CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-3
Class 10thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-3
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 3 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
- Question paper comprises five Sections – A, B, C, D, and E. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section C contains Q. 25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer type questions, carrying S marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section-E – Questions no. from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions arid are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section
A
Section A consists of 20
questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
During the Indian Freedom Struggle, why did the Rowlatt Act
arouse popular outrage? (1)
(a) It curtailed the freedom of religion.
(b)
It curbed trade union activities.
(c) It was against the Champaran
Satyagraha.
(d) It allowed the detention of political prisoners without trial
for two years.
Answer:
During the Indian freedom struggle, the Rowlatt Act
allowed the detention of political prisoners without trial for two years.
Question 2.
Study the picture and answer the question that follows:
[1]
Which of the following events was related to this image of
Gandhi?
(A) Non-Cooperation Movement
(B) Kheda Satyagraha
(C) Dandi
March
(D) None of these
Answer:
(C) Dandi March
Explanation: Gandhiji and his 80 followers marched 241 miles from Sabarmati Ashram to the coastal town of Dandi (Gujarat), breaking the government law by gathering natural salt found on the seashore and boiling seawater to produce salt.
Question 3.
Why was reading the manuscript not easy in India? Choose the
correct answer from the following options. (1)
(a) Manuscripts were highly
cheap.
(b) Manuscripts were widely spread out.
(c) Manuscripts were
written in English and Hindi.
(d) Manuscripts were fragile.
Answer:
(d)
Manuscripts were fragile.
Question 4.
Match the correct column: [1]
| Column A | Column B | ||
| (i) | Union List | (a) | Education |
| (ii) | State List | (b) | Computer Software |
| (iii) | Concurrent List | (c) | Foreign Affairs |
| (iv) | Residuary Subjects | (d) | Agriculture |
Options:
(A) (i)-(c), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
(C) (i)-(d),
(ii)-(c), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
(B) (i)-(a), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(d)
(D) (i)-(b), (ii)-(a), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(d)
Answer:
(A) (i)-(c), (ii)-(d),
(iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
Explanation:
(i) Foreign Affairs is included in Union List because we need
a uniform policy on these matters throughout the country.
(ii) Agriculture is
included in State List as states are entirely competent to enact laws on
agriculture.
(iii) Education is included in Concurrent List as the Indian
Constitution has provisions to ensure that the state provides education to all
its citizens. Education being a concurrent list subject enables the Central
Government to legislate it in the manner suited to it.
(iv) Computer Software
is included in the Residuary Subjects as it was not present at the time when the
Constitution was being written. Union Government has the powers to make laws
regarding this subject.
Question 5.
Identify the appropriate reason for the formation of the
Swaraj Party from the options given below. (1)
(a) It wanted members of
Congress to return to Council Politics.
(b) It wanted members of Congress to
ask for Poorna Swaraj for Indians.
(c) It wanted members of Congress to
oppose the Simon Commission.
(d) It wanted members of Congress to ask the
Dominion State for India.
Answer:
(a) It wanted members of Congress to
return to Council Politics.
Question 6.
Find the incorrect option from the following: [1]
(A)
Belgium is a big country in North America.
(B) It has borders with France,
the Netherlands, Germany and Luxembourg.
(C) It has a population of a little
over one crore.
(D) The ethnic composition of this small country is very
complex.
Answer:
(A) Belgium is a big country in North America.
Explanation: Belgium is a smaller than Haryana. In Europe it shares borders with France, the Netherlands, Germany and Luxembourg.
Question 7.
Arrange the following in the correct sequence (land
degradation by %). (1)
I. Forest degraded area
II. Water eroded area
III. Wind eroded area
IV. Saline and alkaline deposits
Codes
(a) I,
III, IV, II
(b) II, I, ¡II, IV
(c) I, II, IV, III
(d) II, III, IV,
I
Answer:
(b) II, I, III, IV
Question 8.
Analyze the information given below, considering one of the
following correct options: [1]
Laxmi, owning about three hectares of
unirrigated land is dependent only on rain and growing crops like jowar and
arhar. All seven members of her family work in the field throughout the year.
You will see that everyone is working, none remains idle, but their labour
effort gets divided. Each one is doing some work but no one is fully
employed.
(A) Underemployment
(B) Disguised unemployment
(C) Seasonal
unemployment
(D) Both (A) and (B).
Answer:
(D) Both (A) and (B).
Question 9.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below.
Assertion (A) Pulses are
grown in rotation with other crops.
Reason (R) It helps in restoring soil
fertility by fixing nitrogen from the air. (1)
Codes
(a) Both A and R are
true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R
is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is
false, but R is true
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the
correct explanation of A.
Question 10.
Study the pie chart showing production of Manganese
state-wise share in per cent, 2016-17. Answer the question that follows:
[1]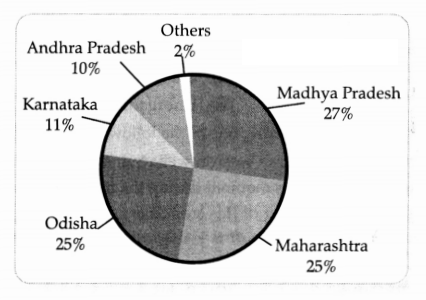
Which of the following events was related to this image of
Gandhi?
(A) Non-Cooperation Movement
(B) Kheda Satyagraha
(C) Dandi
March
(D) None of these
Answer:
(C) Dandi March
Question 11.
Identify the correct statement(s) about unitary form of
government. (1)
Statement I There is either only one level of government or
the sub-units are subordinate to the Central Government.
Statement II The
Central Government can pass an orders to the Provincial Government.
Statement
III Laws made by the centre are equally enforced in rest of the states without
territorial distinction.
Statement IV The powers of State Governments are
guaranteed by the Constitution.
Codes
(a) Statement I and II are right
(b) Statement II and III are right
(c) Statement I, II and III are right
(d) Only Statement IV is right
Answer:
(c) Statement I, II and III are
right
Question 12.
Which of the following revolutions is called as the first
expression of ‘Nationalism’? [1]
(A) French Revolution
(B) Russian
Revolution
(C) Glorious Revolution
(D) The Revolution of the Liberals
Answer:
(A) French Revolution
Explanation: Till 1789, France was a territorial state under the rule of an absolute monarch and through French Revolution the idea of nationalism brightened up the motivated people to own the country
Question 13.
Suppose your teacher has given you an assignment regarding
power arrangements in Belgium and Sri Lanka. According to you
which of these
following statements are appropriate for helping you in preparing your
assignment? (1)
I. In Belgium, the Dutch-speaking majority people tried to
impose their domination on the minority French-speaking community
II. In Sri
Lanka, the policies of the government sought to ensure the dominance of the
Sinhala-speaking majority.
III. The Tamils in Sri Lanka demanded a federal
arrangement of power sharing to protect their culture, language and equality
of opportunity in education and jobs.
IV. The transformation of Belgium from
unitary government to a federal one prevented a possible division of the country
on linguistic lines.
Codes
(a) I, II, III, and IV
(b) III and IV
(c)
I, II, and IV
(d) II, III, and IV
Answer:
(d) II, III, and IV
Question 14.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below: [1]
Assertion (A):
Brussels has a Separate government in which both communities have equal
representation.
Reason (R): In Brussels, French-speaking people accepted
equal representation.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct
explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct
explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(D) (A) is wrong
but (R) is correct
Answer:
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the
correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: The French-speaking people accepted equal representation in Brussels because the Dutch-speaking community has accepted equal representation in the central government.
Question 15.
As a student of economics, identify which among the following
cannot be purchased through money. (1)
I. Full protection from infectious
diseases
II. A pollution-free atmosphere
III. High-quality education
IV. A luxury home
Codes
(a) 1 and III
(b) III and 1V
(c) I and
IV
(d) I and II
Answer:
(d) I and II
Question 16.
Rakesh works in an automobile unit in Gurugram. However, he
does not get any facilities like health insurance, medical leave, provident
fund, gratuity, etc. He is working in : [1]
(A) Public sector
(B)
Organised sector
(C) Private sector
(D) Unorganised sector
Answer:
(D) Unorganised sector
Explanation: Rakesh works in an unorganized sector wherein his employment is not secure, he is generally low-paid and is not regularly paid. His employers do not make provisions for overtime payment, paid leaves or holidays, medical facilities, gratuity, and provident fund
Question 17.
Identify the sector of the economy with the help of the given
information. (1)
It covers activities in which primary goods are used to
produce some other commodity.
This sector mainly includes services such as
manufacturing, construction, gas, water, electricity supply, etc.
It produces
more than half of the total country’s output.
The employees of this sector
are less than half of the working population.
(a) Primary sector
(b)
Tertiary sector
(c) Secondary sector
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c)
Secondary sector
Question 18.
Large reserves of natural gas have been discovered in which
place in India? [1]
(A) Tripura
(B) Krishna and Godavari Delta
(C)
Maharashtra
(D) All of the Above
Answer:
(D) All of the Above
Question 19.
How GDP is calculated? (1)
(a) The value of final goods
and services produced in each sector during last three years provides the total
production of the sector for that year.
(b) The value of final goods and
services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total
production of the sector for that year and the sum of production in the three
sectors.
(c) The value of intermediate goods and services produced in each
sector during a particular year and the sum of production in the three
sectors.
(d) The value of intermediate goods and services produced in each
sector during a particular year provides the approximate production of the
sector for that year.
Answer:
(b) The value of final goods and services
produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production
of the sector for that year and the sum of production in the three sectors.
Question 20.
‘Democratic governments have a much better record than any
non-democratic regime.’ [1]
Instead of the above-given statement, find the
incorrect option regarding democracy from the following:
(A) Democracy
enhances the dignity of the individual.
(B) It provides a method to resolve
conflicts.
(C) Improves the quality of decision-making.
(D) Allows room to
make more mistakes.
Answer:
(D) Allows room to make more mistakes.
Explanation: In Democracy there is a space for public discussion on the mistakes
committed. As in a democracy, the main power is with the citizens so if they
make a wrong choice in choosing the representative then it can be changed by
voting others and the mistake would be corrected.
Section
B
Section B consists of 4
questions of 2 marks each
Question 21.
Study the map thoroughly and mention the sub-groups that are
dominantly found in this country. (2)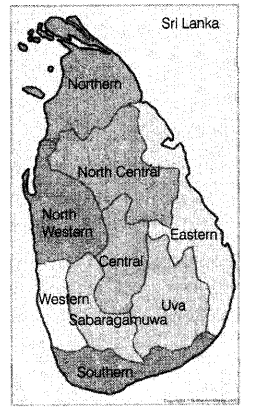
Answer:
The sub-groups that are dominantly found in Sri Lanka are Sri Lankan
Tamils and Indian Tamils.
Question 22.
Compacted substances that comprise the earth’s crust are
called rocks. [2]
Analyze the above statement and write any two
characteristics of rocks.
Answer:
Characteristics of rock:
(i) Rocks
are formed due to chemical compositions and erosion that takes place on the
earth.
(ii) Rocks are the naturally formed aggregate of mineral
particles.
(iii) It is the minerals that impart their texture, colour, shape,
hardness or softness to rocks.
Question 23.
What was an ‘Accordion Book’? Describe any one feature of
hand printing in China. (1+1) (2)
Or
Describe the effects of reading
mania.
Answer:
The Accordion Book’ was the traditional book of China. It
was folded and stitched at the side. This book was hand-printed.
Books in
China were printed by rubbing paper against the inked surface of woodblocks is
the feature of hand printing in China.
Or
The following points show the
effect of reading mania
- Booksellers roamed around for selling almanacs ballads, folktales, etc.
- Penny chapbooks were carried by petty pedlars in England for a penny.
- In France, ‘Bibliotheque Bleue, which were low-priced small books were printed.
- Newspapers, and journals containing information started circulating.
- Texts containing ideas of scientists and philosophers became popular among the masses.
Question 24.
Justify money as a medium of exchange. [2]
Answer:
Money is a medium of exchange:
(i) Allows people and businesses to obtain
what they need to live and thrive.
(ii) It is also accepted as a medium of
exchange because the currency is authorized by the Governments of various
countries.
Section
C
Section C consists of 5
questions of 3 marks each
Question 25.
What were the causes of the ethnic conflict in Belgium?
(3)
Answer:
The causes of the ethnic conflict in Belgium were as
follows
- The minority French-speaking community was relatively rich and powerful. This was resented by the Dutch-speaking community.
- The Dutch-speaking community got the benefit of economic development and education much later than the French-speaking community.
- This led to conflict between the Dutch-speaking and French-speaking communities during the 1950s and 1960s.
- There was a great social disparity between Dutch and French-speaking communities during the 1950s and 1960s.
Question 26.
Conservation in the background of rapid decline in wildlife
population and forestry has become essential. [3]
Study the statement
carefully and tell why we need to conserve our forests and wildlife.
Answer:
We need to conserve our forests and wildlife because:
(i)
Conservation preserves the ecological diversity and our life support system –
air, water and soil.
(ii) Conservation also preserves the genetic diversity
of plants and animals for better growth of species and breeding.
(iii) It
makes the planet Earth safe.
Question 27.
Rahul wants to grow wheat, jowar, and brinjal on his land.
However, these crops are grown in different cropping seasons. In this context,
what are the cropping seasons in India? (3)
Or
Why is subsistence
agriculture still practiced in certain parts of the country? Give three
reasons.
Answer:
India has three cropping seasons. These are as follows
Rabi Season These crop are sown in winter from October to December and harvested
from April to June.
Kharif Season These crops are sown with the onset of monsoon (June-July) in different parts of the country and are harvested in September-October.
Zaid Season It comes in between the Rabi and Kharif seasons. It is a short
season during the summer months.
Or
The three reasons why subsistence agriculture is still practiced are
- Plots of land are fragmented and small, so large-scale farming cannot be done.
- A large number of family members in rural areas depend on agriculture which makes it necessary to grow crops for self-consumption.
- Poor farmers do not have the resources to buy better inputs like fertilizers, pesticides, irrigation, facilities, and other modern means.
Question 28.
The organised sector is well organised by the Government.
[3]
Justify the statement by giving reasons as to why do people prefer to
work in the organised sector.
Answer:
Advantages of organised sector;
(i) People enjoy the security of employment.
(ii) Work for fixed hours.
(iii) If they work more, they get overtime allowances.
(iv) Paid leaves,
payment during holidays, medical benefits, safe working environment, and pension
after retirement.
Question 29.
Why did the Non-Cooperation Movement gradually slow down in
cities? Explain two reasons. (3)
Answer:
The Non-Cooperation Movement in
the cities gradually slowed down for the following reasons
(i) Khadi cloth
was often more expensive than mass-produced mill cloth and poor people could not
afford to buy it. Thus, a boycott of foreign goods could not continue for
long.
(ii) Similarly, the boycott of British institutions posed a problem. No
alternative institutions were set up in their place. So, the students, teachers,
lawyers, and other professionals finally had to resume their studies and jobs in
government institutions like schools, and colleges. courts, etc.
Section
D
Section D consists of 4
questions of 5 marks each
Question 30.
Explain the attitude of the Indian merchants and the
industrialists towards the ‘Civil Disobedience Movement’. [5]
OR
‘Through
the Civil disobedience movement, Mahatma Gandhi sought to unite the nation and
he accomplished his goal. In light of the given statement, discuss the role of
common people in the civil disobedience movement.
Answer:
The attitude of
the Indian merchants and the industrialists towards the Civil Disobedience
Movement:
- During the First World War, Indian merchants and industrialists made huge profits and became powerful.
- They wanted protection against imports of foreign goods and a Rupee¬Sterling Foreign Exchange ratio that would discourage import.
- To organize business interests they formed the Indian Industrial and Commercial Congress (in 1920) and the Federation of Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industries-FICCI (in 1927).
- They gave financial assistance and refused to buy or sell imported goods.
- Most businessmen came to see ‘Swaraj’ as a time when Colonial restrictions on business would no longer exist and trade and industry would flourish without constraints.
- After the failure of the Round Table Conference business groups were no longer uniformly enthusiastic.
- They were apprehensive of the spread of militant activities and worried about prolonged disruption of business.
OR
- Common people from across the nation participated in the civil disobedience movement.
- Thousands of people manufactured salt in different parts of the country and broke the salt law.
- People boycotted foreign cloth and picketed liquor shops.
- Peasants refused to pay revenue.
- Forest people violated forest laws by giving into Reserved forests to collect wood and graze cattle.
Question 31.
Is it right that the national development of a country
depends on the availability of public facilities? State the utilities of any two
public facilities available in India.
Or
Shruti has a development goal of
earning enough income to avail of facilities. However, Deepti has a goal give
her equal respect in society as she is an Adivasi. In this context, give
examples to prove that there are other important developmental goals other than
income. (5)
Answer:
It is right that the national development of a country
depends on the availability of public facilities. Public facilities are those
provided by the government. They may be either highly subsidized or free of cost
for the people.
The utilities of two public facilities available in India are
- The Public Distribution System (PDS) provides fair average quality of foodgrains and other essential items to the weaker sections of the population at subsidized price.
- Health care in government hospitals and dispensaríes is provided to all at
subsidized rates. This includes outpatient as well as hospitalization
facilities.
Or
Besides income, the developmental goals of various categories of people are different from person to person. Some examples of developmental goals other than income are For rich farmers, development means higher support price for crops, cheap labour and subsidized inputs.
For; landless rural labourer, development means more days of work, schools
for their children and no social discrimination.
For Adivasi, development
means no social discrimination, year-round, school education for children, and
PDS shop in his village.
Question 32.
Why has Federalism succeeded in India? Which were the
policies adopted by India that ensured this success? Explain. [5]
OR
The
State Governments are required to share some powers and revenue with Local
Government Bodies.
Given the above statement explain any five features of the
Panchayati Raj system in India.
Answer:
Federalism has succeeded in India
due to the nature of democratic policies in our country.
The policies adopted
by India to ensure this success are:
- Linguistic States: After Independence, the boundaries of several old states were changed to create new states. The creation of Linguistic State is the first and a major test fdr democratic policies in our country.
- Language Policy: The second test for the Indian Federation is the language policy. The Indian Constitution did not give the status of National Language to any one of the languages.
- Centre-State Relations: Restructuring the Centre-State relations is one more way in which Federalism has been strengthened in practice.
- Decentralisation of Power: Power in India has been decentralised to the local government. The local government includes Panchayats in villages and municipalities in Urban areas.
OR
Rural local government is known as Panchyati Raj.
- Panchayati Raj Institution is rural based.
- Each village has Gram Panchayat.
- It has Panchs and a Sarpanch.
- He/She is directly elected by the adult population living in the village.
- Panchayat works under the gram Sabha.
- All the voters meet at least twice or thrice in a year.
- Few Gram Panchayats form Panchayat Samiti or Block or Mandol.
Question 33.
“Democracy is much superior than any other form of government
in promoting dignity and freedom of the individuals”. Justify this statement by
providing suitable examples.
Or
Can we judge democracy by its outcome?
Explain. (5)
Answer:
In our society, every individual wants to receive
respect from fellow beings. In this respect, democratic form of government
stands much superior to any other form of government in promoting dignity and
freedom of the individual.
The following points support the given statement Often conflict arises among individuals because some feel that they are not treated with equal respect in comparison to others. It is very common in non-democratic countries. But ¡n democracy, respect, and freedom are the basis of it. Democracy throughout the world has recognised this atleast in principle.
Most societies were historically male-dominated. The status of women was not satisfactory. After long struggles by women, democracy throughout the world has recognised equal treatment and respect to women at least in principles, In democracy, it becomes easier for women to wage a struggle against what is now unacceptable legally and morally for them.
Democracy in India has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated castes for equal status and opportunity, which is not possible in any non-democratic country.
Value Points
- For getting maximum marks, following value points can be included in the answer
- Mention about equal respect for every one individual in democracy.
- Mention about equal treatment to women in democracy.
- Mention about equal status and opportunity to discriminated castes in democracy.
Or
Democracy should be judged by its outcome because it opens the path of
expectations which is one of the criteria for judging any democratic
country.
The following points justify the above statement
- The examination procedure of democracy is eternal, as it passes one test, it produces another test.
- It automatically gives rise to expectations as well as complaints by the people when they want to know about the functioning of democracy.
- The fact that people also complain about democracy indicates the awareness and the ability of people to expect and to look critically at power holders and the high and the mighty.
- It transforms people from the status of a subject into that of a citizen.
- Most individuals today believe that their vote makes a difference to the way the government is run and to their self-interest.
Section
E
Section E consists of 3
Case-based questions of 4 marks each
Question 34.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that
follow: [4]
Many activities are undertaken by directly using natural
resources. When we produce a good by exploiting natural resources, it is an
activity of the primary sector. Since most of the natural products we get are
from agriculture, dairy, fishing, and forestry, this sector is also called
agriculture and related sectors.
The secondary sector covers activities in which natural products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing that we associate with industrial activity. It is the next step after primary. The product is not produced by nature but has to be made and therefore some process of manufacturing is essential. After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under tertiary sector and is different from the above two.
These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities, by themselves, do not produce a good but they are an aid or a support for the production process. The various production activities in the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors produce a very large number of goods and services. Also, the three sectors have a large number of people working in them to produce these goods and services.
The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. And the sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. GDP shows how big the economy is.
34.1 Production of a commodity, mostly through ways of manufacturing is an
activity of which sector? [1]
Answer:
The secondary sector of the economy
is an economic sector that describes the role of manufacturing. It encompasses
industries that produce a finished, usable product or are involved in
construction
34.2 State one example of tertiary sector. [1]
Answer:
Transport is an
example of tertiary activity.
34.3 Why is secondary sector called industrial? [2]
Answer:
Secondary
sector is also called industrial because the secondary sector is mostly
associated with industries. For example, textile industry, steel industry,
etc.
Question 35.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that
follow.
On 13th April the infamous Jallianwala Bagh incident took place. On
that day, a large crowd gathered in the enclosed ground at Jallianwala Bagh.
Some came to protest against the government’s new repressive measures. Others
had come to attend the annual Baisakhi fair. Being from outside the city, many
villagers were unaware of the martial law that had been imposed. Dyer
entered
the area, blocked the exit points, and opened fire on the crowd, killing
hundreds. His object as he declared later, was to ‘produce a moral effect’, to
create in the minds of Satyagrahis a feeling of terror and awe.
As the news of Jallianwala Bagh spread, crowds took to the streets in many North Indian towns. There were strikes, clashes with the police, and attacks on government buildings. The government responded with brutal repression, seeking to humiliate and terrorize people. Satyagrahis were forced to rub their noses on the ground, crawl on the streets, and do salam to all sahibs; people were flogged and villages (around Gujranwala in Punjab, now in Pakistan) were bombed. Seeing violence spread, Mahatma Gandhi called off the movement.
(i) Why did General Dyer open fire on the peaceful gathering at Jallianwala
Bagh on 13th April 1919? Why Martial Law was imposed in Amritsar?
(ii) What
were the effects of the Jallianwala Bagh massacre? (4)
Answer:
General
Dyer opened fire on the peaceful gathering at Jailianwala Bagh because Martial
Law was imposed in Amritsar instead of which people were gathered there.
Martial Law was imposed in Amritsar because local leaders were picked up from
Amritsar and Mahatma Gandhi was not allowed to enter Delhi.
(ii) The effects of the Jallianwala Bagh massacre were There were strikes, clashes with the police and attacks on the government buildings. The government took repressive measures and forced Satyagrahis to rub their noses on the ground.
Question 36.
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that
follow: [4]
India had a very rich and old tradition of manuscripts- in
Sanskrit, Arabic, Persian, as well as in various vernacular languages.
Manuscripts were copied on palm leaves Or on handmade paper. Pages were
sometimes beautifully illustrated. They would be either pressed wooden covers or
sewn together to ensure preservation.
Manuscripts continued to be produced well after the introduction of print, down to the late nineteenth century. Manuscripts, however, were highly expensive and fragile. They had to be handled carefully, and they could not be read easily as the script was written in different styles. So manuscripts were not widely used in everyday life.
Even though pre-colonial Bengal had developed an extensive network of village primary schools, students very often did not read texts. They only learnt to write. Teachers dictated portions of texts from memory and students wrote them down. Many thus became literate without ever actually reading any kinds of texts.
36.1 What is meant by manuscripts? [1]
Answer:
A manuscript is a
handwritten work.
36.2 Mention any two languages in which the manuscripts were written. [1]
Answer:
Manuscripts were written in Sanskrit, Arabic, and Persian, as well as
in various vernacular languages.
36.3 Write any two features of the manuscripts. [2]
Answer:
(i)
Manuscripts were highly expensive and fragile.
(ii) Manuscripts were not
widely used in everyday life
Section
F
Section F consists of Map based
questions of 5 marks
Question 37.
(a) Two places A and B are marked on the given outline map of
India. Identify them and write their correct names on the line drawn near them.
(5)
A. Movement of Indigo Planters
B. Peasant Satyagraha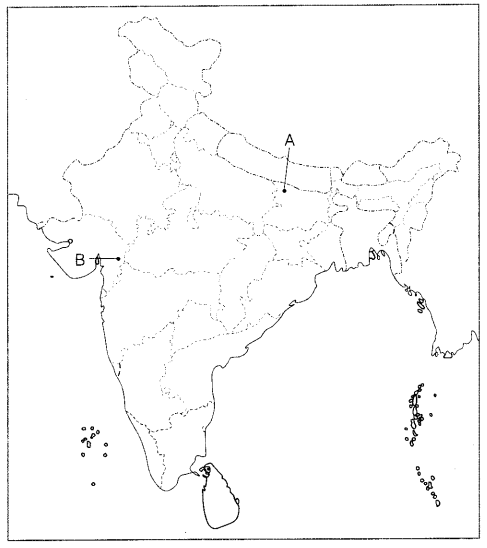
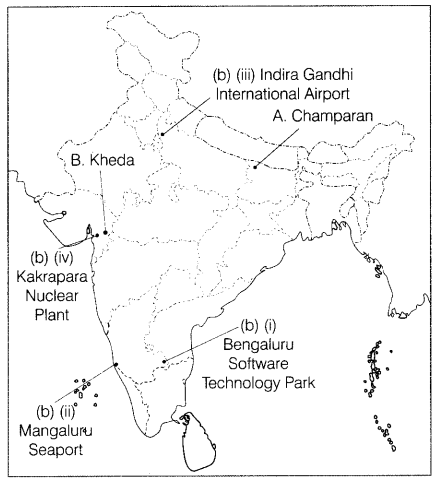
(b) On the same map of India, locate and label any three among the following
with suitable symbols.
(i) Bengaluru Software Technology Park
(ii)
Mangaluru Seaport
(iii) Indira Gandhi International Airport
(iv) Kakrapara
Nuclear Plant
Answer: