Chapter 11 BiotechnologyPrinciples and processes
Class 12th Biology NCERT Book Solution
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Biotechnology: Principles And Processes
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK SOLVED
1. Can you list 10
recombinant proteins which are used in medical practice? Find out where they are
used as therapeutics (use the internet).
Ans:
(i) Human insulin – Diabetes
(ii) Human growth hormone –
Dwarfism cure
(iii) Blood clotting factor Y1H/IX-Haemophilia
(iv) TPA
(tissue plasminogen activator) – Heart attack/strokes
(v) PDGF (platelet
derived growth factor) – Stimulates wound healing.
(vi) Interferon –
Treatment of viral infection.
(vii) Interlinking – Enhances immune
reaction,
(viii) Hepatitis B vaccine – Prevention of infectious disease.
(ix) Herpes Vaccine – Prevention of infectious disease.
(x) DNase I –
Treatment of cystic fibrosis.
2. Make a chart (with
diagrammatic representation) showing a restriction enzyme, the substrate DNA on
which it acts, the site at which it cuts DNA and the product it
produces.
Ans: Name of the
Restriction enzyme – Bam HI.
The substrate DNA on which it acts –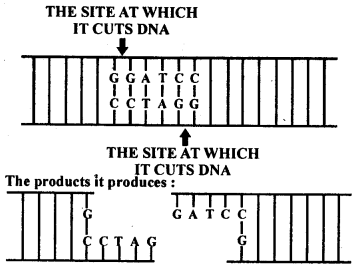
3. From what you have learnt,
can you tell whether enzymes are bigger or DNA is bigger in molecular size? How
did you know?
Ans: Both DNA
(deoxyribonucleic acid) and enzymes are macromolecules. DNA is a polymer of
deoxyribonucleotides and enzymes are proteins hence these are polymers of amino
acids. But DNA is bigger in molecular size as compared to proteins because
synthesis of proteins is regulated by a small segment of DNA, called genes and
also a large number of proteins can be synthesised by a DNA molecule.
4. What would be the molar
concentration of human DNA in a human cell? Consult your
teacher.
Ans: The molar
concentration of DNA in human cell is 2 mg/ml of cell extract.
5. Do eukaryotic cells have
restriction endonucleases? Justify your answer.
Ans:
No, eukaryotic cells do not have restriction endonuclease because DNA
molecules of eukaryotes are heavily methylated. All the restriction
endonucleases have been isolated from various strain of bacteria.
6. Besides better aeration
and mixing properties, what other advantages do stirred tank bioreactors have
over shake flasks?
Ans: Shake flasks are
used for growing and mixing the desired materials on a small scale in the
laboratory. A large scale production of desired biotechnological product is done
by using ‘bioreactors’. Besides better aeration and mixing properties, the
bioreactors have following advantages
(i) Small volumes of cultures are
periodically withdrawn from die reactor for sampling.
(ii) It has a foam
control system, pH control system and temperature control system.
(iii)
Facilitates even mixing and oxygen availability throughout the bioreactor.
7. Collect 5 examples of
palindromic DNA sequences by consulting your teacher. Better try to create a
palindromic sequence by following base-pair rules.
Ans: Palindrome
nucleotide sequences in the DNA molecule are groups of bases that form the same
sequence when read both forward and backward. Five examples of palindromic DNA
sequences are as follows:
(i)
5′-—————GGATCC——————3’
3′—————CCTAGG—————–5′
(ii)
5’—————AAGCTT——————3′
3′——————TTCGAA —————-5′
(iii)
5′—————–ACGCGT—————–3′
3′——————TGCGGA————– 5′
(iv) 5′———- ACTAGT————3′
3′——————TGATCA————5′
(v) 5′—————AGGCCT—————3′
3′——————TCCGGA————–5′
8. Can you recall meiosis and
indicate at what stage a recombinant DNA is made?
Ans: Recombinant DNA is
formed due to crossing over between non-sister chromatids of homologous
chromosome. It occurs during pachytene stage of prophase of meiosis I
9. Can you think and answer
how a reporter enzyme can be used to monitor transformation of host cells by
foreign DNA in addition to a selectable marker?
Ans:
A reporter enzyme can be used to differentiate transformed cells
by tracking down the activity of its co-responding genes (receptor gene). For
e.g., (3-galactosidase (Lac Z) activity is not found in transformed cells so
that they appear white in colour. The others, which appear blue in colour,
indicate that cells do not carry foreign DNA.
10. Describe briefly the
followings:
(a) Origin of replication
(b) Bioreactors
(c) Downstream
processing
Ans: (a) Origin of Replication:
This is a sequence from where replication starts and any piece of DNA when
linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells. This
sequence is also responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA.
So, if one wants to recover many copies of the target DNA it should be cloned in
a vector whose origin support high copy number.
(b) Bioreactor: Bioreactors can be thought of as vessels in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products by microbes, plant and animal cell and/or their enzymes. The bioreactor provides optimum growth conditions and facilitates achieving the desired products. The most commonly used bioreactor is of stirring type. A stirred tank bioreactor is usually a cylindrical vessel or vessel with a curved base to facilitate mixing of the contents. In the sparged stirred tank bioreactor, sterile air bubbles are sparged. The stirrer facilitates the mixing and oxygen availability throughout the bioreactor. A bioreactor has an agitator system, an oxygen delivery system, a foam control system, a temperature control system, pH control system and sampling ports.
(c) Downstream Processing : The product obtained is subjected to a series, of processes collectively called downstream processing before it is made into a finished product ready for marketing. The two main processes are separation and purification. The product is then formulated with suitable preservatives. Such formulations have to undergo clinical trials, in case of drugs.
11. Explain
briefly
(a)
PCR
(b)
Restriction enzymes and DNA
(c) Chitinase
Ans: (a) PCR = Polymerase
chain reaction (in vitro method) is a molecular biological technique for
enzymatically replicating DNA without using a living organism, such as E. coli
or yeast.
3 steps in PCR are –
(i) Denaturation of desired double strand
DNA-to ssDNA.
(ii) Annealing of primer to ssDNA (single standard).
(iii)
Extension of primer by Taq DNA polymerase isolated form Thermits aquaticus.
Uses – Amplification of desired gene/gene cloning.
Advantage- More output,
greater efficiency, less error prone, less human interference and cyclic and
automated.
(b) Restriction enzymes and DNA – Restriction enzymes is a group
of enzymes used to cleave or cut DNA strands each having a characteristics base
sequence at which it cleaves.
(i) It restricts foreign DNA from entering
normal cell by digesting it at various recognition site. Recognition site is
palindromic.
(ii) They are endonuclease and exonuclease both types.
(iii)
They produces sticky ends. Cleavage site and recognition site are different from
each other. Restriction enzymes therefore are believed to be a mechanism evolved
by bacteria to resist viral attack and to help in the removal of viral
sequences.
(c) Chitinase – Chitinase is a enzyme to digest or breakdown
glycosidic bonds in chitin cell wall of fungal cell to facilitate its
transformation.