CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-5
Class 10thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-5
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 5 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
- The question paper comprises five Sections – A, B, C. D, and E There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From questions 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Questions no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. The answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section C contains Q.25 to Q. 29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. The answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section D – Questions no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. The answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no. from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section arid question, wherever necessary.
Section
A
Section A consists of 20
questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Which of the following statements about the ‘French
Revolution’ are correct? (1)
I. After the end of the French Revolution it was
proclaimed that it was the people who would henceforth constitute the nation and
shape its destiny.
II. France will have a constitutional monarchy and the new
republic will be headed by a member of the royal family.
III. A centralised
administrative system will be put in place to formulate uniform laws for all
citizens.
IV. Imposition of internal customs duties and dues will continue to
exist in France.
Codes
(a) II and III
(b) II and 1V
(c) I and
III
(d) III and IV
Answer:
(c) I and III
Question 2.
Study the picture and answer the question that follows:
[1]
Which of the following aspects best signifies this image of the ship
“Alexandra”?
(A) Irish emigrants waiting to board the ship
(B) Meat being
loaded on the ship
(C) Emigrants leaving for the US
(D) Transport to the
gold mines.
Answer:
(B) Meat being loaded on the ship
Explanation: Till the 1870s, animals were shipped live from America to Europe but live animals took up a lot of ship space and also became unfit to eat. Hence, meat became an expensive luxury for the European poor.
Question 3.
Arrange the following events in a chronological order. (1)
I. Integration of Italy
II. Greek struggle for Independence initiated
III.
Unification of Germany
IV. Agreement on Vienna Peace Settlement
Codes
(a) I, IV, II, III
(b) IV, II, III, I
(c) IV, II, I, III
(d) I, II,
III, IV
Answer:
(c) IV, II, I, III
Question 4.
The species whose population has declined to a level from
where it is likely to move into the endangered category shortly if the negative
factors continue to operate are called: [1]
(A) Endemic species
(B)
Extinct species
(C) Vulnerable species
(D) Normal species
Answer:
(C) Vulnerable species
Question 5.
Animesh is a student of humanities. One day he was keen to
know about the reason behind the opposition movements of women and
non-propertied men in the 18th and early 19th centur There are four statements
given below. Can you identify which among the following statements would be most
helpful in clearing the doubt Animesh?
(a) Demanding for property
(b)
Demanding equal political rights
(c) Demanding membership in the Jacobian
Club
(d) Demanding equal distribution of wealth
Answer:
(b) Demanding
equal political rights
Question 6.
The practice of taking power away from the union and state
governments and giving it to local governments is called decentralization.
[1]
Pick the major steps that were taken towards decentralization in
1992.
(A) To hold regular elections of Local Government Bodies.
(B) At
least one-third of all positions are reserved for women.
(C) A State Election
Commission has been created in each State.
(D) All of the above.
Answer:
(D) All of the above.
Question 7.
Rana was asked to list down the names of four crops that were
grown during the Zaid season. She prepared the answer but the answer was a bit
incorrect. About your knowledge. identify the incorrect answer given by
Rana.
(a) Groundnut
(b) Muskmelon
(c) Soybean
(d) Mustard
Answer:
(b) Muskmelon
Question 8.
Which of the following professions belongs to the tertiary
sector of the economy? [1]
(A) Fisherman
(B) Farmer
(C) Factory
worker
(D) Teacher
Answer:
(D) Teacher
Explanation: The tertiary sector is also called! as service sector.; This sector also includes essential services that may not directly help in the production of goods. Examples: education, utilities, transportation, hospitality, etc. For example, teachers, doctors, tailors.
Question 9.
Which of the following statements is incorrect? (1)
I.
Silica is commonly found in sandy soil.
II. Petroleum is commonly found in
Bihar Assarn, offshore Maharashtra, and Rajasthan.
III. Fluorite is majorly
found in the Nasik and Jalgaon areas of Maharashtra.
IV. Bauxite is available
in the Koderma and Hazarihagh areas of Jharkhand, Gava in Bihar, and
Rajasthan.
