Chapter 16 Environmental issues
Class 12th Biology NCERT Book Solution
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Environmental Issues
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK SOLVED
1. What are the various
constituents of domestic sewage? Discuss the effects of sewage discharge on a
river.
Ans: Domestic
sewage contains four kind of impurities:
(i) Suspended
solids: They are soil particles such as sand and silt.
(ii)
Colloidal particles: They are inorganic and organic materials such as
faecal matter, bacteria, paper and cloth.
(iii) Dissolved solids
: They are nitrates, phosphates, ammonia, sodium, calcium and other
nutrients.
(iv) Pathogens : Domestic sewage has pathogens of
various diseases such as typhoid, cholera, dysentery, diarrhoea, etc. Effect of
sewage discharge on river are:
(i) Eutrophication.
(ii) Growth of
pathogenic bacteria.
(iii) Ageing of river where slit and decaying matters
start accumulating and filling river.
(iv) Increase in BOD.
(v)
Destruction of flora and fauna of that river.
2. List all the wastes that
you generate at home, school or during your trips to other places. Could you
very easily reduce the generation of these wastes? Which would be difficult or
rather impossible to reduce?
Ans: Waste
materials generated at home : paper, disposable cups, cloth, plates, spoons,
plastic envelopes, discarded food etc.
Waste materials generated at school are : paper, chalks, plastic envelopes etc.
Wastes materials generated during trips are : paper, disposable cups, plates, spoons, plastic envelopes, discarded food etc.
No, we cannot reduce the generation of these wastes easily, but few can be reduced. The wastes belong to two categories : biodegradable and non-biodegradable. It is difficult or rather impossible to reduce discarded food like peel of potato, peel of banana etc. We can do one important thing i.e., to reduce wastage of food.
3. Discuss the causes and
effects of global warming. What measures need to be taken to control global
warming?
Ans: Increase in
atmospheric concentration of green house gases has resulted in rise of
atmospheric temperature by 0.6°C (global wanning) in die 20th century. This has
been confirmed by intergovernmental panel on climatic change (IPCC) in its
reports of 1991 and 1992. This predictable change in near future may affect
climate, sea level, range of species distribution, food production as well as
fisheries resources in the oceans.
Causes of global
warming:
(i) Increase in concentration of greenhouse gases.
(ii)
Increase of automobile and use of fossil fuel.
(iii) Deforestation and change
in land use.
(iv) CFC and aerosol emission from refrigerator and
aeroplane.
(v) Increased particulate matter in lower
atmosphere.
Effects of global warming:
(i) CO2
fertilisation effect.
(ii )Many species of plants, being sensitive to
temperature will die with sudden rise in temperature and their place will be
taken over by scrub vegetation.
(iii) Loss of biodiversity.
(iv) Rise in
sea level.
(v) Possibilities of drought and floods.
(vi) Erruption of
plant disease and pests.
(vii) Change in rainfall pattern.
Methods that
can reduce the atmospheric concentration of greenhouses gases are
(i)
Reducing the greenhouse gas emission by limiting the use of fossil fuels, and by
developing alternative renewable sources of energy (wind energy, solar energy
etc.)
(ii) Increasing the vegetation cover, mainly the forests, for
photosynthetic utilization of CO2.
(iii) Minimizing the use of
nitrogen fertilizers in agriculture for reducing N2O emissions.
(iv) Developing substitutes for chlorofluorocarbons.
4. Match the items given in
column A and B: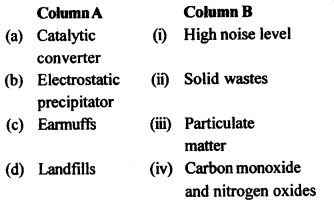
Ans: (a)-(iii),(b)-(iv),(c)-(i),(d)-(ii)
5. Write critical notes on
the following:
(a)
Eutrophication
(b) Biological
magnification
(c) Groundwater depletion and ways
for its replenishment
Ans: (a)
Eutrophication : It is excessive growth of algae, plants and animals in
water bodies due to the nutrient enrichment particularly with nitrogen and
phosphorus. It is both natural and accelerated. It leads to loss of
bio-diversity and cuases chemical accumulation in food chain and ageing of water
body.
(b) Biological magnification : Increase in concentration of persistent chemical at successive trophic levels is called eutrophication. This happens because a toxic substance accumulated by an organism can not be metabolized or excreted, and is thus passed onto next trophic level, e.g., DDT.
(c) Ground water depletion and replacement: Ground water
depletion, a term often defined as long term water level declines caused by
sustained ground water pumping, is a key issue associated with ground water use.
Many areas of India experiencing ground water depletion.
The most servere
consequence of excessive ground water pumping is that the water table, below
which the ground is saturated – with water, can be lowered. If ground water
level declines too far, then the well owner might have to deepen the well, drill
a new well, or at least attempt to lower the pump.
6. Why ozone hole forms over
Antarctica? How will enhanced ultraviolet radiation affect
us?
Ans:
Chlorofluorocarbons, mainly released in the atmosphere by
developed countries, Slowly enters the stratosphere and the winds move them
towards the poles. Environmental conditions prevailing in Antarctica during
winter months; there is no sunlight in Antarctica and extremely low temperature
( – 85°C) facilitates the formation of ice clouds. During winter, natural
circulation of wind (polar vertex) completely isolates Antarctic air from the
rest of the world.
