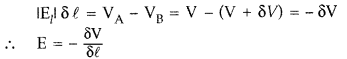
Two important conclusions :
(i) Electric field is in the direction in which
the potential decreases steepest.
(ii) Magnitude of electric field is given
by the change in the magnitude of potential per unit displacement, normal to the
equipotential surface at the point.
Question 37.
Why does current in a steady state not flow in a capacitor
connected across a battery? However momentary current does flow during charging
or discharging of the capacitor. Explain. (All India 2017)
Answer:
In the
steady state, the displacement current and hence the conduction current, is zero
as | \(|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}|\) | between the plates, is constant.
During charging and discharging, the displacement current and hence the conduction current is non zero as | \(|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}|\) | between the plates, is changing with time.
Current is non zero as | \(|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}|\) | between the plates, is changing with time.
Short Answer Type Questions-ll tSA-ll) (3 Marks)
Question 38.
Three identical capacitors C1 C2 and
C3 of capacitance 6 µF each are connected to a 12 V battery as
shown.
Find
(i) charge on each capacitor
(ii) equivalent capacitance of
the network
(iii) energy stored in the network of capacitors. (Delhi
2009)
Answer:
C1 and C2 in series, make
C4 = 3µF
using
\(\frac{1}{\mathrm{C}_{4}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{C}_{2}}\)
(i) 12V of potential is available in C4 and C3.
Charge
in C3 = Q3 = C3V
= 6 × 10-6 × 12
= 72 µC
Charge in C4 = Q4 = C4V
= 3 ×
10-6 × 12 = 36 µC
∴ Charge on C1 and C2 will
also be 36 μC
(ii) C4 and C3 are in parallel to the
source
∴ Ceq = 3 + 6 = 9 μF
(iii) Energy stored = \(\frac{1}{2}
\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{eq}} \mathrm{V}^{2}\)![]()
= 648 × 10-6 = 6.48 × 10-4 joule
Question 39.
The equivalent capacitance of the combination between A and B
in the given figure is 4 μF.![]()
(i) Calculate capacitance of the capacitor C.
(ii)
Calculate charge on each capacitor if a 12 V battery is connected across
terminals A and B.
(iii) What will be the potential drop across each
capacitor? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Ceq = 4 μF
(i) Since 20 μF
and C are in series, we have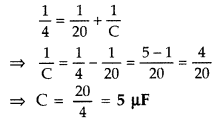
(ii) Charge drawn from 12 V battery is Q
=
Ceq.V = 4 × 12 = 48 μC
So charge on each capacitor = 48 pC
(iii) Potential drop across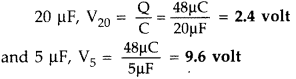
Question 40.
Two parallel plate X and Y capacitors, X and Y, have the same
area of plates and same separation between them. X has air between the plates
while Y contains a dielectric medium of εr = 4.
(i) Calculate
capacitance of each capacitor if equivalent capacitance of the combination is 4
μF.
(ii) Calculate the potential difference between the plates of X and
Y.
(iii) What is the ratio of electrostatic energy stored in X and Y?
(Delhi)
Answer:
Since area A and separation d are same, if Cx =
C then Cy = 4C
(i) Since they are in series,
\(\frac{1}{4}=\frac{1}{C}+\frac{1}{4 C}\)![]()
The two capacitors are therefore 5 μF and 20 μF.
(ii)
Since the capacitance of capacitors are in the ratio 1 : 4,
the potential
drop across them should be in the ratio of 4 : 1 making them \(\left(4 \times
\frac{12}{5}\right) \frac{12}{5}\)
(iii) Since they carry same charge, the
ratio of the electrostatic energy is,![]()
Question 42.
A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery. After
some time the battery is disconnected and a dielectric slab of dielectric
constant K is inserted between the plates. How would
(i) the capacitance,
(ii) the electric field between the plates and
(iii) the energy stored in the
capacitor, be affected? Justify your answer. (All India 2009)
Answer:
Let
C be the capacitance and V be the potential difference.
The charge on the
capacitor plates will then be Q = CV.
The electric field between the plates,
E = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}}{d}\) and the energy stored,![]()
As the dielectric (K) is introduced after disconnecting the
battery
We have the new values of charge, Q’ = Q Capacitance C’ = KC
Potential V’ = \(\frac{Q}{K C}=\frac{V}{K}\)
(i) New capacitance is K times
its original.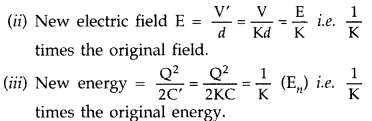
Question 43.
(a) A charge +Q is placed on a large spherical conducting
shell of radius R. Another small conducting sphere of radius r carrying charge
‘q’ is introduced inside the large shell and is placed at its centre. Find the
potential difference between two points, one lying on the sphere and the other
on the shell.
(b) How would the charge between the two flow if they are
connected by a conducting wire? Name the device which works on this fact. (All
India 2009)
Answer:
Potential inside conducting spherical shell of radius
R carrying charge,
q = constant = \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}}
\frac{Q}{R}\)
Let us suppose that in some way we introduce a small sphere of
radius r, carrying charge q, into the large one, and place it at the
centre.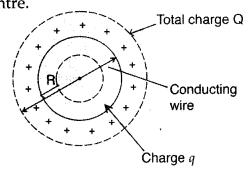
The potential due to this new charge clearly has the
following values at the radii indicated :
Potential due to small sphere of
radius r carrying charge q
of radius R
Taking both charges q and Q into account, we have for the two
potentials :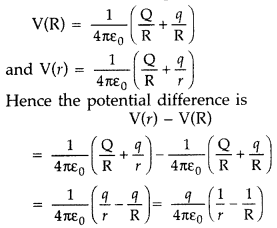
(b) If we connect the smaller and larger sphere by a wire,
the charge will flow from the conducting sphere of radius r to the large
spherical shell of radius R. Van de Graaff generator works on this fact.
Question 44.
A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery. After
sometime the battery is disconnected and a dielectric slab with its thickness
equal to the plate separation is inserted between the plates. How will
(i)
the capacitance of the capacitor,
(ii) electric field between the plates
and
(iii) the energy stored in the capacitor be affected? Justify your answer
in each case.
Answer:
Let C be the capacitance and V be the potential
difference.
The charge on the capacitor plates will then be Q = CV.
The
electric field between the plates, E = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}}{d}\) and the energy
stored,![]()
As the dielectric (K) is introduced after disconnecting the
battery
We have the new values of charge, Q’ = Q Capacitance C’ = KC
Potential V’ = \(\frac{Q}{K C}=\frac{V}{K}\)
(i) New capacitance is K times
its original.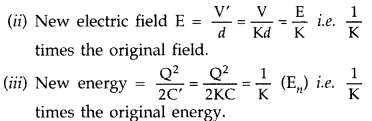
Question 45.
(a) Depict the equipotential surfaces for a system of two
identical positive point charges placed a distance ‘d’ apart.
(b) Deduce the
expression for the potential energy of a system of two point charges
q1 and q2 brought from infinity to the points
\(\overrightarrow{r_{1}}\)and \(\overrightarrow{r_{2}}\) respectively in the
presence of external electric field \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{E}}\). (Delhi
2010)
Answer:
(a)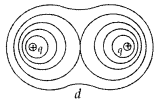
Equipotential surfaces of two identical point charges
(b)
Let \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}\) be the external field
∴ Work done on
q2 against the external field = q2.V(
\(\overrightarrow{r_{2}}\) )
Work done on q2 against the field due
to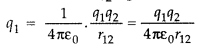
..where [r12 is the distance between q1
and q2
By the superposition principle for fields, we add up the
work done on q2 against the two fields
(\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}\) and that due to q1).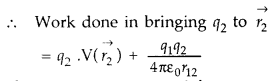
Thus, potential energy of the system = Total work done in
assembling the configuration.![]()
Question 46.
A parallel plate capacitor, each with plate area A. and
separation d, is charged to a potential difference V. The battery used to charge
it remains connected. A dielectric slab of thickness d and dielectric constant k
is now placed between the plates. What change, if any, will take place in :
(i) charge on plates?
(ii) electric field intensity between the plates?
(iii) capacitance of the capacitor?
Justify your answer in each case. (Delhi
2010)
Answer:
Given : Plate area of either plate of parallel plate
capacitor = A
Distance between the plates = d and
potential difference
between the plates = V
∴ Initially capacitance, C = \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0}
A}{d}\),
Charge on plate, Q = CV
As the battery remains connected
throughout, the potential difference between the plates remains unchanged (V’ =
V) on placing, a dielectric slab of thickness ‘d’ and dielectric constant ‘k’
between the plates.
(i) New charge on plates, Q’ = C’ V’ = kCV = kQ
Thus,
charge changes to k times of its original value.
(ii) Electric field
intensity between the plates, E’![]()
Thus, electric field intensity between the plates of
capacitor remains unchanged.
(iii) New capacitance of the capacitor,![]()
Question 47.
A parallel plate capacitor is charged to a potential
difference V by a d.c. source. The capacitor is then disconnected from the
source. If the distance between the plates is doubled, state with reason how the
following will change;
(i) electric field between the plates,
(ii)
capacitance, and
(iii) energy stored in the capacitor. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:![]()
On disconnecting the battery, the charge q on the capacitor plates remains
unchanged.
If the distance d is doubled, then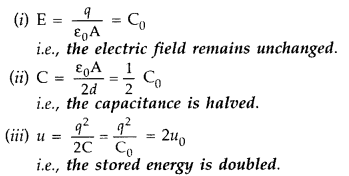
Question 48.
A network of four capacitors each of 12μF capacitance is
connected to a 500 V supply as shown in the figure.
Determine
(a)
equivalent capacitance of the network and
(b) charge on each capacitor. (All
India)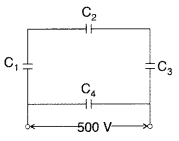
Answer:
(a) Equivalent capacitance of the network,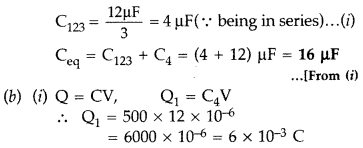
Question 49.
A network of four capacitors each of 15 μF capacitance is
connected cf to a 500 V supply as shown in the figure.
Determine
(a)
equivalent capacitance of the network and
(b) charge on each capacitor. (All
India 2010)
Answer: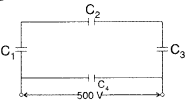
Now CS and C4 are in parallel
∴
Equivalent capacitance of the network,
C = CS + C4 = 15
+ 5 = 20 μF
(b) Charge on capacitor, C4 is
q = C4V =
(15 × 10-6) × 500 = 7500 μC … [V =500
Charge on each capacitor,
C1, C2 and C3 will be, q = CSV = (5
× 10-6) × 500 = 2500 μC
Question 50.
Deduce the expression for the electrostatic energy stored in
a capacitor of capacitance ‘C’ and having charge ‘Q’.
How will the
(i)
energy stored and
(ii) the electric field inside the capacitor be affected
when it is completely filled with a dielectric material of dielectric constant
‘K’? (All India 2012)
Answer:
Potential of capacitor = \(\frac{q}{C}\)
Small amount of work done in giving an additional charge dq to the
capacitor,![]()
Total work done in giving a charge Q to the capacitor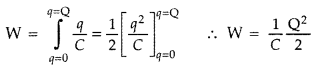
As electrostatic force is conservative, thus work is stored in the form of
potential energy (U) of the capacitor.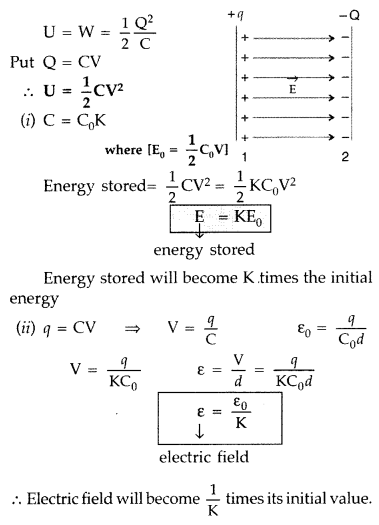
∴ Electric field will become \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{K}}\) times its initial
value.
Question 51.
A capacitor of unknown capacitance is connected across a
battery of V volts. The charge stored in it is 360 μC. When potential across the
capacitor is reduced by 120 V, the charge stored in it becomes 120 μC.
Calculate:
(i) The potential V and the unknown capacitance C.
(ii) What
will be the charge stored in the
capacitor, if the voltage applied had
increased by 120 V? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(i) Let the capacitance be C
∴
Charge on Q1 = CV or 360 μC = CV …(i)
In second case,
Q2 = C(V – 120)
⇒ 120 μC = C(V – 120) …(ii)
From equation (i)
and (ii)![]()
3V – 360 = V ⇒ 2V = 360
By putting this value of V in
(ii)
120 × 10-6 = C(180 – 120)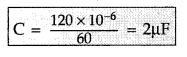
(ii) Charge stored when voltage is increased by 120 V
Q’ =
2μF × (180 + 120) V = 600 μC
Question 52.
A slab of material of dielectric constant K has the same area
as that of the plates of a parallel plate capacitor but has the thickness d/2,
where d is the separation between the plates. Find out the expression for its
capacitance when the slab is inserted between the plates of the capacitor.
(All India 2012)
Answer:
Total potential difference between the
plates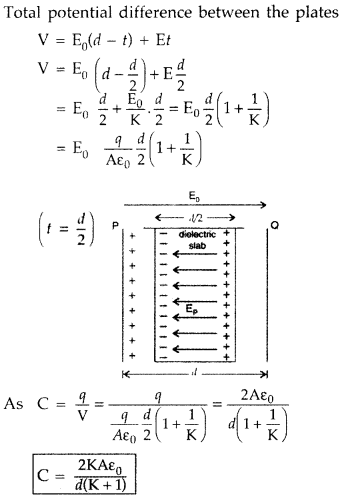
Question 53.
Calculate the amount of work done to dissociate a system of
three charges 1 μC, 1 μC and -4 μC placed on the vertices of an equilateral
triangle of side 10 cm. (Comptt. All india)
Answer: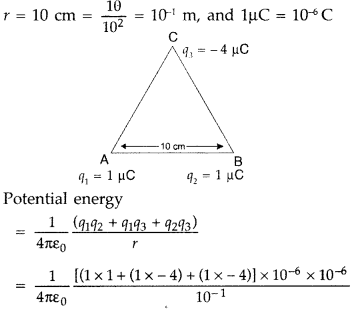
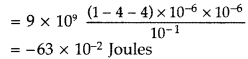
Hence, 0.63 Joules of energy is required to dissociate the
system.
Question 54.
A capacitor of unknown capacitance is connected across a
battery of V volts. The charge stored in it is 300 µC. When potential across the
capacitor is reduced by 100 V, the charge stored in it becomes 100 V. Calculate
the potential V and the unknown capacitance. What will be the charge stored in
the capacitor if the voltage applied had increased by 100 V? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(i) Charge stored, Q = CV
300 µC = C × V ,
When potential is
reduced by 100 V
100 µC = C(V – 100) = CV – 100 C
100 µC = 300 µC – 100
C
⇒ 100 C = 300 µC – 100 µC
⇒ 100 C = 200 µC
Therefore, capacitance C =
2µF![]()
(ii) Charge stored when voltage applied is increased by 100
V
Q’ = 2µF × (150 + 100) = 500µC
Question 55.
Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole.
Locate the points where the potential due to the dipole is zero. (All India
2013)
Answer:
Potential at all points in equatorial plane is zero
everywhere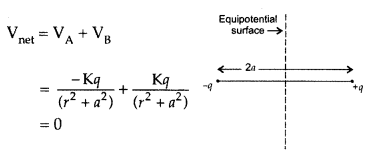
Question 56.
Two thin concentric shells of radii r1 and
r2 (r2 > r1) have charges q1 and
q2. Write the expression for the potential at the surface of inner
and outer shells. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
(i) Potential at the
surface of inner shell,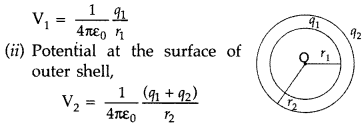
(Since the charge on inner shell will also con-tribute)
Question 57.
(a) Obtain the expression for the energy stored per unit
volume in a charged parallel plate capacitor.
(b) The electric field inside a
parallel plate capacitor is E. Find the amount of work done in moving a charge q
over a closed rectangular loop a b c d a.(Delhi 2013)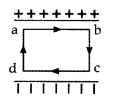
Answer:
(a) Energy of a parallel plate capacitor.
Potential of capacitor = \(\frac{q}{C}\)
Small amount of work done in
giving an additional charge dq to the capacitor,![]()
Total work done in giving a charge Q to the capacitor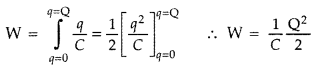
As electrostatic force is conservative, thus work is stored in the form of
potential energy (U) of the capacitor.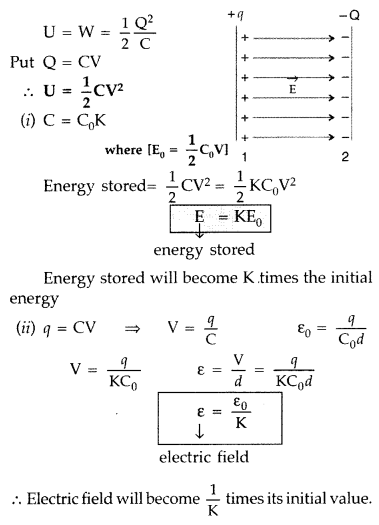
∴ Electric field will become \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{K}}\) times its initial
value.
[Read answer only upto U = \(\frac{1}{2}\) CV2
(b) The amount
of work done in moving a charge Y over a closed rectangular loop abcda is zero,
because net displacement is zero.
W = q\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}} \cdot
\vec{d}\)
Question 58.
Derive the expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate
capacitor having plate area A and plate separation d. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Capacity of a parallel plate capacitor. A parallel plate capacitor
consists of two large plane parallel conducting plates separated by a small
distance. We first take the intervening medium between the plates to be vaccum.
Let A be the area of each plate and d the separation between them. The two
plates have charges Q and – Q. Since d is much smaller than the linear dimension
of the plates (d2 << A), we can use the result on electric
field by an infinite plane sheet of uniform surface charge density. Plate 1 has
surface charge density σ = Q/A and Plate 2 has a surface charge density -σ, the
electric field in different region is: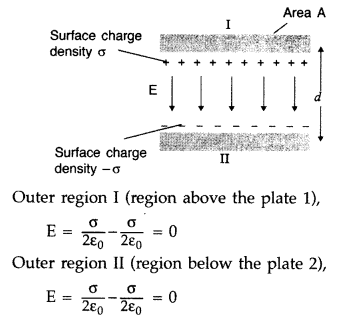
In the inner region between the plates 1 and 2, the electric fields due to the
two charged plates add up, giving![]()
The capacitance C of the parallel plate capacitor is then![]()
Question 59.
Two parallel plate capacitors of capacitances C1
and C2 such that C1 = 3C2 are connected across
a battery of V volts as shown in the figure. Initially the key (k) is kept dosed
to fully charge the capacitors. The key is now thrown open and a dielectric slab
of dielectric constant ‘K’ is inserted in the two capacitors to completely fill
the gap between the plates,
Find the ratio of
(i) the net capacitance and
(ii) the
energies stored in the combination, before and after the introduction of the
dielectric slab. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(i) Net capadtance before
filling the gap with dielectric slab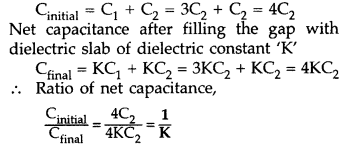
Energy stored in the combination before introduction of dielectric slab,
Question 60.
Two parallel plate capacitors of capacitances C1
and C2 such that C1 = 2C2 are connected across
a battery of V volts as shown in the figure. Initially the key (k) is kept
closed to fully charge the capacitors. The key is now thrown open and a
dielectric slab of dielectric constant ’K’ is inserted in the two capacitors to
completely fill the gap between the plates.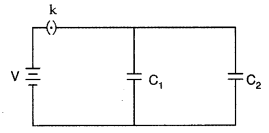
Find the ratio of
(i) the net capacitance and
(ii) the
energies stored in the combination, before and after the introduction of the
dielectric slab. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(i) Net capacitance before
filling the gap with dielectric slab![]()
(ii) Energy stored in the combination before introduction of
dielectric slab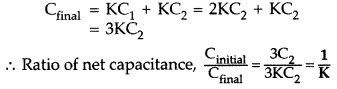
Energy stored in the combination after introduction of dielectric slab
Question 61.
Two parallel plate capacitors of capacitances C1
and C2 such that C1 = (C2)/2 are connected
across a battery of V volts as shown in the figure. Initially the key (k) is
kept closed to fully charge the capacitors. The key is now thrown open and a
dielectric slab of dielectric constant ‘K’ is inserted in the two capacitors to
completely fill the gap between the plates.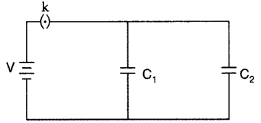
Find the ratio of
(i) the net capacitance and
(ii) the
energies stored in the combination, before and after the introduction of the
dielectric slab. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(i) Net capacitance before
filling the gap with dielectric slab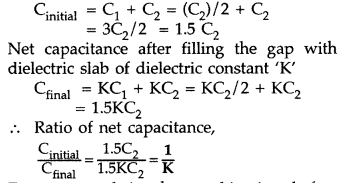
(ii) Energy stored in the combination before introduction of dielectric
slab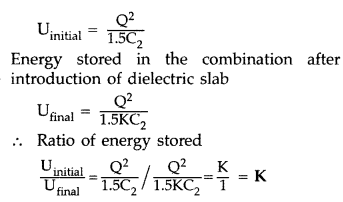
Question 62.
Two capacitors of unknown capacitances C1 and
C2 are connected first in series and then in parallel across a
battery of 100 V. If the energy stored in the two combinations is 0.045 J and
0.25 J respectively, determine the value of C1 and C2.
Also calculate the charge on each capacitor in parallel combination. (Delhi
2015)
Answer:
Energy stored in a capacitor is given by,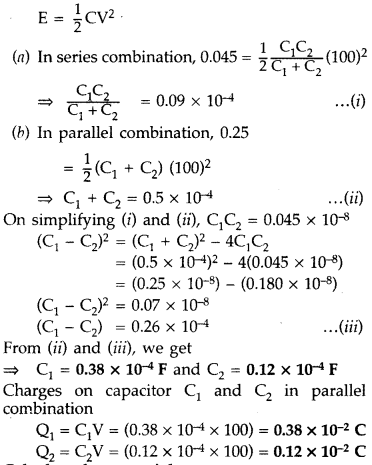
Question 63.
Calculate the potential difference and the energy stored in
the capacitor C2 in the circuit shown in the figure. Given potential
at A is 90 V, C1 = 20 µF, C2 = 30 µF and C3 =
15 µF. (All India 2015)
Answer:
Given VA = 90 V, C1 = 20 µF,
C2 = 30 µF and C3 = 15 µF
Since these capacitors are
connected in series, net capacitance (C) will be,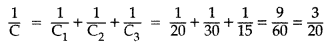
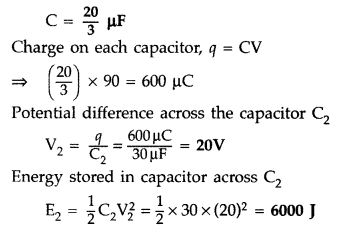
Question 64.
Two parallel plate capacitors X and Y have the same area of
plates and same separation between them. X has air between the plates while Y
contains a dielectric medium of \(\varepsilon_{r}\) = 4.
(i) Calculate capacitance of each capacitor if equivalent
capacitance of the combination is 4 pF.
(ii) Calculate the potential
difference between the plates of X and Y.
(iii) Estimate the ratio of
electrostatic energy stored in X and Y. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(i) Let
Cx = C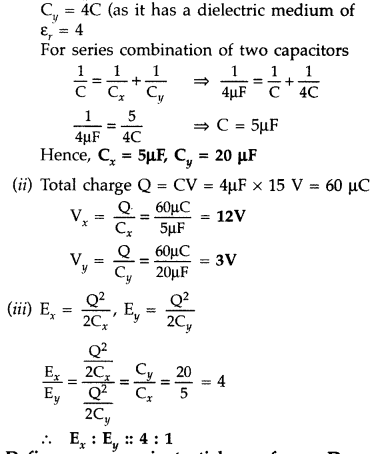
Question 65.
Define an equipotential surface. Draw equipotential surfaces
:
(i) in the case of a single point charge and
(ii) in a constant electtic
field in Z-direction. Why the equipotential surfaces about a single charge are
not equidistant?
(iii) Can electric field exist tangential to an
equipotential surface? Give reason. (All India 2015)
Answer:
A surface
with a constant value of potential at all points of the surface is defined as
‘equipotential surface’ „
(i) Equipotential surface for a single point
charge.
(ii) Equipotential surface in a constant electric field as
shown in the adjoining diagram.
Equipotential surface are not equidistant,
because V \(\propto \frac{1}{r}\)
(iii) No, If the field lines are
tangential, work will be done in moving a charge on the surface which goes
against the definition of equipotential surface.
Question 66.
A parallel plate capacitor, of capacitance 20pF, is conneted
to a 100 V supply. After sometime the battery is disconnected, and the space,
between the plates of the capacitor is filled with a dielectric, of dielectric
constant 5. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor
(i) before
(ii)
after the dielectric has been put in between its plates. (Comptt. Outside Delhi
2015)
Answer: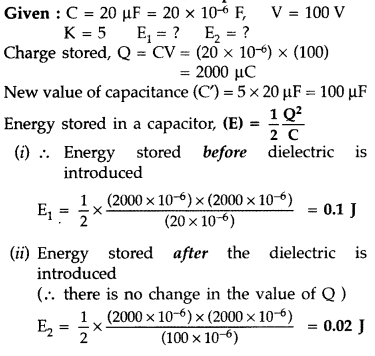
Question 67.
(i) Find equivalent capacitance between A and B in the
combination given below. Each capacitor is of 2 µF capacitance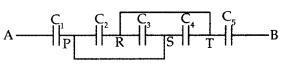
(ii) If a dc source of 7 V is connected across AB, how much
charge is drawn from the source and what is the energy stored in the network?
(Delhi 2015)
Answer: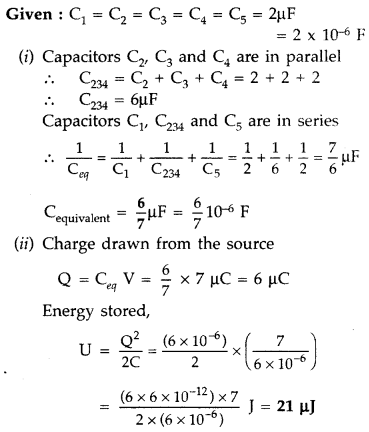
Question 68.
A 12 pF capacitor is connected to a 50 V battery. How much
electrostatic energy is stored in the capacitor? If another capacitor of 6 pF is
connected in series with it with the same battery connected across the
combination, find the charge stored and potential difference across each
capacitor. (Delhi 2015)
Energy stored, in the capacitor of capacitance 12
pF,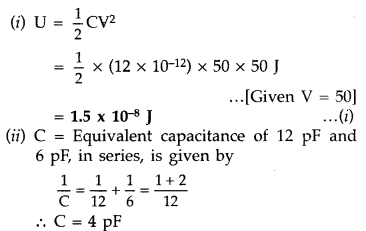
∴ Charge stored across each capacitor
q = CV = (4 × 10-12) × 50 C
= 2 × 10-10C
Charge on each capacitor 12 pF as well as on 6 pF is
2 × 10-10 C
∴ Potential difference across capacitor
C1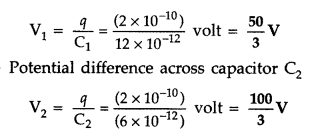
Question 69.
(i) Derive the expression for the electric potential due to
an electric dipole at a point on its axial line.
(ii) Depict the
equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(i)
The potential due to the dipole is the sum of potentials due to the charges q
and – q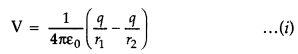
where r1 and r2 are the distances of
the point P from q and – q, respectively.
Now, by geometry,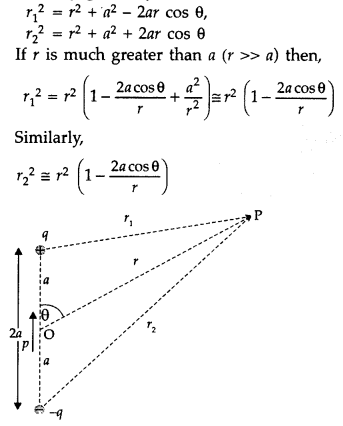
Using the Binomial theorem and retaining terms upto the first order in a/r; we
obtain,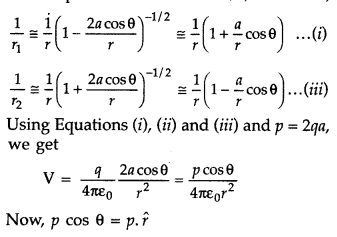
where \(\hat{\gamma}\) is the unit vector along the position vector OP.
The
electric potential of a dipole is then given by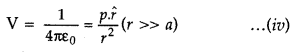
From the above equation (iv), potential on the dipole axis (θ
= 0, n) is given by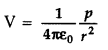
(ii) Equipotential surface for an electric dipole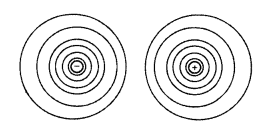
Question 70.
Two identical capacitors of 12 pF each are connected in
series across a battery of 50 V. How much electrostatic energy is stored in the
combination ? If these were connected in parallel across the same battery, how
much energy will be stored in the combination now? Also find the charge drawn
from the battery in each case. (Delhi 2015)
Answer: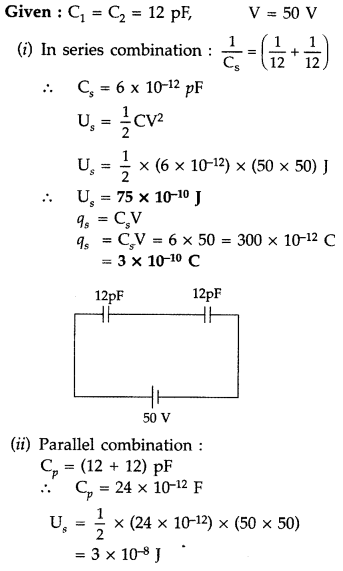
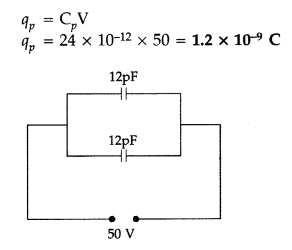
Question 71.
Two identical parallel plate capacitors A and B are connected
to a battery of V volts with the switch S closed. The switch is now opened and
the free space between the plates of the capacitors is filled with a dielectric
of dielectric constant K. Find the ratio of the total electrostatic energy
stored in both capacitors before and after the introduction of the
dielectric.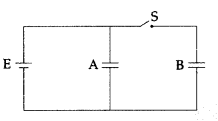
Answer: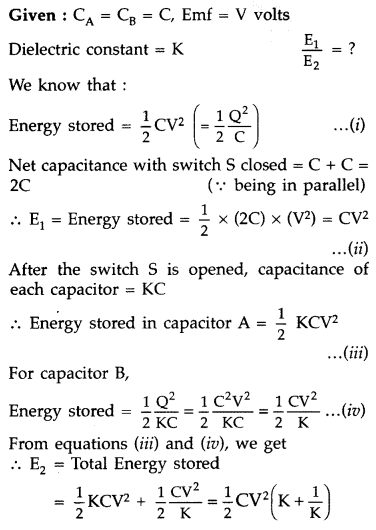
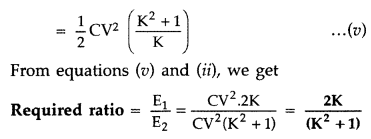
Question 72.
(a) Write two properties by which electric potential is related
to the electric field.
(b) Two point charges q1 and q2,
separated by a distance of r12 are kept in an external electric
field. Derive an expression for the potential energy of the system of two
charges in the field. (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(a) Two properties
which relate electric potential to electric field—
(i) Electric field is in
the direction in which potential decreases at the maximum rate.
(ii)
Magnitude of electric field is given by change in the magnitude of potential per
unit displacement normal to a charged conducting surface, or E =
(b) Work
done in bringing the charge q1 to a point against external electric
field,![]()
Work done in bringing the charge q2 against the
external electric field and the electric field produced due to charge
q1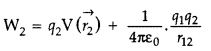
Therefore, Total work done = Electrostatic potential
energy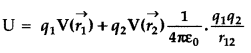
Question 73.
A capacitor of unknown connected across a battery of V volt.
A charge of 360 pC is stored in it. When the potential across the capacitor is
reduced by 120 V, the charge stored in the capacitor becomes 120 pC. Calculate V
and the unknown capacitance. What would have been the charge on the capacitor if
the voltage were increased by 120 V? (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer: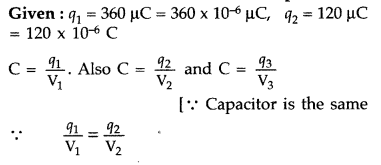
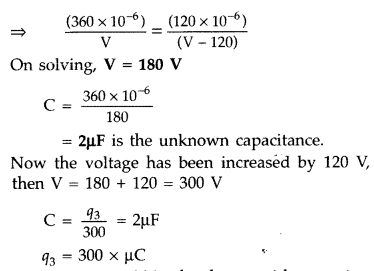
q3 = 600 µC would be charge on the capacitor if voltage were incresed
by 120 V.
Question 74.
A capacitor of unknown capacitance is connected across a
battery of V volt. A charge of 240 pC is stored in it. When the potential across
the capacitor is reduced by 80 V, the charge stored in the capacitor becomes 80
pC. Calculate V and the unknown capacitance. What would have been the charge in
the capacitor if the voltage were increased by 80 V? (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer: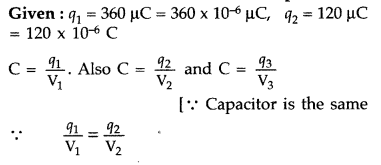
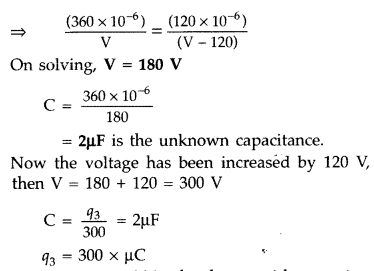
q3 = 600 µC would be charge on the capacitor if voltage were incresed
by 120 V.
[Answer : V = 120 V, c = 2 μF, Q = 400 μC]
Question 83.
A capacitor of unknown capacitance is connected across a
battery of V volt. A charge of 120 μC is stored in it. When the potential across
the capacitor is reduced by 40 V, the charge stored in the capacitor becomes 40
μC. Calculate V and the unknown capacitance. What would have been the charge in
the capacitor if the voltage were increased by 40 V? (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer: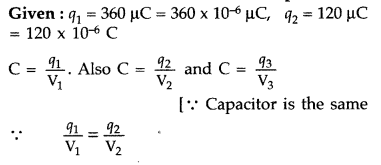
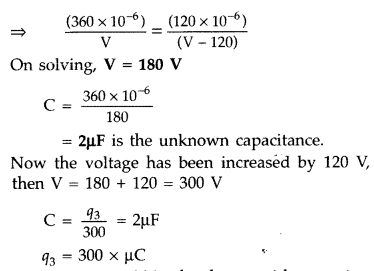 >
>
q3 = 600 µC would be charge on the capacitor if voltage were incresed
by 120 V.
[Ans : V = 60 V, c = 2 pF, Q3 = 200 μC].
Question 75.
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a
potential V by a battery. Without disconnecting the battery, the distance
between the plates is tripled and a dielectric medium of k = 10 is introduced
between the plates is tripled and a dielectric medium of k = 10 is introduced
between the plates of the capacitor. Explain giving reasons, how will the
following be affected:
(i) capacitance of the capacitor
(ii) charge on the
capacitor, and
(iii) energy density of the capacitor. (Comptt. Outside Delhi
2015)
Answer:
Given : d’ = 3d, K = 10, C = ?, Q’ = ?, U’d=
?
(i) For parallel plate capacitor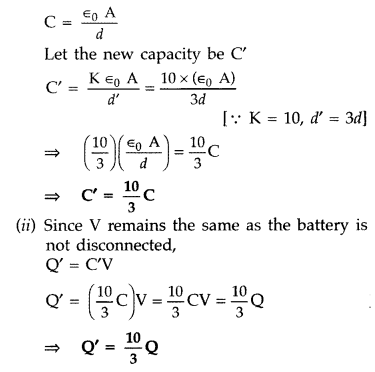
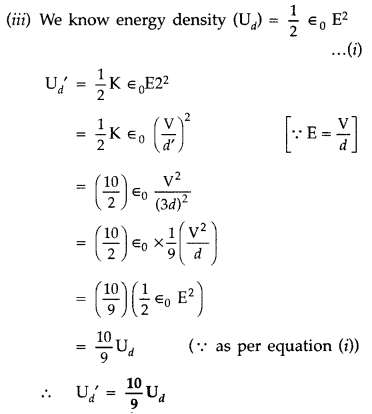
Question 76.
Derive the expression for the electric potential at any point
P, at distance r from the centre of an electric dipole, making angle a, with its
axes. (Comptt. All India 2015)
Answer:
The potential due to the dipole is
the sum of potentials due to the charges q and – q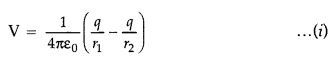
where r1 and r2 are the distances of the point P from q
and – q, respectively.
Now, by geometry,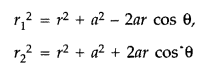
If r is much greater than a (r >> a) then,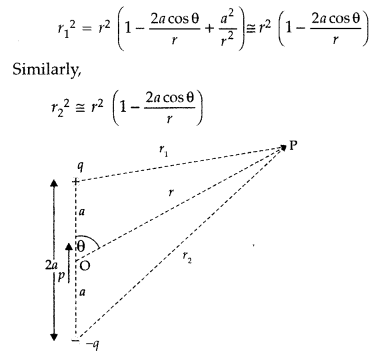
Using the Binomial theorem and retaining terms upto the first order in air; we
obtain,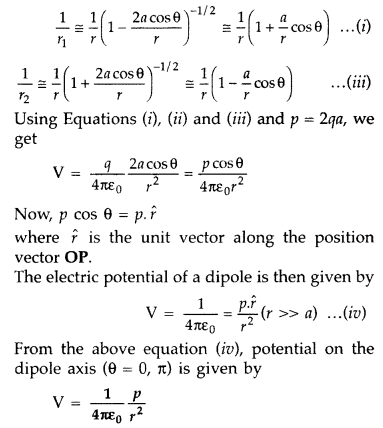
Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Two-point charges 2 μC and —2 μC are placed at points A and B
6 cm apart.
(a) Draw the equipotential surfaces of the system.
Answer:
The diagram is as shown.
(b) Why do the equipotential surfaces get closer to each other near the point
charges? (CBSEAI2O11C)
Answer:
We know that E = – dV/dr
Therefore, dr
=- dV/E
Since near the charge, electric field E is large, dr will be
less.
Question 2.
(a) Obtain the expressions for the resultant capacitance when
the three capacitors C1, C2, and C3 are
connected (i) in parallel and then (ii) in series.
Answer:
(i) Parallel
combination of three capacitors.
Let three capacitors of capacitances
C1, C2, and C3 be connected in parallel, and
potential difference V be applied across A and B. If q be total charge flowing
in the circuit and q1 q2 and q3 be charged
flowing across C1, C2, and C3 respectively,
then
q = q1+ q2 + q3
or q =
C1v + C2V + C3V …(i)
If CP is the capacitance of the arrangement in parallel, then
q
= CPV
So equation (i) becomes
CPV = C1V + C2V +
C3V
Or
CP = C1 + C2 +
C3
(ii) Series combination of three capacitors Let three capacitors
C1, C2, and C3 be connected in series. Let q
charge be flowing through the circuit.
If V1, V2, and
V3 be potential differences across the plates of the capacitor and V
be the potential difference across the series combination, then
V = V1 + V2 + V3
Or
V =
\(\frac{q}{C_{1}}+\frac{q}{C_{2}}+\frac{q}{C_{3}}\) … (i)
If Cs is the capacitance of series combination, then V = \(\frac{q}{\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{s}}}\).
So the equation (i) becomes
\(\frac{q}{\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{s}}}=\frac{q}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}+\frac{q}{\mathrm{C}_{2}}+\frac{q}{\mathrm{C}_{3}}\)
Or
\(\frac{1}{\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{s}}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{C}_{2}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{C}_{3}}\)
(b) In the circuit shown in the figure, the charge on the capacitor of 4 μF
is 16 μC. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor of 12 μF capacitance.
(CBSE 2019C)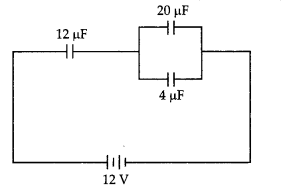
Answer:
Charge q across 4 μF Capacitor is 10 μc Potential difference across
the capacitor of capacitance 4 μF will be
V= \(\frac{q}{C}=\frac{16 \mu C}{4
\mu F}=\frac{16 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{C}}{4 \times 10^{-6}
\mathrm{~F}}\)=4V
∴ Potential across 12 μF Capacitors
= 12V – 4V = 8V
Energy stored in the capacitors of capacitance C = 12 μF
U = \(\frac{1}{2}\) CV2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 12 × 10-6 ×
82 joule
= 384 × 10-6 J = 384 μJ
Question 3.
Two identical plane metallic surfaces A and B are kept
parallel to each other in the air, separated by a distance of 1 cm as shown in
the figure.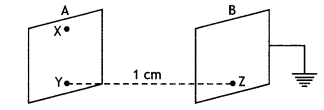
A is given a positive potential of 10 V and the outer surface of B is
earthed.
(i) What is the magnitude and direction of the uniform electric
field between Y and Z?
Answer:
The electric field between the plates
is
E = \(\frac{V}{d}\) = 103 V m-1
directed from
plate A at the higher potential to plate B at a lower potential, i.e. from Y to
Z
(ii) What is the work done in moving a charge of 20 µC from X to Y?
Answer:
Since X and Y are on the same plate A, which is an equipotential
surface, work done in moving a charge of 20 µC from X to Y on the equipotential
surface is zero.
Question 4.
(i) Draw the equipotential surfaces corresponding to a uniform
electric field in the z-direction.
Answer:
The equipotential surfaces are
as shown.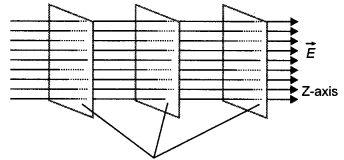
Equipotential surfaces
(ii) Derive an expression for the electric potential at any point along the
axial line of an electric dipole. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Consider an
electric dipole of length 2a and having charges +q and -q. Let us find the
potential on the axial line at point P at a distance OP = x from the center of
the dipole.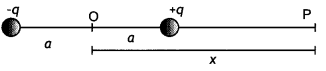
Now potential at point P is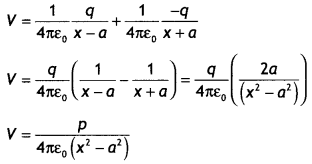
Question 5.
A network of four capacitors, each of capacitance 15 µF, is
connected across a battery of 100 V, as shown in the figure. Find the net
capacitance and the charge on the capacitor C4. (CBSE Al
2012C)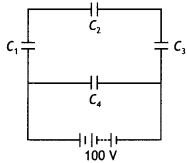
Answer:
Capacitors C1 C2 and C3 are in series, therefore their equivalent
capacitance is
\(\frac{1}{C_{\mathrm{s}}}=\frac{1}{C_{1}}+\frac{1}{C_{2}}+\frac{1}{C_{3}}=\frac{1}{15}+\frac{1}{15}+\frac{1}{15}=\frac{3}{15}\)
Hence CS = 5 µF
Now CS and C4 are in
parallel, hence
CP = CS + C4 = 5 + 15 = 20
µF
Now C4 is connected to 100 V, therefore charge on it is
Q = CV=15 ×
10-6 × 100=15 × 10-4 C
Question 6.
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a
potential V. It is then connected to another uncharged capacitor having the same
capacitance. Find out the ratio of the energy stored in the combined system to
that stored initially in the single capacitor. (CBSE AI 2014)
Answer:
Ui = \(\frac{1}{2}\) CV2
When the capacitors are connected then the energy stored is
UF
= \(\frac{1}{2}\left(C_{1}+C_{2}\right)\left(\frac{C_{1} V_{1}+C_{2}
V_{2}}{C_{1}+C_{2}}\right)^{2}\)
Since C1 = C2 = C, and V2 = 0, we have
Uf
= \(\frac{1}{2}(C+C)\left(\frac{C V}{C+C}\right)^{2}=\frac{1}{2}(2 C) \times
\frac{V^{2}}{4}=\frac{1}{4} C V^{2}\)
Hence we have
\(\frac{U_{f}}{U_{i}}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 7.
An isolated air capacitor of capacitance C0 is
charged to a potential V0. Now if a dielectric slab of dielectric
constant K is inserted between its plates, completely filling the space between
the plates, then how to do the following change, when the battery remains
connected
(i) capacitance,
Answer:
When the battery remains connected,
the potential on the capacitor does not change.
The capacitance of the
capacitor becomes K times the original value, i.e. C = K C0.
(ii) charge
Answer:
Now new charge is Q = CV = K C0 V = K
Q0.
(iii) the field between the plates
Answer:
The field between the plates
becomes
E = \(\frac{V}{d}=\frac{V_{0}}{d}\) = E0, i.e. no
change.
(iv) energy stored by the capacitor?
Answer:
The energy stored
becomes
U = \(\frac{1}{2} C V^{2}=\frac{1}{2} K C_{0} V^{2}\) =
KU0.
Question 8.
Derive an expression for the energy stored in a parallel
plate capacitor.
On charging a parallel plate capacitor to a potential V, the
spacing between the plates is halved, and a dieletric medium of εr =
10 is introduced between the plates, without disconnecting the d.c. source.
Explain, using suitable expressions, how the
(i) capacitance,
(ii)
electric field and
(iii) energy density of the capacitor change. (All India
2008)
Answer:
(a) Consider a parallel plate capacitor with plate area ‘A’
and separation between the plates equal to ‘d’. Suppose at any instant of time
charge on the capacitor plate is ‘q’ and potential difference due to this charge
is V. To supply a charge ‘dq’ further to the capacitor amount of work required
is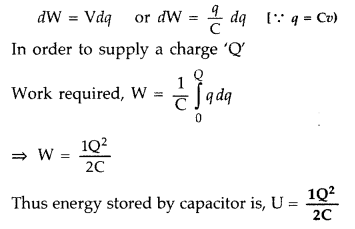
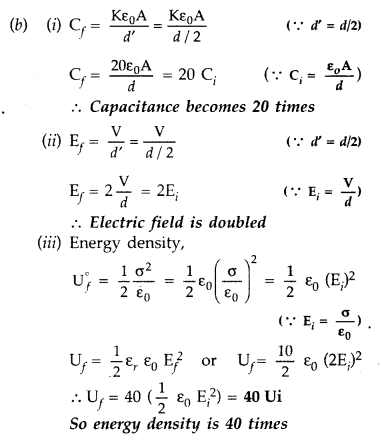
Question 9.
(a) Write two properties of equipotential surfaces. Depict
equipotential surfaces due to an isolated point charge. Why do the equipotential
surfaces get closer as the distance between the equipotential surface and the
source charge decreases?
(b) An electric dipole of dipole moment \(\vec{p}\),
is placed in a uniform electric field \(\vec{E}\),. Deduce the expression for
the torque ‘x acting on it. (Comptt. All India 2008)
Answer:
(a)
Properties of equipotential surfaces:
(i) No work is done in moving a test
charge over an equipotential surface.
(ii) No two equipotential surfaces can
inter-sect each other.
(iii) Equipotential surface due to an isolated point
charge is spherical.
(iv) The electric field at every point is normal to the
equipotential surface passing through that point. (any two)![]()
For the same charge in the value, V, i.e., when dV =
constant,
we have dr \(\propto \frac{1}{\mathrm{E}}\)
Hence, equipotential
surface gets closer as the distance between the equipotential surface and the
source charge decreases.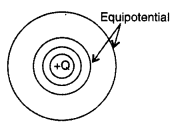
Equipotential surface due to an isolated charge
(b)
Consider a dipole with charges +q and -q placed in a uniform electric field
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}\) such that AB = 2a as shown in the figure
Since the dipole experiences no net force in a uniform electric field but
experiences a torque (τ) is given by![]()
It tends to rotate the dipole in clockwise direction. To
rotate the dipole anti-clock wise has to be done on the dipole.
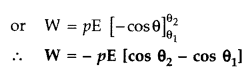
Question 10.
(a) Obtain the expression for the potential due to an
electric dipole of dipole moment p at a point V on the axial line.
(b) Two
identical capacitors of plate dimensions l × b and plate separation d have
di-electric slabs filled in between the space of the plates as shown in the
figure.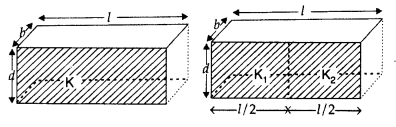
Obtain the relation between the dielectric constants K, K1 and
K2.(Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
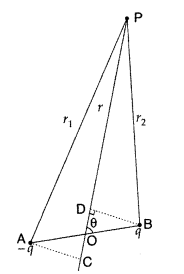
(a) Potential at a point
due to an electric dipole : Let us consider an electric dipole consisting of two
equal and opposite charges -q at A and +q at B, separated by a distance 21 with
centre at O. We have to calculate potential at a point P, whose polar
co-ordinates are (r, 0); i.e. OP = r and ∠BOP = θ, as shown in the figure.
Here AP = r1, and BP = r2, we can easily calculate
potential as P due to point charges at A and B using V = \(\frac{1}{4 \pi
\varepsilon_{0}} \frac{q}{r}\).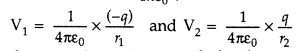
Total potential at P due to both the charges of the dipole is given by
v =
v1 + v2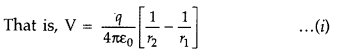
To put this result in a more convenient form, we draw normals from A and B on
the line joining O and P. From ∆BOD, we note that OD = l cos θ and from ∆OAC we
note that OC = l cos θ. For a small dipole (AB << OP), from the figure, we
can take PB = PD and PA = PC.
Hence r1 = r + l cos θ,
Using
these results in equation (1), we get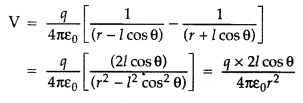
where we have neglected the term containing second power of l
since l << r
In terms of dipole (p = q × 21), we can express this
result as![]()
This result shows that unlike the potential due to a point
charge, the potential due to a dipole is inversely proportional to the square r
of the distance.
Let us now consider its special cases.
Special Cases
Case I : When point P lies on the axial line of the dipole on the side of
positive charge,
θ = 0 and cos θ = 1
Then equation (ii) reduces to![]()
Case II : When point P lies on the axial line of the dipole but on the side of
negative charge,
θ = 180° and cos θ = 1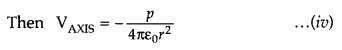
Case III :When point P lies on the equatorial line of the dipole (perpendicular
bisector of AB), θ = 90° and cos θ = 0
Then Vequitorial = 0 …
(i)
Thus, electric potential due to a dipole is zero at every point on the
equatorial line of the dipole.![]()
In second case, these two apartments are in parallel, their net capacity would
be the sum of two individual capacitances
C2 = C’2 +
C”2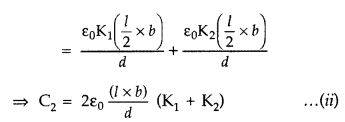
Since these are identical capacitors, comparing (i) and (ii),
We have
C1 = C2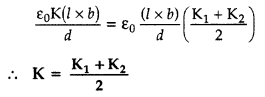
Question 11.
(a) Explain, using suitable diagrams, the difference in the
behaviour of a
(i) conductor and
(ii) dielectric in the presence of
external electric field. Define the terms polarization of a dielectric and write
its relation with susceptibility.
(b) A thin metallic spherical shell of
radius R carries a charge Q on its surface. A point charge \(\frac{Q}{2}\) is
placed at its centre C and another charge +2Q is placed outside the shell at a
distance x from the centre as shown in the figure.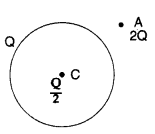
Find
(i) the force on the charge at the centre of shell
and at the point A,
(ii) the electric flux through the shell. (Delhi
2015)
Answer:
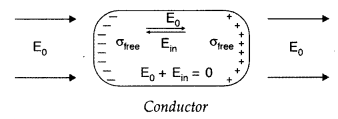
(a) (i) Behaviour of conductor in an external electric field
:
(ii) Behaviour of a dielectric in an external electrical field :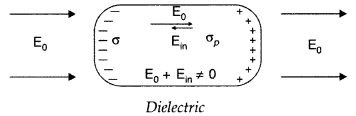
Explanation: In the presence of electric field, the free charge carriers in a
conductor move the charge distribution and the conductor readjusts itself so
that the net Electric field within the conductor becomes zero.
In a dielectric, the external electric field induces a net dipole moment, by stretching / reorienting the molecules. The electric field, due to this induced dipole moment, opposes, but does not exactly cancel the external electric field.
Polarisation: Induced Dipole moment, per unit volume, is called the
polarisation. For Linear isotropic dielectrics having a susceptibility
xc, we have polarisation (p) as:
p = XcE
(b) (i) Net
Force on the charge y, placed at the centre of the shell, is zero.
Force on
charge ‘2Q’ kept at point A,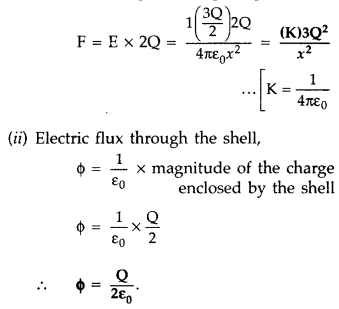
Question 12.
(i) If two similar large plates, each of area A having
surface charge densities +a and -a are separated by a distance d in air, find
the expressions for
(a) field at points between the two plates and on outer
side of the plates. Specify the direction of the field in each case.
(b) the
potential difference between the plates.
(c) the capacitance of the capacitor
so formed.
(ii) Two metallic spheres of radii R and 2R are charged so that
both of these have same surface charge density a. If they are connected to each
other with a conducting wire, in which direction will the charge flow and why?
(All India 2016)
Answer:
(i) Given :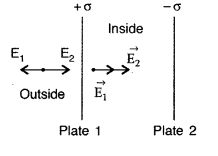
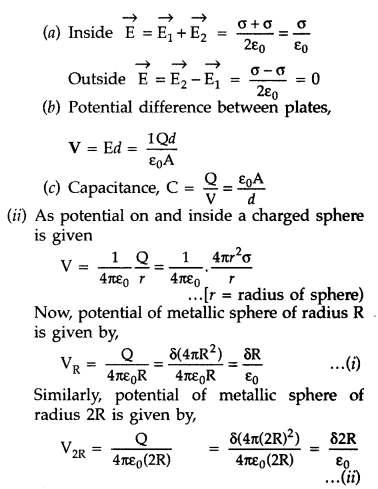
From (i) and (ii), we know that V2R > VR
Hence, the
bigger sphere will be at a higher potential, so charge will flow from bigger
sphere to smaller sphere.
Question 13.
(a) Obtain the expression for the potential due to a point
charge.
(b) Use the above expression to show that the potential, due to an
electric dipole (length 2a), varies as the ‘inverse square’ of the distance r of
the ‘field point’ from the centre of the dipole for r > a. (Comptt. Delhi
2016)
Answer:
(a) Consider a point charge ‘Q’ kept at point O. Let P be
the field point at distance r.
At some point p’, the electrostatic force on
the unit positive charge is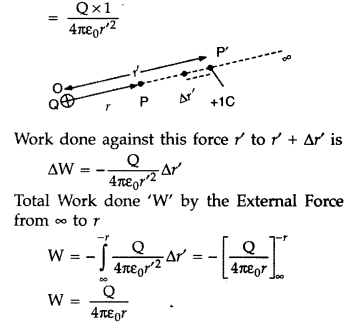
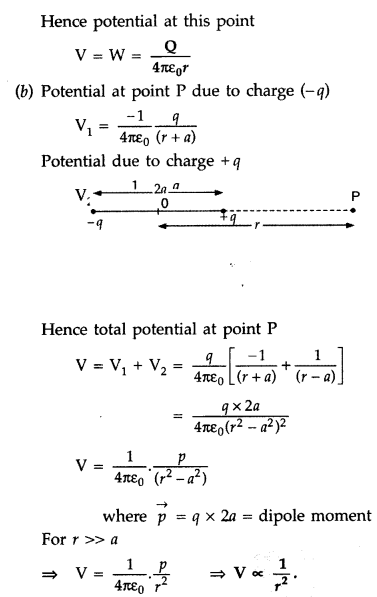
Question 14.
(a) Define the SI unit of capacitance.
(b) Obtain the
expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor.
(c) Derive the
expression for the affective capacitance of a series combination of n
capacitors. (Comptt. Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) When a charge of one coulomb
produces a potential difference of one volt between the plates of capacitor, the
capacitance is one farad.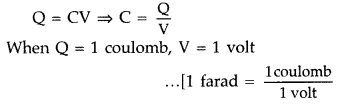
(b)
Capacity of a parallel plate capacitor. A parallel plate capacitor
consists of two large plane parallel conducting plates separated by a small
distance. We first take the intervening medium between the plates to be vaccum.
Let A be the area of each plate and d the separation between them. The two
plates have charges Q and – Q. Since d is much smaller than the linear dimension
of the plates (d2 << A), we can use the result on electric
field by an infinite plane sheet of uniform surface charge density. Plate 1 has
surface charge density σ = Q/A and Plate 2 has a surface charge density -σ, the
electric field in different region is:
In the inner region between the plates 1 and 2, the electric fields due to the
two charged plates add up, giving![]()
The capacitance C of the parallel plate capacitor is then![]()
(c) In series combination, charge on each capacitor is same.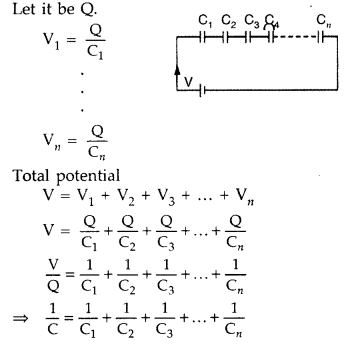
Question 15.
An isolated air capacitor of capacitance C0 is charged to a
potential V0. Now if a dielectric slab of dielectric constant K is inserted
between its plates, completely filling the space between the plates, then how to
do the following change, when the battery is disconnected
(i) charge
Answer:
If battery is disconnected then charge remains same, Q =
Q0
(ii) electric field between the plates,
Answer:
V = \(\frac{V_{0}}{K}\)
,
∴E = \(\frac{E_{0}}{K}\) ,
(iii) capacitance
C = KCO [∵ C = \(\frac{Q_{0}}{V}=\frac{Q_{0}}{V_{0} /
K}=\frac{K Q_{0}}{V_{0}}\)]
(iv) energy stored by the capacitor
U =
\(\frac{U_{0}}{K}\left[U=\frac{1}{2} C V^{2}=\frac{1}{2}\left(K
C_{0}\right)\left(\frac{V_{0}}{K}\right)^{2}\right]\)
Question 16.
The figure shows two identical capacitors, C1 and
C2, each of 1 µF capacitance connected to a battery of 6 V. Initially
switch ‘S’ is closed. After some time ‘S’ is left open and dielectric slabs of
dielectric constant K = 3 are inserted to fill completely the space between the
plates of the two capacitors. How will (i) the charge and (II) potential
difference between the plates of the capacitors be affected after the slabs are
inserted? (CBSE Delhi 2011)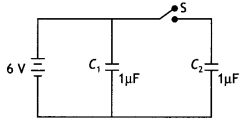
Answer:
When switch S is opened then capacitor C1 remains
connected to the battery white capacitor C2 is disconnected. Thus for
the two capacitors, we have
| Physical quantity | Capacitor C1 | Capacitor C2 |
| Charge | Becomes K times, i.e. Q = CV = K C0V = 3 × 1 × 10-6 × 6 = 1.8 × 10-5 C | Remains same Q = Q0 = CV = 1 × 10-6 × 6 = 6 × 10-6 C |
| Potential difference | Remains same V = V0 = 6 V | Becomes 1/K times V =V0/K = 6/3 = 2V |
Question 17.
A particle, having a charge +5 µC, is initially at rest at
the point x = 30 cm on the x axis. The particle begins to move due to the
presence of a charge Q that is kept fixed at the origin. Find the kinetic energy
of the particle at the instant it has moved 15 cm from its initial position if
(i) Q = +15 µC and (ii) Q = -15 µC (CBSE Sample Paper 2018-19)
Answer:
From energy conservation, Ui + Ki = Uf +
Kf
kQq/ri + 0 = kQq/rf + Kf
Kf = kQq (1/ri — 1/rf)
When Q is +15 µC, q will move 15 cm away from it. Hence rf = 45
cm
Kf = 9 × 109 × 15 × 10-6 × 5 ×
10-6 [1/(30 × 10-6) – 1/(45 × 10-2)] = 0.75
J
When Q is -15 µC, q will move 15 cm towards it. Hence rf = 15 cm Kf = 9 × 109 × (-15 × 10-6) × 5 × 106 [1/(30 × 10-2) – 1/(15 × 10-2)] = 2.25 J
Question 18.
Two metal spheres, one of radius R and the other of radius
2R, both have same surface charge density σ. They are brought in contact and
separated. What will be new surface charge densities on them? (NCERT
Exemplar)
Answer:
Let the two spheres have charges Q1 and
Q2 respectively. Since σ1 = σ2, before contact,
we have
\(\frac{Q_{1}}{4 \pi R^{2}}=\frac{Q_{2}}{4 \pi(2 R)^{2}}\)
Or
Q2 = 4 Q1
After contact
Let q1 and q2 be the charges on them, then
q1
+ q2 = Q1 + Q2= Q1 + 4Q1
= 5Q1 = 5(σ × 4πr²)
The two will exchange charge till their potentials are equal, therefore we
have
\(\frac{q_{1}}{R}=\frac{q_{2}}{2 R}\)
Or
q2 = 2
q1
Therefore 3q1 = 5(σ × 4πr²)
Or
q1 =
\(\frac{5}{3}\)(σ x 4πr²) and q2 = 2q1 =
\(\frac{10}{3}\)5(σ x 4πr²)
Therefore
σ1 = \(\frac{q_{1}}{4 \pi
R^{2}}=\frac{5}{3}\left(\frac{\sigma \times 4 \pi R^{2}}{4 \pi
R^{2}}\right)=\frac{5 \sigma}{3}\)
And
σ2 = \(\frac{q_{2}}{4
\pi(2 R)^{2}}=\frac{10}{3}\left(\frac{\sigma \times 4 \pi R^{2}}{4 \pi(2
R)^{2}}\right)=\frac{5 \sigma}{6}\)
Question 19.
(a) Derive an expression for the capacitance of a parallel
plate capacitor when the space between the plates is partially filled with a
dielectric medium of dielectric constant ‘K’.
Answer:
Consider a parallel
plate capacitor having each plate of area A and separated by a distance d. When
there is a vacuum between the two plates, the capacitance of the parallel plate
capacitor is given by
C0 = ε0 A/d.
Suppose that when the capacitor is connected to a battery, the electric field
of strength E0 is produced between the two plates of the capacitor.
Further, suppose that when a dielectric slab of thickness t (t < d) is
introduced between the two plates of the capacitor as shown in the figure, the
electric field reduces to E due to the polarisation of the dielectric. Therefore
between the two plates of the capacitor, over a distance of t, the strength of
the electric field is E, and over the remaining distance (d – f)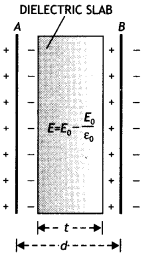
the strength is E0. If V is the potential between the plates of the
capacitor, then
V = Et + E0(d – t)
Since E = E0/K where K
is the dielectric constant, the above equation becomes
V = \(\frac{E_{0}}{K} t+E_{0}(d-t)=E_{0}\left(d-t+\frac{t}{K}\right)\)
The electric field between the plates of the capacitor is given by
E0 = σ / ε0 = Q/ A ε0
Hence the potential between the two plates becomes.
V =
\(E_{0}\left(d-t+\frac{t}{K}\right)=\frac{Q}{\varepsilon_{0}
A}\left(d-t+\frac{t}{K}\right)\)
Hence the capacitance of the parallel plate capacitor is given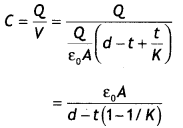
∴ clearly, C > C0. Therefore, capacitance increases in the presence of a dielectric medium.
(b) Explain why the capacitance decreases when the dielectric medium is
removed from between the plates.
Answer:
On removing the dielectric, the
capacitance will decrease.
Question 13.
(a) Obtain the expression for the energy stored per unit
volume in a charged parallel plate capacitor.
(b) The electric field inside a
parallel plate capacitor is E. Find the amount of work done in moving a charge q
over a closed rectangular loop a b c d a. (CBSE Delhi 2014)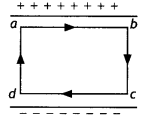
Answer:
(a) Suppose the capacitor is charged fully, its final charge is Q.
and a final potential difference is V. These are related as Q = CV
Let q and V be the charge and potential difference, respectively.
At an intermediate stage during charging process q = CV. At this stage the small work done dW to transfer an additional charge dq is
dW = Vdq = \(\frac{q d q}{C}\)
The total work W needed to increase the capacitor’s charge q from zero to its
final value Q is given by
W = \(\int_{0}^{w} d W=\int_{0}^{Q} \frac{q d
q}{C}=\frac{1}{C} \int_{0}^{Q} q d q\)
Or
W =
\(\frac{1}{C}\left|\frac{q^{2}}{2}\right|_{0}^{Q}=\frac{Q^{2}}{2 C}\)
This work is stored in the capacitor in the form of its electric potential
energy. Hence,
U = \(\frac{Q^{2}}{2 C}\) … (1)
substituting Q = CV in equation (1) we have
U = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
CV2
Energy density = Energy stored per unit volume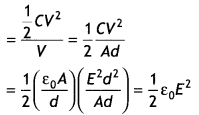
(b) Since the surface is an equipotential surface, work done is zero.
Question 20.
(a) Derive the expression for the capacitance of a parallel
plate capacitor having plate area A and plate separation d.
Answer:
Suppose Q. is the charge on the capacitor, and c is the uniform surface charge
density on each plate as shown in the figure. Therefore by Gauss’s theorem, the
electric field between the plates of the capacitor (neglecting fringing of
electric field at the edges) is given by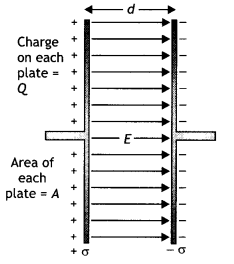
E = \(\frac{\sigma}{\varepsilon_{0}}=\frac{Q}{\varepsilon_{0} A}\) …. (1)
The field is uniform, and the distance between the plates is d, so the
potential difference between the two plates is
V = Ed =
\(\frac{1}{\varepsilon_{0}} \frac{Q d}{A}\) ….. (2)
Therefore by the definition of capacitance we have
C =
\(\frac{Q}{V}=\frac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d}\) …. (3)
This gives the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with a vacuum between plates.
(b) Two charged spherical conductors of radii R1 and R2
when connected by a conducting wire acquire charges q1 and
q2 respectively. Find the ratio of their surface charge densities in
terms of their radii. (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
The ratio of the surface charge densities is given by
\(\frac{\sigma_{1}}{\sigma_{2}}=\frac{q_{1}}{4 \pi R_{1}^{2}} \times \frac{4 \pi
R_{2}^{2}}{q_{2}}\) ….(4)
Now when they are connected with a wire, their potentiaLs wilt be same:
therefore, from the expression.
V = \(\frac{Q}{c}=\frac{Q}{R}\)
∵ C = 4πε0R for a spherical body
∴\(\frac{q_{1}}{q_{2}}=\frac{R_{1}}{R_{2}}\)
Substituting in equation (4) we have
\(\frac{\sigma_{1}}{\sigma_{2}}=\frac{R_{1}}{R_{1}^{2}} \times
\frac{R_{2}^{2}}{R_{2}}=\frac{R_{2}}{R_{1}}\)
Question 21.
(a) Describe briefly the process of transferring the charge
between the two plates of a parallel plate capacitor when connected to a
battery. Derive an expression for the energy stored in a capacitor.
Answer:
The electrons are transferred to the positive terminal of the battery
from the metallic plate connected to the positive terminal, leaving behind a
positive charge on it. Similarly, the electrons move on to the second plate from
the negative terminal, hence it gets negatively charged. This process continues
till the potential difference between the two plates becomes equal to the
potential of the battery.
Suppose the capacitor is charged fully; its final charge is Q and the final
potential difference is V.
These are related as Q = CV
Let q and V be the charge and potential difference respectively, after some time during the charging of the capacitor, then q = CV. At this time, the small work done dW required to transfer an additional charge dq is given by
dW = Vdq = \(\frac{q d q}{C}\)
The total work W needed to increase the capacitor’s charge q from zero to its
final value Q is given by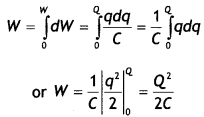
This work is stored in the capacitor in the form of its electric potential
energy. Hence,
U = \(\frac{Q^{2}}{2 C}\) …(1)
Substituting Q= CVin equation (1) we have
U = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
CV2
(b) A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery to a potential
difference V. It is disconnected from the battery and then connected to another
uncharged capacitor of the same capacitance. Calculate the ratio of the energy
stored in the combination to the initial energy on the single capacitor. (CBSE
Delhi 2019)
Answer:
The charge stored on the capacitor q = CV, when it is
connected to the uncharged capacitor of same capacitance, sharing of charge,
takes place between the two capacitors till the potential of both the capacitors
becomes V/2.
Energy stored on the combination (U2)
= \(\frac{1}{2}
C\left(\frac{V}{2}\right)^{2}+\frac{1}{2}
C\left(\frac{V}{2}\right)^{2}=C\left(\frac{V}{2}\right)^{2}=\frac{C
V^{2}}{4}\)
Energy stored on single capacitor before connecting
U1 =
–\(\frac{1}{2}\) CV2
Ratio of energy stored in the combination to that in the single
capacitor.
\(\frac{U_{2}}{U_{1}}=\frac{C V^{2} / 4}{C V^{2} /
2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 22.
(a) Obtain the expression for the potential due to an
electric dipole of dipole moment p at a point ‘x’ on the axial line.
(b) Two
identical capacitors of plate dimensions l × b and plate separation d have
dielectric slabs filled In between the space of the plates as shown In the
figures.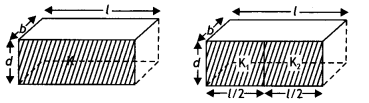
Obtain the relation between the dielectric constants K, K1, and
K2. (CBSE Al 2013C)
Answer:
(a) Consider an electric dipole of
length 2a and having charges + q and — q. Let us find the potential on the axial
Une at point P at a distance OP = x from the center of the dipole.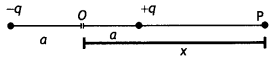
Now potential at point P is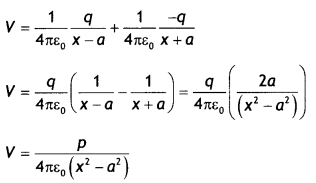
(b) When there is no dieLectnc then
C = \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} l
b}{d}\)
For the first capacitor
C’ = \(\frac{K \varepsilon_{0} l b}{d}\) = KC
The second case is a case of two capacitors connected in paralleL,
therefore
C1 = \(\frac{K_{1} \varepsilon_{0} l b}{2 d}\) and
C2 = \(\frac{K_{2} \varepsilon_{0} l b}{2 d}\)
These two are connected in parallel, therefore we have
C” = C1
+ C2 = \(\frac{K_{1} \varepsilon_{0} l b}{2 d}\) + \(\frac{K_{2}
\varepsilon_{0} l b}{2 d}\)
= C\(\left(\frac{K_{1}+K_{2}}{2}\right)\)
If the capacitance in each case be same, then C’ = C”
Hence K= \(\left(\frac{K_{1}+K_{2}}{2}\right)\)
Question 23.
(a) Explain using suitable diagrams the difference in the
behavior of a
(i) conductor:
Answer:
The diagram is as shown.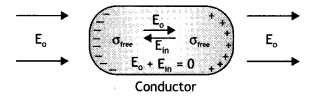
When a conductor is placed in an external electric field, the free charge
carriers move and charge distribution in the conductor adjusts itself in such a
way that the electric field due to induced charges opposes the external field
within the conductor. This happens until in the static situation, the two fields
cancel each other and the net electrostatic field in the conductor is zero.
(ii) dielectric In the presence of the external electric field. Define the
term polarisation of a dielectric and write its relation with
susceptibility.
Answer: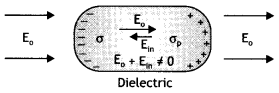
In a dielectric, this free movement of charges is not possible. It turns out
that the external field induces dipole moment by stretching or re-orienting
molecules of the dielectric. The collective effect of all the molecular dipole
moments is that the net charges on the surface of the dielectric produce a field
that opposes the external field. However, the opposing field so induced does not
exactly cancel the external field. It only reduces it. The extent of the effect
depends on the nature of the dielectric.
Dielectric polarization is defined as the dipole moment per unit volume of a dielectric. It is related to susceptibility as P = χeε0\(\vec{E}\)
(b) A thin metallic spherical shell of radius R carries a charge Q on its
surface. A point charge is placed at its center C and another charge +2Q.
outside the shell, at a distance r from the center as shown in the figure. Find
(i) the force on the charge at the center of the shell and at the point A
and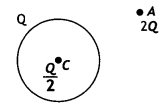
Answer:
(i) F = \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \frac{Q^{2}}{2 R^{2}}\)
and
F = \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \frac{(Q+Q / 2) \times 2
Q}{r^{2}}\)
(ii) the electric flux through the shell. (CBSE Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Flux = \(\frac{Q}{2 \varepsilon_{0}}\)
Question 24.
(a) Define the SI unit of capacitance.
Answer:
The
capacity of a capacitor is said to be one farad when a charge of 1 coulomb is
required to raise the potential difference by 1 volt.
(b) Obtain the expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate
capacitor.
Answer:
Let Q. be the charge on the capacitor, and o be the
uniform surface charge density on each plate as shown in the figure.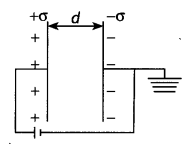
d = distance between plates of the capacitor.
Therefore by Gauss’ theorem, the electric field between the plates of the
capacitor is given by
E =
\(\frac{\sigma}{\varepsilon_{0}}=\frac{Q}{\varepsilon_{0} A}\)
The field is uniform, so the potential difference between the two plates
is
V = Ed = \(\frac{1}{\varepsilon_{0}} \frac{Q d}{A}\)
Therefore, by the definition of capacitance we have
C =
\(\frac{Q}{V}=\frac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d}\)
This gives the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor.
(c) Derive the expression of the effective capacitance of a series
combination of n capacitance (CBSE Delhi 2016C)
Answer:
Capacitors in
series. Capacitors are said to be connected in series if the second plate of one
capacitor is connected to the first plate of the next and so on as shown in the
figure.
Resultant capacitance will be
\(\frac{1}{C}=\frac{1}{C_{1}}+\frac{1}{C_{2}}+\ldots \ldots \ldots
\ldots=+\frac{1}{C_{n}}\)
Question 25.
A charge Q is distributed over the surfaces of two concentric
hollow spheres of radii r and R (R >> r), such that their surface charge
densities are equal. Derive the expression for the potential at the common
center.
Or
Three concentric metallic shells A, B, and C of radii a, b, and
c (a <b < C) have surface charge densities +a, -a, and + o respectively as
shown. Obtain the expressions for the potential of three shells A, B, and C. If
shells A and C are at the same potential, obtain the relation between a, b and
c. (CBSE Al 2019)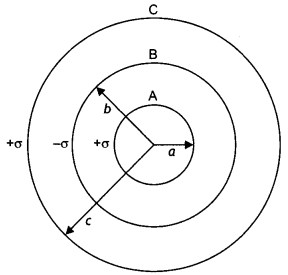
Answer:
Let the charges on the spheres be q, and q2 such that
Q=q1 + q2
= 4πσ(r² + R²)
Or
σ = \(\frac{Q}{4
\pi\left(r^{2}+R^{2}\right)}\)
Now potential at the common centre V=V1 + V2
V =
\(\frac{1}{4 \pi
\varepsilon_{0}}\left(\frac{q_{1}}{r}+\frac{q_{2}}{R}\right)\)
= \(\frac{1}{4
\pi \varepsilon_{0}}\left(\frac{4 \pi r^{2} \sigma}{r}+\frac{4 \pi R^{2}
\sigma}{R}\right)\)
V = \(\frac{(r+R) \sigma}{\varepsilon_{0}}\)
Substituting for o, we have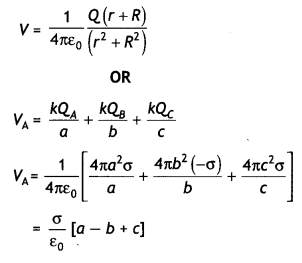
Numerical Problems :
Formulae for solving numerical problems
- V = \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \frac{q}{r}\) electric potential at a point.
- Q = CV for a capacitor.
- C = 4πε0R for a spherical conductor.
- C =\(\frac{Q}{V}=\frac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d}\) capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with air as dielectric.
- C = \(\frac{K \varepsilon_{0} A}{d}\) capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with a dielectric.
- For capacitors in senes
\(\frac{1}{C_{s}}=\frac{1}{C_{1}}+\frac{1}{C_{2}}\) and for capacitors in
parallel Cp = C1 + C2
- U = \(\frac{1}{2} \frac{Q^{2}}{c}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)CV2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\)QV Energy stored in a capacitor.
- Energy density u = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
ε0E2
- Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with a conducting slab of thickness t between plates is C = \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d-t}\)
- Capacitance of a capacitor with dielectric slab of thickness t << d , C = \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d+t\left(\frac{1}{K}-1\right)}\)
- Common potential V = \(\frac{C_{1} V_{1}+C_{2} V_{2}}{C_{1}+C_{2}}\)
- Loss of energy when two conductors are combined, U1 – U2 = \(\frac{C_{1} C_{2}}{2\left(C_{1}+C_{2}\right)}\left(V_{1}-V_{2}\right)^{2}\)
- If n small drops each having a charge Q, capacitance C, and potential V coalesce to form a big drop, then
- The charge on the big drop = nQ
- The capacitance of the big drop = n1/3 C
- Potential of the big drop = n2/3 V
- The potential energy of the big drop = n5/3 U
Question 1.
Electric field intensity at point B due to a point charge Q
kept at point A is 24 N C-1 and the electric potential at point B due
– to the same charge is 12 J C-1. Calculate the distance AB and also
the magnitude of the charge Q.
Answer:
Given E = 24 N C-1 , V =
12 J C-1 , r = ? and Q = ?
Using the relation
E = \(\frac { V }{ r }\)
Or
\(\frac { V }{ E }\)
= \(\frac { 12 }{ 24 }\) = 0.5 m
Also V = \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \frac{Q}{r}\)
Therefore 12 = 9 × 109 × \(\frac { Q }{ 0.5 }\) , solving for Q
we have Q = 6.67 × 10-10C
Question 2.
A capacitor of unknown capacitance is connected across a
battery of V volts. The charge stored in it is 360 μC. When the potential across
the capacitor is reduced by 120 V, the charge stored in it becomes 120 μC.
Calculate:
(i) The potential V and the unknown capacitance C.
(ii) What
will be the charge stored in the capacitor, if the voltage applied had increased
by 120 V? (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Given Q1 = 360 μC,
Q2 = 120 μC,
V2 = (V- 120) volt, V1 = V
(i) We know that C = \(\frac { Q }{ V }\)
Since capacitance is same, we have
\(\frac{Q_{1}}{V_{1}}=\frac{Q_{2}}{V_{2}}\)
Or
\(\frac{360 \times
10^{-6}}{V}=\frac{120 \times 10^{-6}}{V-120}\)
Solving for V we have V= 180 volt
Also C = Q1/ V1 = 360 × 10-6 / 180 = 2 × 10-6 C = 2 pF
(ii) V= 180 + 120 = 300 V
Therefore Q = CV = 2 x 10-5 × 300 =
600 x 10-6 = 600 pC
Question 3.
Two identical capacitors of 12 pF each are connected in series
across a 50 V battery. Calculate the electrostatic energy stored in the
combination. If these were connected in parallel across the same battery, find
out the value of the energy stored in this combination. (CBSE Al 2019)
Answer:
Given C = 12 pF = 12 × 10-12 F, V= 50 V,
In series
Cs = \(\frac{C_{1} C_{2}}{C_{1}+C_{2}}=\frac{12 \times 12}{12+12}\) =
6 pF
Hence energy stored
Us = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
CsV2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 6 × 10-12×
(50)2
Us = 7.5 × 10-9 J
In parallel
CP = C1 + C2 = 12 + 12 = 24
pF
UP = \(\frac{1}{2}\) CPV2 =
\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 24 × 10-12 × (50)2
UP = 3
× 10-8 J
Question 4.
The figure shows a network of three capacitors C1 =
2 μF; C2 = 6 μF and C3 = 3 μF connected across a battery
of 10 V. If a charge of 6 μC is acquired by the capacitor C3,
calculate the charge acquired by C1 (CBSE Al 2019)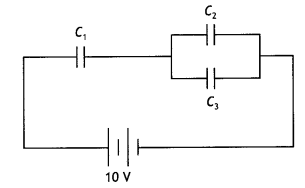
Answer:
Capacitors C2 and C3 are connected in parallel,
therefore, the net capacitance of the combination.
C23 = (6 + 3) =
9 μF
Let V1, be the potential across C1 and V2 be the potential across
C23
Now C1 = Q/V, or V1 = Q/C1 =
Q/2
Also V2 = Q/9
But V = V1 + V2
Solving for Q we get
Q= 16.4 μC
Question 5.
(a) Find equivalent capacitance between A and B in the
combination given below. Each capacitor is of 2 μF capacitance.
Answer:
This can be redrawn as
Like C2, C3 and C4 are in parallel,
C234 = C2 + C3 + C4 = 6 μF
Further, C1, C234 and C5 are in series
\(\frac{1}{C_{\text {net
}}}=\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{6}+\frac{1}{2}=\frac{3+1+3}{6}=\frac{7}{6}\)
\(C_{\text {net }}=\frac{6}{7}\)μF
(b) If a DC source of 7 V is connected across AB, how much charge is drawn
from the source and what is the energy stored in the network? (CBSE Delhi
2017)
Answer:
∴ Cnet = \(\frac { 6 }{ 7 }\) μF ,
q = Cnet V = \(\frac { 6 }{ 7 }\) × 10-6 × 7 = 10-6C
∴ Energy stored = \(\frac{1}{2}\)qV
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 6 × 10-6 × 7 = 21 × 10-6J
Question 6.
Two identical capacitors of 12 pF each are connected in series
across a battery of 50 V. How much electrostatic energy is stored in the
combination? If these were connected in parallel across the same battery, how
much energy will be stored in the combination now? Also, find the charge drawn
from the battery in each case. (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) Net
capacitance Cnet = \(\frac{C_{1} C_{2}}{C_{1}+C_{2}}\)
=
\(\frac{12 \times 12}{12+12}\)pF = 6 pF
∴ Energy stored = \(\frac{1}{2}\)Cnet V2
=
\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 6 × 10-12 × (50)2 = 75 ×
10-10J
q = Chargedrawn = Cnet V=6 × 10-12 ×
50 = 3 × 10-10 C
(ii) Cnet=12 + 12 = 24pF
∴ Energy stored = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Cnet V2
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 24 × 10-12 ×
(50)2
= 3 × 10-8J
Charge drawn, q = CnetV
= 24 × 10-12 × 50
= 1200
× 10-12
= 12 × 10-10 C
Question 7.
In the following arrangement of capacitors, the energy stored
in the 6 μF capacitor is E. Find the value of the following. (Foreign 2016)
(a) Energy stored in 12 pF capacitor.
(b) Energy stored in 3 pF
capacitor.
(c) Total energy drawn from the battery.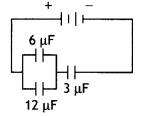
(a) Energy stored in 6 μ capacitor is E. Capacitors 6 μF and 12 μF are connected
in parallel.
So, the voltage across 6 μF capacitor
= voltage across 12 μF
capacitor
= voltage across 12 μF capacitor
= V (say)
As E = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 6 × V²
∴ V = \(\sqrt{\frac{E}{3}}\)
Similarly energy U’ stored in 12 pF capacitor
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 12 ×
V²
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) ×12 × \(\frac{E}{3}\) = 2E
U’ = 2 E
(b) Equivalent capacitance of 6 µF and 12 µF is 6 + 12 = 18 µF
Charge on 18 µF and 3 µF is same as they are in series as they are in
series
∴ Q = CV= 18 × V
∴ Energy in 3 µF capacitor
U” = \(\frac{1}{2} \frac{Q^{2}}{C}=\frac{1}{2}
\frac{(18 V)^{2}}{3}\)
U” = \(\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{18 \times 18}{3} \frac{E}{3}\)
U” =
18E
(c) Total energy drawn from battery U = E + 2E + 18E = 21E
Question 8.
Two parallel plate capacitors X and Y have the same area of
plates and the same separation between them, X has air between the plates, while
Y contains a dielectric medium of εr = 4.
(a) Calculate the
capacitance of each capacitor if the equivalent capacitance of the combination
is 4 μF.
CX = \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d}\) = C(say)
CY=
4\(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d}\) = 4C
EquivaLent capacitance = 4 μF
Ceq = \(\frac{C_{X}
C_{Y}}{C_{X}+C_{Y}}\) = 4
= \(\frac{C \times 4 C}{C+4 C}\)
Or
=
\(\frac{4C}{5}\) = 4
C = 5 μF
∴ CX = C = 5 μF and
CY = 4C = 20 μF
(b) Total charge, q = Ceq V = 4 × 12 = 48μC
CX and
CY are in series. Hence, charge on both is 48 μC each.
∴ The potential difference across CX,
VX =
\(\frac{q}{C_{X}}=\frac{48}{5}\) = 9.6 V0lt
The potential difference across CY,
VY =
\(\frac{q}{C_{Y}}=\frac{48}{20}\) = 2.4 Volt
(c) UX=\(\frac{1}{2}\)CXVX² ; UY = \(\frac{1}{2}\)CYVy²
∴ \(\frac{U_{x}}{U_{Y}}=\frac{5 \times(9.6)^{2}}{20 \times(2.4)^{2}}\)
=
\(\frac{1}{4} \times \frac{9.6 \times 9.6}{2.4 \times 2.4}\) = 4
\(\frac{U_{x}}{U_{r}}\) = 4
Question 9.
Find the ratio of the potential differences that must be
applied across the parallel and series combination of two capacitors
C1 and C2 with their capacitances in the ratio 1:2 so that
the energy stored in these two cases becomes the same. (CBSE Al 2016)
Answer:
(i) Let C1 = C, ∴ C2 = 2C
For series
combination equivalent capacitance is
\(C_{s}=\frac{C_{1} \times
C_{2}}{C_{1}+C_{2}}=\frac{C \times 2 C}{3 C}=\frac{2}{3} C\) …. (1)
and
energy stored,
\(U_{\mathrm{s}}=\frac{1}{2} C_{s}
V_{\mathrm{s}}^{2}=\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{2}{3} C V_{\mathrm{s}}^{2}\) ….
(2)
For parallel combination equivalent capacitance
Cp = C + 2C =
3C ….(3)
and energy stored
∴ \(U_{D}=\frac{1}{2} 3 C \times V_{p}^{2}\)
…(4)
But Us = Up [Given]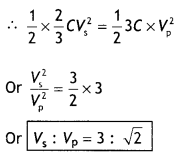
Question 10.
Calculate the potential difference and the energy stored in
the capacitor C2 in the circuit shown in the figure. Given potential
at A is 90 V, C1 = 20 μF, C2 = 30 μF, and C3=
15 μF. (CBSEAI 2015)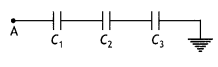
Answer: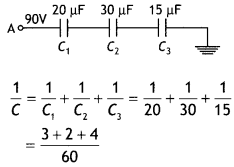
C = \(\frac{60}{9}\) μF = \(\frac{20}{3}\) μF
The potential at A = 90V
∴ Charge on each capacitor
Q = C x V= \(\frac{20}{3}\) x 90 =600 μC.
∴ Charge on C2 = 600 μC
∴ V2 = \(\frac{Q}{C_{2}}=\frac{600}{30}\) ; V2 = 20 V
Energy stored in C2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\)C2V2²
U2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 3o × 10-6 × 20 × 20
U2
= 6000 × 10-6J = 6 × 10-3J