Chapter 1 Reproduction in organisms
Class 12th Biology NCERT Book Solution
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Reproduction in Organisms
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK SOLVED
1. Why is reproduction
essential for organisms?
Ans: Reproduction is
the ability of living organisms to produce a young one similar to itself.
It ensures continuity of a species generation after generation. Reproduction
introduces variation in the organisms. Useful variations are essential for
adaptation and evolution. Therefore, it is essential for organisms.
2. Which is a better mode of
reproduction sexual or asexual? Why?
Ans:
Sexual reproduction is a better mode of reproduction because of
the following reasons:
- Variation : Since fusion of gametes from different parents occur during sexual reproduction, hence genetic recombination takes place causing variations.
- Evolution : Variation being a major factor of natural selection, therefore, it plays an important role in evolution.
- Adaptation : The offspring produced due to sexual reproduction adapt better to the changing environmental conditions.
- Vigour and Vitality : Genetic recombination, interaction, etc. during sexual reproduction provide vigour and vitality to the offspring.
3. Why is the offspring
formed by asexual reproduction referred to as clone?
Ans: Asexual
reproduction is a type of reproduction in which a single individual is capable
of producing offspring. These offspring are not only genetically and
morphologically similar to one another but also similar to their parent. Clone
is the term given to individuals that are genetically and morphologically
similar. Thus the offspring produced by asexual reproduction are called
clones.
4. Offsprings formed due to
sexual reproduction have better chances of survival. Why? Is this statement
always true?
Ans: The offsprings
obtained from sexual reproduction have better chances of survival because the
genetic material of such organisms are formed from both the parents. Daughter
organisms/offsprings show variation that leads to the evolution of species.
This statement is always true. The offspring produced due to sexual reproduction adapt better to the changing environmental conditions. Genetic recombination, interaction, etc. during sexual reproduction provide vigour and vitality to the offspring.
5. How does the progeny
formed from asexual reproduction differ from those formed by sexual
reproduction?
Ans: Production of
offspring by a single parent without the formation and fiision of gametes is
called asexual reproduction. It involves only mitotic cell division that gives
rise the daughter cells which are genetically identical to the parent cell.
Sexual reproduction is the production of offspring by two parents, male and
female. It involves meiotic cell divisions producing haploid nuclei which on
fusion produce offspring that are genetically different from their parents.
6. Distinguish between
asexual and sexual reproduction. Why is vegetative reproduction also considered
as a type of asexual reproduction?
Ans: The
difference between asexual and sexual reproduction are as follows :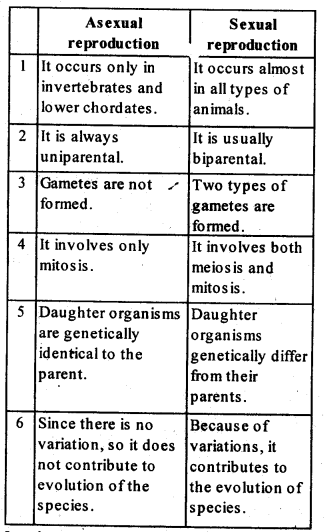
In plants asexual reproduction is called vegetative
reproduction because vegetative plant parts like rhizome, runner, sucker, tuber,
bulb all are capable of producing off springs These parts give rise to daughter
individuals without the involvement of two parents.
7. What is vegetative
propagation? Give two suitable examples.
Ans:
Vegetative propagation is the formation of new plants from
vegetative units. In plants, the units of vegetative propagation are runner,
rhizome, sucker, tuber, offset, bulb, etc. These are capable of producing new
offsprings. These structures are called v vegetative propagules.
Modified tuberous roots of sweet potato, tapioca, yam, Dahlia and Tinospora can be propagated vegetatively when planted in soil. Small plants emerging from the buds (called eyes) of the potato tuber, from the rhizomes of banana and ginger are other examples.
8.
Define:
(a)Juvenile
phase
(b)Reproductive
phase
(c)Senescent
phase.
Ans: (a)Juvenile
phase : All organisms have to reach a certain stage of growth and
maturity in their life before they can reproduce sexually. That period of growth
is called juvenile phase. However, this phase is known as vegetative phase in
plants. This phase is of different durations in different
organisms.
(b)Reproductive phase: The end of juvenile/
vegetative phase marks the beginning of reproductive phase. During this phase,
the organisms produce offspring. In higher plants, this phase can be easily seen
when they come to flower but in animals, the juvenile phase is followed by
morphological and physiological changes prior to active reproductive behaviour.
The reproductive phase is also of variable period in different organisms like
some plants, flower throughout the year while others show seasonal flowering. In
animals like birds lay eggs seasonally “but when in captivity (as in poultry
farms) can be made to lay eggs throughout the year. Placental female mammals,
undergo cyclical changes in reproductive organs during this
phase.
(c) Senescent phase: It begins from the end of the
reproductive phase. During this phase of life span, there is progressive
deterioration in the body (like slowing of metabolism, etc.). Old age ultimately
leads to death.
9. Higher organisms have
resorted to sexual reproduction in spite of its complexity.
Why?
Ans: Higher
organisms have resorted to sexual reproduction in spite of its complexity
because sexual reproduction results in multiplication and perpetuation of
species and also contributes to evolution of species by introducing variation
much more faster than asexual reproduction in a particular population. Sexual
reproduction enables higher organisms to survive during unfavourable
conditions.
10. Explain why meiosis and
gametogenesis are always interlinked?
Ans: Gametogenesis
is the process of formation of two types of haploid gametes (male and female).
In gametogenesis, gametes are haploid in number and formed by meiosis so the
chromosome number is haploid. Thus gametogenesis is always linked with
meiosis.
11. Identify each part in a
flowering plant and write whether it is haploid (n) or diploid
(2n).
(a)Ovary ————————
(b)Anther
————————
(c)Egg ————————
(d)Pollen
————————
(e)Male gamete ————————
(f)Zygote
————————
Ans: (a)2n (b)2n
(c)n (d)n (e)n (f)2n
12. Define external
fertilization. Mention its disadvantages.
Ans: When
fusion of the gametes takes place outside the body of the organisms, it is
called external fertilization or external syngamy. The external medium like
water is required for this form of fertilization. This form, is found in many
aquatic animals like fishes, amphibians, majority of algae.
In this, parents
release eggs and sperms in the surrounding water, then fertilization and
development of offspring occur externally. Disadvantages of external
fertilization:
(i)if occurs only in aquatic medium.
(ii)A chance factor is
involved requiring synchronous release of gametes nearby and absence of
turbulence of water.
(iii)There is no protection to young ones. They are
vulnerable to a number of predators.
13. Differentiate between a
zoospore and a zygote.
Ans: The zoospore is
flagellated, motile, haploid or diploid spore formed inside a zoosporangium. It
is the result of asexual reproduction.
The zygote is always diploid and formed by the fusion of gametes. It is usually non- flagellated and non-motile or motile. It is the net result of sexual reproduction.
14. Differentiate between
gametogenesis from embryogenesis.
Ans: Differences
between gametogenesis and embryogenesis are as follows :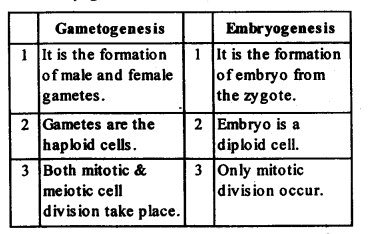
15. Describe the
post-fertilization changes in a flower.
Ans: In
sexual reproduction, events that occur after the formation of zygote are called
post-fertilization events. In flowering plants, the zygote is formed inside the
ovule. After fertilization the sepals, petals and stamens of the flower wither
and fall off. But the pistil remains attached to the plant. The zygote develops
into the embryo and the ovules develop into the seed. The ovary develops into
die fruit that develops.a thick wall called pericarp which is protective in –
function. After dispersal, seeds germinate under favourable conditions to
produce new plants.
16. What is % bisexual
flower? Collect five bisexual flowers from your neighbourhood and with the help
of your teacher find out their common and scientific
names.
Ans: Flowers in
which male and female sex organs (stamens and carpels) are borne on the same
flowers are called bisexual flowers. You can observe following bisexual flowers
in your kitchen and colony gardens :
(i)Brassica (sarson) – Brassica
campestris
(ii)Onion – Allium cepa
(iii)Garden Pea (Edible pea) – Pisum
sativum
(iv)Petunia – Petunia hybrida
(v)China rose (shoe flower) –
Hibiscus rosa- sinensis.
17. Examine a few flowers of
any cucurbit plant and try to identify the staminate and pistillate flowers. Do
you know any other plant that bears unisexual flowers?
Ans: The male or
staminate flowers of cucurbits bear bright coloured petals and a prominent group
of stamens. Male plants or staminate flowers do not bear fruits. The female or
pistillate flowers bear fruits. In a fertilised young pistillate flower very
small fruit is visible below petals and sepals. Some unisexual plants are :
Papaya, Mulberry and Date-palm.
18. Why are offspring of
oviparous animals at a greater risk as compared to offspring of viviparous
animals?
Ans: On the basis of the
development of the zygote, animals are grouped into oviparous and viviparous.
The oviparous animals such as reptiles and birds lay eggs. Their fertilised eggs
are covered by hard calcareous shell and are laid in a safe place in the
environment. After incubation period, young ones hatch out. In viviparous
animals such as majority of mammals including human beings, the zygote develops
into a young one inside the body of the female individual. After a certain
growth period, the young ones are delivered by the female individual. Due to
proper care and protection, the chances of survival of young ones are more in
viviparous individuals. Oviparous offsprings are at a greater risk than
viviparous ones.