The ice clouds provide the catalytic surface for the reaction of chlorine
atoms and then ozone. But this degradation of ozone occurs with the return of
solar radiations to Antarctica during spring (September and October). This
results in the thinning of ozone layer every year over most of Antarctica. This
hole disappears in summer due to warming up of air and the mixing up of
Antarctic air with that of the rest of the world.
Enhanced UV radiations on
earth would affect humans and other animals by causing:
- Skin cancer
- Blindness and increased chances of cataract in eyes.
- Malfunctioning of immune system.
- Higher number of mutations.
7. Discuss the role of women
and communities in protection and conservation of
forests.
Ans:
Amrita Bishnoi Wildlife protection project The Bishnoi community
is known for its peaceful coexistence with nature. It was in 1730 AD. Amrita
Devi protested against king’s men’s attemptto cut trees as it was prohibited in
Bishnoi religion. It was a party of Maharaja Abhay Singhji, Rular of Marwar
(Jodhpur) state who wanted to fell green khejdali trees. Amrita Devi fy her
three daughter & more than 360 of other Bishnois lost their lives in saving
trees & became martyers. Later ‘Chipko’ movement’ was started by Sunderlal
Bahuguna and others to prevent cutting of trees. The people showed enormous
bravery in protecting trees from the axe of contractors by hugging them.
8. What measures, as an
individual, would you take to reduce environmental
pollution?
Ans: To reduce
environmental pollution we should take following measures:
(i) Reducing use
of CFC.
(ii) Disposing off waste safely.
(iii) Reducing use of
polythene.
(iv) Not disposing off waste in water bodies.
(v) Making
automobiles pollution free.
(iv) Prevention of noise pollution by using fire
crackers/TV/musical instruments at permissible limits.
(vii) Tree plantation
in school, around residence.
9. Discuss briefly the
following:
(a) Radioactive wastes
(b) Defunct ships and e-wastes
(c) Municipal solid wastes
Ans: (a)
Radioactive waste : Radioactive waste include materials that are
radioactive & for which there is no further practical use. These are
generated by nuclear reactor, nuclear fallout, man made (refining and mining of
platinum and thorium), natural radioactive waste and release of radiation in
radiation therapy.
Increased risk of cancer, birth defects & infertility
are few harmful effects caused by nuclear waste. So, nuclear waste is an
extremely potent pollutant.
(b) Defunct ships & e-wastes – The dismantling of
defunct ship is a technically complex process, which is potentially harmful to
the environment & human health. Defunct i ships contain toxicants like
asbestos, mercury, etc. The workers breaking the ships are not suitably
protected and are exposed to toxic chemicals. The coastal areas in the vicinity
of the ship-breaking yard also becomes polluted. At the international level, it
is accepted that there is uncertainty about the relevant controls for the
dismantling of such vessels & there is an urgent need to establish a
specific enforceable control framework.
Electronic waste comprised of
irrepairable computer and other electronic goods, generated by developed
countries.
It is valuable source of secondary raw materials, if treated
properly, however if not treated properly it is the major source of toxins.
Eventually recycling is the only solution for the treatment of e-wastes provided
it is carried out in an environment friendly manner.
(c) Municipal solid wastes : These are commonly known as
trash or garbage. It consists of everyday items such as product packaging,
furniture, clothing, bottles, food scraps, newspapers.
appliances, paints,
batteries etc. Source reduction, recycling and compositing are several municipal
social waste management practices. Source reduction involves altering the
design, manufacture or use of products & materials to reduce die amount and
toxicity of what gets thrown away. Recycling diverts items such as paper, glass,
plastic & metals into anew products. Composting decomposes organic waste
such as food scraps & yard trimmings with micro-organisms, producing a
humus-like substance.
10. What initiatives were
taken for reducing vehicular air pollution in Delhi? Has air quality improved in
Delhi?
Ans: The initiatives
were taken for reducing vehicular air pollution in Delhi are :-
(i)
Introduction of CNG
(ii) Enforcement of pollution control law
(iii)
Introduction of green zones
(iv) Use of unleaded fuels
(v) Replacement of
old vehicle with new one. The result is that the air quality of Delhi has
improved considerably with a substantial fall in pollutant gases.
(vi)Use of
catalytic converters in vehicles.
(vii)Application of Euro II norms for
vehicle.
11. Discuss briefly the
following:
(a) Greenhouse gases
(b) Catalytic
converter
(c) Ultraviolet B
Ans: (a)
Greenhouse gases: Gases that trap the heat of the sun in the earth’s
atmosphere increasing atmospheric temperature effect are called greenhouses
gases. CO2, CH4, N2O and CFC, cause greenhouse.
In the absence of greenhouse gases, the temperature of earth would go down to
-18°C. The net effect of higher GHGs will be disastrous, (i) Melting of polar
ice caps and mountain snow caps resulting in rising of sea level threatening
submergence of many islands and coastal areas. Odd climate changes like El Nino.
Increased floods and drought.
(b) Catalytic converter :
Catalytic converter ‘are used to reduce emission of poisonous gases like
nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide & un reacted hydrocarbon in automotive
emission. It is made of platinum, palladium and rhodium and is used as catalyst.
It converts unbumt hydrocarbons into CO2. The only precaution
required is not to use gasoline having lead as lead inactivates the catalysts of
the converter.
(c) Ultraviolet B : Ultraviolet B is one of
the three types of invisible light rays given off by the sun. Ultraviolet B
penetrates the ozone layer in attenuated form & reaches earths. This is more
over equator than poles due to thinning of ozone shield over equator. It causes
skin cancer, reduce rate of photosynthesis in phytoplanktons, reduces diversity
of aquatic ecosystem.