CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology Set-4
Class 11thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology Set-4
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology Set 4 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section – A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section – B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section – C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section- D has 2 case – based questions of 4 marks each; and Section – E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
Section – A
Question 1.
A prothallus is: (1)
(A) A structure in pteridophytes
formed before the thallus develops.
(B) A sporophytic free living structure
formed in pteridophytes.
(C) A gametophyte free living structure formed in
pteridophytes.
(D) A primitive structure formed after fertilisation in
pteridophytes
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Prothallus is
a free living gametophyte structure formed in pteridophytes. It consists of
haploid male sex organ, antheridia, female sex organ, archegonia.
Question 2.
When CO2 is added to PEP, the first stable product
synthesised is: (1)
(A) Pyruvate
(B) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
(C)
Phosphoglycerate
(D) Oxaloacetate.
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: The first stable product formed after fixation of CO2
with PEP.
Question 3.
Match the column A with column B and choose the correct
option. (1)
| Column A | Column B |
| a. Porifera | (i) Canal system |
| b. Aschelminthes | (ii) Water-vascular system |
| c. Annelida | (iii) Muscular Pharynx |
| d. Arthropoda | (iv) Jointed appendages |
| e. Echinodermata | (v) Metameres |
(A) a – ii, b – iii, c – v, d – iv, e – i
(B) a – ii, b – v, c – iii, d –
iv, e – i
(C) a – i, b – iii, c – v, d – iv, e – ii
(D) a – i, b – v, c –
iii, d – iv, e – ii
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
| Column A | Column B |
| a. Porifera | (i) Canal system |
| b. Aschelminthes | (iii) Muscular Pharynx |
| c. Annelida | (v) Metameres |
| d. Arthropoda | (iv) Jointed appendages |
| e. Echinodermata | (ii) Water-vascular system |
Question 4.
Members of phycomycetes are found in: (1)
(i) Aquatic
habitats
(ii) On decaying wood
(iii) Moist and damp places
(iv) As
obligate parasites on plants
Choose from the following options:
(A) None of the above
(B) (i) and
(iv)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) All of the above
Answer:
Option (D) is
correct.
Explanation: The members of phycomycetes can be aquatic, parasitic
and can also live in moist and damp places.
Question 5.
Which of the following pairs of animals has non glandular
skin? (1)
(A) Snake and Frog
(B) Chameleon and Turtle
(C) Frog and
Pigeon
(D) Crocodile and Tiger
Answer:
Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: Chameleon and Turtle have dry and non- glandular skin with scales
and they are the member of class reptelia.
Question 6.
The term systematics refers to: (1)
(A) Identification and
study of organ systems.
(B) Identification and preservation of plants and
animals.
(C) Diversity of kinds of organisms and their relationship.
(D)
Study of habitats of organisms and their classification.
Answer:
Option
(C) is correct.
Explanation: Systematics refers to the diversity of organism
and their relationship.
Question 7.
A conjoint and open vascular bundle will be observed in the
transverse section of: (1)
(A) Monocot root
(B) Monocot stem
(C) Dicot
root
(D) Dicot stem
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: In
dicot stem vascular bundles are of conjoint, collateralor bicollateral, endarch
and open type.
Question 8.
Identify the given types of bacteria (1)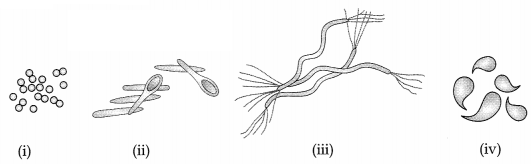
(A) (i) – Vibrio, (ii) – Spirilla, (iii) – Cocci, (iv) – Bacilli
(B) (i) –
Cocci, (ii) – Bacilli, (iii) – Spirilla, (iv) – Vibrio
(C) (i) – Spirilla,
(ii) – Vibrio, (iii) – Bacilli, (iv) – Cocci
(D) (i) – Bacilli, (ii) –
Vibrio, (iii) – Spirilla, (iv) – Cocci
Answer:
Option (B) is correct.
Question 9.
Many elements are found in living organisms either free or in
the form of compounds. One of the following is not, found in living organisms:
(1)
(A) Silicon
(B) Magnesium
(C) Iron
(D) Sodium
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: Elements like Magnesium, iron and sodium
have their specific functions such as magnesium in ATP bonding, iron for Oxygen
transport, in blood and sodium maintains the blood pressure. But silicon does
not have any such function in living organism.
Question 10.
Identify the given structure of amino acid : (1)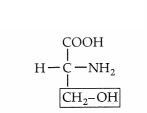
(A) Serine
(B) Alanine
(C) Glycine
(D) Arginine
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Question 11.
Naked cytoplasm, multinucleated and saprophytic are the
characteristics of: (1)
(A) Monera
(B) Protista
(C) Fungi
(D) Slime
moulds
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: Naked cytoplasm,
multinucleated and saprophytic are the characteristics of slime mould, they are
saprophytic and do not posses cell wall.
Question 12.
Identify the stage in which chromosome replication occurs:
(1)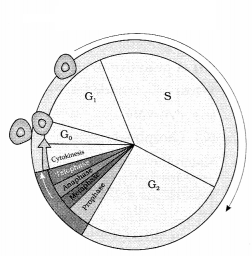
(A) G1 – phase
(B) G2 – phase
(C)
S – phase
(D) M – phase
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation:
During G1- growth and protein synthesis takes place.
S- phase- DNA
replication takes place G2- Growth and preparation for division M- phase- cell
division takes place
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion is followed
by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) Both A and R
are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but
R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A
is false but R is true
Question 13.
Assertion (A): Red algae contribute in producing coral reefs.
(1)
Reason (R): Some red algae secrete and deposit calcium carbonate over
their walls.
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: Red algae
contribute in producing coral reefs as they secrete and deposit calcium
carbonate over their walls, for example, red algae and coralline algae deposit
CaCO3 in their cell wall, coral reef is made of thin layers of
CaCO3.
Question 14.
Assertion (A): An anti-coagulant hirudin is present in
salivary glands of leech. (1)
Reason (R): It leads to blood clotting while
the leech is feeding.
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: An
anti-coagulant hirudin is present in the salivary glands of leech. It prevents
the blood from clotting while the leech is feeding.
Question 15.
Assertion (A): Mustard and china rose has hypogynous flowers.
(1)
Reason (R): In hypogynous flowers, ovary is said to be inferior.
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: In hypogynous flowers, ovary
is said to be superior while in epigynous flowers, ovary is inferior.
Question 16.
Assertion (A): Trichomes are hairs which are often found as
epidermal outgrowths. (1)
Reason (R): Hairs are glandular which secrete
essential oil and provide characteristic odours to the plant
Answer:
Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: Trichomes are hairs which are often found
as epidermal outgrowths. Hairs are glandular structure which secretes essential
oil and provide characteristic odours to the plant.
Section – B
Question 17.
Mango and coconut are ‘drupe’ type of fruits. In mango fleshy
mesocarp is edible. What is the edible part of coconut? What does milk of tender
coconut represent? (2)
Answer:
The edible part of coconut is endosperm.
The milk of tender coconut represents free nuclear endosperm in liquid form.
Later, this endosperm gets deposited along the walls of the endocarp and forms
edible flesh.
Question 18.
Study the given diagram of T.S. of dicot stem. (2)
(a)
Identify the given parts- (i), (ii), (iii), (iv).
(b) Write the
characteristic function of a vascular bundle of dicot stem.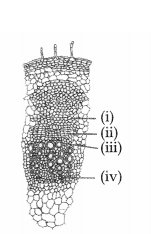
Answer: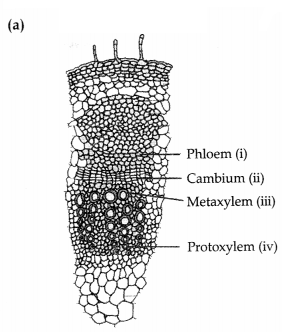
(b) A large number of vascular bundles are arranged in a ‘ring’; this ‘ring’
arrangement of vascular bundles is a characteristic feature of the dicot
stem.
