Chapter 4 Reproductive health
Class 12th Biology Chapter hots
1. Define reproductive health. Why is it important for overall societal development?
Answer:
Reproductive health refers to a state of complete physical, mental, and social
well-being in all matters relating to the reproductive system.
Importance:
- Reduces maternal and infant mortality.
- Prevents sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Promotes responsible family planning, ensuring population stability.
- Enhances gender equality by empowering women with reproductive choices.
- Boosts socio-economic development by reducing healthcare costs.
2. Discuss the objectives and significance of the Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) program in India.
Answer:
Objectives:
- Provide comprehensive reproductive healthcare services.
- Reduce maternal and infant mortality rates.
- Promote contraceptive use and family planning.
- Spread awareness about STIs and adolescent health.
Significance:
- Encourages safe motherhood practices.
- Increases immunization rates.
- Improves access to healthcare facilities in rural areas.
3. Explain the role of contraception in population control. What are its social and ethical implications?
Answer:
Contraceptives help regulate population growth by preventing unintended
pregnancies.
Social Implications:
- Improves women’s health by reducing frequent pregnancies.
- Enhances family stability by allowing planned parenting.
Ethical Concerns: - Access disparity due to socio-economic inequality.
- Religious or cultural opposition to contraceptive use.
4. Compare natural and artificial methods of contraception. Discuss their effectiveness.
Answer:
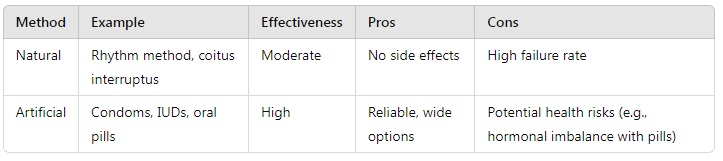
5. Explain how amniocentesis is performed. Why is its misuse a serious concern in India?
Answer:
Amniocentesis:
- A needle is inserted into the amniotic sac to collect fluid for genetic
analysis.
Misuse: - Used for sex determination, leading to female feticide.
Concerns: - Skewed sex ratio in India.
- Violation of ethical and legal rights.
6. Discuss the causes and consequences of infertility in males and females.
Answer:
Causes in Males: Low sperm count, hormonal imbalances,
lifestyle factors.
Causes in Females: PCOS, endometriosis, blocked fallopian
tubes.
Consequences:
- Psychological stress and societal stigma.
- Strain on marital relationships.
7. Explain the concept of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART). How do IVF and ICSI differ?
Answer:
ART: Techniques like IVF, ICSI, and surrogacy to aid
conception.
IVF: Fertilization occurs in a lab, and the embryo is
transferred to the uterus.
ICSI: A single sperm is injected into an ovum, used in severe
male infertility cases.
8. Why is it crucial to educate adolescents about reproductive health? Propose measures to spread awareness.
Answer:
Importance:
- Prevents STIs and early pregnancies.
- Promotes responsible behavior.
Measures: - School programs on sexual health.
- Accessible helplines for confidential advice.
- Media campaigns highlighting safe practices.
9. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of permanent contraceptive methods like vasectomy and tubectomy.
Answer:
Advantages:
- Highly effective.
- No need for repeated intervention.
Disadvantages: - Irreversible.
- Requires surgical procedures with minor risks.
- Social stigma may discourage acceptance.
10. Explain the role of hormonal pills in contraception. What are their side effects?
Answer:
Hormonal pills inhibit ovulation and alter cervical mucus.
Side Effects:
- Nausea, weight gain, mood swings.
- Risk of thromboembolism.
11. What are sexually transmitted infections (STIs)? Explain their causes, symptoms, and prevention methods.
Answer:
Examples: Gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV.
Causes: Unprotected sex, multiple partners, poor hygiene.
Symptoms: Discharge, sores, genital warts.
Prevention:
- Use of condoms.
- Regular screening.
- Avoiding multiple partners.
12. Evaluate the significance of the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act. What are the ethical concerns?
Answer:
Significance:
- Reduces unsafe abortions.
- Empowers women with reproductive rights.
Ethical Concerns: - Conflict between maternal rights and fetal life.
- Misuse for gender-selective abortions.
13. How do social taboos and myths hinder reproductive health awareness? Suggest strategies to overcome them.
Answer:
Impact of Taboos:
- Hesitation to seek medical help.
- Misconceptions about contraception and STIs.
Strategies: - Community workshops.
- Involving religious leaders for awareness.
- Inclusive health education in schools.
14. What are the physiological and psychological impacts of teenage pregnancies?
Answer:
Physiological: Higher risk of complications like anemia,
preterm labor.
Psychological: Stress, stigma, interrupted education.
15. Discuss the use of barrier methods of contraception in preventing both pregnancy and STIs.
Answer:
Barrier methods (e.g., condoms) prevent sperm entry and block STI transmission.
Advantages: Cost-effective, no hormonal side effects.
Limitations: Potential for improper use or breakage.
16. How does family planning contribute to national health and economy?
Answer:
- Reduces burden on healthcare systems.
- Promotes maternal and child health.
- Controls population growth, enhancing resource allocation.
17. Why is breastfeeding considered a natural contraceptive? What are its limitations?
Answer:
Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM): High prolactin levels
suppress ovulation.
Limitations:
- Effective only for six months postpartum.
- Requires exclusive breastfeeding.
18. What is GIFT, and how does it differ from ZIFT?
Answer:
- GIFT: Gametes are transferred to the fallopian tube for in vivo fertilization.
- ZIFT: Zygote is transferred to the fallopian tube after in vitro fertilization.
19. Analyze the role of NGOs and government agencies in promoting reproductive health.
Answer:
NGOs: Provide counseling, distribute contraceptives, and raise
awareness.
Government Agencies: Implement family planning programs, offer
subsidies for contraceptives, and ensure rural healthcare access.
20. Explain the difference between primary infertility and secondary infertility. How are they diagnosed?
Answer:
Primary infertility: Inability to conceive after one year of
unprotected intercourse.
Secondary infertility: Difficulty conceiving after a previous
successful pregnancy.
Diagnosis: Hormonal tests, imaging (e.g., ultrasound), and
semen analysis.
21. What are IUDs, and how do they prevent pregnancy? Compare copper-based IUDs with hormonal IUDs.
Answer:
IUDs are intrauterine devices preventing fertilization or implantation.
- Copper IUDs: Release copper ions toxic to sperm.
- Hormonal IUDs: Release progestin, thickening cervical mucus and thinning the endometrium.
22. Discuss the ethical and legal challenges of surrogacy in India.
Answer:
Challenges:
- Exploitation of poor women as surrogates.
- Issues of parental rights and child citizenship.
- Legal restrictions under the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act.
23. How do lifestyle choices impact reproductive health?
Answer:
- Smoking and alcohol affect fertility.
- Poor diet leads to hormonal imbalances.
- Stress disrupts menstrual cycles or sperm production.
24. Explain the socio-economic factors influencing contraceptive use in India.
Answer:
- Rural-urban divide in access.
- Educational levels affecting awareness.
- Cultural preferences for larger families.
25. Critically evaluate the effectiveness of awareness campaigns in reducing adolescent pregnancies.
Answer:
Campaigns like “Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao” have increased awareness about gender
equality and reproductive rights. However, gaps in rural education and societal
stigma persist, reducing their overall impact.