CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-4
Class 10thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-4
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 4 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
- Question paper comprises five Sections – A B, C, D, and E. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions. carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section C contains Q.25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each, Answer to each question should riot exceed 60 words.
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no. from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section
A
Section A consists of 20
questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Identify the correct option that describes the act given
below. (1)
The Act was passed by the Imperial Legislative Council.
It gave
power to the government to repress political activities.
It empowered the
government to detain political prisoners without trial.
(a) Rowlatt Act
(b) Vernacular Press Act
(c) Government of India Act
(d) Inland Emigration
Act
Answer:
(a) Rowlatt Act
Question 2.
Find the incorrect option from the following: [1]
(A)
Against this background the new Tory Government in Britain constituted a
Statutory Commission under Sir John Simon.
(B) Set up in response to
Nationalist Movement, the Commission was to look into the functioning of the
Constitutional System in India and suggest changes.
(C) The problem was that
the Commission did not have a single Indian Member.
(D) They were all
Americans.
Answer:
(D) They were all Americans.
Explanation: All members were Britishers
Question 3.
Read the data given below and answer the question. Educational
Achievement of Rural Population of Uttar Pradesh
| Category | Male | Females |
| Literacy rate for rural population | 76% | 54% |
| Literacy rate for rural children in age group 10 – 14 Years | 90% | 87% |
| Percentage of rural children aged 10 – 14 attending school | 85% | 82% |
As per the data given above, who has the least percentage of literacy rate in
rural population? (1)
(a) Male
(b) Children
(c) Male and Female
(d)
Female
Answer:
(d) Female
Question 4.
Study the pie chart showing production of Iron ore state-wise
share in percent, 2016-17. [1]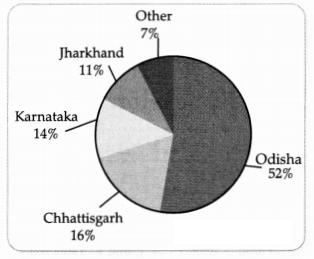
Which state has the maximum production of iron ore?
(A)
Karnataka
(B) Jharkhand
(C) Chhattisgarh
(D) Odisha
Answer:
(D)
Odisha
Question 5.
When many countries of Europe came together to form the
European Union, …………………… was chosen as its headquarters. (1)
(a) Brussels
(b) Paris
(c) London
(d) Zurich
Answer:
(a) Brussels
Question 6.
The creation of linguistic states was the first and a major
test for democratic politics in our country.
Identity the status given to
Hindi by the Constitution of India. [1]
(A) Regional language
(B) Official
language
(C) National language
(D) Community language
Answer:
Option
(B) is correct.
Explanation: Article 343 (1) of the Constitution provides that Hindi in Devanagari script shall be the Official Language of the Union. Article 343 (2) also provided for continuing the use of English in official work of the Union for 15 years (i.e., up to 25 January 1965) from the date of commencement of the Constitution.
Question 7.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below. (1)
Assertion (A)
Democracy are based on political equality.
Reason (R) All individuals have
equal say in electing representatives.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are truc and
R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the
correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but
R is true
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct
explanation of A
Question 8.
Activities that help in the development of primary and
secondary sectors come under one of the following sectors: [1]
(A)
Primary
(B) Secondary
(C) Tertiary
(D) Quaternary
Answer:
(C)
Tertiary
Explanation: The tertiary sector refers to the commercial services that support the production and distribution process in any economy, e.g. transport, etc. It helps in the development of primary and secondary sectors of a country.
Question 9.
You are a citizen of a country that has a democratic form of
government. You want to ensure that the system of power-sharing
in your count
is effective and that no one branch of government has absolute power. Which of
the following measures would best meet this goal? (1)
(a) All power is
concentrated in the hands of the Central Government, which has the final say in
all matters.
(b) Power is divided between the Central Government and the
states or provinces, with each level having its sphere of influence.
(c)
Power is separated among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with
each branch having its responsibilities and powers.
(d) Power is shared among
different levels of government, such as the national, regional, and local
governments, with each level having some degree of autonomy.
Answer:
(c)
Power is separated among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with
each branch having its responsibilities and powers.
Question 10.
Find the incorrect option from the following: [1]
(A)
Kisan Credit Card (KCC), Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS) are some
other schemes introduced by the Government of India for benefit of the
farmers.
(B) Moreover, special news bulletins and entertainment programs for
farmers were introduced on the radio and television.
(C) The government also
announces minimum support price, and remunerative and procurement prices for
important crops to check the exploitation of farmers by speculators and
middlemen.
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(B) Moreover, special news
bulletins and entertainment programmes for farmers were introduced on the radio
and television.
Explanation: Moreover, special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers were introduced on the radio and television.
Question 11.
Evaluate the impacts of opening foreign trade on the global
economy by identifying the appropriate statements among the
following
options. (1)
I. The choice of goods in the markets increases.
II.
Producers from two countries closely compete against each other despite the
distance between their locations.
III. Foreign trade thus results in
connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries.
IV.
The quality of the product is always good.
Codes
(a) Statements I and II are appropriate
(b) Statements I, II, and
III are appropriate
(c) All the statements are appropriate
(d) Only
statement IV is appropriate
Answer:
(b) Statements I, II, and III are
appropriate
Question 12.
Study the picture and answer the question that follows:
[1]
Which of the following aspects best signifies this image of ‘Ghor Kali?
(A) Traditional family roles
(B) Destruction of proper family relations
(C) Cultural impact of the West
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(B)
Destruction of proper family relations
Question 13.
Arrange the following statements in sequential order based on
the events that shaped the Non-Cooperation Movement (1)
I. General Dyer
opened fire at the large crowd gathered in the enclosed ground of Jallianwala
Bagh.
II. ‘Forced recruitment’ carried out by the British government and the
economic hardships faced by the people during the
First World War.
III.
The defeat of the Ottoman Emperor of Turkey led to the formation of the Khilafat
Movement.
IV. Gandhiji launched a nationwide Satyagraha against the Rowlatt
Act.
Codes
(a) IV, III, II, I
(b) II, I, III, IV
(c) I, IV, III, II
(d) I, II, III, IV
Answer:
(b) II, I, III, IV
Question 14.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below: [1]
Assertion (A):
Political parties are easily one of the most visible institutions in a
democracy.
Reason (R): For most ordinary citizens, democracy is equal to
political parties.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct
explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct
explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(D) (A) is wrong
but (R) is correct.
Answer:
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the
correct explanation of (A).
Question 15.
Consider the statements given below and choose the correct
answer. (1)
I. Western printing techniques and mechanical press were imported
in the late 19th century as Western powers established their outposts in
China.
II. Beijing became the hub of the new print culture, catering to
Western-style schools.
Codes
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) Both I and II are incorrect
(d)
Both I and II are correct
Answer:
(a) Only I
Question 16.
Which of the following statements defines Sustainable
Development? [1]
(A) Sustainable use of natural resources without considering
the need of the future generation.
(B) Present generation fulfils its needs
while considering the needs of the future generation as well.
(C) It means
utilization of natural resources by the past, present and forthcoming future
generation.
(D) To meet the needs of the future generations even if the needs
of present generation go unfulfilled.
Answer:
(B) Present generation
fulfils its needs while considering the needs of the future generation as
well.
Question 17.
The emergence of is directly connected to the rise of
political parties. (1)
(a) monitory democracies
(b) direct democracies
(c) representative democracies
(d) constitutional democracies
Answer:
(c) representative democracies
Question 18.
96.5 percent of the total volume of the world’s water is
estimated to exist as ___________ and only 2.5 percent as __________. [1]
(A)
freshwater, oceans
(B) oceans, freshwater
(C) groundwater, oceans
(D)
None of the above
Answer:
(B) oceans, freshwater
Question 19.
Which of the following statements is correct keeping the
requirement of formation of government in view? (1)
Statement I It is
possible for independent candidates to form a government.
Statement II
Government formation is exclusively reserved for political parties.
Statement
III The formation of government is limited to only elected political
parties.
Statement IV Government can only be formed by political parties that
are elected and hold a majority.
(a) Statements I and II are right
(b)
Statements I, II, and III are right
(c) Statement III is right
(d) Only
statement IV is right
Answer:
(d) Only statement IV is right
Question 20.
What is the guiding philosophy of the Bharatiya Janata Party?
[1]
(A) Bahujan Samaj
(B) Revolutionary Democracy
(C) Integral
humanism
(D) Modernity
Answer:
(C) Integral humanism
Section
B
Section B consists of 4
questions of 2 marks each
Question 21.
Study the map thoroughly and mention the languages that are
dominantly present in Belgium. (2)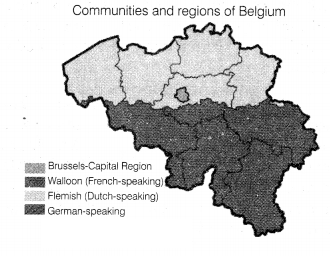
Answer:
The languages that are dominantly present in Belgium are Dutch and
French.
Question 22.
The Chipko Movement can essentially be called a women’s
movement. [2]
Write a note on the Chipko Movement.
Answer:
The Chipko
Movement was a forest conservation movement in India.
(i) It was a nonviolent
social and ecological movement by rural villagers, particularly women, in India
in the 1970s.
(ii) It aimed at protecting trees and forests slated for
government-backed logging
Question 23.
Mr. Palani is from Tamil Nadu and wishes to cultivate either
tea or wheat. Which one of the crops out of the two can he cultivate in
his
state? Substantiate your answer with any two reasons. (2)
Answer:
Mr.
Palani must cultivate tea in Tamil Nadu as the soil and climatic conditions in
Tamil Nadu are suitable for growing tea. Two reasons to cultivate tea in the
state of Tamil Nadu are The tea plant grows well in tropical and sub-tropical
climates endowed with deep and fertile well-drained laterite soil, rich in humus
and organic matter. Tea bushes require a warm and moist frost-free climate all
through the year. Frequent showers evenly distributed over the year ensure
continuous growth of tender leaves.
Question 24.
Agriculture is an unorganized sector activity in India.
[2]
Do you agree with this statement? Justify your answer with suitable
examples
Answer:
Yes, I agree that agriculture is an unorganized sector
because, in agricultural activities, people are exploited like landless
laborers.
(i) Their income level is low.
(ii) There is no job
security.
(iii) Agriculture is seasonal and there is no fixed pay.
(iv) No
other benefits such as a pension, medical facility, paid leave, provident fund,
safe environment, etc. are available
Section
C
Section C consists of 5
questions of 3 marks each
Question 25.
Provide evidence to support the claim that print culture had
a significant impact on the social life of women in India. (3)
Answer:
The
rise of print culture in India during the 19th century played a crucial role in
awakening the social life of women. The printing press allowed women to access
information, knowledge and ideas that were previously inaccessible to them.
Women’s magazines, newspapers, and books provided a platform for women to
express their views, ideas and opinions on various social issues such as
education, gender equality, women’s rights, and social reform.
liberal husbands and fathers began educating their womenfolk at home and sent
them to schools In East Bengal, Rashsundari Debi, a young married girl in a very
orthodox household, learnt to read in the secrecy of her kitchen and wrote her
autobiography
Amar Jiban (1876). It was the first full-length autobiography
published in the Bengali language. Bengali women like Kailashbashini Debi wrote
books highlighting the experiences of women – about how women were imprisoned at
home, kept in ignorance, forced to do hard domestic labor, and treated unjustly
by their families.
Question 26.
How has the ever-increasing number of industries in India
worsened the problem of the water crisis by exerting pressure on existing
freshwater resources? Explain. [3]
Answer:
An increasing number of
industries exerting pressure on freshwater resources:
(i) Industries are
heavy users of water.
(ii) More demand of hydroelectric power.
(iii)
Industrial wastes and effluents are discharged into rivers causing water
pollution.
(iv) Multiplying urban centers, due to industries, has caused
pressure on resources.
(v) Any other relevant point.
Question 27.
“Agriculture gives a boost to the industrial sector’. Justify
the statement with any three relevant points. (3)
Answer:
Agriculture
gives a boost to the industrial sector in the following ways
Raw Material
Supply Agriculture is a significant source of raw materials for various
industries, such as food processing, textiles, and paper. For instance, the
cotton industry relies heavily on the production of cotton from agricultural
fields.
Market Expansion Agriculture provides a vast market for industrial products. For example, the use of agricultural machinery such as tractors, tillers, and harvesters creates a demand for industrial goods. including steel, plastics, and rubber.
Employment Generation Agriculture is a labor-intensive sector that generates employment opportunities for a significant population in India.
Question 28.
“Democratic Governments in practice are accountable.” Support
the statement with arguments. [3]
Answer:
Democratic Governments in
practice are accountable because:
- It is right to expect democracy to form a government that follows procedures and is accountable to the people.
- It is also expected that the Democratic Government develops mechanisms for citizens to take part in decision-making whenever they think it is fit.
- The Democratic Government is accountable to the people. If it ignores the will of the people, they will not elect their Rule,r in the next General Election.
- The procedures and decision-making process should be transparent for the Democratic Government to be accountable to the people.
Question 29.
Compare Tables “A” and “B” and answer the question given
below. (3)
Table-A
| Share of Sectors In GDP in % | |||
| Year | Tertiary | Secondary | Primary |
| 1973-74 | 50 | 10 | 40 |
| 2013-14 | 68 | 21 | 11 |
Table -B
| Share of Sectors In Employment In % | |||
| Year | Tertiary | Secondary | Primary |
| 1977-78 | 18 | 11 | 71 |
| 2017-18 | 31 | 25 | 44 |
A remarkable fact about India is that while there has been a change in the
share of the three sectors in GDP, a similar shift has not taken place in
employment. Why didn’t a similar shift out of primary sector happen in case of
employment? Substantiate your answer.
Answer:
A substantial shift in
employment in primary sector hasnt happened because of the following reasons
Insufficient job creation in the secondary and tertiary sectors The primary
reason for the limited shift in employment from the primacy sector is the
failure to generate an adequate number of jobs in the secondary (industrial) and
tertiary (service) sectors.
The growth of industrial output and service sector production has been significant, but the corresponding increase in employment opportunities has been comparatively lower.
Underemployment ¡n the agricultural sector The primary section. particularly
agriculture, suffers from underemployment, with more people engaged in farming
than necessary. Even if a few individuals are moved out of agriculture, it does
not significantly
affect production. This indicates that workers in the
agricultural sector are not fully utilised, leading to a lower productivity
level.
Section
D
Section D consists of 4
questions of 5 marks each
Question 30.
“Nationalism no longer retained its idealistic liberal
democratic sentiment by the last quarter of the nineteenth century in
Europe.”
Analyse the statement with examples. [5]
OR
” Nationalism
spreads when people begin to believe that they are all part of the same nation”.
Justify the statement
Answer:
Sentiment of Nationalism in the later half
of the 19th century:
- Towards the last quarter of the 19th century, nationalism could not retain its idealistic liberal-democratic sentiments of the first half of the century but became a narrow belief with inadequate ends.
- Nationalist groups became increasingly intolerant, which led to war.
- Major European powers manipulated the nationalist aspirations to further their own imperialist aims.
- Source of nationalist tension in Europe was the area called Balkans.
- Idea of romantic nationalism in the Balkan together with the disintegration of the Ottoman Empire made this region very explosive.
- One by one, European nationalists broke away from its control and declared independence.
- The Balkan people based their claims for independence or political rights on nationality to prove that they were once independent but were subjugated by a foreign power.
- Slavic nationalities struggled to define their identity and independence. Hence, the Balkan area became an area of intense conflict.
OR
- The romanticism and cultural movements focused on emotions, Intuitions and mystical feelings to create a sense of a shared collective heritage, a common cultural past of a nation.
- Folk songs, folk poetry and folk dances are true cultural spirits of a nation and these are essential to bind the people in a bond.
- Importance of vernacular language also bind the people into a nation so that they can collectively think for their Nation
- Music also helps to light up the feeling of nationalism-connection to one nation
- The collection of local folklore was not just only to recover the national spirit, but also spread the message of nationalism among the illiterate people.
Question 31.
How would you evaluate Napoleon as an administrator who
created a more rational and efficient system? Elucidate
with suitable
examples.
Or
Analyze the decisions taken by the conservatives at the
Congress of Vienna in the year 1815. (5)
Answer:
- Napoleon was an administrator who created a more rational and efficient system This statement can be justified by the following reason
- The Civil Code of 1804 usually known as the Napoleonic Code, secured the property right, established equality before the law, and removed all privileges based on birth.
- The Napoleonic Code was followed by the regions under French control.
- New businessmen, artisans, peasants and workers enjoyed a new-found freedom. in territories under French control such as Italy, Germany, Switzerland, and Dutch Republic, peasants were freed from manorial dues, peasants were freed from serfdom, feudal system was abolished, administrative divisions were simplified
- Guild restrictions were removed in towns.
- There were improvements in communication and transport systems.
To facilitate the movement and exchange of goods and capital from one region
to another, small-scale producers of goods and businessmen began to realise that
common national currency. standardized measures and weights. and uniform laws
were of
great help.
Or
The representatives of the four great European powers – Britain,
Russia, Prussia, and Austria who had collectively defeated Napoleon, met at
Vienna to draw up a settlement for Europe. The Congress was hosted by the
Austrian Chancellor Duke Metternich. The result was the Treaty of Vienna of
1815.
Its object was to undo the changes that had come about in Europe during the Napoleonic wars and to restore the monarchies that had been overthrown by Napoleon, and create a new conservative order in Europe.
The Bourbon dynasty, (deposed during the French Revolution) was restored to power. France lost the territories it had annexed under Napoleon.
A series of states were set up on the boundaries of France to prevent it from expanding in the future. E.g., kingdom of the Netherlands, which included Belgium, was set up in the North.
Genoa was added to Piedmont in the South. Prussia was given territories on its Western frontiers. Austria was given control of Northern Italy.
The German confederation of 39 states set up by Napoleon was left untouched in the East, Russia was given part of Poland while Prussia was given a portion of Saxony.
Thus, conservative regimes set up in 1815 were autocratic. They did not tolerate criticism and dissent. They curbed activities that questioned the ‘legitimacy of autocratic governments.
Question 32.
The focus on caste in politics can sometimes give an
impression that elections are all about caste and nothing else. Do you agree
with the given statement? Explain. [5]
OR
Assess the influences of
politics on the caste system.
Answer:
No, I do not agree with this
statement. This is far from the truth because:
- No parliamentary constituency in the country has a dear majority of one single caste. So, every candidate and party needs to win the confidence of more than one caste and community to win elections.
- No party wins the votes of all the voters of a caste or community. When people say that a caste is a ‘vote bank’ of one party, it usually means that a large proportion of the voters from the caste vote for the party.
- Many political parties may put up candidates from the same caste (if that caste is believed to dominate the electorate in a particular constituency). Some voters have more than one candidate from their caste, while many voters have no candidates from their caste.
- The Ruling Party of the sitting MP or MLA frequently loses elections in our country. That could not have happened if all castes or communities were frozen in their political preferences.
OR
Influence of politics on caste :
- Each caste group tries to become bigger by incorporating within its sub-castes.
- Various caste groups are required to enter into a coalition with other castes or communities.
- New kinds of caste groups have entered politics like ‘backward’ and ‘forward’ castes.
- Politics in caste has allowed many disadvantaged caste groups to demand their share of power.
- Caste politics has helped the Dalits and OBCs to gain better access to decision-making.
Question 33.
A farmer has borrowed money from a money-lender at a high
rate of interest, and as he could not pay the interest, he was forced to
borrow from another landlord to settle the amount for the interest borrowed from
the money-lender. State the consequences he may face in this situation.
Or
“Self Help Groups eliminate poverty and empower women”. Substantiate with
a suitable answer. (5)
Answer:
The farmer has fallen into a debt trap. He
is in a situation where he will not be able to repay the debt incurred because
the informal sector was the source of credit opted by the farmer, where the rate
of interest is high, no proper documentation is sought no set of rules and
regulations will be followed.
- He may face the following consequences
- The farmer may face ongoing harassment and physical harm from the men sent by the money lender.
- He will not be able to make regular interest payments or repay the full amount borrowed.
- This could lead to significant stress and anxiety, as well as potential physical injuries.
Borrowing from another landlord to repay the original loan may create a cycle of debt for the farmer particularly if the interest rates on the second loan are also high.
The farmer may experience personal consequences, such as mental stress. anxiety and depression due to the constant pressure 01 repayments and harassment from the lenders.
Or
- Self-help groups eliminate poverty and empower women due to the following features
- They avail the facilities of loans from formal sources like banks at low rate of interest.
- They do not demand collateral so it is easy to access The poor.
- Self-help groups are exclusively meant for rural women to make them economically independent through self-employment opportunities.
It helps to improve other development factors such as literacy levels, improved healthcare and better family planning. SHGs provide women with a platform to save and access credit at affordable rates, which enables them to start and expand small businesses. Thus, improving the standard of living.
Section
E
Section E consists of 3
Case-based questions of 4 marks each
Question 34.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that
follow: [4]
Globalization expands and accelerates the movement and exchange
of ideas and commodities over vast distances. Globalisation has created more
competitive environment in India. In the past two to three decades, more and
more MNCs have been looking for locations around the world which would be cheap
for their production. Foreign investment by MNCs in these countries has been
rising. At the same time, foreign trade between countries has been rising
rapidly. A large part of the foreign trade is also controlled by MNCs.
The result of greater foreign investment and greater foreign trade has been greater integration of production and markets across countries. Globalisation is this process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries. MNCs are playing a major role in the globalisation process. More and more goods and services, investments and technology are moving between countries. Besides the movements of goods, services, investments and technology, there is one more way in which the countries can be connected. This is through the movement of people between countries. People usually move from one country to another in search of better income, better jobs or better education.
- Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the Globalisation process. Even more remarkable have been the developments in information and communication technology. Globalisation and greater competition among producers – both local and foreign producers – has been of advantage to consumers, particularly the well-off sections in the urban areas. There is greater choice before these consumers who now enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products. As a result, these people today, enjoy much higher standards of living than was possible earlier. Globalisation has also created new opportunities for companies providing services, particularly those involving IT.
- 34.1 How has globalisation led to higher standards of living ? [1]
Answer:
Globalisation has led to higher standards of living of well-off customers. There is greater choice before these consumers who now enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products. - 34.2 Name one major factor which has stimulated the globalisation process.
[1]
Answer:
Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the Globalisation process. - 34.3 For whom has globalization posed a major challenge? [2]
Answer:
Globalisation has posed a major challenge to the small scale producers having low capital investment and poor strategies to develop. They have been hit hard due to severe competition. Several units have been shut down rendering many workers jobless.
Question 35.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that
follow.
Maharashtra is a state located in Western India, with a population of
over 110 million people. The state is home to several large
cities, including
Mumbai, and has a significant agricultural sector. However, the state is facing
a severe water crisis, with its water
resources coming under increasing
pressure due to climate change, industrialisation, and urbanisation. The main
challenges faced by water resource management in Maharashtra are:
Overexploitation of groundwater Maharashtra is one of the most
groundwater-stressed states in India, with the demand for water exceeding the
supply. Overexploitation of groundwater for agriculture and urban usc has led to
a decline in water levels, which has severe implications for the sustainability
of water resources.
Pollution of surface water Industrialisation and urbanisation have led to the pollution of surface water bodies such as rivers and lakes. The pollution has led to water quality degradation, which poses risks to human health and the environment.
Inefficient irrigation practices The agricultural sector is the largest user of water in Maharashtra, accounting for around 80% of total water use. However, traditional irrigation practices such as flood irrigation are inefficient and lead to the wastage of water.
(i) Mention any two reasons for the water crisis faced by the state of
Maharashtra.
(ii) Despite being the second highest rainfall-receiving state
of the country, Maharashtra still faces water crisis. Substantiate this
statement in 40 words.
(iii) Propose any one solution to mitigate the water
crisis faced by Maharashtra state. (4)
Answer:
(i) Two reasons for
Maharashtra facing a water crisis are overexploitation of groundwater and
pollution of surface water bodies due to industrialisation and urbanisation.
(ii) Despite receiving the second-highest rainfall in thern country. traditional irrigation practices like flood irrigation leading to water shortages in Maharashtra. This is because flood irrigation involves excessive water use, and the water gets lost due to runoff. leading to less water available for other uses.
(iii) To mitigate the water crisis in Maharashtra, one solution could be to promote the adoption of more efficient irrigation practices, such as drip irrigation and sprinkler systems. that use less water and are more targeted in their delivery. The state can also use rainwater harvesting system to improve groundwater levels along the Western side of the Western Ghats which receives maximum rainfall. This will increase the efficiency of water use in the state of Maharashtra.
Question 36.
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that
follow: [4]
Before the age of machine industries, silk and cotton goods from
India dominated the international market in textiles. Coarser cotton was
produced in many countries, but the finer varieties often came from India.
Armenian and Persian merchants took the goods from Punjab to Afghanistan,
Eastern Persia and Central Asia. Bales of fine textiles were carried on
camelback via the northwest frontier, through mountain passes, and across
deserts.
A vibrant sea trade operated through the main pre-colonial ports. Surat on the Gujarat coast connected India to the Gulf and Red Sea Ports; Masulipatnam on the Coromandel Coast and Hooghly in Bengal had trade links with Southeast Asian Ports. Bengal had trade links with Southeast Asian Ports. A variety of Indian merchants and bankers were involved in the network of export trade — financing production, carrying goods, and supplying exporters.
Supply merchants linked the port towns to the inland regions. They gave advances to weavers, procured the woven cloth from weaving villages, and carried the supply to the ports. At the port, the big shippers and export merchants had brokers who negotiated the price and bought goods from the supply merchants operating inland. By the 1750s this network, controlled by Indian merchants, was breaking down. The European companies gradually gained power—first securing a variety of concessions from local courts, then the monopoly rights to trade.
This resulted in a decline of the old ports of Surat and Hoogly through which local merchants had operated. Exports from these ports fell dramatically, the credit that had financed the earlier trade began drying up, and the local bankers slowly went bankrupt. In the last years of the seventeenth century, the gross value of trade that passed through Surat had been Rs. 16 million. By the 1740’s it had slumped to Rs 3 million.
36. 1 Which Indian goods dominated the international markets in textiles
before the age of machine industries? [1]
Answer
Before the age of machine
industries, silk and cotton goods from India dominated the international
markets.
36. 2 What kind of cotton was produced in India? [1]
Answer:
The finer
varieties of cotton were produced in India.
36. 3 How was the trade carried? [2]
Answer:
The Armenian and Persian
merchants took the goods from Punjab. The two old ports in India are Surat and
Hooghly.
Section
F
Section F consists of Map based
questions of 5 marks
Question 37.
(a) Two places A and B have been marked on the given outline
map of India. Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn
near them.
(i) Indian National Congress session at this place in 1920.
(ii) The place where Mahatma Gandhi broke the salt law.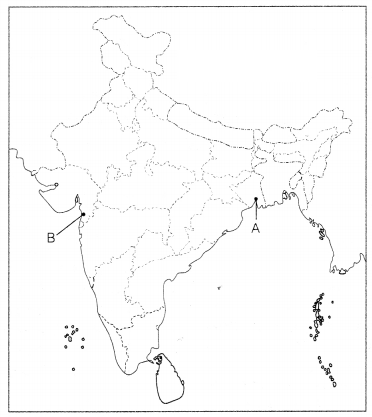
(b) On the same outline map of India, locate and label any three of the
following with suitable symbols.
(i) A coal mine in Tamil Nadu
(ii) A dam
built on the river Chenab
(iii) A large natural major seaport located in
Andhra Pradesh
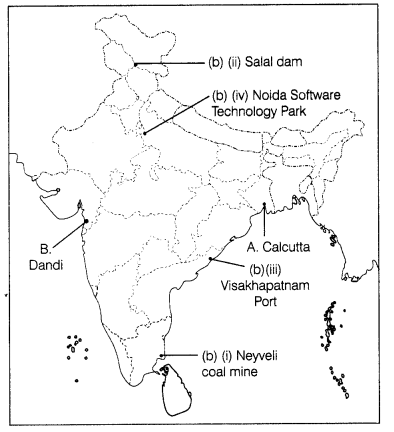
(iv) Noida Software Technology Park (5)
Answer: