CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-9
Class 10thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-9
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 9 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
- Question paper comprises five Sections – A, B, C, D, and E. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section C contains Q.25 to Q. 29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each, Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no. from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section
A
Section A consists of 20
questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below. (1)
Assertion (A) By the
17th century, the use of print diversified in China because of a blooming urban
culture.
Reason (R) The Imperial Statç in China was the major producer of
printed materials.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct
explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct
explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is
true
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct
explanation of A
Question 2.
Which of the following social reformers fought against the
caste system?
(a) Jyotiba Phule
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(c) B. R.
Ambedkar
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 3.
Which of the following options is/are correct about Balkan
nationalism? (1)
I. The Balkan region became part of the conflict because of
the Ottoman Empire.
II. The region comprised of ethnic groups including
Greeks, Serbs, Montenegro, etc.
III. British and ethnic nationalities
struggled to establish their identity.
Codes
(a) I and II
(b) II and
III
(c) Only II
(d) Only I
Answer:
(a) I and II
Question 4.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
I. The IMF
and the World Bank started their financial operations.
II. The US became a
colonial power by taking over some colonies which earlier held by Spain.
III.
Due to the efforts of Indian nationalist leaders, the system of indentured
labour was abolished.
IV. The big European powers met in Berlin to complete
the carving up of Africa between them.
Options:
(a) I, III, IV, II
(b)
II, IV, III, I
(c) IV, II, III, I
(d) I, II, III, IV
Answer:
(c) IV,
II, III, I
Question 5.
The following image is the personification of Germany corn mon
1v associated with the Romantic Era and the Revolutions of 1848.
Identify its
name from among the following options. (1)
(a) Marianna
(b) Philip Viet
(c) Germania
(d)
Laltalia
Answer:
(c) Germania
Question 6.
Which subjects are included in the Concurrent List?
(a)
National Importance
(b) State importance
(c) Both national and state
importance
(d) Local Importance
Answer:
(c) Both national and state
importance
Question 7.
The piece of land left uncultivated For the past 1 to 5
agricultural veau’s is called .. (1)
(a) barren land
(b) forest land
(c) grazing land
(d) fallow land
Answer:
(d) fallow land
Question 8.
Consider the following statements regarding caste in politics
and identify the incorrect one from the following:
(a) Caste in politics
always produces positive results.
(b) The caste factor played an important
role in the formation of the Central Government.
(c) Social reformers and
laws have played an important role in reducing casteism.
(d) Routes of
casteism are visible in our society from ancient times.
Answer:
(a) Caste
in politics always produces positive results.
Question 9.
Which one of the following conferences was convened to discuss
environmental protection and sod economic development
at the global level in
1992? (1)
(a) Kyoto Protocol
(b) Montreal Protocol
(c) Rio de Janeiro
Earth Summit
(d) World Summit on Sustainable Development
Answer:
(c)
Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit
Question 10.
‘Coming together federation’ is not found in ………………………
(a)
India
(b) U.S.A.
(c) Switzerland
(d) Australia
Answer:
(a)
India
Question 11.
Identify the significant reason for power sharing from the
following options. (1)
(a) Reduces socio-economic conflicts
(b) provides
ethnic-cultural development
(c) Allows people to enjoy specific rights
(d)
Restricts supremacy of one party.
Answer:
(a) Reduces socio-economic
conflicts
Question 12.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below.
Assertion (A): Workers
in organised sectors enjoy security of employment.
Reason (R): Organised
sector is registered by the government and have to follow the rules and
regulations which are given in laws such as Factories Act, and Minimum Wages
Act.
Options:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct
explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct
explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct, but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is
wrong, but (R) is correct.
Question 13.
Consider the following statements and choose the incorrect
option.
(a) Democracy promotes equality among citizens.
(b) Democracy
enhances the dignity of the individual.
(c) Democracy provides a method to
resolve conflicts.
(d) Democracy does not have enough room to correct
mistakes.
Answer:
(d) Democracy does not have enough room to correct
mistakes.
Question 14.