Question 19.
Pyruvic acid is the end product of glycolysis. What are the
three metabolic fates of pyruvic acid under aerobic and anaerobic conditions?
Write in the space provided in the diagram. (2)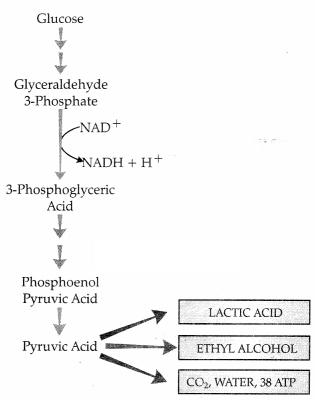
Answer:
A = Lactic acid + 2ATP
B = Ethanol + CO2
C = Carbon
dioxide and water + 36/38 ATP.
Question 20.
(a) Label the parts of endomembrane system in the given
diagram. (2)
(b) Name the site of synthesis of glycolipids in a cell.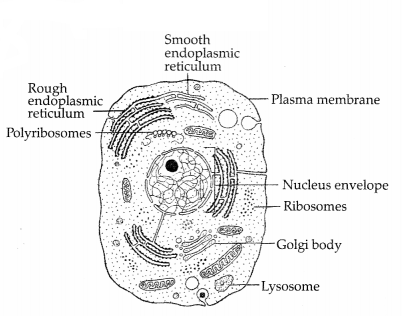
Answer:
(a) The labeled parts in an eukaryotic cell represents an
endomembrane system: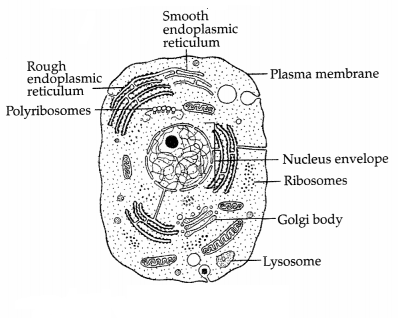
(b) Golgi apparatus.
Question 21.
Persons suffering from very low blood pressure pass no urine.
Why? What suggestion would you offer for the removal of waste products from the
blood in such a situation? (2)
Answer:
It is true that a person suffering
from very low blood pressure does not pass sufficient urine. The reason for this
is, the blood to pass through the glomerulus of the nephron must have required
amount of pressure in it. If the pressure is insufficient, it will not flow
through the glomerulus and filtration would not take place, hence no urine would
be formed. This is quite harmful to the person as waste products go on
accumulating in the body.
To avoid this, a person should be advised to take a sufficient amount of water and medicines to keep the blood pressure at an optimum level.
Section – C
Question 22.
Figure shows the effect of light on the rate of
photosynthesis. Based on the graph, answer the following questions: (3)
Graph
of Light Intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
(a) At which point/s (A, B
or C) in the curve is light a limiting factor?
(b) What do C and D represent
on the curve?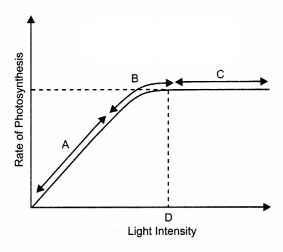
Answer:
(a) At higher light intensities, the rate of
photosynthesis becomes limiting. Light is limiting in A and 50% of B.
(b) C
is saturation of light. Here, the rate of photosynthesis is not increased by
increasing the intensity of light.
D represents the intensity of light at
which same factor may be limiting.
Question 23.
Give an account of alimentary canal of frog. (3)
Answer:
Alimentary canal of frog: It is a short tube starting from mouth to
cloaca. Mouth opens into buccopharyngeal cavity. It has many maxillary teeth at
the margin of the upper jaw. Vomerine teeth lie at the floor of this cavity. The
tongue is bilobed and muscular. It is used to capture the prey. Gullet opens
into the oesophagus which is distended into stomach. Stomach follows the small
and large intestine. The rectum opens into the cloaca. Liver and pancreas are
digestive glands.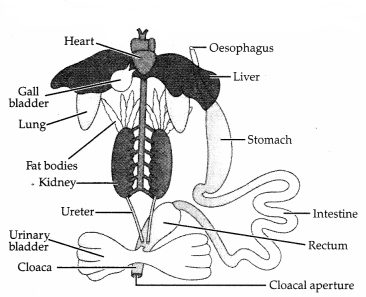
Question 24.
(a) What are nodal tissues? (3)
(b) Explain their role in
heartbeat.
Answer:
(a) The heartbeat results from a wave of electrical
potential called the cardiac impulse, which originates from nodal tissue like
sino-atrial node (SAN), auriculo-ventricular node (AVN), a bundle of His and
Purkinje fibres.
(b) Role of heartbeat:
- SAN is located in the right auricle at the opening of the vena cava. It is part of the conducting system of heart. The stimulation arises initially in the sino-atrial node.
- The AVN is located in the right auricle in the inter-auricular septum. It gives rise to the bundle of His, a muscular bridge that conducts stimulation from the auricles to the ventricles.
- The bundle of His divides into two branches. The terminal branches of the conducting system are represented by a network of Purkinje fibres which convey stimuli to the myocardium.
Question 25.
In the figure given below, the black line (upper) indicates
action spectrum for photosynthesis and the lighter line (lower) indicates the
absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a, answer the followings: (3)
(a) What
does the action spectrum indicate? How can we plot an action spectrum? Explain
with an example.
(b) How can we derive an absorption spectrum for any
substance?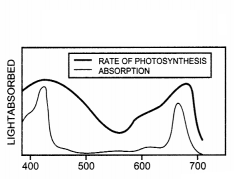
Answer:
(a) Action spectrum indicates the relative rates
of photosynthesis at different wavelengths of light. Action spectrum of
photosynthesis can be plotted by measurements of oxygen evolution at different
wavelengths. For example, Englemann in 1882, plotted an action spectrum using
green algae.
(b) Absorption spectrum for any substance can be derived by calculating the amount of energy at different wavelength of light absorbed.
Question 26.
What is bacteriophage? Also describe its structure? (3)
Answer:
Bacteriophage: Viruses infecting bacteria are known as
bacteriophage.
- These are obligate parasites that occur in soil, sewage water, fruits.
- The phage possesses a tail and a head.
- The viral DNA is thread-like double-stranded macromolecule.
- There are 4 segments of the tail.
- Bacteriophage are of two types: (a) Lytic and (b) Lysogenic phages e.g., phage (Lambda), T2 phage, etc.
Question 27.
(a) Why is ABA known as ‘stress hormone’? (3)
(b) Mention
any two functions of this hormone.
(c) How are they antagonistic to
gibberellins?
OR
Auxins are growth hormones capable of promoting cell
elongation. They have been used in horticulture to promote growth, flowering and
rooting.
(a) Write a line to explain the meaning of the following terms
related to Auxins.
(i) Auxins precursors
(ii) Anti-Auxins
(b) What are
synthetic auxins?
Answer:
(a) Abscisic acid (ABA) is also called stress
hormone because the synthesis of abscissic acid is stimulated by drought, water
logging and other adverse environmental conditions. It is produced in many parts
of the plants but more abundantly inside the chloroplast of green cells.
(b) Abscisic acid owes its name to its role in the abscission of plant leaves. In preparation for winter, ABA is produced in terminal buds. This slows plant growth and directs leaf primordia to develop scales to protect the dormant buds during the cold season.
(c) They are antagonistic to gibberellins, as gibberellins promotes stem
elongation while abscisic acid acts as growth inhibitor.
OR
(a)
(i)
Auxin precursors: These are the raw materials used in the synthesis of Auxins.
For example, tryptophan is a precursor of indole-3- acetic acid.
(ii) Anti-auxins: These are the compounds which inhibit the action of auxin. For example, TIBA acts as anti-auxins by blocking the transport of auxin.
(b) Synthetic auxin: Auxins which are manufactured synthetically and do not grow naturally in plants, e.g., 2,4-D, NAA, etc.
Question 28.
What are the reasons that you can think of for the arthropods
to constitute the largest group of the animal kingdom? (3)
Answer:
- Tough cuticle protects the arthropods against predators and forms jointed exoskeleton for muscles attachment. This has enabled the arthropods to survive on land in almost any environment.
- Bilaterally symmetrical, ‘segmented’, triploblastic, coelomate animals, found almost everywhere in all habitats.
- Body enclosed by chitinous cuticle (exoskeleton).
- They have joined appendages.
- They have mouth parts of various types.
- Trachea/book lungs or book gills for respiration.
Section D
Question 29.
Calcium is an essential mineral for human body. It helps in
blood clotting , muscle contraction, etc. Exchange of
calcium between bone
and extracellular fluid takes place under the influence of certain hormones .
(4)
(A) What will happen if more of Ca++ is in extracellular
fluid?
OR
What will happen if very less amount of Ca++ is in
the extracellular fluid? .
(b) Calcium ion concentration in blood affects
muscle contraction
(i) Does it lead to tetany in certain cases?
(ii) How
will you correlate fluctuation in blood calcium with tetany?
(c) Name at
least two hormones which result in fluctuation of Ca++ level.
Answer:
(a) More calcium concentration in extracellular fluid is associated
with hyperparathyroidism. It may cause demineralisation, resulting in softening
and bending of the bones. This condition is known as osteoporosis.
OR
Very
less amount of calciumin extracellular fluid is associated with
hypoparathyroidism. It may increase the excitability of nerves and muscles,
causing cramps, sustained contraction of the muscles of larynx, face, hands and
feet. This disorder is called parathyroid tetany.
(b) (i) Calcium plays an important role in regulation of muscle contraction. The low level of calcium in blood leads to higher level of calcium in muscles. This may result in uncontrolled contraction of muscles which is called tetany.
(ii) Parathyroid hormone secreted by parathyroid gland increases the calcium level in the blood. Due to deficiency of parathyroid hormone, the calcium level in the blood decreases. This increases the excitability of nerves and muscles, causing cramps and convulsions. Sustained contraction of the muscles of larynx, face, hands and feet are produced. This disorder is called parathyroid tetany.
(c) Parathyroid and calcitonin results in fluctuation of calcium level.
Question 30.
In the following diagram shows the myofibrils in different
state of action. Answer the questions as follows : (4)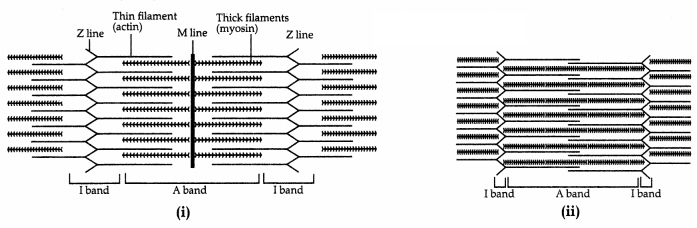
(a) What is the state of myofibrils in (i) and (ii) respectively?
(b) What
are I band and A band also called as respectively?
(c) Which ion is
responsible for contraction or relaxation of myofibrils?
OR
(a) Identify
the following type of mechanisms shown in the diagram (i) and
(ii),below.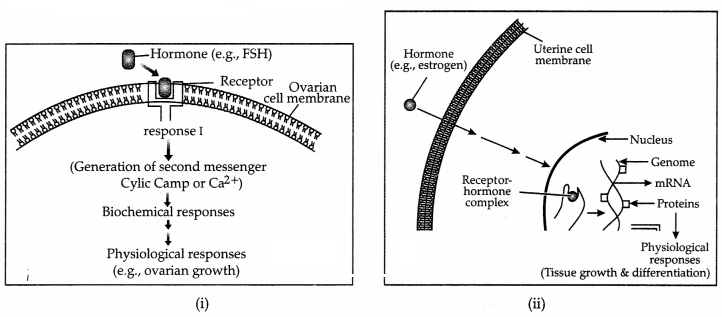
(b) Explain the mechanisms which are illustrated through the given diagram(i)
and (ii).
(c) Write other examples which can possess these mechanisms,
respectively.
Answer:
(a) (a) is relaxed state and (b) is contracted state
of myofibril.
(b) I band is light band or isotropic band while A band is a
dark band or anisotropic band
(c) Ca2+ ions are responsible for
the contraction or relaxation of myofibril.
OR
(a) (i) Mechanism of
peptide hormone action.
(ii) Mechanism of steroid hormone action
(b) (i) Peptide hormone action :
Protein being water soluble normally do
not enter the target cells but interact with membrane-bound receptors to
generate second messengers like cAMP, IP3, Ca2+ etc.
(ii) Steroid hormone action :
Steroid hormone being lipid soluble, enter
the target cell and interact with intracellular receptors and regulate gene
expression by the interaction of hormone receptor complex with the genome.
(c) (i) Example: Oxytocin, Insulin, Glucagon, Vasopressin, etc.
(ii)
Example: Cortisol, Testosterone, Estrogen and Progesterone
Section – E
Question 31.
Write the functions for the each lobe of cerebrum:
| S. No. | Cerebral lobe | Major functions |
| (i) | Frontal lobe | |
| (ii) | Temporal lobe | |
| (iii) | Occipital lobe | |
| (iv) | Pariental lobe |
There are two types of leucocytes; Granulocytes and agranulocytes.
State
the structure , life span /formation and function of the following types of
Granulocytes :
| Name | Structure | Life span/Formation | Function |
| Basophils | |||
| Eosinophils | |||
| Neutrophils |
Answer:
| S. No. | Cerebral lobe | Major functions |
| (i) | Frontal lobe | Reasoning, will power, monitoring of thoughts and actions, creative ideas, translation of perceptions and memories into plans, muscle movement, reality testing by judgement, intellectual insight. |
| (ii) | Temporal lobe | Memory, smell, as well as emotions. |
| (iii) | Occipital lobe | Decoding and interpretation of visual information: colour and shape. |
| (iv) | Parietal lobe | Taking information from environment, organising it and communicating it to rest part of brain, registration of sensory perception called the feelings about touch, pain, heat and cold; knowledge about position in space. |
OR
| Name | Structure | Life span/Formation | Function |
| Basophils | Three lobed nucleus | Formation: Bone marrow Life: 4-8 hrs in blood | Secrete histamine, serotonin, heparin etc. Involved in inflammatory reactions. |
| Eosinophils | Bilobed nucleus, granules in cytoplasm | Formation: Bone marrow Life: 4-8 hrs in blood | Play a role in immunity, non- phagocytic |
| Neutrophils | Multilobed nucleus | Formation: Bone marrow Life: less than 24 hrs in blood. | Phagocytic cells destroys foreign organisms entering body. |
Question 32.
(a) Who proposed the fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane ?
(5)
(b) Describe the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane with the help
of labelled diagram.
(c) Name the major interaction responsible for
stabilising plasma membrane.
OR
Plastids are small bodies, found free in
the cytoplasm of most plant cells. They are absent in animal cells.
(a) Is
there a species specific or region specific type of plastids?
(b) How does
one distinguish it from the other?
(c) Are the different types of plastids
interchangeable? If yes, give examples where they are getting converted from one
type to another.
Answer:
(a) Fluid mosaic model was proposed by Singer and
Nicolson.
(b)
- According to this model, there is a central lipid bilayer of phospholipids with their polar head group towards the outside and the non-polar tails pointing inwards.
- Some proteins which are embedded in the lipid layer are called integral or intrinsic proteins and they cannot be separated from the membrane.
- There are large globular integral proteins which project beyond the lipid layer on both the sides are believed to have channels through which water-soluble materials can pass across.
- Superficially attached proteins are called extrinsic or peripheral proteins and can be easily removed.
- Some membrane lipids and integral proteins remains bound to oligosaccharides which project into the extracellular fluid and influence the manner in which cells interact with one another.
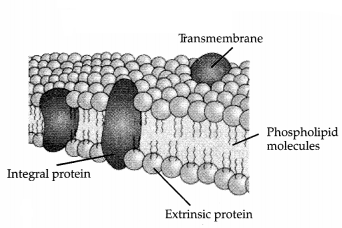
(c) Hydrophobic interactions.
OR
(a) Yes, plastids can be species-specific
region. Plastids are present in plants cells and they are also present in some
species of phylum Prostista e.g. Euglenoids.
(b) On the basis of pigments present in them, plastids are of the following three types:
- Leucoplasts: Leucoplasts are colourless plastids. They are found in storage cells of roots, seeds and underground stems. They take part in the storage of food. Leucoplasts are of three types depending on the storage products: amyloplasts stores starch, Aleuroplasts stores protein while elaioplasts stores oil and fat.
- Chromoplasts: They are coloured plastids. The colour varies from red, orange, yellow etc., due to the presence of carotenoids. They are mostly found in flowers and fruits. They provide colouration to organs for attracting pollinators.
- Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts are green colour plastids, found in the mesophyll cells of the leaves. The green colour is due to the presence of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll traps the solar energy which is used for manufacturing food. They are the sites of photosynthesis. So, chloroplasts are the “Kitchen of the cells”.
(c) Yes, plastids are interchangeable in their form. Generally, three types
of plastids are present in plant cells, i.e., leucoplasts, chromoplast and
chloroplasts.
Depending upon the condition and maturity stage, one type of
plastid can get converted into another plastid.
For example:
- In capsicum, the cells of ovary consist of leucoplasts. When ovary changes into fruit, leucoplasts are transformed into chloroplasts. When the fruit ripens, chloroplast are converted into chromoplast.
- In stem tubers of potato, the leucoplast, on exposure to sunlight transform into chloroplasts.
- In some cases, the chloroplast gets converted into chromoplast during the ripening of fruits, e.g., change of colour from green to red during the ripening of tomato and chili.
Question 33.
An organism has two pair of chromosomes (i.e., chromosome
number = 4). Diagrammatically represent the
chromosomal arrangement during
different phases of meiosis-II.
OR
Describe the structure of DNA proposed
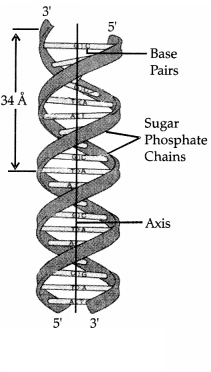
by Watson and Crick.
Answer:
The chromosomal arrangement during different
phases of meiosis-II.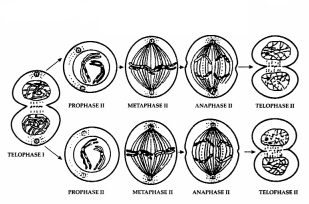
Based on X-ray diffraction, Watson and Crick in 1953, proposed a double helical
model of DNA.
The model proposed that:
- Each DNA molecule consists of two helical polynucleotide chains or strands.
- The strands run anti-parallel i.e., their 3′-5′ phosphodiester bonds are in opposite direction and the 3′ end of one strand lies besides the 5′ end of the other.
- In each polynucleotide chain, the phosphate molecules lie on the outer side of deoxyribose and the nitrogenous bases inward, perpendicular to the helical axis.
- The nitrogenous bases of two strands are linked through hydrogen bonds. Base pairing is specific. (Adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine)
- There are two hydrogen bonds between A = T and three between G ≡ C.
- Length of H – bond is 3Å. Two strands are therefore complementary.
- One turn of helix is about 34Å and contains 10 nucleotides.
- The distance between the adjacent nucleotide is 3.4 Å.
- The diameter of helix is about 20Å.
- In a DNA molecule, the two complementary chains are twisted to form double helix around a common central axis.