Codes
(a) I and III
(b) II and IV
(c) I and IV
(d) II
and III
Answer:
(b) II and IV
Question 10.
Study the given graph and answer the following: [1]
About
how much percent of land area is plains?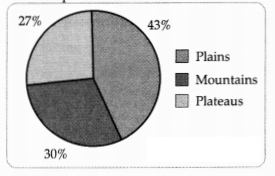
(A) 27%
(B) 72%
(C) 30%
(D)43%
Answer:
(D)43%
Explanation: India has a variety of relief features. About 43 percent of the land area is plain, which is utilized for agriculture and industry.
Question 11.
Read the given data which gives the estimate ut reserves of
crude oil. (1)
| Region/ Country | Reserves (2017) (Thousand Million Barrels) | The number of Years Reserves will last |
| Middle East | 80 | 70 |
| United States of America | 50 | 10.3 |
| World | 1697 | 50.2 |
Select the correct option which defines how it is essential for the
development process of a country.
(a) Reserves of crude oil are going to last
for 50 years and more.
(b) Crude oil is the major source of energy for
agricultural and industrial development.
(c) If prices of crude oil increase
then this becomes a burden for all.
(d) The Middle East and the USA may face
energy crises in the future due to the exhaustion of crude oil.
Answer:
(b) Crude oil is the major source of energy for agricultural and industrial
development.
Question 12.
Which one of the following Italian states was ruled by an
Italian princely house? [1]
(A) Papal State
(B) Lombardy
(C)
Venetia
(D) Sardinia-Piedmont
Answer:
(D) Sardinia-Piedmont
Explanation: During the middle of the nineteenth century, Italy was divided into seven states of which only One Sardania-Piedmont, was ruled by an Italian princely house.
Question 13.
Choose the correct statement associated with democracy.
(1)
(a) Democracy is not to lag behind dictatorship.
(b) Democracy is not
a guarantee of economic development.
(c) Economic growth is better in a
non-democratic government.
(d) The USA has a democratic government but also
has a remarkable economic development.
Answer:
(b) Democracy is not a
guarantee of economic development.
Question 14.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below: [1]
Assertion (A): We
are most concerned with ensuring that people will have the right to choose their
rulers and the people will have control over the rulers.
Reason (R): The most
basic outcome of democracy should be that it produces a Government that is
accountable to the citizens, and responsive to the needs and the expectations of
the citizens.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct
explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct
explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(D) (A) is wrong
but (R) is correct.
Answer:
Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: The people of India have the Right to Vote and choose their ruler and they can also have control over their Rulers. Wherever possible and necessary, citizens should be able to participate in decision making and that affects them all in knowing the public opinion and drawbacks of the ruling party. Then only the government would be accountable to the citizens and responsible to their needs and expectations.
Question 15.
Which of the following federal principles are found in the
Indian federation? (1)
Statement I Equal representation of states in the
Second House of Parliament.
Statement II Bicameral Legislature at federal
level.
Statement III Double citizenship.
Statement IV Independent and
Impartial Judiciary.
Codes
(a) Statement I and II are right
(b)
Statement 11 and III are right
(c) Statement II and IV are right
(d)
Statement III and IV are right
Answer:
(c) Statement II and IV are
right
Question 16.
Find the incorrect option from the following: [1]
(A) For
development, people look at a mix of goals.
(B) It is true that if women are
engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society decreases.
(C) However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would
be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of working women.
(D) A
safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or
run a business.
Answer:
(B) It is true that if women are engaged in paid
work, their dignity in the household and society decreases.
Explanation: In Indian society, the dignity of a person is measured by their work or job. So if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity increases in society.
Question 17.
Which of the following neighboring countries of India has
better performance in terms of human development than India? (1)
(a)
Bangladesh
(b) Sri Lanka
(c) Nepal
(d) Pakistan
Answer:
(b) Sri
Lanka
Question 18.
Sacred Groves are: [1]
(A) parts of large forests that
have been left untouched by the local people.
