CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology Set-1
Class 11thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology Set-1
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology Set 1 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section – A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section – B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section – C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section- D has 2 case – based questions of 4 marks each; and Section – E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
Section – A
Question 1.
As we go from species to kingdom in a taxonomic hierarchy, the
number of common characteristics: (1)
(A) Will decrease
(B) Will
increase
(C) Remain the same
(D) May increase or decrease
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: The maximum similarities occurs in
species which is the lowest category,. Similarly as we go lower to higher the
number of characters will decrease.
Question 2.
Holdfast, stipe and frond constitute the plant body in case
of: (1)
(A) Rhodophyceae
(B) Chlorophyceae
(C) Phaeophyceae
(D) All
of the above
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: In
Phaeophyceae the plant body is often differentiated into a holdfast, a stalk and
stipe.
Question 3.
Match the following and choose the correct option. (1)
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Family | (i) Tuberosum |
| (b) Kingdom | (ii) Polemoniales |
| (c) Order | (iii) Solanum |
| (d) Species | (iv) Plantae |
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v)
(a) (a) (iv), (b) (iii), (c) (v), (d) (ii), (e)
(i)
(b) (a) (v), (b) (iv), (c) (ii), (d) (i), (e) (iii)
(c) (a) (iv), (b)
(v), (c) (ii), (d) (i), (e) (iii)
(d) (a) (v), (b) (iii), (c) (ii), (d) (i),
(e) (iv)
Answer:
Option (B) is correct.
Question 4.
During anaphase-I of meiosis: (1)
(A) Homologous
chromosomes separate
(B) Non-homologous autosomes separate
(C) Sister
chromatids separate
(D) Non-sister chromatids separate
Answer:
Option
(A) is correct
Explanation: During Anaphase -I of meiosis stage homologous
chromosomes breaks their connections with each other and get separated. This
separation is called disjunction.
Question 5.
A hormone responsible for normal sleep-wake cycle is: (1)
(A) Epinephrine
(B) Gastrin
(C) Melatonin
(D) Insulin
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Melatonin hormone is secreted by pineal
gland and regulate the sleep- wakefulness cycle so it is also called sleep
hormone.
Question 6.
Which among the following a cell which does not exhibit
phagocytic activity: (1)
(A) Monocytes
(B) Neutrophils
(C) Basophil
(D) Macrophage
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Phogocytes
are the cells which can kill or damage the foreign cells in blood monocytes ,
neutrophils and macrophages have this ability but basophil do not have this
function.
Question 7.
Knee joint and elbow joints are examples of: (1)
(A) Saddle
joint
(B) Ball and socket joint
(C) Pivot joint
(D) Hinge joint
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: There are several joints
present in our skeleton system out of these Hinge joint allows movement only in
one direction, such as knee and elbow joints.
Question 8.
Filtration of the blood takes place at: (1)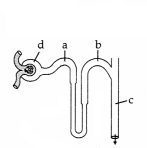
(A) a
(B) b
(C) c
(D) d
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: In the given diagram part D which is Glomerulus ensure the
filtration of blood carried out by renal arties.
Question 9.
Which one of the following is oviparous? (1)
(A)
Platypus
(B) Flying fox (Bat)
(C) Elephant
(D) Whale
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: Platypus is an example of egg laying
mammal or showed oviparity.
Question 10.
A nerve impulse leaves a neuron via the: (1)
(A)
Dendrites
(B) Axon
(C) Cyton
(D) Nucleus
Answer:
Option (B) is
correct.
Explanation: A neuron is a special type of tissues found in nervous
system, for conduction of impulses from sense organ to the brain and vice versa.
Axon send the messages through neurotransmitters by the process of synapse.
Question 11.
Which of the following statements is true for a secretory
cell? (1)
(A) Golgi apparatus is absent.
(B) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
(RER) is easily observed in the cell.
(C) Only Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
(SER) is present.
(D) Secretory granules are formed in the nucleus.
Answer:
Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: RER (Rough endoplasmic
reticulum) have an important role in secretion and protein synthesis.
Question 12.
Name the pigment whose absorption spectrum is not represented
through the following graph. (1)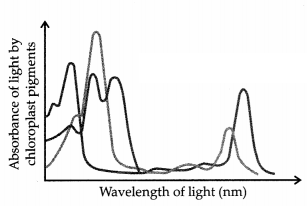
(A) Chlorophyll b
(B) Carotenoids
(C) Chlorophyll a
(D) Xanthophyll
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is
followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(A) Both
Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation
of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason
(R) is NOT the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is
true but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is
true.
Question 13.
Assertion (A): Glucagon is known as a hyperglycemic hormone.
(1)
Reason (R): Glucagon stimulates the liver to convert stored glycogen into
glucose and increases the level of blood glucose.
Answer:
Option (A) is
correct.
Explanation: Glucagon is known as a hyperglycemic hormone because
glucagon stimulates the liver to convert stored glucagon into glucose and
increases the level of blood glucose.
Question 14.
Assertion (A) : Human skull is described as dicondylic.
(1)
Reason (R) : It articulates with the first vertebrae of the vertebral
column by means of two occipital condyles.
Answer:
Option (A) is
correct.
Explanation: Human skull is described as dicondylic because it
articulates with the first vertebrae of the vertebral column by means of two
occipital condyles.
Question 15.
Assertion (A) : Palmitic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid.
(1)
Reason (R) : These are fatty acids without double bond.
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: Palmitic acid is a saturated fatty acid.
These are fatty acids without double bond.
Question 16.
Assertion (A): Hypothalamus is called “thermostat” of the
body. (1)
Reason (R): It keeps body temperature at roughly 37°C by means of a
complex thermostat system.
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation:
Hypothalamus is a thermoregulatory centre. Hence, it is called the “thermostat”
of the body. It keeps body temperature at roughly 37°C using a complex
thermostat system.
Section – B
Question 17.
Why have unicellular algae not been kept in kingdom Protista
by Whittaker? (2)
Answer:
A distinction between unicellular and
multicellular organisms is not possible in case of algae. It is because of this
unicellular green algae have not been included in kingdom Protista by
Whittaker.
Question 18.
Study the given diagram: (2)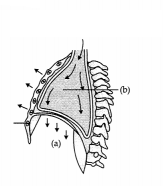
(a) Name the process shown in the above diagram.
(b)
Identify the labelling (a) and (b).
Answer:
(i) Inspiration
(ii) (a)
Diaphragm
(b) Volume of thorax increased.
Question 19.
Label the parts in the following diagram. (2)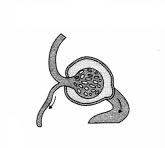
(a) Afferent arteriole,
(c) Bowman’s capsule,
Answer: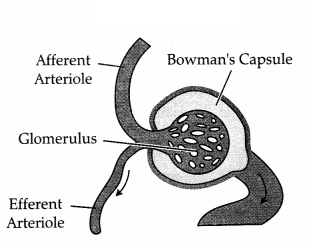
Question 20.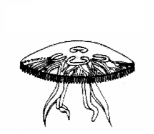
(a) Identify the given animal, and write down the name of the
phylum to which it belongs.
(b) Give some more examples of this phylum
(2)
Answer:
(a) Aurelia, Phylum- Coelenterata (Cnidaria)
(b) Hydra,
Adamsia, etc.
Question 21.
A student got injured someday. He took the medicine from the
doctor and got cured. He wonders that how medicine got to know where to act. He
asks the doctor about the reason. What could be the possible reason according to
you? (2)
OR
(a) Label the given diagram .
(b) Determine the stage at
which this structure is visible.
Answer:
Every cell membrane has some receptor over it, which perceives the
drugs and this stimulate cascade effects in the cell and hence, the disease can
be cured.
OR
(a) 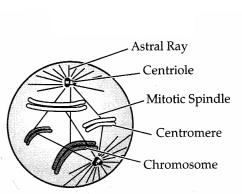
(b) The given structure shows the transition from prophase to
metaphase.
Section – C
Question 22.
(a) What are the various types of nitrogenous bases found in
DNA? (3)
(b) Name the type of bond seen between –
(i) two nitrogen
bases of DNA and
(ii) phosphate and hydroxyl group of sugar of DNA.
Answer:
(a) Types of nitrogenous bases found in DNA are:
- Adenine: Abbreviated as ‘A’, has a 2-ring structure, so that it is a purine.
- Thymine: Abbreviated as ‘T’, is a pyrimidine, which means it has a 1-ring structure. It is only present in DNA, where it pairs with adenine.
- Guanine: Abbreviated as ‘G’, is part of both DNA, where it bonds with cytosine.
- Cytosine: Abbreviated as ‘C’, is part of DNA and bonds with guanine. It has one ring, so it’s a pyrimidine.
(b)
(i) Hydrogen bond
(ii) Phosphodiester bond
Question 23.
Describe the habit, habitat and morphology of mosses. (3)
Answer:
Habit, habitat and morphology of moss:
- These are the good example of leafy bryophyte. It grows in moist shady places.
- The plant (2.3 cm in height) has a tiny stem with a number of small leaves.
- The true roots are absent but rhizoids fix the plant to the ground and perform the functions of roots.
- The leaves and stem portion bear chlorophyll with the help of which it manufactures food.
- The adult plant represents the gametophyte.
- It bears antheridia and archegonia which produce antherozoids (male gametes) and egg.
- Fertilisation takes place inside the archegonium.
- The zygote formed by the fusion of the two gametes develops into a sporophyte.
- It grows and consists of three parts: foot, seta and capsule.
Question 24.
Analyse the events during every stage of cell cycle and
notice how the following two parameters change. (3)
(a) Number of chromosomes
(n) per cell
(b) Amount of DNA content
(c) per cell
Answer:
(a)
- In G1 phase, the number of chromosome (N) per cell remains the same.
- In S or synthetic phase of cell cycle, DNA synthesis or the replication occurs. The amount of DNA per cell doubles. If it is 2C then it becomes 4C. There is no increase in chromosome number.
- Same above condition continues in G2– phase.
- In M-phase the sister chromatids separate and move to different cells but the number of chromosomes remain the same in mitosis.
(b)
- In G1-Phase, the amount of DNA content (c) per cell remains same.
- In S-phase it is doubled due to DNA replication.
- It remains double in G2-phase.
- It is halved in M-phase of the cell cycle. Shoot apex
Question 25.
Label the diagram. (3)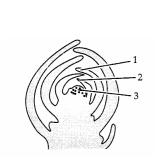
(a) Given diagram represent which part of a dicotyledonous plant?
(b) What
will happen if we remove part 1 from the plant?
Answer:
(i) Shoot
apex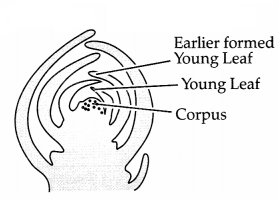
(ii) Removal of shoot apex will help to overcome apical
dominance. As a result, the lateral buds grow faster, giving rise to branches
and give the plant a bushy appearance.
Question 26.
Does it make any difference to have the haemoglobin in the
corpuscles rather than in plasma? Explain. (3)
Answer:
There is great
difference in respects of efficiency of carrying the oxygen from respiratory
organs to the body tissue as follows:
| Haemoglobin in corpuscles | Haemoglobin in plasma |
| As RBC are small, rounded and in more quantity, so haemoglobin is exposed with a large combined surface area to absorb O2 | In plasma, the exposed surface area for haemoglobin is very limited in comparison to the RBC, the result is the absorption of O2 in less amount. |
Question 27.
Certain plants growing in tropical region suffer from
photorespiratory loss. (3)
(a) How do they overcome it?
(b) Mention the
anatomical adaptation.
(c) Mention the first stable C02 fixation
product and the enzyme responsible for it.
OR
Enzymes are biological
catalysts which accelerate chemical reactions. They are essential for different
physiological processes. They are proteins that helps to speed up the process of
metabolism.
(a)
(i) Name the enzyme that catalyses carboxylation as well
as oxygenation reaction.
(ii) In which cell organelle is this enzyme
found?
(b) In what way is that organelle different in the mesophyll and
bundle sheath cells ?
Answer:
(a) Plants like sugarcane, and maize shows a
C4 pathway for CO2 fixation during photosynthesis to
overcome the problem of photorespiration which is energy consuming process.
(b) These plants have kranz anatomy. In kranz’s anatomy, the mesophyll is undifferentiated and its cells occurs in concentric layers around vascular bundles. Vascular bundles are surrounded by large-sized bundle sheath cells. The chloroplast of mesophyll cells are smaller and perform light reactions of photosynthesis and also possess PEPcase for CO2 fixation.
(c) The first stable product of the C4 pathway is oxaloacetic
acid. The enzyme responsible for the fixation of atmospheric CO2 is
PEP carboxylase (Phosphoenol pyruvate carboxylase).
OR
(a) (i) RubisCO
enzyme catalyses carboxylation and oxygenation reactions.
(ii) It is found in
the chloroplast (cell organelle).
(b) Chloroplasts in mesophyll cells are granal but chloroplast of bundle sheath cells are agranal. Granal chloroplasts have thylakoids stacked to form grana (as in C3 plants). Agranal chloroplasts are without grana but thylakoids are found as stroma lamellae.
Question 28.
Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. (3)
Answer:
| S. No. | Endocrine glands | Exocrine glands |
| (i) | They do not have ducts. | They possess ducts. |
| (ii) | They secrete hormones directly into the blood. | They secrete their secretions into ducts. |
| (iii) | Thyroid, hypothalamus, pituitary, etc. | Sweat and oil glands (of skin), liver and salivary glands. |
Section – D
Question 29.
Animals belonging to the phylum Chordata possess three
characteristic features (4)
(a) What are the three fundamental features of
chordates?
OR
Give an example of Urochordata and Cephalochordata?
(b)
Identify the labelling (i), (ii), (iii), (iv).
(c) What is the position of
the heart in chordates?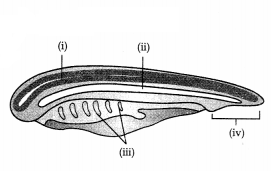
Answer:
(a) (i) Presence of notochord.
(ii) A dorsal
hollow nerve cord.
(iii) Paired pharyngeal gill slits.
OR
Example –
Urochordata- Doliolum
Cephalochordata – Branchiostoma.
(b)
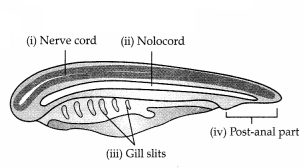
(c) Heart is ventral in position.
OR
(a) As we go from species to
kingdom in a taxonomic hierarchy, the number of common characteristics will
decrease.
(b) ‘-Ales’ is the suffix used for the order, ‘-one is the suffix used for class,’ – Aceae’ is the suffix used for family, and ‘-Ae’ is the suffix used for division in the classification of plants.
(c) Phylum in the classification of animals is equivalent to the division level in the classification of plants.
Question 30.
Mitosis takes place both in somatic and reproductive cells of
plants and animals. In multicellular organisms, mitosis produces more cells for
growth and repair. Mitosis division is responsible for the growth and
development of a single-celled zygote into a multicellular organism. Mitosis
division helps in maintaining the proper size. Mitosis also helps in restoring
wear and tear in body tissues, replacing damaged or lost part, healing wounds
and regeneration of detached parts. Mitosis is a method of multiplication of
unicellular organisms. It produces diploid daughter cells with identical genetic
complements (both quantitatively and qualitatively) as in the parent cell.
Mitosis is a continuous process and it is divided into four phases viz: prophase
metaphase, anaphase and telophase. (4)
(a) What is the significance of
mitosis?
(b) What happens during the mitotic cell division?
(c) What is
the characteristic feature of mitosis?
OR
Proteins are polypeptide chains
made up of amino acids. There are 22 types of amino acids joined together by
peptide bonds when carboxylic groups two amino acids: Essential and
non-essential amino adds. The Primary structure of a protein is the linear
sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. The first amino acid of the
enzyme is called a terminal acids and the last amino acid of the peptide is
called C-terminal amino acid. The secondary structure proteins forms a helix.
There are three types of secondary structure: a helix, p pleated and collagen
helix. In tertiary structure long protein chain is folded upon itself like a
hollow woollen ball to give three dimensional view of the protein. In quaternary
structure, each polypeptide develops its own tertiary structure and function as
a subunit of protein.
(a) Amino acids, as the name suggests, have both an amino group and a
carboxyl group in their structure. In addition, all naturally occurring amino
acids (those which are found in proteins) are called L-amino acids. From this,
can you guess from which compound the simplest amino acid can be made?
(b)
Many organic substances are negatively charged e.g., acetic acid, while others
are positively charged e.g., ammonium ion. An amino acid under certain
conditions would have both positive and negative charges
simultaneously in
the same molecule. Name such form of amino acid.
(c) A primary protein
normally have how many ends?
(d) Name the bond present in the tertiary
structure of a protein contain.
Answer:
(a) Mitosis is an equational
division and is a means of multiplication in unicellular organisms.
(b) Daughter cells formed have the same genetic constitution as the qualitatively and quantitatively and as the parent cell.
(c) Mitosis is an equational division. Daughter cells formed are genetically
identical and similar to the mother cell. Number of chromosomes remain the same
in parental and progeny cell.
OR
(a) Glycine is the simplest amino acid
which has both an amino group of a carboxyl group in its structure and a single
hydrogen atom as its side chain.
(b) Explanation: Under certain conditions, an amino acid may have both positive and negative charges simultaneously in the same molecule. Such a form of amino acid is known as zwitter ionic form.
(c) Primary protein is simply an amino acid sequence that has two ends, the carboxyl amino terminals.
(d) Tertiary structure of protein is maintained by several types of bonds such as hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, sulphide bonds, and hydrophilic and hydrophobic bonds formed between the part of a polypeptide and another.
Section – E
Question 31.
Calvin cycle occurs in all photosynthetic plants whether they
have C3 or C4 pathways. With the help of photosynthesis,
plants turn light, carbon dioxide, and water into sugars that fuel plant growth
using the primary photosynthetic enzyme RuBisCO. Various plant species on Earth
use C3 photosynthesis, and some show C4. (5)
With context to the given paragraph complete the following table :
| Characteristics | C3 Plants | C4 Plants |
| Place of photosynthesis: | ||
| CO2 acceptor: | ||
| Kranz anatomy: | ||
| 1st stable product: | ||
| Optimum temperature: | ||
| Photorespiratorv loss: |
OR
In relation with the Calvin cycle and photorespiration complete the
following table, defining carboxylation and oxygenation:
| Characteristics | Carboxylation | Oxygenation |
| Define: | ||
| First step of the cycle: | ||
| Acceptor molecule: | ||
| Process: |
Answer:
| S.No. Characteristics | C3 Plants | C4 Plants |
| Place of photosynthesis | Photosynthesis occurs in mesophyll tissues | Photosynthesis occurs both in mesophyll and bundle sheath cells |
| C02 acceptor | The carbon dioxide acceptor is RuBisCO. | The carbon dioxide acceptor is PEP carboxylase. |
| Kranz anatomy | Kranz anatomy is absent. | Kranz anatomy is present. |
| 1st stable product | The 1st stable compound formed is 3 C compound called 3-Phospho glyceric acid (PGA). | The 1st stable corn-pound is carbon oxaloacetic acid (OAA). |
| Optimum temperature | The optimum temperature is 20 – 25°C. | The optimum temperature is 35 – 44°C. |
| Photo respiratory loss | Photo- respiratory loss is high. | Photorespiration does not take place. |
OR
| Characteristics | Carboxylation | Oxygenation |
| Define | Fixation of CO2 is called carboxylation. | The activity of RuBP to catalyse the combination of O2 with RuBP is oxygenation |
| First step of the cycle | It is the first step of Calvin cycle (C3 in biosynthetic phase). | The oxygenation of RuBP in the presence of O2 is the first reaction of photo-respiration. |
| Acceptor molecule | Ribulose 1, 5 bisphosphate is acceptor molecule in it. | The initial acceptor molecule is RuBP. |
| Process | Ribulose 1, 5 bisphosphate combines with a molecule of C02in the presence of light regulated enzyme RuBP carboxylase | The photo-respiration is initiated in the chloroplasts in light only. The oxygenation of RuBP occurs in the presence of O2 |
Question 32.
Each of the following terms has some anatomical significance.
What do these terms mean? Explain with the help of
line diagrams. (5)
(a)
Plasmadesmoses/Plasmodesmata
(b) Middle lamella
(c) Secondary wall
OR
Flowers are determinate structures with a typically defined number of
organs bearing pistillate and staminate parts. Floral formula helps to remember
the characteristics of different families.
(a) What is a floral diagram ?
(b) What special features does a floral diagram inform?
(c) Write down the
floral formula for the family “Solanaceae”.
Answer:
(a) Plasmodesmata:
These are cytoplasmic bridges between the two cells through the cell wall. They
form a protoplasmic continuum called symplast. It allows communication and
transport between two neighboring cells.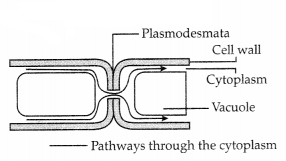
(b) Middle lamella: It is a thin layer in the cell wall
mainly made up of calcium pectate. It performs the function of cementing between
the two neighboring cells.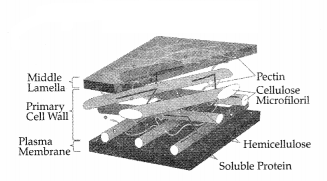
(c) Secondary’ wall: It is the non-extensible layer made up of hemicellulose
fibres, in the cell wall of plant cells. It
provides rigidity to the cell
wall in plant
OR
(a) A floral diagram is the diagrammatic representation of the ground part
of a flower illustrating the number, arrangement and inter-relationship of
various floral parts.
(b) The special features depicted by a floral diagram are-
- Symmetry of the flower.
- Sex of the flower.
- Bracts present or absent, bracteoles present or absent; position of bracts and bracteoles in relation to other floral parts;
- Number of floral whorls.
- Number of floral parts.
- Position of odd sepal or odd petal, if the number of sepal or petal is odd.
- Aestivation of sepals and petals.
- Number of stamens arranged in one or more than one whorl, their position in relation to petals, attachment of stamens with petals of free, adelphous condition, monothecous or dithecous, extrose or introse.
- Number of carpels, free or fused, number of locules, number of ovules in each locule, tyPe °f placentation, and any special feature.
- Position of floral parts in relation with the mother axis.
(c) The floral formula for the family ” Solanaceae” is –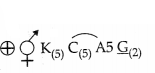
Question 33.
(a) (i) What is root? (5)
(ii) Briefly explain the regions
or parts present in a typical root.
OR
(b) (i) What is venation
(ii)
Explain its types.
Answer:
(a) (i) Root:
The root is a non-green,
cylindrical descending part of the plant that normally grows downwards into the
soil.
(ii) A typical root possesses five parts or regions:
- Root Cap: It is a thimble-shaped or cap-like, structure present at the tip of the root. It protects the tender apex of the root as it makes its way through the soil.
- Growing or meristematic zone: It lies above the root cap. The cells of this zone divide actively and add new cells to the root and root cap.
- Zone of elongation: It lies behind the meristematic zone. The cells of this region are newly formed cells, which lose the power of division. These also possess the power of absorption of water from the soil.
- Zone of root hair: It lies above the region of elongation and bears clusters of very fine tubular outgrowths called root hairs. This zone is also called the zone of differentiation because different types of primary tissues mature in this region.
- Zone of maturation: This region forms the major part of the root and no change occurs in this region. It forms the permanent zone of the root and also gives out lateral roots.
OR
(b) (i) Venation: The arrangement of veins and veinlets in the lamina
of a leaf is called venation. The veins are not only the conducting channels for
water, minerals, and organic food, but they also provide firmness to the lamina
and keep it expanded. They give rise to lateral veins, which traverse the entire
lamina.
(ii) Venation is of two types: Reticulate and parallel.
- Reticulate venation: When the veinlets form a network, the venation is termed reticulate venation, e.g., leaves of dicot plants.
- Parallel venation: When the veins arising from midrib or main veins, run parallel to each other towards the margin or the apex of the lamina, venation is termed as parallel venation. Present in the leaves of monocot plants. Parallel venation is of two sub-types:
- Pinnate or unicostate parallel venation:
The lamina has a single prominent vein or midrib running from the base to the apex of the lamina, e.g., Banana, Canna, etc. - Palmate or multicostate parallel venation: The lamina has several principal veins arising from the base and running towards the apex or margin of the lamina.