Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
Class 11th Biology NCERT Book Solution
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom
NCRT TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED
1.What are the difficulties
that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features
are not taken into account?
soln.
The common fundamental features used for classifying animals include body
symmetry, arrangement of cells, nature of coelom, level of organisation. Animal
classification would be very confusing if fundamental features are not
considered.
(i)Animals having different levels of organisation would have
been placed in same group. E.g., Sponges and Cnidarians having cellular and
tissue level of organisation respectively.
(ii)Animals showing varied types
of germinal layers would have been placed together, as diploblastic cnidarians
and triploblastic platyhelminthes.
(iii)Animals having different body
symmetry would have been placed together, as coelenterates with radial symmetry
and platyhelminthes with bilateral symmetry.
(iv)There would have been no
classification of animals based on with or without body cavity..
(v)Placing
of oviparous and viviparous animals together.
2.If you are given a
specimen, what are the steps that you would follow to classify
it?
soln. Various steps
considered to classify a specimen are:
(i)Mode of nutrition – It can be
autotrophic, holozoic, saprophytic or parasitic.
(ii)Complexity of body
structure – Whether the specimen is unicellular or multicellular.
(iii)Presence or absence of membrane bound organelles.
(iv)Body symmetry,
i.e., the plane by which organism can be divided into two equal halves.
(v)Presence or absence of coelom, it can be acoelomates, pseudocoelomates,
eucoelo- mates.
(vi)Phylogenetic relationship.
More Resources for CBSE Class 11
3.How useful is the study of
the nature of body cavity and coelom in the classification of
animals?
soln. Organisms can be
classified according to presence or absence of the coelom. The body cavity,
which is lined by mesoderm is called coelom. Animals possessing coelom are
called coelomates, e.g., annelids, molluscs, arthropods, echinoderms,
hemichordates and chordates. In some animals, the body cavity is not lined by
mesoderm, instead, the mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the
ectoderm and endoderm. Such a body cavity is called pseudocoelom and the animals
possessing them are called pseudocoelomates, e.g., aschelminthes. In
pseudocoelomates, body cavity is derived from blastocoel of the embryo. The
animals in which the body cavity is absent are called acoelomates, e.g.,
platyhelminthes.
4.Distinguish between
intracellular and extra-cellular digestion.
soln.
Differences between intracellular and extracellular digestion are: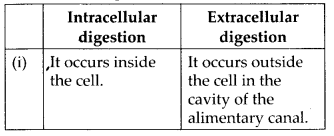
5.What is the difference
between direct and indirect development?
soln.
Differences between direct development and indirect development are :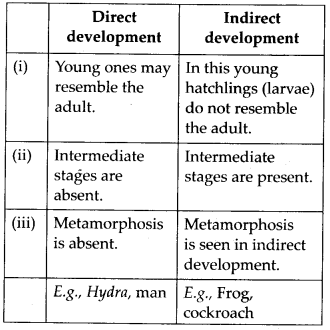
6.What are the peculiar
features that you find in parasitic platyhelminthes?
soln.Following are the
peculiar features of parasitic platyhelminthes:
(i) The thick tegument (body
covering) resistant to the host’s digestive enzymes and anti-toxins.
(ii)Adhesive organs like suckers in flukes and the hooks and suckers in
tapeworms for a firm grip on or in the host’s body.
(iii)Loss of locomotory
organs.
(iv)Digestive organs are absent in tapeworms because digested and
semidigested food of the host is directly absorbed’ through the body
surface.
(v) Reproductive system is best developed in parasitic
flatworms.
(vi)Parasitic flatworms, such as liver fluke and tapeworms perform
anaerobic respiration.
(vii)They possess a considerable osmotic adaptability,
as they can successfully live in different media.
7.What are the reasons that
you can think of for the arthropods to constitute the largest group of the
animal kingdom?
soln. Arthropods are most
successful animals and constitute the largest group of the animal kingdom. They
have conquered land, sea and air and make up over three fourth of currently
known living and fossil organisms. They range in distribution from deep sea to
mountain peaks. Thick, tough, non-living chitinous cuticle forms the exoskeleton
which protects the organism from predators, help to withstand temperature upto
100°C or more and prevents water loss. They have ability to reproduce very fast
and less time is needed for young ones to hatch from their eggs. Due to
metamorphosis, there is less competition among larval and adult forms for food.
Cockroaches can even survive nuclear radiations and poisoned earth. All these
factors made arthropods the largest phylum among animals.
8.Water
vascular system is the characteristic of which group among the following
?
(a)
Porifera
(b)
Ctenophora
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Chordata
soln. (c)
Echinodermata
9.”All vertebrates are
chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates”. Justify the
statement.
soln. Chordates are the
animals that possess notochord (a stiff, supporting rod like structure present
on the dorsal side) at some stage of their lives. Phylum Chordata is divided
into three Subphyla: Urochordata or tunicata, Cephalochordata and Vertebrata.
Subphyla Urochordata and Cephalochordata are often referred to as protochordates
and are exclusively marine. In urochordata, notochord is present only in tail of
larva and disappears in adults, while in cephalochordata, it extends from head
to tail region and persists throughout the life.
The members of Subphylum
Vertebrata a possess notochord during the embryonic period and is replaced by a
cartilaginous or bony vertebral column in the adult. Thus all vertebrates are
chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
10.How important is the
presence of air bladder in
Pisces?
soln. Bony fishes have a
sac-like outgrowth, the swim bladder also called air bladder, that arises as an
outgrowth from the dorsal wall of oesophagus. It is hydrostatic in function. It
regulates buoyancy and helps them to swim up and down, thus preventing them from
sinking. In some species air bladder also helps in respiration. It also serves
as resonating chamber to produce or receive sound.
11.What are the modifications
that are observed
in birds that help them
fly?
soln. Birds have adapted
to aerial mode of life through the following modifications:
(i) Body is
streamlined and spindle shaped which minimise resistance to the wind.
(ii)Body is covered with feathers. It reduces the friction, prevent loss of heat
and help to maintain constant temperature.
(iii)Forelimbs are modified into
wings, which help during flight.
(iv)Flight muscles are greatly developed
(v) Most of the bones are pneumatic, hollow and filled vvith air which makes the
body lighter and helps in flight.
(vi)Birds are warm-blooded. They maintain a
high body temperature (40° – 46°C). This is necessary for flight.
(vii)Heart
is four-chambered and functions efficiently with double circulation.
(viiiJAir sacs are present which act as reservoir of air and helps in
temperature regulation
(ix)Urinary bladder is absent (except in Rhea) and
only one ovary is present which reduces the weight, which is essential for
flight.
12. Could the number of eggs
or young ones produced by an oviparous and viviparous mother be equal?
Why?
soln. No, the number of
eggs or young ones produced by an oviparous and viviparous mother respectively
cannot be equal. Oviparous mother lays large number of eggs, as the eggs are
laid outside the body, so they are not protected from predators and harsh
environmental conditions, and therefore destroyed. However in viviparous mother,
eggs are not laid outside, but the embryos develop inside the mother and thus
are protected from the outside harsh environment, thus, the number of eggs
produced are less. Therefore, the number of eggs or young ones produced by an
oviparous and viviparous mother respectively cannot be equal.
13.Segmentation in the body
is first observed in which of the following?
(a) Platyhelminthes
(b)
Aschelminthes
(c) Annelida
(d)
Arthropoda
soln. (c) Annelida
14.Match the
following:
(a) Operculum (i) Ctenophora
(b) Parapodia (ii)Mollusca
(c) Scales (iii)Porifera
(d) Comb plates (iv)Reptilia
(e) Radula (v) Annelida
(f) Hair (vi)Cyclostomata and
Chondrichthyes
(g) Choanocytes
(vii)Mammalia
(h) Gill slits (viii
Osteichthyes
soln.(a) – (viii), (b) –
(v), (c) – (iv), (d) – (i),
(e) – (ii), (f) – (vii), (g) – (iii), (h) –
(vi).
15. Prepare a list of some
animals that are found parasitic on human beings.
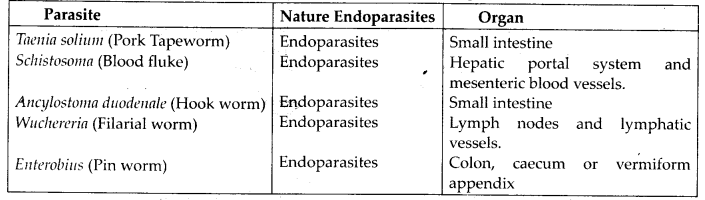
soln.List of some animals
that are found parasitic on human beings :