Arrange the following in the correct sequence:
(i)
Transporting paper to factory
(ii) Sale of books in the bookstore
(iii)
Printing of pages
(iv) Compilation of pages
Options:
(a) (iv), (iii),
(i), (ii)
(b) (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
(c) (ii), (i), (iii), (iv)
(d)
(iii), (ii), (iv), (i)
Answer:
(b) (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
Question 15.
Identify the correct statements about the theory of
Federalism in the Indian Constitution. (1)
Statement I The Constitution
declared India as a Union of States.
Statement II Sharing of power between
the Union Government and the State Government is basic to the structure of the
Constitution.
Statement III It is easy to make changes to this power-sharing
arrangement.
Statement IV The Parliament can on its change this
arrangement.
Codes
(a) Statement I and II are right
(b) Statemcnt II
and III are right
(c) Statement I and III are right
(d) Statement II and
IV are right
Answer:
(a) Statement I and II are right
Question 16.
Find the odd one out from the following:
(a) Iron ore,
Manganese, Nickel, Cobalt
(b) Copper, Lead, Tin, Bauxite
(c) Gold, Silver,
Iridium, Platinum
(d) Coal, Petroleum, Limestone, Natural gas
Answer:
(d) Coal, Petroleum, Limestone, Natural gas
Question 17.
Kamala owns a small flower shop near a temple. She wants to
expand her shop by keeping exotic flowers and flower bouquets.
To whom she
should approach for a very short-term credit? (1)
(a) Moneylenders as they
provide short-term credit.
(b) Banks as they charge low interest.
(c)
Cooperatives as they do not require collateral.
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Cooperatives as they do not require collateral.
Question 18.
Shivangi took a loan of 9 lakhs from the bank to purchase a
car. The annual interest rate on the loan is 12.5 percent and the loan is to be
repaid in 4 years in monthly instalments. The bank retained the papers of the
new car as collateral, which will be returned to Rita only when she repays the
entire loan with interest. Analyse the loan information given above, considering
one of the following correct options:
(a) Interest on loan
(b) Deposit
criteria
(c) Mode of repayment
(d) Terms of credit
Answer:
(d) Terms
of credit
Question 19.
According to 2017-2018 data, the share of different sectors
in employment (percentage) in India was (1)
| Primary Sector | 44 % |
| Secondary Sector | 25% |
| Tertiary Sector | 31% |
0ut of the three sectors, why is the ratio of employment in the primary
sector high?
(a) Workers in the primary sector are underemployed.
(b) Low
job opportunities in the secondary sector
(c) Efforts of labour are not
equivalent in all the sectors.
(d) Outsourcing of job opportunities in the
secondary sector.
Answer:
(a) Workers in the primary sector are
underemployed.
Question 20.
Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the
………………………………. of the borrowers is used to repay the loan.
(a) Collateral
(b) Expenses
(c) Earnings
(d) Savings
Answer:
(c) Earnings.
Section
B
Section B consists of 4
questions of 2 marks each
Question 21.
Why Martial law was imposed in Amritsar? (2)
Answer:
Martial law was imposed in Arnritsar because local leaders were picked up from
Ainritsar and Mahatma Gandhi was not allowed to enter Delhi. On 10th April, the
police in Amritsar fired upon a peaceful procession, provoking widespread
attacks on banks, post offices and railway stations,
Question 22.
Differentiate between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals.
OR
Differentiate between conventional and non-conventional sources of
energy.
Answer:
| Ferrous Minerals | Non-Ferrous Minerals |
| (i) These minerals have iron content. | These minerals do not have iron content. |
| (ii) For example, iron ore, manganese, cobalt, etc. | For example, copper, lead, bauxite, etc. |
OR
| Conventional Sources of Energy | Non-Conventional Sources of Energy |
| (i) These are the traditional sources of energy such as, fossil fuels, firewood, cattle dung cake, etc. | These are the recently developed sources of energy such as, solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy, etc. |
| (ii) They are exhaustible. | They are non-exhaustible. |
| (iii) They pollute the environment on a large scale. | They are environment-friendly. |
Question 23.
Write any one major difference between agro and mineral-based
industries. (2)
Or
what are minerals? Give two eatnp1es. Also, name two
carrier rocks of minerals. (1+1)
Answer:
Agro-based industries are those
industries that are dependent on agriculture to obtain their raw material. On
the other hand, mineral-based industries are those industries that are dependent
on mineral resources to obtain their raw material.
Or
The mineral is a
homogeneous naturally occurring substance that has a definable internal
structure. Minerals are important resources which are very useful for the
national economy. The two examples of minerals are coal and iron-ore, Two
carrier rocks of minerals are igneous and metamorphic.
Question 24.
Mention any two common developmental goals of the people.
Answer:
The two common developmental goals of the people are:
- Freedom and security
- Better living conditions
Section
C
Section C consists of 5
questions of 3 marks each
Question 25.
Study the pie chart properly and answer the following
questions (1+2)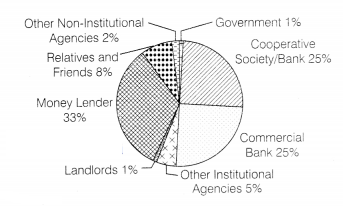
(i) What are the constituents of formal and informal sources of credit?
(ii)
Evaluate the credit features of cooperatives and banks.
Answer:
(i) Banks
and cooperative societies are the constituents of the formal sector and
moneylenders, friends and relatives, traders, landowners, large farmers, etc are
the constituents of informal sector.
(ii) The credit features of cooperative
and banks are as follows
Loan from Cooperatives This is the major source of
cheap credit in rural areas. Loans to member of cooperative societies can be
provided for the purchase of agricultural implements, cultivation and
agricultural trade fisheries, construction of houses and other expenses. Loan
from Banks Some farmes take loan for cultivation from banks, at very low
interest rates and at easy repayment terms. Banks also provide other facilities
to such borrower.
Question 26.
Why did Gandhiji decide to launch a nationwide Satyagraha
against the proposed Rowlatt Act 1919? Explain any three reasons.
OR
Analyse any three reasons for slowdown of the Non-Cooperation Movement in
cities.
Answer:
In 1919, Mahatma Gandhi aimed to initiate a nationwide
Satyagraha against the proposed nefarious Rowlatt Act (1919). The citizens of
India vehemently protested against the Black Act. Nevertheless, the Act was
passed and it empowered the government to subdue political activities.
- On 6th April, 1919, Gandhiji started a nationwide Satyagraha that garnered huge response. People from various cities supported the movement.
- Most of the leaders were selected from Amritsar. Gandhiji was prevented from entering Delhi.
- The colonial government detained the political prisoners without trial for two years.
OR
The Non-Cooperation Movement was initiated with the participation of
the middle-class stratum in cities and gained momentum. In the cities, the pace
of movement subsequently slowed down. The few reasons are enumerated as
follows:
- Khadi cloth was relatively more expensive than mass-produced mill cloth. Poor people could not afford to buy it.
- The boycott of British institutions posed a serious problem as substitute Indian institutions were unavailable.
- Students and teachers began to take positions in colonial government schools. At the same time, lawyers resumed their work in government courts.
Question 27.
Deepa. an 11-year-old girl, helps her parents in farming
throughout the day. She is pale and thin. On the other hand. Geeta, living in
Kerala goes to school daily and eats mid-day meals there. In the evening, she
helps her parents in farming. What does this show? (3)
Answer:
This shows
that Deepa lives in that part of rural India where the literacy level is low.
She neither goes to school nor takes proper nutrition, She is not healthy. On
the other hand, Geeta lives in that part of rural India which is prosperous such
as the state of Kerala. She goes to school and eats mid-day meals that fulfills
her nutritional needs, She is healthy also, ft also shows that the public
facilities like free school nearby, provision of meals in the school hr the
children ‘s provided by the State Government, This means that in the long run,
Geeta will lead a better life than Deepa.
Question 28.
Discuss the difficulties faced by a borrower when a loan is
taken from an informal sector.
Answer:
The difficulties faced by a
borrower when a loan is taken from an informal source are:
- Compared to the formal money lenders, most of the informal money lenders charge a much higher interest rate on loans. The cost to the borrower of informal loans is much higher.
- The higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan as a result borrowers have less income left with them. This can lead to an increasing debt and debt trap.
- People who might wish to start an enterprise by borrowing may not do so because of the high cost of borrowing.
Question 29.
‘Credit has its unique role for development’. Justify the
statements with an argument. (3)
Answer:
Credit has its unique role in
development because of the following reasons
Cheap and affordable credit can
be used to set up small-scale or cottage industries.
Farmers can buy
agricultural inputs with credit and thereby increase their crop production.
Credit is also needed by the manufacturing sector to buy raw materials, and
machines, and pay wages to labourers. etc.
Section
D
Section D consists of 4
questions of 5 marks each
Question 30.
Discuss the various factors that led to the rise of
nationalism in Europe.
OR
Describe the cause of the Silesian weaver’s
uprising. Comment on the viewpoint of the journalist Wilhelm Wolff.
Answer:
The factors that led to the rise of Nationalism in Europe are:
- The decline of Feudalism: Feudal lords were a disruption in the way of the rising nationalism feelings among the people. But the wars and crusades weakened them.
- The weakness of the Papacy and the Roman Empire: The Reformation and Renaissance movements led to the awakening of the people and weakened the authority of the Holy Roman Empire and the Pope. As a result, national states and national churches were established in many countries.
- Foreign Rule: Foreign rule also played a significant part in the growth of nationalism in certain countries.
- The reaction against Injustice: The reactions against the rule of unjust monarchs gave rise to the feeling of nationalism.
- Contribution of great writers: The writings of politicians, great poets, and philosophers like J.S. Mill, Machiavelli, Garibaldi, Fitch, Mazzini, etc., contributed strongly in rousing national spirit and political consciousness among the people.
OR
The perspectives of the journalist Wilhelm Wolff are as follows:
- The main reason behind the Silesian weaver’s uprising was lower payment for the accomplishment of a job.
- Contractors who manufactured raw materials and procured finished textiles from the weavers paid less money for the service of the weavers.
- The weavers were tortured mercilessly if they asked for their dues. This resulted in logical agitation and uprising by the weavers against the contractor.
- The perspective of the journalist Wilhelm Wolff was that the hardship of the workers was colossus and the contractor made their lives infernal. In this context, the viewpoint of the journalist was apposite and logical.
Question 31.
Minerals are integral parts of our lives. Justify this
statement with suitable examples. (5)
Or
How can biogas solve the energy
problems in rural India? State some suggestions for the same.
Answer:
Minerals are indeed an integral part of our lives.
- This can be understood through the following examples
- Almost everything that we use in our daily life, from a tiny pin to a towering building or a big ship, are all made from minerals.
- The railway lines and the paving of the roads, machinery, implements and tools too are made from minerals.
- Minerals form the basis of all industries
- Our food contains various minerals that are essential for our body. They are absorbed by the body.
- In conclusion, we can say that in all stages of development, human beings have used minerals for their livelihood,
- decoration, festivities, religious and ceremonial rites.
Or
Biogas can solve the energy problems in the rural areas due to the
following reasons
- It produces gas having higher thermal efficiency than charcoal and kerosene.
- It provides a way for optimum utilization of animal and plant waste.
- It produces enriched organic manure that can supplement or even replace chemical fertilizers.
- It burns smoothly and does not leave much residue behind.
- It is easy to produce and store.
Some suggestions to improve the biogas energy precautions in rural areas are
as follows
The government should provide monetary assistance to people in
rural areas to set up biogas plants.
Awareness must be created for using
these alternative sources of energy.
The terms of credit become difficult for small and marginal farmers
because
They are not capable of providing collateral such as land titles,
deposits with banks, livestock, etc.
The terms of credit include interest
rate, collateral, documentation, and the mode of repayment. They vary
substantially from one credit arrangement to another depending on the nature of
the lender and the borrower.
Question 32.
Write the difference between vertical division of
power-sharing and horizontal division of power-sharing.
OR
What are the
advantages of horizontal power-sharing? Explain with the help of examples.
Answer:
The difference between vertical division of power-sharing and
horizontal division of power-sharing.
| Vertical Division of Power-sharing | Horizontal Division of Power-sharing |
| (i) In the vertical division of power-sharing, power is divided among the different levels of the government like the State government, Union government, and Lower levels. | In the horizontal division of power, the power is shared between different organs of the government like Executive, Legislature and Judiciary. |
| (ii) Different levels of government exercise power. | Different organs of the government exercise power. |
| (iii) There is no specification of the system of checks and balance. | It specifies the concept of checks and balance. |
| (iv) It ensures the concept of deepening of democracy. | It ensures the concept of the expansion of democracy. |
| (v) State government, Central government and Panchayati Raj are examples of the vertical division of power-sharing. | For examples: Executive, Legislature and Judiciary are the organs of the Government of India. |
OR
The advantages of horizontal power sharing are enumerated as
follows:
- The power that is shared among different organs of government is known as horizontal power sharing.
- Horizontal power-sharing places all the organs of the government i.e., legislature, executive, and judiciary at an identical level.
- Under this type of power-sharing, no organs will exercise unlimited powers.
- This method is also known as the system of checks and balances.
- For instance in India, ministers and government officials exercise power. At the same time, they are accountable to the Parliament or State Assemblies. Similarly, although judges are appointed by the executive, they can check the functioning of the executive or laws made by the legislatures.
Question 33.
Explain the term secularism. Explain four features of
secularism in India. (5)
Or
How caste inequalities are still prevalent in
India?
Answer:
Secularism refers to the separation of religion from the
state. It means that the state should not discriminate among its citizens based
on religion. It should neither encourage nor discourage the followers of any
religion. Four features of secularism in India are as follows There is no
official religion for the Indian states, i.e. unlike Sri Lanka (Buddhism),
Pakistan (Islam), and England (Christianity).
All individuals and communities have the freedom to profess, practice and
propagate any religion or not to follow any religion.
It prohibits
discrimination on grounds of religion.
It allows the state to interfere in
the matters of religion to ensure equality within religious communities, viz it
bans untouchability.
Or
Caste inequalities are still prevalent in India.
This statement can be explained in the following ways
In India, hereditary
occupational division was sanctioned by rituals. Members of the same caste group
form a social community. Often they maintain the same or similar occupation.
In India, most of the marriages are held in the same caste group. Intercaste
marriage is not welcomed by all.
Sometimes people do not eat with members
from other caste groups.
Untouchability has not ended completely, although it
is prohibited by our Constitution.
Discrimination against the ‘outcast group’
is still prevalent in our society.
Section
E
Section E consists of 3
Case-based questions of 4 marks each
Question 34.
Read the source given below and answer the question that
follows:
The earliest kind of print technology was developed in China, Japan,
and Korea. This was a system of hand printing. From AD 594 onwards, books in
China were printed by rubbing paper – also invented there – against the inked
surface of woodblocks. As both sides of the thin, porous sheet could not be
printed, the traditional Chinese ‘accordion book’ was folded and stitched at the
side. Superbly skilled craftsmen could duplicate, with remarkable accuracy, the
beauty of calligraphy. The imperial state in China was, for a very long time,
the major producer of printed material.
China possessed a huge bureaucratic system that recruited its personnel through civil service examinations. Textbooks for this examination were printed in vast numbers under the sponsorship of the imperial state. From the sixteenth century, the number of examination candidates went up and that increased the volume of print.
Question 34.1
Name the nations where the earliest print technology was
developed.
Answer:
The earliest print technology was developed in China,
Japan, and Korea.
Question 34.2
How the books were printed in China from 594 AD?
Answer:
If the books in China were printed by rubbing paper against the inked
surface of woodblocks.
Question 34.3
Discuss the relationship between the bureaucratic system of
China and the production of printed materials.
Answer:
China had a large
bureaucratic system in which recruitment was made through the medium of civil
service examinations. For this examination, textbooks were printed in large
numbers. From the 16th century, the number of examination candidates increased
and that raised the demand of printed textbooks.
Question 35.
Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
Shyamal tells us that every season he needs loans for cultivation on his 1.5
acres of land. Till a few years back, he would borrow money from the village
moneylender at an interest rate of five percent per month (60% per annum). For
the last few years, Shyamal has been borrowing from an agricultural trader in
the village at an interest rate of three percent per month. At the beginning of
the cropping season, the trader supplies the farm inputs on credit, which is to
be repaid when the crops are ready for harvest. Besides the interest charge on
the loan, the trader also makes the farmer promise to sell the crop to him.
This way the trader can ensure that the money is repaid promptly. Also, since the crop prices are low after the harvest, the trader can make a profit from buying the crop at a low price from the farmers and then selling it later when the price has risen. Wc next meets Arun who is supervising the work of one farm labourer. Arun has seven acres of land. He is one of the few persons in Sonpur to receive a bank loan for cultivation. The interest rate on the loan is 8.5 percent per annum and can be repaid anytime in the next three years. Arun plans to repay the loan after harvest by selling a part of the crop.
Then, he intends to store the rest of the potatoes in cold storage and apply
for a fresh loan from the bank against the cold
storage receipt. The bank
offers this facility to farmers who have taken crop loans from them.
(i) When
Shyarnal was borrowing from a local agricultural trader, he paid a lesser
interest rate. Why? (1)
(ii) In the above case/source, which is the most
favorable term of credit/loan borrowed by Arun for land cultivation? (1)
(iii) State the merits of the formal sector of credit. (2)
Answer:
(i)
When Shyamal was borrowing from a local agricultural trader in the village, he
paid a lesser interest rate because a part of the credit was to be paid in kind
and another in cash.
(ii) The most favorable terms of credit/loan borrowed by
Arun for land cultivation are the specified rate of interest and fixed
period.
(iii) The merits of the formal sector of credit are
- It provides loans at a fixed rate and terms.
- It gives loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries small borrowers, etc.
Question 36.
Read the given extract and answer the following
questions.
Democracies are based on political equality. All individuals have
equal weight in electing representatives. Parallel to the process of bringing
individuals into the political arena on an equal footing, we find growing
economic inequalities. A small number of ultra-rich enjoy a highly
disproportionate share of wealth and incomes. Not only that, their share in the
total income of the country has been increasing. Those at the bottom of the
society have very little to depend upon. Their incomes have been declining.
Sometimes they find it difficult to meet their basic needs of life, such as
food, clothing, housing, education, and health.
Question 36.1
“Democracy ensures reduction of inequalities and poverty”.
Explain the statement.
Answer:
Democracy ensures equal distribution of
goods, income, and opportunities. A democratic government always tries to reduce
the poverty ratio and works for the welfare of the people.
Question 36.2
How can the accommodation of social diversity work in a
democracy?
Answer:
- In a democracy, the majority needs to work with the minority so that the government functions to represent the general view.
- Every citizen has a chance of being in the majority at some point in time.
Section F
Section
F consists of Map based questions of 5 marks
Question 37.
(a) Two places A and B have been marked on the given outline
map of India. Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn
near them. (2)
A. A place where the movement of Indigo workers took
place.
B. A place where the Civil Disobedience Movement took place.
(b) On
the same outline map of India, locate and label any three of the following with
suitable symbols. (3)
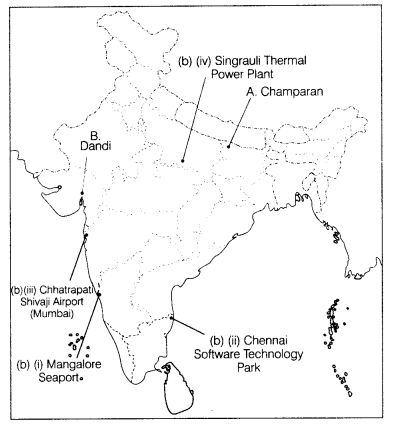
(i) Ncw Mangalore Seaport
(ii) Software Technology
Park in Tamil Nadu.
(iii) Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport
(iv)
Singrauli Thermal Power Plant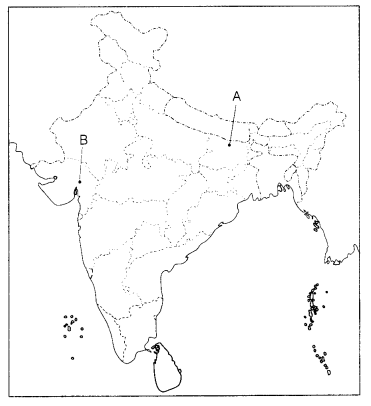
Answer: