Communication system
Class 12th Physics Chapter Important Questions
Class 12 Physics Chapter 15 Important Extra Questions Communication Systems
Very Short Answer
Question 1.
What is sky wave propagation? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Propagation of frequencies less than 40 MHz using the reflecting property of
ionosphere is called Sky wave propagation.
Question 2.
What is ground wave propagation? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
A
radiowave that can travel directly from one point to another following the
surface of the earth is called a ground wave propagation. Ground wave
propagation is possible only when the transmitting and receiving antenna are
close to the surface of the earth.
Question 3.
What is space wave propagation? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
When the signal travels in a straight line from the transmitting antenna to the
receiving antenna with frequencies more than 40 MHz, it is called space-wave
propagation. Space waves are used for line of sight (LOS) communication as well
as satellite communication.
Question 4.
What is the function of a repeater used in communication
system? (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The function of a repeater in
communication system is to extend the range of communication.
Question 5.
What does the term ‘attenuation’ used in communication system
mean? (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Attenuation used in communication
system means loss of strength of a signal during its propagation through the
communication channel.
Question 6.
What is the function of a transducer used in a communication
system? (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Transducer : Any device/arrangement
that converts one form of energy into another is called a transducer.
Question 7.
The carrier wave is given by C(t) = 2 sin (8πt) volt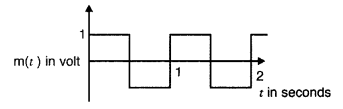
The modulating signal is a square wave as shown. Find
modulation index. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:![]()
[Hint: Comparing the general expression for a wave C(f) = a
sin ωt with the expression given here, we get the value of amplitude of carrier
wave (Ac) = 2 volts.
In the diagram shown here for modulating
signal, amplitude of modulating signal (Am) is 1 volt]
Question 8.
The given figure shows the block diagram of a generalized
communication system. Identify the element labelled ‘X’ and write its function.
(Delhi 2012)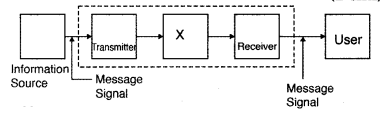
Answer:
X = Channel
Function: The physical path between the transmitter and reciver is known as the communication channel. It comprises of the wire links, wireless and optic fibres.
Question 9.
The carrier wave is represented by C(t) = 5 sin (10πt)
volt.
A modulating signal is a square wave as shown. Determine modulation
index. (Delhi 2012)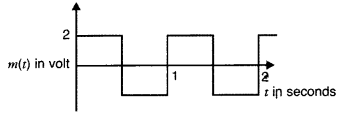
Answer:
Similar to Q. 7, Page 335 = 0.4
Question 10.
Tire carrier wave of a signal is given by C(t) = 3 sin (8πt)
volt.
The modulating signal is a square wave as shown. Find its modulation
index. (Delhi 2012)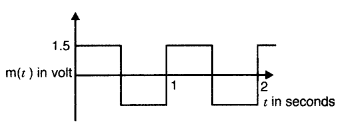
Answer:
Similar to Q. 7, Page 335![]()
Question 11.
How does the effective power radiated from a linear antenna
depend on the wavelength of the signal to be transmitted? (Comptt. Delhi
2012)
Answer:
Effective power radiated decreases with an increase in
wavelength, i.e.,![]()
Question 12.
Draw a block diagram of a detector for amplitude modulated
signal. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer: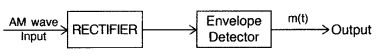
Question 13.
What is the meaning of the term ‘attenuation’ used in
communication system? (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
‘Attenuation’ means the
loss of strength of a signal while propagating through the medium.
Question 14.
Give one example of point-to-point communication mode.
(Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Example of point-to-point communication
mode : Telephone
Question 15.
Give one example of broadcast mode of communication. (Comptt.
All India 2012)
Answer:
- Radio
- Television (any one)
Question 16.
Define the term ‘modulation index’ in communication system.
(Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Modulation index is defined as the ratio
of amplitude of modulating signal to the amplitude of carrier wave,
i.e.,![]()
Question 17.
What does the term ‘demodulation’ in communication system
mean? (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Demodulation is the process of
retrieval of information from the carrrier wave at the receiver end.
Question 18.
Distinguish between ‘point-to-point’ and ‘broadcast’ modes of
communication. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
In a point-to-point
communication, the communication takes place over a single link between
transmitter and receiver, whereas, in the broadcast mode, there are a large
number of receivers corresponding to a single transmitter.
Question 19.
How are side bands produced? (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Side
bands are produced due to superposition of carrier waves of frequencey cof over
modulating/ Audio signal of frequency com; with the frequencies (ωc ±
ωm).
Question 20.
Which basic mode of communication is used for telephonic
communication? (All India 2012)
Answer:
Point to point communication mode
is used for telephonic communication.
Question 21.
Why is the frequency of outgoing and incoming signals
different in a mobile phone? (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
To avoid
overlapping of signals.
Question 22.
Distinguish between amplitude modulation and frequency
modulation. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
The amplitude modulation
provides a larger coverage area, while frequency modulation provides a better
quality transmission.
Question 23.
Write two factors which justify the need of modulating a low
frequency signal into high frequencies before transmission. (All India 2012)
Answer:
Need of modulating a low frequency signal :![]()
(ii) Transmission of audio frequency electrical signals need
long impracticable antenna.
(iii) To avoid mixing-up of signals from
different transmitters.
Question 24.
Name the essential, components of a communication system.
(All India 2016)
Answer:
Transmitter, medium (channel) and receiver are
three essential components of communication system.
Question 25.
Write the full forms of the terms :
(i) LAN
(ii) WWW
(Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) Local Area Networking
(ii) World Wide
Web
Question 26.
Name the two basic modes of communication system. (Comptt.
All India 2017)
Answer:
- Point to Point Communication and
- Broadcast are the two basic modes of communication.
Question 27.
Define modulation index. Why is it generally kept less than
one? (Comptt. All India 2017)
Answer:
Modulation index is defined as the
ratio of amplitude of modulating signal (Am) to amplitude of carrier
wave (Ac)![]()
It is kept less than one to avoid distortion
Question 28.
Why is sky wave propagation of signals restricted to a
frequency of 30 MHz? (Comptt. All India 2017)
Answer:
Sky wave propagation
of signals is restricted to a frequency of 30 MHz, because waves of frequency
greater than 30 MHz get penetrated through the ionosphere and thus they do not
get reflected by it.
Question 29.
State two reasons why high frequency carrier waves are needed
in transmitting a message signal. (Comptt. All India 2017)
Answer:
For the
following reasons, high frequency carrier waves are needed in transmitting a
message signal :
- Length of transmitting antenna is short.
- Power radiated is more.
- Mixing of signals can be avoided.
Question 30.
A transmitting antenna at the top of a tower has a height of
36 m and the height of the receiving antenna is 49 m. What is maximum distance
between them, for satisfactory communication in the LOS mode? (Radius of earth =
6400 km) (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
dM = Maximum line of sight
distance between the transmitting and receiving antennas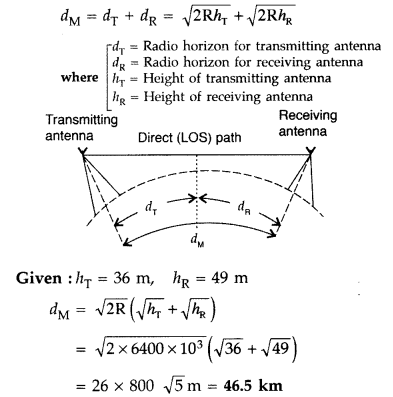
Question 31.
Draw a block diagram of a simple amplitude modulation.
Explain briefly how amplitude modulation is achieved. (All India 2017)
Answer:
Production of Amplitude Modulated wave : A conceptually simple method
to produce Am wave is shown in the following block diagram :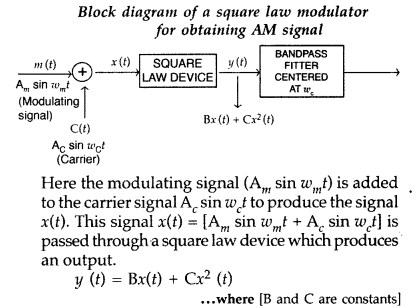
This signal is passsed through a band pass filter which
rejects dc. The output of the band pass filter is therefore, Am
wave
Question 32.
By what percentage will the transmission range of a TV tower
be affected when the height of the tower is increased by 21%? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Range of a TV tower of height,
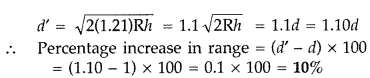
Question 33.
Why are high frequency carrier waves used for transmission?
(Delhi 2008)
Answer:
- Radiation loss at low frequencies is more.
- Length of receiver antenna becomes very high for low frequency. So we use high frequency carrier waves for transmission.
Question 34.
What is meant by term ‘modulation’? Draw a block diagram of a
simple modulator for obtaining an AM signal. (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
The
process of placement or mounting of a low frequency signal over the high
frequency signal is known as modulation.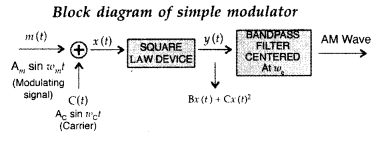
Question 35.
Answer the following questions :
(a) Optical and radio
telescopes are built on the ground while X-ray astronomy is possible only from
satellites orbiting the Earth. Why?
(b) The small ozone layer on top of
the
stratosphere is crucial for human survival. Why? (All India 2017)
Answer:
(a) The earth’s atmosphere is transparent to visible light and
radio-waves but it absorbs X-rays. X-ray astronomy is possible only from
satellites orbitting the earth. These satellites orbit at a height of 36,000 km,
where the atmosphere is very thin and X- rays are not absorbed.
(b) Ozone layer absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the Sun and prevents it from reaching the earth and thus avoids causing damage to life.
Question 36.
Write the function of
(i) Transducer and
(ii) Repeater
in the context of communication system. (All India 2017)
Answer:
(i)
Transducer : A transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into
another.
(ii) Repeater : A repeater is a combination of receiver and
transmitter used for extending the range of communication system.
Question 37.
Write two factors justifying the need of modulation for
transmission of a signal. (All India 2017)
Answer:
- Length of receiving antenna (a wavelength) becomes practicable with larger frequency carrier wave used in the process of modulation.
- With larger frequency or reduced wavelength, the power radiated will be larger from the transmitter and the loss will be less.
Question 38.
Explain the function of a repeater in a communication system.
(Delhi 2017)
Answer:
A repeater is a combination of a receiver and a
transmitter. A repeater picks up the signal from the transmitter, amplifies and
retransmits it to the receiver sometimes with a change in carrier frequency.
Repeaters are used to extend the range of a communication system.
Question 39.
Explain the function of a repeater in a communication system.
(Delhi 2017)
Answer:
A repeater is a combination of a receiver and a
transmitter. A repeater picks up the signal from the transmitter, amplifies and
retransmits it to the receiver sometimes with a change in carrier frequency.
Repeaters are used to extend the range of a communication system.
Question 40.
What is the range of frequencies used for TV transmission?
What is common between these waves and light waves? (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Television frequencies lie in the range of 54-890 MHz which cannot be reflected
by ionosphere. Both waves are electromagnetic waves and can travel through
vaccum with same speed.
Question 41.
What is the range of frequencies used in satellite
communication? What is common between these waves and light waves? (Delhi
2017)
Answer:
Range of frequencies used in satellite communication is
:
uplink = 5.925 to 6.425 GHz and downlink = 3.7 to 4.2 GHz.
Both the waves uplink and downlink used in satellite communication and light waves are electromagnetic waves and can travel through vaccum with the same speed.
Question 42.
Write two factors justifying the need of modulating a
signal.
A carrier wave of peak voltage 12 V is used to transmit a message
signal. What should be the peak voltage of the modulating signal in order to
have a modulation index of 75%? (All India 2017)
Answer:
(a) A signal
requires modulation because :
(i) a modulated signal being of high frequency
can be transmitted with the help of an antenna of reasonable size.
(ii) a
modulated signal can be transmitted with more power because power radiated is
proportional to \(\left(\frac{1}{\lambda^{2}}\right)\)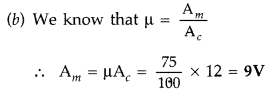
Question 43.
(i) Define modulation index.
(ii) Why is the amplitude of
modulating signal kept less than the amplitude of carrier wave? (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) Modulation index : The modulation index is defined as the ratio
of the change in the amplitude of the carrier wave to the amplitude of the
original carrier wave.![]()
(ii) The amplitude of modulating signal is kept less than the
amplitude of carrier wave to avoid distortion.
Question 44.
What is sky wave communication? Why is this mode of
propagation restricted to the frequencies only upto few MHz? (All India
2017)
Answer:
Sky wave communication : A radiowave directed towards the
sky and reflected by the ionosphere . towards the desired location of the earth
is called a sky wave. The ionospheric layers act as a reflector for a certain
range of frequencies. Radio waves of frequencies between 3 MHz to 30 MHz can be
reflected by the ionosphere. This mode of propagation is used by short wave
broadcast service.
The propagation is restricted to the electro-magnetic waves of frequencies greater than 30 MHz because they penetrate the ionosphere and escape.
Question 45.
What is ground wave communication? On what factors does the
maximum range of propagation in this mode depend? (All India 2017)
Answer:
Ground wave propagation : A radio wave that can travel directly from
one point to another following the surface of the earth is called a ground wave.
Groud wave propagation is possible only when the transmitting and receiving
antenna are close to the surface of the earth.
The maximum range of ground
wave propagation depends on two factors :
- The frequency of the transmitted wave, and
- The power of the transmitter.
Question 46.
What is space wave communication? Write the range of
frequencies suitable for space wave communication? (All India 2017)
Answer:
When the signal travels directly from the transmitting antenna to the
receiving antenna with frequencies more than 30 MHz, is called space wave
communitaion.
High frequencies (above 40 MHz) can be transmitted through
space wave propagation.
Question 47.
Distinguish between ‘Analog and Digital signals’. (Delhi
2017)
Answer:
Analog signal: A signal v- in which current or voltage
varies continuously with time is called analog signal.
Example : Sinosidal
wave
Digital signal : A signal in which current or voltage can
take only two discrete values, is called a digital signal.
A digital signal
can take only two values 1 and 0 which are labelled as high and low values.
Question 48.
Mention the function of any two of the following used in
communication system:
(i) Transducer
(ii) Repeater
(iii)
Transmitter
(iv) Bandpass Filter (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) Transducer.
It converts energy from one form to another.
(ii) Repeater. It picks up a
signal from the transmitter, amplifiers and retransmits it to the receiver,
sometimes with a change of carrier frequency.
(iii) Transmitter. It is a device which processes a message
signal into a form suitable for transmission and then transmits it to the
receiving end through a transmission channel.
(iv) Bandpass filter. A
bandpass filter blocks lower and higher frequencies and allows only a band of
frequencies to pass through.
Question 49.
In the given block diagram of a receiver, identify the boxes
labelled as X and Y and write their functions. (All India 2017)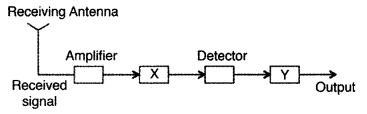
Answer:
X ➝ IF (Intermediate frequency) stage
Y ➝
Amplifier/Power amplifier
Function of IF Stage : IF stage represents
intermediate frequency stage preceding the detection. The carrier frequency is
usually changed to a lower frequency by the IF stage.
Function of Amplifier :
It is to amplify the signal i.e. to increase the strength of the input
signal.
Question 50.
A carrier wave of peak voltage 12 V is used to transmit a
message signal. Calculate the peak voltage of the modulating signal in order to
have a modulation index of 75%.(Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer: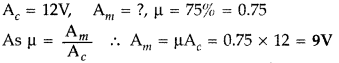
Question 51.
(a) Identify the boxes, ‘P’ and ‘Q’ in the block diagram of a
receiver shown in the figure.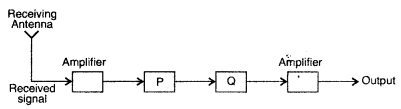
(b) Write the functions of the blocks ‘P’ and ‘Q’. (Comptt.
Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(a) ‘P’ is IF (Intermediate frequency) Stage.
‘Q’
is Detector.
(b) IF stage represents intermediate frequency stage preceding the detection, the carrier frequency is usually changed to a lower frequency by the IF stage. Detection is the process of recovering the modulating signal from the modulated carrier wave.
Question 52.
A carrier wave of peak voltage 18 V is used to transmit a
message signal. Calculate the peak voltage of the modulating signal in order to
have a modulation index of 50%.(Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer: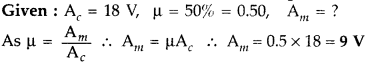
Question 53.
A carrier wave of peak voltage 15 V is used to transmit a
message signal. Calculate the peak voltage of the modulating signal in order to
have a modulation index of 60%.(Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer: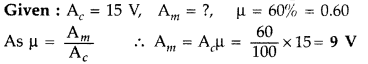
Question 54.
Which mode of wave propagation is suitable for television
broadcast and satellite communication, and why? Draw a suitable diagram
depicting this mode of propagation of wave. (Comptt. All India 2017)
Answer:
Space wave propagation is suitable for television broadcast and
satellite communication.
Reason: These waves, having frequency > 40 MHz,
are not likely to be reflected back by the ionosphere.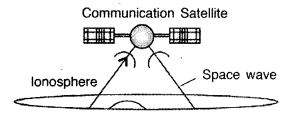
Question 55.
Block diagram of a receiver is shown in the figure :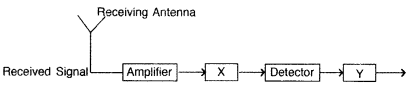
(a) Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
(b) Write their functions (Delhi
2013)
Answer:
X is IF stage (intermediate frequency stage).
Function:
The carrier frequency is changed to a lower frequency by intermediate frequency
(IF) stage preceding the detection. .
Y is Amplifier.
Function : To
strengthen the detected signal, it is fed to an amplifier.
Question 56.
In the block diagram of a simple modulator for obtaining an
AM signal, shown in the figure, identify the boxes A and B. Write their
functions. (All India 2013)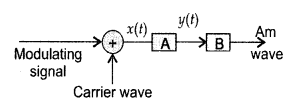
Answer:
Box A is square law device while Box B is band
pass filter centred at ωc.
Function of (A) square law device :
It is a non-linear device which gives an output in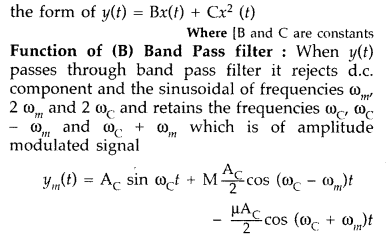
Question 57.
A message signal of frequency 10 kHz and peak voltage 10 V is
used to modulate a carrier of frequency 1 MHz and peak voltage 20 V.
Determine
(i) the modulation index,
(ii) the side bands produced. (Comptt.
Delhi 2013)
Answer: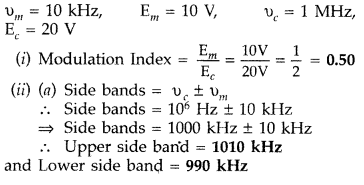
Question 58.
Explain briefly how ground waves are propagated? Why can’t
this mode be used for long distance using high frequency?
(Comptt. All India
2013)
Answer:
When the radiowaves from the transmission antenna propagate
along surface of the earth, so as to reach the receiving antena, these are known
as ground waves propagation.
Ground waves are rapidly attenuated due to
scattering by the curved surface of earth. It is why these cannot be used for
long distances.
Question 59.
Explain briefly how sky waves are propagated. Why are sky
waves not used for transmission of TV signals? (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
Sky wave propagation. When the radio-waves from the transmitting
antenna reach the receiving antenna after reflection in the ionosphere, the wave
propaga-tion is called sky wave propagation.
Sky waves are not used in transmitting TV signals because of high frequency (> 80 MHz). These waves are not reflected back by the ionosphere and . penetrate into outer space.
Question 60.
Describe briefly the space wave mode of propagation. Name one
transmission which uses space wave mode. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
Space wave propagation. When the radio-waves from the transmitting antenna reach
the receiving antenna either directly or after reflection from the ground or in
the troposphere, the wave propagation is called space wave propagation.
In practice, direct wave mode is more dominant. However, it is limited to the
so called ‘line-of-sight’ transmission distances and curvature of earth as well
as height of antenna restrict the extent of coverage.
TV transmission uses
the space wave mode.
Question 61.
Write the functions of the following in communication systems
:
(i) Transducer
(ii) Repeater (All India 2014)
Answer:
(i)
Transducer : A transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into
another.
(ii) Repeater : A repeater is a combination of receiver and
transmitter used for extending the range of communication system.
Question 62.
Write the functions of the following in communication systems
:
(i) Transmitter
(ii) Modulator (All India 2014)
Answer:
(i)
Transmitter. A set-up that transmits the message to the receiver through a
communication channel.
(ii) Modulator. A set-up which makes necessary
modification of message signal to make it suitable for transmission to long
distances through carrier waves.
Question 63.
Write the functions of the following in communication systems
:
(i) Receiver
(ii) Demodulator (All India 2014)
Answer:
(i)
Receiver. It extracts the desired message signals from the received signals at
the channel output.
(ii) Demodulator. It is the set-up which makes the
process of retrival of information from the carrier wave at the receiver. It is
the reverse of ‘modulator’
Question 64.
Explain the terms
(i) Attenuation and
(ii) Demodulation
used in communication system. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(i) The loss of
strength of a signal while propagating through a medium is called
‘Attenuation’.
(ii) The process of separation of information signal from
modulated wave at the receving end is called ‘Demodulation’.
Question 65.
Define modulation index. Why is it kept low? What is the role
of a bandpass filter? (All India 2016)
Answer:
(i) Modulation index is the
ratio of the amplitude of modulating signal to that of carrier wave and is given
by \(\mu=\frac{A_{m}}{A_{c}}\)
(ii) It is kept low to avoid distortion.
(iii) Role of bandpass filter is that it rejects low and high frequencies and
allows a band of frequencies to pass through.
Question 66.
Distinguish between ‘Sky wave’ and ‘Space wave’ modes of
propagation in a communication system. (Comptt. Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Distinction between ‘Sky Wave’ and ‘Space Wave’
| S.No. | Sky Wave | Space Wave |
| 1. Range of frequencies
|
Restricted upto a few MHz frequency (30 to 40 MHz).
|
Can take place (even) beyond 40 MHz frequency.
|
| 2. Mode of propagation
|
Waves are reflected back from ionosphere.
|
Space waves travel in a straight line, either direct
from transmitting antenna to receiving antenna or through satellite.
|
Question 67.
Which basic mode of communication is used in satellite
communication? What type of wave propagation is used in this mode? Write, giving
reason, the frequency range used in this mode of propagation. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
- Broadcast/point to point is the mode of communication used in satellite communication.
- Space wave propagation is used in this mode.
- The frequency range is above 40 MHz, because e.m. waves of frequency above 40 MHz, are not reflected back by the ionosphere and penetrate through the ionosphere.
Question 68.
Distinguish between a transducer and a repeater. (Delhi
2017)
Answer:
Transducer : A device which converts one form of energy into
another.
Repeater : A combination of receiver and transmitter. It picks
signals from a transmitter; amplifies and retransmits them.
Question 69.
(i) What is the line of sight communication?
(ii) Why is
it not possible to use sky waves for transmission of TV signals? tJpto what
distance can a signal be transmitted using an antenna of height ‘h’ (Delhi
2017)
Answer:
(i) Communication, using waves which travels in straight
line from transmitting antenna to receiving antenna, constitutes line of sight
communication.
(ii) (a) We cannot use sky waves because T.V. . signal waves
are not reflected back by the ionosphere.
(b) d = \(\sqrt{2 h R}\) (where ‘R’
is the radius of Earth)
Question 70.
State the two points to distinguish between sky wave and
space wave modes of propagation. (Comptt. All India 2017)
Answer:
Distinction between ‘Sky Wave’ and ‘Space Wave’
| S.No. | Sky Wave | Space Wave |
| 1. Range of frequencies
|
Restricted upto a few MHz frequency (30 to 40 MHz).
|
Can take place (even) beyond 40 MHz frequency.
|
| 2. Mode of propagation
|
Waves are reflected back from ionosphere.
|
Space waves travel in a straight line, either direct
from transmitting antenna to receiving antenna or through satellite.
|
Question 71.
Distinguish between point-to-point and broadcast modes of
communication. Give one example for each. (Comptt. All India 2017)
Answer:
Point to point communication takes place between a single transmitter
and a receiver; While in broadcast mode, a large number of receivers can receive
signal from a single transmitter.
Example of point to point mode : telephony
Example of broadcast mode : Radio/TV
Question 72.
flow will you classifi.’ communication systems?
Answer:
Communication systems can be classified based on the nature of source. mode of
communication. type of modulation and nature of channel used.
Question 72.
What are the lips of channels used for transmission?
Answer:
i. Space communication (Broadcasting, microwave mobile etc.)
ii.
Line communication (Two wire, co-axial cables, fiber optical etc.)
Question 73.
What is the length of antenna required to transmit wave of
frequency 40 Hz and 40 MHz?
Answer:
The minimum length of antenna required
is \(\frac {λ}{4} \)
Velocity,c = υλ
λ = \(\frac {c}{υ} \)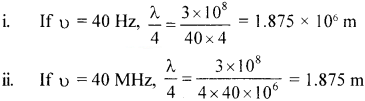
Question 74.
Identify the sound that can travel a longer distance – siren
from a factory or horn of a car. Why?
Answer:
Siren from a factory. High
intensity.
Question 75.
Mention the factors on which power of electromagnetic wave
transmitted depends.
Answer:
The power of electromagnetic wave is related
to the length of antenna and wavelength of the wave.
Power α
\(\left(\frac{l}{\lambda}\right)^{2}\), where l is the length and λ-the
wavelength.
Question 76.
Which range of wave is more reliable of intermixing – shorter
or longer wavelength?
Answer:
Longer wavelength
Question 77.
is there any change in the frequency or phase due to amplitude
modulation?
Answer:
No change of either frequency or phase.
Question 78.
Which physical quantity of wave is varied in AM. FM and
PM?
Answer:
In AM. the physical quantity of carrier that changes is
amplitude.
In FM, the physical quantity of carriers that change is
frequency.
In PM, the physical quantity of carrier that changes is a
phase.
Question 79.
What are the advantages and limitations of AM and FM?
answer:
| Advantages | Limitations | |
| AM | Wireless transmission possible, simple circuit, two-sided bands | Low efficiency, small operating range. noisy receptions, interference-effect. |
| FM | More resistant to noise, a large number of sidebands, carrier frequency high (television broadcast), more economical space wave propagation | Bandwidth wide, circuit more complex, a smaller area of reception |
Question 80.
What is ground wave propagation?
Answer:
Ground wave
follows curvature of the earth and has carrier frequencies up to 2MHz. e.g. AM
radio.
Ground waves progress along the surface of the earth and must be
vertically polarized to prevent short circuiting the electric equipments. A wave
induces currents in the ground over which it passes and thus loses some energy
by absorption. This is made up by energy diffracted downwards from the upper
portion of the wavefront.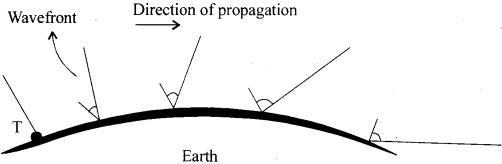
There is another way also by which the ground waves get attenuated. Because of
diffraction, the wavefront gradually tilts over, as shown in the figure. As the
wave propagates over the earth, the tilt increases and this tilt causes greater
short-circuiting of the electric component of the wave. Hence there is a
reduction in the field strength. Eventually, at some distance from the antenna,
the wave gets weakened and dies off. The maximum range of such a transmitter
depends on its frequency and power. The ground wave propagation is effective
only at VLF.
Question 81.
Ground waves are not sustained for long-range communication.
Why?
Answer:
Because of damping by earth surface.
Question 82.
What is the range of frequencies used in ground wave
propagation? Why?
Answer:
VLF. The attenuation of surface waves increases
very rapidly with an increase in frequency.
Question 13.
How can we overcome this limitation?
Answer:
By
changing to space wave communication.
Question 84.
What is the basic requirement of space wave
communication?
Answer:
There should be a transmitter and receiving
antenna.
Question 85.
Why is space communication also known as the line of sight
communication?
Answer:
The transmitting and receiving antenna are on
sight.
Question 86.
Why are repeaters needed in the line of sight
communication?
Answer:
To compensate for the loss of energy during
propagation.
Question 87.
What are the limitations of space wave propagation?
Answer:
This method needs repeaters and a suitable antenna length
(height).
Question 88.
What is skywave communication?
Answer:
Skywave
communication is otherwise called ionospheric communication. In this the
electromagnetic wave of high frequency is directed towards the ionosphere which
reflects the wave back to earth.
Question 89.
Which space transmission technology makes use of total
internal reflection?
Answer:
ionospheric transmission.
Question 90.
is sky wave propagation possible on moon? Why?
Answer:
No. Moon has no ionosphere.
Question 91.
Can all frequencies be transmitted using sky wave
propagation?
Answer:
No. Only frequencies below the critical value.
Question 92.
How does sky wave propagation depend on refractive index of
atmosphere?
Answer:
The refractive index of ionosphere decreases below
that of free space by the change of velocity of electrons in the ionosphere and
the electromagnetic saves undergo total internal reflection.
Question 93.
Through which atmospheric layer. does the propagation take
place in ground. space and sky communications?
Answer:
Ground wave –
Troposphere
Space wave – Troposphere
Sky wave – Ionosphere
Question 94.
Which type of space communication has maximum range of
transmission?
Answer:
Satellite
Question 95.
Compare the principle applied for each type of
communication.
Answer:
Ground wave – Wireless
Space wave – Line of
sight
Skywave – Total internet reflection by the ionosphere.
Question 96.
What is the range of frequency used ¡n each case?
Answer:
Ground wave – <2 MHz
Space wave -> 30 MHz
Skywave -<
10 MHz
Question 97.
Point out the limitations and uses in each case.
Answer:
Ground wave – Damping effect, wireless communication.
Space wave –
Finite curvature of the earth, line of sight
Skywave – Critical frequency,
long-distance coverage
Question 98.
Name the type of channel used in telephone, cable TV, and
high-speed internet connections.
Answer:
Telephone – Two-wire
Cable TV
– Coaxial cable
Internet – Space (satellite) .
Question 99.
Which ¡s the cheapest mode of line communication?
Answer:
Two-wire system
Question 100.
What are the merits and demerits of two wire
communication?
Answer:
Signals can travel kilometres without
amplification, digital and analogue signals can be sent cheap.
Attenuation of
signal, interference etc.
Question 101.
Why twisted wires are preferred?
Answer:
To reduce
interference of electromagnetic radiations.
Question 102.
Under which condition, does maximum power transmission occur
through two wire lines?
Answer:
When the impedance of the detecting device
at the receiver (load) is matched (i.e., equal) to the characteristic impedance
of the two wire system.
Question 103.
What kind of cable is used to connect VC’R to TV?
Answer:
Coaxial
Question 104.
Draw the figure of coaxial cable.
Answer: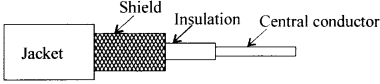
Question 105.
What is the structure of coaxial cable?
Answer:
Coaxial
cables are shielded i.e., outer conductor surrounds the insulated inner wire and
the outer is always grounded.
Question 106.
Which type of material is suitable to use as spacer in
coaxial cable? Why?
Answer:
Solid dielectric material, for insulation.
Question 107.
What are the merits of coaxial cables?
Answer:
These
cables do not suffer from radiation problem and can he used for microwaves.
Question 108.
For establishing a communication between a transmitting and
receiving station, a physical medium is used.
Answer:
(a) Name the two
principal classes of communication based on the physical medium used for
propagation.
(b) Construct a table showing advantages and one practical
application each for the two wire, coaxial cable and optic fiber
communication.
(c) in cable TV transmission usually channel in UHF band
carries relatively more noise, compared to VHF band. Justify
Answer:
(a)
Line communication and space communication.
(c) At higher frequency, radiation loss is high.
Question 109.
Schematic diagram for three types of satellite orbits are
shown below and named as A.B.C.
Answer: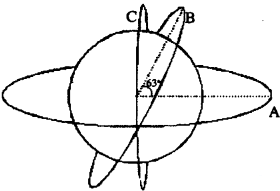
(a) Identify the polar orbit and give its approximate height from earth.
(b)
Give the criteria for selecting frequency of em wave to be used in photographs
from satellites.
(c) A satellite T V company attempts to use 25,000 kHz for
up linking signal to a sat ellite. Say whether they have selected apt frequency.
Justify.
Answer:
(a) Orbit C. Its height is about 1000 km.
(b) i.
Nature of the atmosphere.
ii. Reluctance of the object.
(c) No. Because
frequency below 20 MHz will undergo total internal reflection at the
ionosphere.
Question 110.
The following diagrams represent some of ihe modulated
signals.

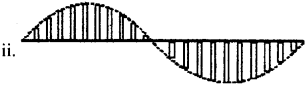
Which among is following correct
a. i only
b. ii only
c. iii only
d.
both i and ii
Answer:
d. both i and ii
Question 111.
in communication the concept of information is the central
thing. Instead of information we deal with messages, since there is no precise
definition for the word information.
(a) Name the two distinct message
categories.
(b) Explain them with examples.
Answer:
(a) In electronic
communication systems, we use
i. analog
ii. digital signals
(b) i. Analog signal is continuous in amplitude and time variables. e.g.
Speech converted microphone signal, the ECO etc.
ii Digital – This signal is
discrete in amplitude and time. Here, the analog signal is subjected to
time-sampling and amplitude quantization. e.g. Digital video stream, Data files
etc.
Question 112.
List the various types of communications according to
(a)
nature of information
(b) mode of transmission
(c) transmission
channel
(d) types of modulation
Answer:
(a) Speech. picture, fax, data
transmission
(b) Analog and digital communication
(c) i. Space
communication
ii. Line communication
(d) i. Sinusoidal waves – AM, FM,
PM
ii. Pulsed carrier waves – PAM, PTM, PPM, PNM, PCM
Question 113.
Explain the necessity of modulation.
Answer:
The
unmodified signal from the source will be usually weak to be transmitted to long
distance through channel. The Long-wave signal is then suitably combined with a
high frequency (short wave) wave called carrier. During combining some property
of the carrier is allowed to vary in proportion to that of the signal. This
process is called modulation.
Question 114.
(a) What is meant by demodulation?
(b) What is its
necessity?
(c) What are the different types of demodulation?
Answer:
(a) The process of extracting the information from a modulated wave is called
demodulation or detection.
(b) Demodulation is an essential process for
realization at the receiving end.
(c) There are different types of detectors
depending on the type of modulation. e.g. optical detector, diode detector,
etc.
Question 115.
(a) What does the figure represent?
(b) What is the
function of ‘C’?
(c) What is the function of ‘R’?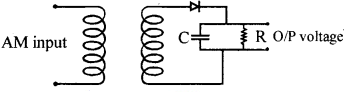
Answer:
(a) This is an AM demodulate (or detector)
(b) The capacitor charges to the
peak voltage and then discharges through R. It serves as a capacitor filter. The
diode rectifies the incoming AM signal. The rectified wave, while passing
through the network, gets the RF carrier component removed thus producing the
original signal.
(c) The voltage across R is the envelope of modulated wave
(the signal)
Question 116.
Space wave communication is called troposphere wave
propagation or LOS.
Answer:
It takes place at line of sight condition.
Question 117.
Name the four areas in which space technology finds
application.
Answer:
Meteorology, climatology, oceanography, and coastal
studies
Question 118.
“For long TV transmission, we need satellites “. Give
reason.
Answer:
The bandwidth of picture from TV camera is about 64 Hz.
Because of various factors that alternate the wave, a signal directly
transmitted may not reach the destination.
Question 119.
Flow Kepler’s III law plays an important role in satellite
communication?
Answer:
The stable orbit is designed by the condition that
square of time period is x to the cube of mean distance of the satellite from
earth.
Question 120.
(a) What do you understand by synchronous satellite?
(b)
Why are such satellites used for world wide communications?
Answer:
(a) A
satellite with period of revolution 24 hrs.
(b) High availability,
reliability and wide coverage area.
Question 121.
Draw a plot of the variation of amplitude versus ω for an
amplitude modulated wave. Define modulation index. State its importance for
effective amplitude modulation. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) Plot of
‘amplitude’ versus ‘ω’ for an amplitude modulated signal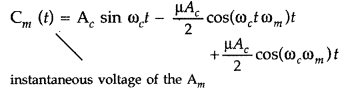
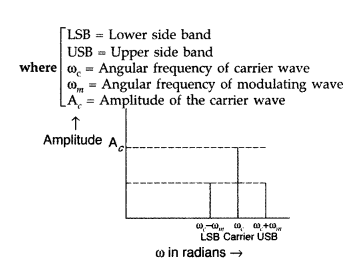
(ii) Modulation index : It is the ratio of amplitude of
message or modulating signal to the amplitude of the carrier wave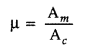
(iii) Importance :
- Modulation index determines the strength and quality of the transmitted signal.
- Distortions are avoided by keeping p < 1.
Question 122.
Explain, why high frequency carrier waves are needed for
effective transmission of signals.
A message signal of 12 kHz and peak
voltage 20 V is used to modulate a carrier wave of frequency 12 MHz and peak
voltage 30 V. Calculate the
(i) modulation index
(ii) side-band
frequencies. (All India 2017)
Answer:
(a) With high frequency carrier
waves
- transmission can take place with reasonable antenna length.
- as power radiated is proportional to 1/λ2, power radiation increases.
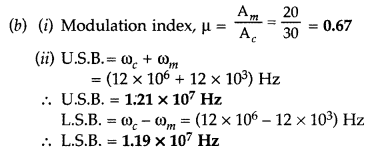
Question 123.
Distinguish between sky wave and space wave propagation. Give
a brief description with the help of suitable diagrams indicating how these
waves are propagated. (All India 2017)
Answer:
Sky wave propagation
involves frequencies in the range 30 to 40 MHz and ionospheric reflection. Space
wave propagation facilitates line of sight communication at frequencies more
than 40 MHz. For the space wave to be received beyond the horizon, the receiving
antenna of higher lengths are used.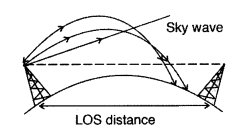
Question 124.
What is space wave propagation? Give two examples of
communication system which use space wave mode.
A TV tower is 80m tall.
Calculate the maximum distance upto which the signal transmitted from the tower
can be received. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
If a radiowave transmitted from an
antenna, travelling in a straight line, directly reaches the receiving antenna,
it is called a space wave and the wave propagation is called space wave
propagation.
Space waves used for line of sight (LOS) communication as well
as satellite communication travels in straight line from transmitting antenna to
the receiving antenna.
The figure shows the communication by LOS. If height of transmitting and
receiving antenna are hT and hR, the maximum distance
dM between two antenna is given by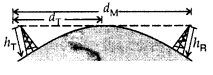

Question 125.
(i) Why is communication using line of sight mode limited to
frequencies above 40 MHz?
(ii) A transmitting antenna at the top of a tower
has a height 32 m and the height of the receiving antenna is 50 m. What is the
maximum distance between them for satisfactory communication in line of sight
mode? (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) It is evident that above 40 MHz
frequencies, the size of transmitting and receiving antenna reduces and has to
be placed at a sufficient . height from the ground. Whereas below this
frequency, the waves from transmitting antenna get interrupted and blocked at
many points by curvature of earth.
(ii) Given : hT = 32 m,
hR = 50 m,
R = 6400 = 64 × 105 m
Maximum line of
sight distance dm between the transmitting antenna and receiving antenna is
given by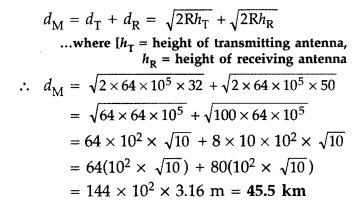
Question 126.
Which mode of propagation is used by short wave broadcast
services having frequency range from a few MHz upto 30 MHz? Explain
diagrammatically how long distance communication can be achieved by this mode.
Why is there an upper limit to frequency of waves used in this mode? (All India
2017)
Answer:
(a) Sky wave propagation is used by Broadcast services.
(b) As signals get reflected back to the earth (due to internal reflection) from
65 km to 100 km above its surface range of transmission g increases from
ionosphere.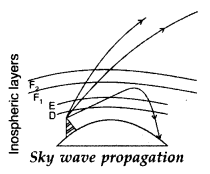
(c) Electromagnetic waves of frequencies higher than 30 MHz,
penetrate the ionosphere and escape.
Question 127.
Draw a schematic diagram showing the
(i) ground wave
(ii) sky wave and
(iii) space wave propagation modes for em waves.
Write
the frequency range for each of the following :
(i) Standard AM broadcast
(ii) Television
(iii) Satellite communication (Delhi 2011)
Answer: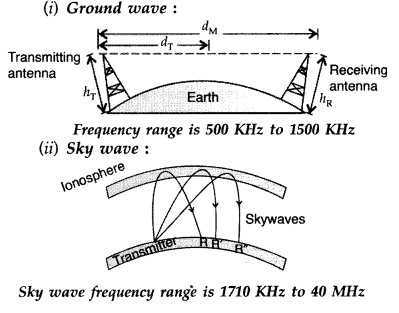
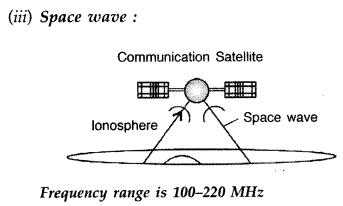
Frequency range is 100-220 MHz Frequency range for
(i)
Standard AM broadcast 540-1600 kHz
(ii) Televisiuon 54-890 MHz
(iii)
Satellite communication
5.925-6.425 GHz Uplink
3.7-4.2 GHz Downlink
Question 128.
Write briefly any two factors which demonstrate the need for
modulating a signal.
Draw a suitable diagram to show amplitude modulation
using a sinusoidal signal as the modulating signal. (All India 2011)
Answer:
Need for modulation :
(i) Audio frequencies below 20 kHz are poor
to radiate. They die out after covering small distance in air. Hence they cannot
travel large distance from the point of transmission.
(ii) To transmit audio
waves, a very small antenna is needed. For example, if a 15 kHz signal is to be
broadcasted then it requires a vertical antenna of heights 5 km which is
impossible to think even.
Diagram showing amplitued modulation: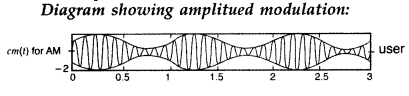
Question 129.
Write any three factors which justify the need for modulating
a signal.
Draw a diagram showing an amplitude modulated wave by superposing a
modulating signal over a sinusoidal carrier wave. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Need for modulation:
(i) Size of an tenna: For transmitting a signal, an
antennaa or an aerial of a practical size comparable to the wavelength of the
signal is required. If 15 kHz signal is to be broadcasted then it requires a
vertical antenna of height 5 km which is impossible to even think off.
(ii) Effective power radiated by an antenna: Audio frequencies are below 20 kHz. The low frequencies are poor to radiate. They die out after covering small distance in air. For good transmission, high powers and high frequency transmission is needed.
(iii) Mixing up of signals from different transmitters : If many transmitters
are transmitting message signals simultaneously, all these signals will get
mixed up and it will be difficult to distinguish between them.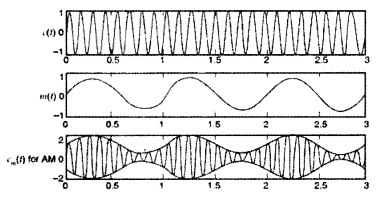
Question 130.
Name the three different modes of propagation of
electromagnetic waves. Explain, using a proper diagram the mode of propagation
used in the frequency range above 40 MHz. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The modes
of propagation of electromagnetic waves are :
(i) Ground waves
(ii) Sky
waves
(iii) Space waves
Above 40 MHz, the mode of propagation used is via
space waves. A space wave travels in a straight line from the transmitting
antenna to the receiving antenna. Space waves are used for line of sight (LOS)
communications as well as satellite communication.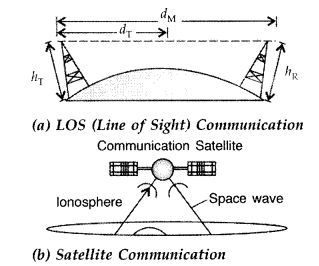
Question 131.
Mention three different modes of propagation used in
communication system. Explain with the help of a diagram how long distance
communication can be achieved by ionospheric reflection of radio waves. (All
India 2012)
Answer:
Three different modes of propagation used in
communication are :
(i) Space wave propagation.
(ii) Ground wave
propagation
(iii) Sky wave or ionospheric propagation
The radio waves of
the high frequency band having frequency range 3-30 MHz cannot penetrate through
the ionosphere. They are reflected back towards the earth. This region of the AM
band is called short wave band. Above 40 MHz, the ionosphere bends the
electromagnetic waves and does not reflect them back towards the earth.
Question 132.
Explain briefly the following terms used in communication
system :
(i) Transducer
(ii) Repeater
(iii) Amplification (All India
2012)
Answer:
(i) Transducer: Any device which converts energy from one
form to another is called a transducer. We may define an electrical transducer
as a device which converts variation in physical quantity such as pressure,
displacement, force, temperature etc., into corresponding variations in the
electrical signal at its output.
(ii) Repeater: As signal while passing through the transmission medium may get attenuated due to the various energy losses along its path. So a signal booster or amplifying repeater is placed at suitable distance along its path. A repeater is a combination of a transmitter, an amplifier and a receiver which picks up a signal from the transmitter, amplifiers and retransmits it to the receiver sometimes with a change of carrier frequency.
(iii) Amplification : It is the process of increasing the amplitude and hence the strength of an electrical signal by using a suitable electric circuit (consisting of atleast one transistor) is called the amplifier.
Question 133.
(a) Distinguish between sinusoidal and pulse-shaped
signals.
(b) Explain, showing graphically, how a sinu-soidal carrier wave is
superimposed on a modulating signal to obtain the resultant amplitude modulated
(AM) wave. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer: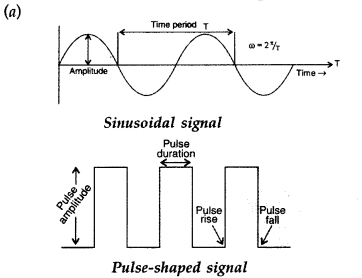
| Sinusoidal signal | Pulse-shaped signals |
| In a sinusoidal signal, the value of its characteristic parameter (voltage, current etc.) varies with time in the same manner as sin θ varies with θ. | In a pulse-shaped signal, the value of its characteristic parameter (voltage, current etc.), after remaining (nearly) constant for a small time interval, suddenly reverses its sign, remains constant for a small time interval and then again reverses its sign. This gets repeated again and again. |
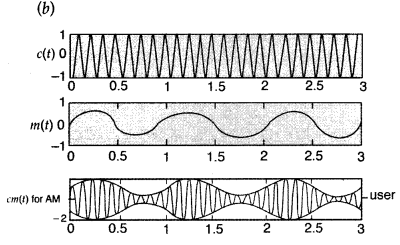
When a modulating signal (Figure b) is superimposed on
sinusoidal carrier wave (Figure a), and as a result, the amplitude of the
carrier wave varies in accordance with the modulating signal, the resultant wave
(Figure c) is known as an amplitude modulated wave.
Question 134.
Write three important factors which justify the need of
modulating a message signal. Show diagrammatically how an amplitude modulated
wave is obtained when a modulating signal is superimposed on a carrier wave.
(Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Need for modulation:
(i) Size of an tenna: For
transmitting a signal, an antennaa or an aerial of a practical size comparable
to the wavelength of the signal is required. If 15 kHz signal is to be
broadcasted then it requires a vertical antenna of height 5 km which is
impossible to even think off.
(ii) Effective power radiated by an antenna: Audio frequencies are below 20 kHz. The low frequencies are poor to radiate. They die out after covering small distance in air. For good transmission, high powers and high frequency transmission is needed.
(iii) Mixing up of signals from different transmitters : If many transmitters
are transmitting message signals simultaneously, all these signals will get
mixed up and it will be difficult to distinguish between them.
Question 135.
Distinguish between ‘sky waves’ and ‘space waves’ modes of
propagation in communication system.
(a) Why is sky wave mode propagation
restricted to frequencies upto 40 MHz?
(b) Give two examples where space wave
mode of propagation is used. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Difference between
skywave and space wave modes :
| S.No. | Sky Wave | Space Wave |
| 1. Range of frequencies
|
Restricted upto a few MHz frequency (30 to 40 MHz).
|
Can take place (even) beyond 40 MHz frequency.
|
| 2. Mode of propagation
|
Waves are reflected back from ionosphere.
|
Space waves travel in a straight line, either direct
from transmitting antenna to receiving antenna or through satellite.
|
(a) The radio waves of frequencies more than 40 MHz penetrate into the
ionosphere.
(b) Television broadcast, microwave link and satellite
communication.
Question 136.
Name the type of waves which are used for line of sight (LOS)
communication. What is the range of their frequencies?
A transmitting antenna
at the top of a tower has a height of 20 m and the height of the receiving
antenna is 45 m. Calculate the maximum distance between them for satisfactory
communication in LOS mode. (Radius of the Earth = 6.4 × 106 m) (All
India 2013)
Answer:
(i) Space waves
(ii) More than 50 Hz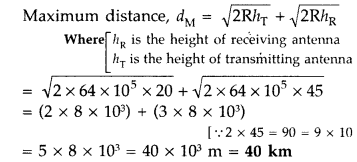
Question 137.
Name the type of waves which are used for line of sight (LOS)
communication. What is the range of their frequencies?
A transmitting antenna
at the top of a tower has a height of 45 m and the receiving antenna is on the
ground. Calculate the maximum distance between them for satisfactory
communication in LOS mode. (Radius of the Earth = 6.4 ∞ 106 m) (All
India 2013)
Answer:
• Space waves
• Frequency range above 40
MHz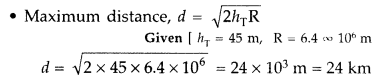
Question 138.
What is meant by ‘detection of a modulated signal’? Draw
block diagram of a detector for AM waves and state briefly, showing the
waveforms, how the original message signal is obtained. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Detection of a modulated signal: Detection is the process of
recovering the modulated signal from the modulated carrier wave. The modulated
carrier wave contains the frequencies <oc, eoc+ com and In order to obtain
the original message signal m (+) of angular frequency com following simple
method is shown in the form of a block diagram.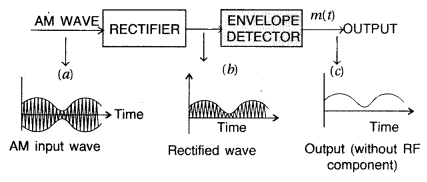
Question 139.
Write the function of each of the following used in
communication sytem :
(i) Transducer
(ii) Repeater
(iii) Transmitter
(Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(i) Transducer. It converts energy from one
form to another.
(ii) Repeater. It picks up a signal from the transmitter, amplifiers and
retransmits it to the receiver, sometimes with a change of carrier
frequency.
(iii) Transmitter. It is a device which processes a message signal into a form suitable for transmission and then transmits it to the receiving end through a transmission channel.
(iv) Bandpass filter. A bandpass filter blocks lower and higher frequencies and allows only a band of frequencies to pass through.
Question 140.
(a) Describe briefly the three factors which justify the need
for translating a low frequency signal into high frequencies before
transmission.
(b) Figure shows a block diagram of a detector for AM
signal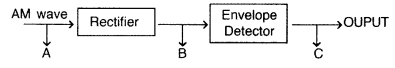
Draw the waveforms for the
(i) input AM wave at A,
(ii)
output B at the rectifier, and
(iii) output signal at C. (Comptt. All India
2013)
Answer:
(a) Modulation is needed
- to transmit a low frequency signal to a distant place.
- to keep the height of antenna small.
- not to allow the signals from different stations getting mixed up.
(b)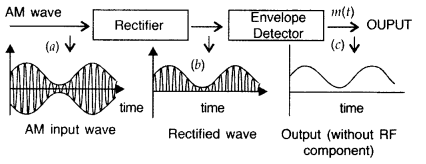
Question 141.
Write two basic modes of communication. Explain the process
of amplitude modulation. Draw a schematic sketch showing how amplitude modulated
signal is obtained by superposing a modulating signal over a sinusoidal carrier
wave. (All India 2013)
Answer:
The two basic modes of communication are
:
(1) point-to-point communication
(2) broadcast communication
Amplitude modulation. It is produced by varying the amplitude of carrier waves
in accordance with the amplitude of the modulating wave.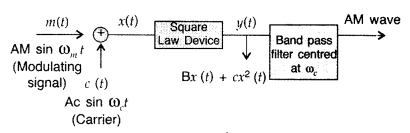
Production of amplitude modulated wave. A conceptually simple
method to produce AM wave is shown in block diagram.
Question 142.
Draw a block diagram of a detector for AM signal and show,
using necessary processes and the waveforms, how the original message signal is
detected from the input AM wave. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Detection of a
modulated signal: Detection is the process of recovering the modulated signal
from the modulated carrier wave. The modulated carrier wave contains the
frequencies ωc, (ωc + ωm) and (ωc –
ωm). In order to obtain the original message signal m (+) of angular
frequency ωm following simple method is shown in the form of a block
diagram.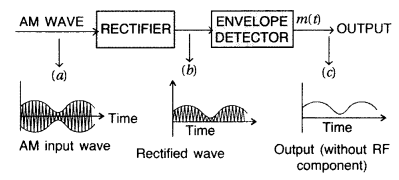
Question 143.
Define modulation index. Why is its value
kept, in practice, less than one?
A carrier wave of frequency 1.5 MHz and
amplitude 50 V is modulated by a sinusoidal wave of frequency 10 kHz producing
50% amplitude modulation. Calculate the amplitude of the AM wave and frequencies
of the side bands produced. (All India 2015)
Answer:
(i) Definition of
Modulation Index. It is defined as the ratio of the amplitude of modulating
signal (Am) to the amplitude of carrier wave (Ac)
= (1500 kHz ± 10 kHz)
= 1510 and 1490 kHz
respectivley.
Question 144.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Why is the thin ozone
layer on top of the stratosphere crucial for human survival? Identify to which a
part of electromagnetic spectrum does this radiation belong and write one
important application of the radiation.
(ii) Why are infrared waves referred
to as heat waves? How are they produced? What role do they play in maintaining
the earth’s warmth through the greenhouse effect? (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(i) The thin ozone layer on the top of stratosphere is crucial for
human survival, because it absorbs ultraviolet radiations from the Sun and thus
prevents them from reaching the earth’s surface causing damage to life.
Identification : ultraviolet radiations. Its correct application is
Sanitization.
(ii) (a) Water molecules present in most materials readily absorb infra red
waves. Hence, their thermal motion * increases. Therefore, they heat their
surroundings and are hence referred to as heat waves.
(b) They are produced
by hot bodies and molecules.
(c) Incoming visible light is absorbed by
earth’s surface and radiated as infra red radiations. These radiations are
trapped by green house gases.
Question 145.
(a) Given a block diagram of a generalized communication
system.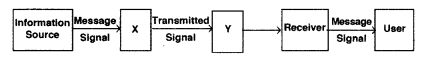
Identify the boxes ‘X’ and ‘Y’ and write their functions.
(b) Distinguish between “Point to Point” and “Broadcast” modes of communication.
Answer:
(a) X : Transmitter Y : Channel Their
function:
Transmitter : To convert the message signal into suitable form for
transmission through channel.
Channel : It sends the signal to the
receiver.
(b) In point to point mode, communication takes place between a single transmitter and receiver while in broadcast mode, large number of receivers are connected to a single transmitter.
Question 146.
Explain the following terms in relation to the use of
internet :
(i) Internet surfing
(ii) Social networking
(iii) E-mail
(Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(i) Internet surfing : “It is the exploration
of me world wide web (www) by following one interesting link to another one
usually without a definitive object or search strategy, through the
internet.”
(ii) Social networking : It is a platform to build social networks or social relations among people who share similar interests, activities, backgrounds or real life connections. A social network service consists of a representation of each user (often a profile), his or her social links, and a variety of services.
(iii) E-mail : E-maii (Electronic mail) is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients. E-mail operates across the internet or other complex networks. E-mail servers accept, forward, deliver and store messages.
An internet Email message consists of these components :
(a) message
envelope,
(b) message header and
(c) message body. Thus e-mail is an
information and communications technology.
Question 147.
(a) Explain any two factors which justify the need of
modulating a low frequency signal.
(b) Write two advantages of frequency
modulation over amplitude modulation. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) Need of
modulation : A low frequency signal is modulated for the following purposes
:
(i) It reduces the wavelength of transmitted signal, and the minimum height
of antenna for effective communication is \(\frac{\lambda}{4}\).
Therefore
height of antenna becomes practically achievable.
(ii) Power radiated into the space by an antenna is inversely proportional to λ2. Therefore, the power radiated into the space increases and signal can travel larger distance.
(b) Advantages of frequency modulation :
- High efficiency
- Less noise .
- Maximum use of transmitted power.
Question 148.
(i) Which mode of propagation is used by shortwave broadcast
services having frequency range from a few MHz upto 30 MHz? Explain
diagrammatically how long distance communication can be achieved by this
mode.
(ii) Why is there an upper limit to frequency of waves used in this
mode? (All India 2015)
Answer:
(i) (a) Sky wave propagation
(b)
Three different modes of propagation used in communication are :
- Space wave propagation.
- Ground wave propagation
- Sky wave or ionospheric propagation
The radio waves of the high frequency band having frequency range 3-30 MHz
cannot penetrate through the ionosphere. They are reflected back towards the
earth. This region of the AM band is called shortwave band. Above 40 MHz, the
ionosphere bends the electromagnetic waves and does not reflect them back
towards the earth.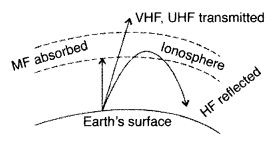
(ii) Electromagnetic waves of frequencies higher than 30 MHz, penetrate the ionosphere and escape whereas the waves less than 30 MHz are reflected back to the earth by the ionosphere.
Question 149.
What does the term ‘Modulation’, used in communication
system, mean?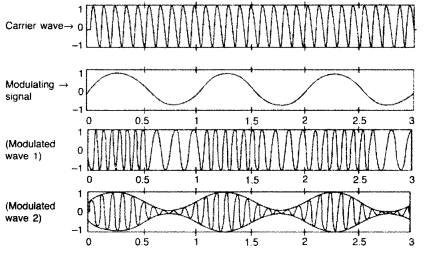
Identify the two types of modulation shown here. Give two
advantages of any one of these over the other. (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(i) Modulation is a process in which one of the characteristics
(amplitude, frequency, phase) of a high frequency carrier wave is made to change
in accordance with a given low frequency message signal.
(ii) (a) Modulated
wave 1 : Frequency Modulation (FM)
(b) Modulated wave 2 : Amplitude
Modulation (AM)
Two advantages of FM over AM :
- Lower noise, better power efficiency.
- Higher operating range.
- Higher fidelity reception.
Two advantages of AM over FM :
- Simple circuits are required.
- Lower frequency space for transmission.
Question 150.
Give (brief) reasons for the following :
(a) We use the
‘sky wave’ mode of propagation, of electromagnetic waves, only for frequencies
up to 30 to 40 MHz.
(b) The LOS communication, via space waves, has a
(fairly) limited range.
(c) A mobile phone user gets an ‘uninterrupted link
to talk’ while walking. (Comptt. All India 2015)
Answer:
(a) The
ionosphere can act as a ‘reflector’ only for e.m. waves of frequencies upto 30
to 40 MHz. Higher frequency e.m. waves penetrate into the atmosphere and
escape.
(b) The range is (fairly) limited because the e.m. waves lose energy (fairly rapidly) when they glide over the surface of the earth.
(c) This is because of the presence of a network of base stations’/cells’ which keep on passing the signals from one base station/cell to the other.
Question 151.
Define the term ‘amplitude modulation’.
Explain any two
factors which justify the need for modulating a low frequency base-band signal.
(Delhi 2017)
Answer:
‘Amplitude modulation’ is the process of
superposition of information/message signal over a carrier wave in such a way
that the amplitude of carrier wave is varied according to the information
signal/message signal.
Direct transmission, of the low frequency base band
information signal, is not possible due to the following reasons :
(i) Size
of Antenna: For transmitting a signal, minimum height of antenna should be
\(\frac{\lambda}{4}\). With the help of modulation, wavelength of signal
decreases, hence height of antenna becomes manageable.
(ii) Effective power radiated by an antenna :
Effective power radiated by
an antenna varies inversely as λ2, hence effective power radiated
into the space, by the antenna, increases.
(iii) To avoid mixing up of signals from different transmitters.
Question 152.
(a) How is amplitude modulation achieved?
(b) The
frequencies of two side bands in an AM wave are 640 kHz and 660 kHz
respectively. Find the frequencies of . carrier and modulating signal. What is
the bandwidth required for amplitude modulation? (All India 2017)
Answer:
(a) Amplitude modulation is achieved by applying the message signal, and the
carrier wave, to a non-linear (square law device) followed by a band pass filter
as shown below in the block diagram: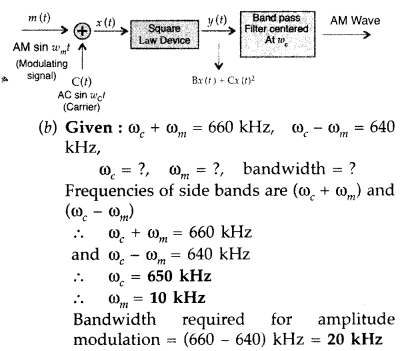
Question 153.
Draw a block diagram of generalized communication system.
Write the functions of each of the following:
(a) Transmitter
(b)
Channel
(c) Receiver (All India 2017)
Answer:
Block diagram of
generalized communication system :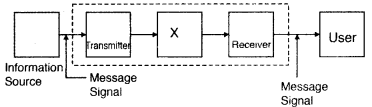
Functions:
(a) Transmitter : A transmitter processes the
incoming message signal so as to make it suitable for transmission through a
channel and subsequent reception.
(b) Channel: It carries the message signal
from a transmitter to a receiver.
(c) Receiver : A receiver extracts the
desired message signals from the received signals at the channel output.
Question 154.
Explain the term, ‘amplitude modulation’ of a signal. For an
amplitude modulated wave, the maximum amplitude is 10 V and the minimum
amplitude is 2 V. Calculate the modulation index. (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Amplitude modulation is the process of superposition of a message
signal over a carrier, wave in which amplitude of the carrier wave is varied in
accordance with the message/ information signal.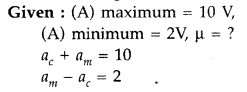
Question 155.
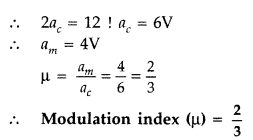
Distinguish between sky wave and space modes of
communication. What is the main limitation of space wave mode? Write the
expression for the optimum separation between the transmitting and receiving
antenna for effective reception of signals in this mode of communication.
(Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) In sky wave mode of communication, waves
reach from transmitting antenna to receiving antenna through reflections from
ionosphere; while in space wave mode of communication, waves travel either
directly from the transmitter to receiver or through satellites.
(ii) Direct waves get blocked at some point due to the curvature of earth.
(iii) Optimum distance between transmitting and receiving antenna![]()
Question 156.
Explain the meaning of terms : Attenuation and Demodulation.
For an amplitude modulated wave, the maximum amplitude is 12 V and the minimum
amplitude is 2 V. Calculate the modulation index. (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Attenuation : It is the loss of strength of signal, while propagating
through a medium.
Demodulation : It is the process of recovery of audio
signal from the modulated wave.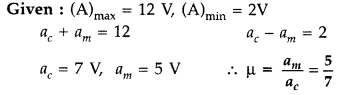
Question 157.
Write the functions of
(i) Repeater and
(ii) Receiver.
For an amplitude modulated wave, the maximum amplitude is 15 V and the minimum
amplitude is 3 V. Calculate the modulation index. (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Repeater is a combination of a receiver and a transmitter. It is used
to increase the range of communication of signals. A repeater picks up the
signal from the transmitter, amplifies it and retransmits it to the
receiver.
Receiver extracts the desired message signals from the received signals at
the channel output. It is the combination of receiving antenna, amplifier,
intermediate frequency converter, demodulator and amplifier of audio
signal.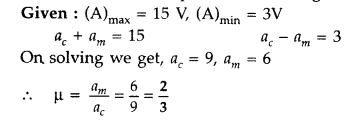
Question 158.
Briefly explain the three factors which justify the need of
modulating low frequency signal into high frequencies. (Comptt. All India
2017)
Answer:
(a) Modulation is needed
- to transmit a low frequency signal to a distant place.
- to keep the height of antenna small.
- not to allow the signals from different stations getting mixed up.