(B) places for grazing
animals
(C) forests earmarked for commercial felling of trees.
(D) forests
used for planting trees with medicinal properties.
Answer:
(A) parts of
large forests that have been left untouched by the local people.
Question 19.
Sheela owns a small flower shop near a temple. She wants to
expand her shop by keeping exotic flowers and flower bouquets.
To whom she
should approach for’ an ever short-term credit? 1
(a) Moneylenders as the’
provide short-term credit
(b) Banks as they charge low interest.
(c)
Cooperatives as they do not require collateral.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Cooperatives as they do not require collateral.
Question 20.
In terms of ____________ India is perhaps the most diverse
country in the world. [1]
(A) population
(B) languages
(C) forests
(D) religions
Answer:
(B) languages
Section
B
Section B consists of 4
questions of 2 marks each
Question 21.
State the role of Dr BR Ambedkar in the upliftment of Dalits.
(2)
Answer:
- The role of Dr B R Ambedkar in uplifting the Dalits was
- He joined active politics in 1930 and organized the Depressed Classes Association to uplift the Dalits,
- He demanded Separate Electorates for Dalits and reservation of seats in educational institutions for them.
Question 22.
Bauxite is an ore from which aluminum is obtained. [2]
Mention any two uses of Bauxite keeping the above statement in mind
OR
Copper metal is malleable, ductile, and a good conductor. List down the names of
the industries in which copper is used because of its properties and the
copper-rich regions of India.
Answer:
Uses of Bauxite:
(i) Bauxite is
used in a lot of industries like the chemical industry, refractory, abrasive,
cement, steel, and petrol industry amongst others.
(ii) Bauxite is the best
and only material used for making aluminum metal. More than 90 percent of the
world’s production of bauxite is consumed in the aluminum industry.
OR
(i) Copper is mainly used in electrical cables, electronics, and chemical
industries.
(ii) The Balaghat mines in Madhya Pradesh and the Khetri mines in
Rajasthan and Singhbham district of Jharkhand are leading producers of
copper.
Question 23.
State any two features of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural
Employment Guarantee Act.
Answer:
- The two features of Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act are
- The scheme targets people suffering from poverty in the rural areas.
- The scheme guarantees 100 days (recently amended to 150 days in drought-hit areas) of wage employment in a year to every household in 625 districts of the country.
Question 24.
Why is it necessary to increase the number of banks mainly in
rural areas? Explain. [2]
Answer:
It is necessary to Increase the number
of banks:
- To reduce the dependence on the informal sector of credit.
- To provide cheaper loans.
- To provide accessibility towards loans for the poor.
Section C
Section
C consists of 5 questions of 3 marks each
Question 25.
Describe the three major features of federalism. (3)
Answer:
The three major features of federalism are as follows
(i)
Different Levels of Government with Separate Jurisdiction The government
consists of two or more levels (or tiers) which govern the same citizens, but
each tier has its own jurisdiction in specific matters of legislation, taxation
and administration. Sources of revenue for each level of government are
specified to ensure its financial autonomy.
(ii) Jurisdiction Guaranteed The jurisdictions of levels of government are specified in the Constitution. So, the existence and authority of each tier of government is constitutionally guaranteed.
(iii) Courts Settle Disputes between Levels of Government Courts have the power to interpret the Constitution and the powers of different levels of government. The highest court acts as an umpire, if disputes arise between different levels of government in the exercise of their respective powers.
Question 26.
“A wide ranging choice of goods are available in the Indian
markets.” [2]
Support the statement with examples in context of
Globalisation.
Answer:
A wide ranging choice of goods:
- We have a wide variety of goods and services before us in the market.
- The latest models of the digital cameras, mobile phones and televisions manufactured by leading manufacturers of the world are available in the market.
- Every season, new models of automobiles can be seen on Indian roads.
- Today Indians are buying cars produced by nearly all the top companies in the world.
- A similar explosion ofbrands can be seen for many other goods.
Question 27.
Sohan wants to sell his rice and purchase oils. Similarly,
Mohan wants to sell his oil to purchase rice. They both exchange
their
commodities with each other What is this system called? Why this system
considered difficult to trade a commodity? Give any three reasons. (3)
Or
Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India? (3)
Answer:
This system is called barter system. Three reasons for the barter system being
considered difficult to trade a commodity are as follows
(i) There are many
products which cannot be divided or sub-divided For example, If the price of a
cow is equal to 100 shirts, then a person having one shirt cannot exchange ¡t
for a part of the cow, as it is not possible to divide the cow into small pieces
without destroying its utility.
(ii) Deciding the value of goods is difficult. For example, one can offer 1 kg rice for a pair of shoes whereas the shoe owner can demand 2 kg rice for the same shoes.
(iii) Double coincidence of wants is necessary. It means that both parties
have to agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities. Thus, if a farmer wants
to sell his rice in exchange for a pair of shoes, then he has to find a shoe
owner who wants to exchange a pair of shoes for rice.
Or
The reasons for
expanding formal sources of credit in India are High cost of borrowing leads to
a major share of earnings going into payment of interest on the loan so formal
source of credit is needed.
Sometimes the higher interest rate leads to the requirement to pay more than the earnings, thus falling into a debt trap To eliminate this, formal sources are needed
Formal sources of lending to more borrowers will lead to higher incomes and many people could then borrow cheaply for a variety of needs like growing crops, set-up business or small-scale industries.
Question 28.
Describe three advantages of the political expression of
caste differences. [2]
Answer:
The advantages of the political expression
of caste differences are:
- It allows disadvantaged groups to demand a share in power and decision-making.
- Many political parties take up the issue of 31. ending caste discrimination.
- Measures for uplifting the status of the backward castes will be undertaken.
Question 29.
In this question, you have two diagrams. Compare them and
find out the land use category which had the highest increase
during the
period 1960-61 to 2014-15 and the category which had the highest decrease during
the period. Give one major reason for each. (3)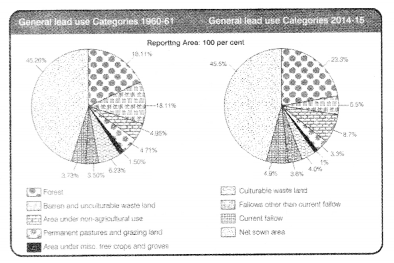
Answer:
The highest increase was in forest cover i.e. from 18.11%in 1960-61 to23.3%in2014-15, This increase is due to government efforts made in the field of conservation of environment by demarking the forest areas, Still, is below the outline of 33% set in National Forest Policy, 1952.
The highest decrease was in barren and unculturable wasteland i.e. from 18.11% to 55%. It is due to rise in area under non-agricultural uses. Massive urbanisation, development of roads, railways and other uses have brought waste land into area under non-agricultural uses.
Section
D
Section D consists of 4
questions of 5 marks each
Question 30.
‘Public sector contributes to the economic development of
India.’ Justify the statement. [5]
OR
’Public welfare is primarily the
responsibility of the public sector’ Given the given statement, list down the
reasons that limit the role of the private sector in public welfare.
Answer:
- It promotes rapid economic development through the creation and expansion of infrastructure.
- It creates employment opportunities.
- It generates financial resources for development.
- It ensures equality of income, and wealth and thus, a balanced regional development.
- It encourages the development of small, medium, and cottage industries.
- It ensures easy availability of goods at moderate rates.
- Contributes to community development, Human Development Index, i.e. health and educational services.
OR
- Activities in the private sector are guided by the motive to earn profits and not public welfare.
- Some of the services require large sums of money, which is beyond the capacity of the private sector.
- Collecting money from thousands of people who would use this facility is a humongous task.
- Even if the private sector provides these facilities, the rate charged for it would be very high.
- Thus, the government has to undertake the task of providing facilities such as the construction of roads, public hospitals, and schools to ensure their availability for everyone.
Question 31.
Write a brief note on waterways mentioning the National
Waterways of India. (5)
Or
Enlist and describe the five major ports
situated on the Western coast of India alongside the Arabian Sea. (5)
Answer:
Waterways are the cheapest means of transport. It is fuel-efficient, environment-friendly, and suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods India has inland navigation waterways of about 14,500 km in length Out of which 5685 km are navigable by mechanized boats.
The waterways declared as National Waterways are
- NW-1 Allahabad to Haldia (1.620 km) on the Ganga river system.
- NW-2 Sadiya to Dhubri (891 km) on the Brahmaputra river.
- NW-3 West-Coast canal in Kerala (205 km), (Kottapuram-Komman, Uctyogamandal, and Champakkara canals).
- NW-4 Parts of Krishna and Godavari rivers along with Kakinada-Puducherry stretch of canals (1,078 km).
- NW-5 Parts of Brahrnani River along with Matai River, delta channels of Mahanadi and Brahmani rivers, and East coast canal (588 km).
There are some other inland waterways on which substantial transportation takes place. These are Mandavi, Zuari and Cumberjua, Sunderbans, Barak, and backwaters of Kerala.
Or
The following are the major ports lying on the Western coast along the
side of the Arabian Sea.
(i) Kandla It is located in the Gulf of Kutch. It
was the first port which was developed soon after independence when the Karachi
port went to Pakistan due to partition. It was developed to facilitate the
volume of trade on the Mumbai port. It is also known as the Deendayal Port. It
is a tidal port. It handles exports and imports of highly productive granary and
industrial belts stretching across The states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal
Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana. Rajasthan and Gujarat.
(ii) Mumbal It is the biggest port in India with a natural harbour. Jawaharlal Nehru port developed nearby to case off the decongestant in Mumbal port.
(iii) Marmagao (Goa) It is the premier iron ore exporting port in India. This port accounts for about 50% of India’s iron ore exports.
(iv) New Mangalore It is located in Karnataka. It caters to export of iron ore from Kudremukh mines.
(v) Kochchi It is the extreme South-Western port located at the entrance of a lagoon with a natural harbour.
Question 32.
“Complaints are treated as a testimony to the success of
Democracy.” Justify this statement. [5]
OR
“Democracy is very important
for promoting dignity and freedom of the citizens.” GP supports this statement
with arguments.
AnsComplaints are treated as testimony:
It shows that people have developed awareness and the ability to expect and to look critically at powerholders and the high and the mighty.
A public expression of dissatisfaction with democracy shows the success of the democratic project. It transforms people from the status of a subject into that of a citizen.
OR
Democracy stands much superior to any other form of government in promoting dignity and freedom of the individual because:
- Every individual wants to receive respect from fellow beings.
- The passion for respect and freedom are the basis of Democracy.
- Democracy in India has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated groups for equal status and equal opportunities.
- It provides methods to resolve conflicts.
- Any other relevant point?
Question 33.
Describe the advantages of decentralization.
Or
Why has
federalism succeeded in India? Which three policies adopted by India have
ensured this success? (1+4)
Answer:
When power is taken from Central and
State Governments and given to local government, it is called
decentralisation.
The advantages of decentralisation are
(i) The basic
idea behind decentralisation is that there are large number of problems and
issues which are best settled at the local level. People have better knowledge
of the problems of their own locality. They have better idea on where to spend
money and how to manage things efficiently.
(ii) Decentralisation makes it possible for the people to directly participate in decision-making. This helps the people to develop a habit to participate in democratic activities. Thus, local government is the best way to realise the significance of local self-government in democracy.
(iii) Decentralisation reduces the burden of Central and State Governments. It helps to concentrate on matters of national of state importance in a better way
(iv) Decentralisation leads to women’s empowerment as it provides that at
least one-third of all positions are reserved for women in all the local
bodies.
Or
The policies adopted by the Indian Government have ensured the
success of federalism in India, Policies adopted by India to ensure this success
are
(i) Centre-State Relations Federalism has been strengthened by
restructuring of centre-state relations.
(ii) Decentralisation In India,
power has been decentralized to the local government. The local government
includes panchayats and municipalities.
(iii) Linguistic States The policy of
creating linguistic states has also strengthened federalism. Despite of
division, this policy united the nation.
(iv) Language Policy The Indian
federation did not give the status of national language to any language. This
ultimately has strengthened federalism.
Section
E
Section E consists of 3
Case-based questions of 4 marks each
Question 34.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that
follow: [4]
The failure of the Cripps Mission and the effects of World War II
created widespread discontentment in India. This led Gandhiji to launch a
movement calling for the complete withdrawal of the British from India. The
Congress Working Committee, in its meeting in Wardha on 14 July 1942, passed the
historic ‘Quit India’ resolution demanding the immediate transfer of power to
Indians and quit India.
On 8 August 1942, in Bombay, the All India Congress Committee endorsed the resolution which called for a non-violent mass struggle on the widest possible scale throughout the country. It was on this occasion that Gandhiji delivered the famous ‘Do or Die’ speech. The call of ‘Quit India’ almost brought the state machinery to a standstill in large parts of the country as people voluntarily threw themselves into the thick of the movement.
People observed hartals, and demonstrations and processions were accompanied by national songs and slogans. The movement was truly a mass movement that brought into its ambit thousands of ordinary people, namely students, workers, and peasants. It also saw the active participation of leaders, namely, Jayprakash Narayan, Aruna Asaf Ali, and Ram Manohar Lohia, and many women such as Matangini Hazra in Bengal, Kanaklata Barua in Assam, and Rama Devi in Odisha. The British responded with much force, yet it took more than a year to suppress the movement.
34.1 What factors led Gandhi to launch the Quit India Movement? [1]
Answer:
The failure of the Cripps Mission and the effects of World War II
created widespread discontentment in India. This led Gandhi to launch a movement
calling the complete withdrawal of the British from India.
34.2 What was the main demand of the Quit India Movement? [1]
Answer:
The main demand of the movement was to end British rule in India and to get the
cooperation of Indians against fascism.
34.3 When and where was the Quit India Resolution passed? [2]
Answer:
The Quit India Resolution was passed by the Congress Working Committee on 8
August 1942 in Bombay.
Question 35.
Read the given extract and answer the following
questions.
The Bretton Woods conference established the International
Monetary Fund (IMF) to deal with external surpluses and deficits of its member
nations. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (popularly
known as the World Bank) was
set up to finance post-war reconstruction: The
IMF and the World Bank are referred to as the Bretton Woods institutions or
sometimes the Bretton Woods twins. The post-war international economic system is
also often described as the Bretton Woods
system. The ¡MF and the World Bank
commenced financial operations in 1947.
Decision-making in these institutions is controlled by the Western industrial powers. The US has an effective right of vote over key IMF and World Bank decisions. The International Monetary System is the system linking national currencies and monetary system. The Bretton Woods system was based on fixed exchange rates.
In this system, national currencies, for example, the Indian rupees were
pegged to the dollar at a fixed exchange rate. The
dollar itself was anchored
to gold at a fixed price of $35 per ounce of gold.
(i) What was the reason
behind setting up of International Monetary Fund? (1)
Describe the Bretton
Woods System. (1)
A significant decision was taken at Bretton Woods in New
Hampshire. Explain. (2)
Answer:
(i) The IMF was set up to promote
International Monetary Cooperation.
(ii) The Bretton Woods System was based
on fixed exchange rates. In this system, national currencies viz. the Indian
rupees were pegged to the dollar at a fixed exchange rate. The dollar used was
anchored to gold at a fixed price of $ 35 per ounce of gold.
(iii) In Bretton
Woods Conference New Hampshire USA, decisions were taken to establish World Bank
and International Monetary Fund (IMF) to preserve global economic stability and
full employment in the industrial world. These institutions would also deal with
the surplus and deficit of member nations and finance post-war
reconstruction.
Question 36.
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that
follow: [4]
How do we count the various goods and services and know the total production
in each sector?
With so many thousands of goods and services produced, you
might think this is an impossible task! Not only would the task be enormous, you
might also wonder how we can add up cars and computers and nails and furniture.
It won’t make sense!
You are right in thinking so. To get around this problem, economists suggest that the values of goods and services should be used rather than adding up the actual numbers. For example, if 10,000 kgs of wheat is sold at? 8 per kg, the value of wheat will be? 80,000. The value of 5000 coconuts at? 10 per coconut will be? 50,000. Similarly, the value of goods and services in the three sectors are calculated and then added up.
Remember, there is one precaution one has to take. Not every good (or service) that is produced and sold needs to be counted. It makes sense only to include the final goods and services. Take, for instance, a farmer who sells wheat to a flour mill for? 8 per kg. The mill grinds the wheat and sells the flour to a biscuit company for? 10 per kg. The biscuit company uses flour and things such as sugar and oil to make four packets of biscuits.
It sells biscuits in the market to the consumers for? 60 (? 15 per packet). Biscuits are the final goods, i.e., goods that reach the consumers. Why are only ‘final goods and services’ counted? In contrast to final goods, goods such as wheat and wheat flour in this example are intermediate goods. Intermediate goods are used up in producing final goods and services. The value of final goods already includes the value of all the intermediate goods that are used in making the final good.
Hence, the value of? 60 for the biscuits (final good) already includes the value of flour (Rs 10). Similarly, the value of all other intermediate goods would have been included. To count the value of the flour and wheat separately is therefore not correct because then we would be counting the value of the same things several times. First as wheat, then as flour, and finally as biscuits. The value of official goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. The sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. GDP shows how big the economy is.
In India, the mammoth task of measuring GDP is undertaken by a central government ministry. This Ministry, with the help of various government departments of all the Indian states and union territories, collects information relating to the total volume of goods and services and their prices and then estimates the GDP.
36.1 What method do the economists suggest for counting the various goods and
services? [1]
Answer:
In counting the various goods and services,
economists suggest that the value of goods and services should be used rather
than adding up the actual numbers.
36.2 What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)? [1]
Answer:
The value of all
final goods and services produced within a country during a particular period in
all three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a
country.
36.3 What is the role of the Central Government Ministry in measuring GDP?
[2]
Answer:
In India, the mammoth task of measuring GDP is undertaken by a
Central Government Ministry. This ministry, with the help of various government
departments of all the Indian states and union territories, collects information
relating to the total volume of goods and services and their prices and then
estimates the GDP.
Section
F
Section F consists of Map based
questions of 5 marks
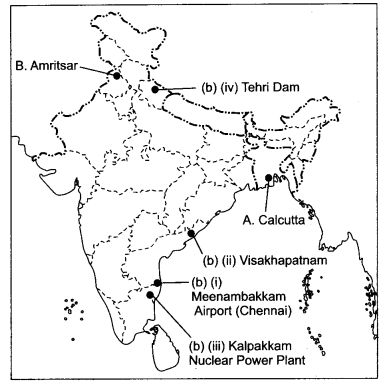
Question 37.
(a) Two places A and B are marked on the given outline map of
India. Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them.
(2)
A. The place where the Indian National Congress Session was held in
September 1920.
B. The place where the Jallianwala Bagh incident took
place.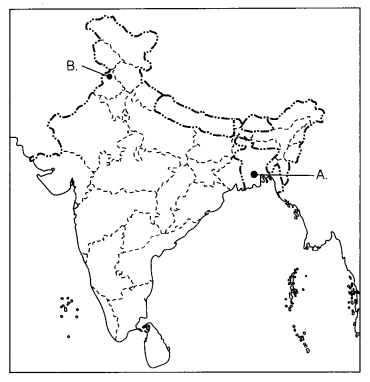
(b) On the same outline map of India, locate any three features of the following
with suitable symbols. (3)
(i) Meenambakkam Airport (Chennai)
(ii) A major
port in Andhra Pradesh
(iii) A Nuclear Power Plant
(iv) Tehri Dam
Answer: