CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-12
Class 10thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-12
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 12 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
There are
total 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Question paper comprises five Sections – A, B, C, D, and E. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21. to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section C contains Q. 25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section D – Question no, 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no. from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided n few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section
A
Section A consists of 20
questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Which of the following incidents mobilised nationalist
feelings among the educated elite class across Europe? (1)
(a) German
Unification
(b) Greek War of Independence
(c) Unification of Italy
(d)
Unification of Britain
Answer:
(b) Greek War of Independence
Question 2.
What did Mahatma Gandhi declare in his book, ‘Hind
Swaraj’?
(a) British ruled India because the latter was militarily weak.
(b) British ruled India because Indians cooperated with them.
(c) British
ruled India because they got international support.
(d) None of the
above.
Answer:
(b) British ruled India because Indians cooperated with
them.
Question 3.
Consider the following statements and choose the incorrect
ones. (1)
I. In 1925, Ahuri Sitaram Raju was arrested ending a two years
armed tribal struggle.
II. In 1932, the Poona Pact was signed between Dr.
Babasaheb Ambedkar and Mahatma Gandhi.
III. In 1929, Lord Cornwallis
announced a vague offer of ‘dominion status’ for India.
IV. In 1927, the
Federation of the Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industries (FICCI) was
formed.
Codes
(a) I and III
(b) III and II
(c) II and IV
(d) I,
II, and IV
Answer:
(a) I and III
Question 4.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
I. Print
culture created the conditions for the French Revolution.
II. Martin Luther’s
writings led to the beginning of the Protestant Reformation.
III. Menocchio
reinterpreted the message of the Bible.
IV. Johann Gutenberg invented the
printing press.
Options:
(a) III, II, I and IV
(b) I, II, III, and
IV
(c) IV, III, II and I
(d) IV, II, III and I
Answer:
(d) IV, II,
III and I
Question 5.
The tricolour flag had a spinning wheel in the center of a
red, green, and white banner The red stripe was for Hindus and the green was for
Muslims. The white band represented peace and the rest of the communities living
in India. Who was the designer of this flag? (1)
(a) Abanindranath Tagore
(b) Rabindranath Tagore
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) Natesa Sastri
Answer:
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
Question 6.
In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation
practiced?
(a) Punjab
(b) Plains of Uttar Pradesh
(c) Haryana
(d)
Uttarakhand
Answer:
(d) Uttarakhand
Question 7.
What percentage of land in India consists of fertile plains?
(1)
(a) 38%
(b) 43%
(c) 46%
(d) 61%
Answer:
(b) 43%
Question 8.
Consider the following statements regarding language policy of
India and identify the correct one from the following:
(a) Hindi is the
national language.
(b) English is the official language.
(c) No language
is given the status of national language.
(d) English is the national
language.
Answer:
(c) No language is given the status of national
language.
Question 9.
The famous Bcej Bachao Andolan took place in (1)
(a)
Maharashtra
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) Uttarakhand
(d) Punjab
Answer:
(c) Uttarakhand
Question 10.
Who among the following decides on saving and loan activities
in the Self-Help Groups (SHGs)?
(a) Manager of a Bank
(b) Members of
Non-Governmental Organisation (NGO)
(c) Local Moneylenders
(d) Members of
Self-Help Group (SHG)
Answer:
(d) Members of Self-Help Group (SHG)
Question 11.
The Badampahar mine in Mayurbhanj and Kendujhar district is
situated in which of the following Indian states?
(a) Karnataka
(b)
Odisha
(c) Chhattisgarh
(d) Jharkhand
Answer:
(b) Odisha
Question 12.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below:
Assertion (A): India
is a federal state.
Reason (R): Power is shared among different tiers of the
government.
Options:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct
explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct
explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct, but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is
wrong, but (R) is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R)
is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 13.
Consider the following statements regarding the current
ruling party of India ‘The Bharatiya Janata Party’. (1)
I. The party wants to
ban religious conversions and promote anti-conversion laws to stop religious
conversion in the country.
II. The party wants full territorial and political
integration of Tibet with India.
III. Cultural nationalism or Hindutva is an
important element in BJP’s conception of Indian nationhood and politics.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Codes
(a) I, II and
III
(b) Only I
(c) Both I and III
(d) Both II and III
Answer:
(c)
Both I and III
Question 14.
Read the given data and find out which one of the following
options has the highest contribution in loan activities in rural India.
| Source of Credit per ₹ 1000 of Rural Households in India in 2012 | |
| Category | Category |
| Commercial Banks | 25% |
| Cooperative Banks | 25% |
| Moneylenders | 33% |
| Government | 1% |
(a) Commercial Banks
(b) Cooperative Banks
(c) Moneylenders
(d)
Government
Answer:
(c) Moneylenders
Question 15.
According to the Human Development Report of UNDP, 2018, the
HDI ranking of countries are mentioned below. (1)
| Country | Rank |
| Sri Lanka | 78 |
| India | 120 |
| Pakistan | 150 |
| Nepal | 149 |
Why Sri Lanka have a better rank than India in the Human Development Report
of 2018?
Choose the correct option from the following.
(a) The per capita
income of Sri Lanka is higher than in India.
(b) Sn Lanka has low population
as compared to India.
(c) The literacy ratio i.e. enrollment ratio in all
levels of schools in Sri Lanka is comparatively better than in India.
(d)
Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Question 16.
Find the odd one out from the following options:
(a)
Tourist Guide, Barber, Tailor, and Potter
(b) Teacher, Doctor, Vegetable
Vendor and Lawyer
(c) Postman, Cobbler, Soldier and Police Constable
(d)
Indian Railways, Jet Airways, Doordarshan and Metro
Answer:
(d) Indian
Railways, Jet Airways, Doordarshan and Metro
Question 17.
Which of the following terms is defined as the average
expected length of life of a person at the time of birth? (1)
(a) Birth
rate
(b) Life expectancy
(c) Life span
(d) Mortality rate
Answer:
(b) Life expectancy
Question 18.
Read the information given below and select the correct
option.
Ravi lives in Gurugram. When he was in school, there were very few
call centers in Gurugram. Now he finds hundreds of call centres and BPOs in the
city. Which one of the following is the most appropriate reason for this
growth?
(a) High FDI
(b) High average income
(c) Developed network of
transportation
(d) High tariffs
Answer:
(a) High FDI
Question 19.
Identify the sector of the economy with the help of given
information. (1)
It covers activities in which primary goods are used to
produce some other commodity.
This sector mainly includes services such as
manufacturing, construction, gas, water electricity supply, etc.
It produces
more than half of the total by country’s output.
The employees of this sector
are less than half of the working population
(a) Primary sector
(b)
Secondary sector
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Secondary sector
Question 20.
Identify the correct statement/s Unorganised Sector:
I.
There are no rules and regulations.
II. There is no provision for overtime,
paid leave, holidays, etc.
III. Employment is not secure.
IV. Workers get
pensions after their retirement.
Options:
(a) I & II
(b) II &
III
(c) I & III
(d) II & IV
Answer:
(b) II & III
Section
B
Section B consists of 4
questions of 2 marks each
Question 21.
Study the map thoroughly, and mention any one mineral that is
found in the highlighted region. (2)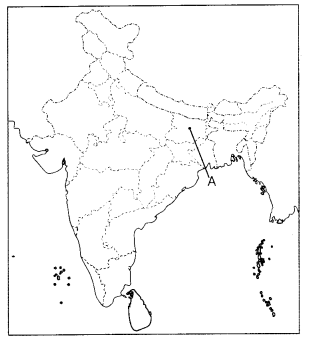
Answer:
Gaya district is mainly known for deposits of Mica. It is also found
in Jamui, Bhagalpur and Munge districts. Bihar comes in the third position with
an estimated production of 3,381 tonnes of mica.
Question 22.
Suggest two ways to conserve energy resources in India.
OR
Suggest two ways to improve the usage of solar energy.
Answer:
Energy can be conserved in different ways. Some of them are as below:
- Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy sources. The people should be made aware of the fact that energy should be conserved and used sustainably. They should use renewable energy sources.
- We have to adopt a cautious approach to the judicious use of our limited energy resources. A sustainable use of non-renewable energy resources is very important to conserve them.
- Use public transport systems instead of individual vehicles. People should use public transport instead of private vehicles to save excess use of fossil fuels.
- Switch off electricity when not in use. One should switch off electricity when one is not using it. It can save a huge amount of energy in the whole world.
- Using power-saving devices is another method to conserve energy.
- One should use non-conventional sources of energy.
OR
Some ways to improve the usage of solar energy are as follows:
- it can be improved by reducing the cost of solar panels.
- The use of efficient solar panel models is another method of improving the usage of solar energy.
- Rising awareness about the importance of renewable energy is very important. In society, people should be made aware of this fact.
- Easy installation process. The installation process of solar panels is very easy. People can easily install them in their houses on their own.
- One should buy solar panels with High Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV) Cells.
- One should avoid installing solar panels in shaded areas as it will act as a barrier to the production of solar energy.
Question 23.
Name the national political party which espouses secularism
and the welfare of weaker sections and minorities. Mention any two features of
that party. (1)
Answer:
The national political party which espouses
secularism and the welfare of weaker sections and minorities is the Indian
National Congress.
- The features of this party are listed below
- It was founded in 1885.
- It dominated Indian politics, both at the national and state levels, for several decades after India’s independence.
Question 24.
Mention any two major differences between the policies of CPI
and CPI(M).
Answer:
| Policies of CPI | Policies of CPI (M) |
| (i) It considers democratic elections as a valuable and influential tool for ensuring the objective of socio-economic justice in India. | It considers parliamentary democracy as a tool for promoting the interests of the poor, the working class and farmers. |
| (ii) It is critical of the new economic policies that allow free flow of foreign money and goods into the country. | It is against secessionism and communalism. |
Section
C
Section C consists of 5
questions of 3 marks each
Question 25.
Analyze the data properly and answer the following questions.
(1.5+ 1.5)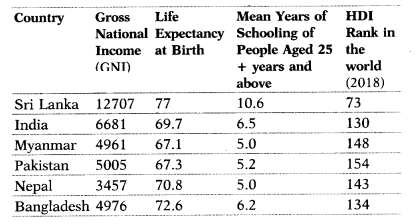
(i) By reading the data carefully, find out which country is at the top and
which is at the bottom.
(ii) What is the main criterion used by the World
Bank in classifying different countries?
Answer:
(i) Data Top (Country)
Bottom (Country)
- Per Capita Income Sri Lanka Nepal
- Lite Expectancy at Birth Sri Lanka Pakistan
- HDI Rank in the World Sri Lanka Pakistan
(ii) The World Bank uses the criterion of per capita income for classifying counties. Countries with an income of US $ 2500 or less were classified as low per capita income countries. Countries with per capita income of US $ 49,300 per annum and above in 2019 are classified as high-income countries.
Question 26.
“Tribal peasants interpreted the message of Mahatma Gandhi
and the idea of swaraj in another way and participated in the Non-Cooperation
Movement differently.” Justify the statement.
OR
Why did Congress become
unhappy with the proceedings of the Awadh Peasant Movement?
Answer:
The
tribal people had developed their interpretation of the meaning of swaraj and
reacted differently during the non-cooperation movement:
- There was the initiation of a militant guerilla movement in the Gudem Hills of Andhra Pradesh.
- They became resistive towards the colonial laws and policies and tried to break those laws on several occasions.
- Large number of peasants left plantations and defied the authority of the British government. They also resorted to violence on many occasions.
OR
There were several reasons why the Congress became unhappy with the
proceedings of the Awadh Peasant Movement.
- The movement became violent and the houses of Talukdars and merchants were attacked and bazaars were looted.
- Peasants were told that Gandhiji was told not to pay taxes to the landlords which was not true in reality. The name Gandhiji was widely used to spread rumors.
- The movement did not adopt the non-violent approach which was deemed by Congress and Mahatma Gandhi for the freedom struggle.
Question 27.
Briefly explain how caste inequalities are still prevailing
in India. (3)
Or
What is secularism? Mention any two provisions of the
Indian Constitution which make it a secular state. (1+ 2)
Answer:
Caste
inequalities are still prevailing in India. This can be clear by looking at the
following facts
According to the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO). the
average economic status of caste groups in India remains the same as was in the
past. Most of the rich section belongs to higher castes while people of lower
castes are generally poor. Despite the Constitutional prohibition. many people
are still considered untouchables in the country. Even now most people marry
within their own caste or tribe Political parties often field their candidates
in a constituency according to the caste prevailing in that constituency. people
also tend to vote on the caste lines.
Or
Secularism means all religions are given the same respect and there is
no state religion.
Two provisions of the Indian Constitution which make it a
secular state are
(i) No religion has a special status.
(ii) Freedom to
practice, profess, and propagate one’s religion is allowed by the
Constitution.
Question 28.
Why do most of the rural households remain dependent on
informal sources of credit? Explain.
Answer:
There are several reasons why
rural people are still dependent on informal sources of credit:
- The availability of banks in rural areas is very less due to which people are unable to acquire credit from them.
- The documentation procedures of the banks are too lengthy and on several occasions, rural people are unable to fulfil the formalities of documents due to which they do not receive loans.
- One of the most prominent reasons is the absence of collateral and the easiness of securing loans from rich landlords.
Question 29.
Name the national political party that gets inspiration from
India’s ancient culture and values. Mention four features of that party.
(1+2)
Answer:
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) founded in 1980 draws
inspiration from India’s ancient culture and values. Features of the Bharatiya
Janata Party (BJP) Cultural Nationalism (Hindutva) is an important element in
its conception of Indian nationhood and politics. They focused on the full
territorial and political integration of Jammu and Kashmir with India. They want
a uniform civil code for all people living in the country irrespective of
religion and a ban on religious conversions. BJP was earlier limited to North
and West and urban areas, but the party expanded support in the South-East. the
North-East and rural areas.
Section D
Section
D consists of 4 questions of 5 marks each
Question 30.
Why did the Roman Catholic Church begin keeping an Index of
Prohibited Books from the mid-sixteenth century? Explain by giving five
reasons.
OR
Explain how print culture assisted the growth of nationalism
in India.
Answer:
The Roman Catholic Church kept an Index of Prohibited
Books from the mid-sixteenth century. The reasons are as follows:
- It was felt that if there was no control over the printed materials, then rebellion and irrational thoughts might permeate.
- Many monarchs thought that if there is no control, then printed books could lead to rebels against the state authorities.
- Many religious prerogatives feared that printed materials could make the people rebel against their religious beliefs and faith.
- The Roman Catholic Church wielded control over publishers and book retailers. The Church began to maintain an Index of Prohibited Books.
- In the same way, many writers and artists felt that if nobody exercised control on the printed material, then the prerogatives of the precious publications would be perished.
OR
Print culture culminated in the development of nationalism in India.
The points are as follows:
- Print culture resulted in the publication of most newspapers in vernacular languages. Many journals were published after 1870.
- These journals and newspapers published cartoons and caricatures refuting the imperial rule and gave comments on social and political issues. The vernacular newspapers such as Kesari and Maratha in Marathi languages were overtly nationalist and reflected on colonial misrule and stimulated nationalist current.
- The British government advocated repressive policies that led to militant protests. Tilak was incarcerated for reporting on repressive measures in his Kesari in 1908. It resulted in widespread resentment.
- Print culture encouraged the leaders to pass on the ideas to people across the nation. This initiative brought them closer and assisted in the development of nationalism.
Question 31.
Suggest any five measures to make formal sector beneficial
for poor farmers and workers. (5)
Or
Gautam is a farmer who take a loan
from a moneylender to do farming on his land. In collateral, the moneylender ask
Gaurav for his land. Why do lenders ask for collateral while lending? How the
terms of credit becomes difficult for the small and marginal farmers? (3+2)
Answer:
The measures to make formal sector loans beneficial for poor farmers
and workers are
- The formal sector like banks and cooperatives should lend more to poor people and workers, particularly in rural areas.
- The formal sector should provide cheap and affordable credit to the poor people so that repayment ¡s easy.
- Formal sector should work out other ways of arranging collateral from the poor people.
- By providing linkage between Self Help Groups and banks, the formal sector of credit can be increased.
- There should be more cooperatives and banks in rural areas and people should be made aware of their presence.
Or
The lenders ask for collateral while lending due to the following
reasons
Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns and uses as a guarantee
to a lender until the loan is repaid. Lenders ask for collateral as a security
against loans. If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has the right
to sell the asset or collateral to obtain the amount. For a bank in case of
taking collateral, the repayment of the loan becomes easy because banks has no
risk of non-performing assets.
Question 32.
Democracy’s ability to generate its support is itself an
outcome that cannot be ignored.’ Support the statement with examples.
OR
‘There is overwhelming support for the idea ot democracy in South Asia.’
Support the statement with examples.
Answer:
There are several reasons why
democracy has wide support from society:
- The decision-making in democracy is based on rigorous deliberations and debates which ensure the quality of decision-making.
- People have been given the right to choose their political representatives through the medium of Universal Adult Franchise, which gives voting rights to people above 18 years of age.
- A democratic government is an accountable government and people have the right to know about the functioning of the government.
- The interests of the majorities as well as the minorities are secured in a democratic government.
- A democratic government is a form of government for the people, of the people, and by the people.
OR
Most of the South Asian nations have adopted the democratic form of
government and there is strong support for such a government due to the
following reasons:
- Democratic government is chosen by the people by exercising their right to vote.
- A democratic government is generally accountable for its work to the people.
- A democratic government ensures dignity and equality among the individuals of the country.
- It also accommodates social, cultural, and religious diversity in the country.
- The democratic government gives rise to the process of debates and deliberations in the country.
Question 33.
“Roadways still have an edge over railways in India”. Give
reasons. (5)
Or
Describe any five points of importance of mass
communication. (5)
Answer:
Roadways still have an edge over railways in
India because of the following reasons
- Construction cost of roadways is much lower than that of railways.
- Roads can traverse comparatively more dissecting and undulating plains.
- Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and can traverse mountains like Himalayas.
- Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and small amount of goods over short distances.
- It also provides door to door services.
- Cost of loading and unloading is much lower.
- Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide link between railway station, airports and seaports.
Or
Importance of mass communication is discussed as follows
Mass
communication is required to spread the flow of information upto the grassroots
level. Therefore, government has made special provisions to extend 24 hours STD
facility to every village in the country.
All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional, and local languages for various categories of people spread over different parts of the country.
Doordarshan broadcasts a variety of programmes for entertainment, educational
programmes to sports, etc for people of different age groups. India publishes a
large number of newspapers and periodicals annually to provide information.
India is the largest producer of feature films in the world. It produces short
films, video feature films and video short films for entertainment.
Section
E
Section E consists of 3
Case-based questions of 4 marks each
Question 34.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that
follows:
In Africa, in the 1890s, a fast-spreading disease of cattle plague
or rinderpest had a terrifying impact on people’s livelihoods and the local
economy. This is a good example of the widespread European imperial impact on
colonised societies. It shows how in this era of conquest even a disease
affecting cattle, reshaped the lives and fortunes of thousands of people and
their relations with the rest of the world. Historically, Africa had abundant
land and a relatively small population. For centuries, land and livestock
sustained African livelihoods, and people rarely worked for a wage. In late
nineteenth-century Africa, there were few consumer goods that wages could buy.
If you had been an African possessing land and livestock — and there was plenty
of both – you too would have seen little reason to work for a wage.
Question 34.1
What was Rinderpest?
Answer:
Rinderpest was a
fast-spreading disease of cattle plague which led to the death of millions of
cattle in African continent during the 1890s.
Question 34.2
What were the two main sources of African economy for past
centuries?
Answer:
From several centuries, the African economy was
primarily dependent on land and livestock. The African people were rarely seen
working for the wages.
Question 34.3
How cattle plague affected the situation of people in
Africa?
Answer:
The cattle plague proved to be disastrous for the African
people as it led to the death of millions of livestock which were the source of
livelihood for them. This resulted in the turning of the African people into
labourers by the colonisers who gave meagre wages to the people for large amount
of manual work.
Question 35.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that
follow. Another important feature of the Civil Disobedience Movement was the
large-scale participation of women. During Gandhi’s Salt March, thousands of
women came out of their homes to listen to him. They participated in protest
marches, manufactured salt, and picketed foreign cloth and liquor shops. Many
went to jail. In urban areas, these women were from high-caste families. In
rural areas, they came from rich peasant households moved by Gandhiji’s call,
they began to see service to the nation as a sacred duty of women.
Gandhiji was convinced that it was the duty of women to look after home and heart, be good mothers and good wives, and for a long time, the Congress was reluctant to allow women to hold any position of authority within the organisation. It was keen only on their symbolic presence.
(i) When did Gandhiji initiate a movement in Champaran in Bihar against the
oppressive indigo plantation system? (1)
(ii) What was the reason behind
launching the Civil Disobedience Movement? (1)
(iii) State any two impacts of
the Civil Disobedience Movement. (2)
Answer:
(i) In 1916, Gandhiji
initiated a movement in Champaran in Bihar against the oppressive indigo
plantation system.
(ii) Mahatma Gandhiji launched the Civil Disobedience
Movement because Lord Irwin ignored Gandhi’s eleven demands including the
abolition of the salt tax. Gandhi ji started a Civil Disobedience Movement with
the famous Dandi March.
(iii) Two impacts of the Civil Disobedience Movement
were
Women and students participated in large numbers in this movement, which
was a liberating experience for Indian women who were entering public space in
such large numbers for the first time. Due to this movement, women started
playing an active role in India’s political movements.
The Civil Disobedience Movement had a far-reaching impact. It instilled distrust in the British government and laid the groundwork for the freedom struggle, as well as popularising new methods of propaganda.
Question 36.
Read the given source and answer the questions that
follow:
COMMUNITY AND CONSERVATION
Conservation strategies are not new in
our country. We often ignore that in India, forests are also home to some of the
traditional communities. In some areas of India, local communities are
struggling to conserve these habitats along with government officials,
recognizing that only this will secure their long-term livelihood. In Sariska
Tiger Reserve, Rajasthan, villagers have fought against mining by citing the
Wildlife Protection Act.
In many areas, villagers themselves are protecting habitats and explicitly rejecting government involvement. The inhabitants of five villages in the Alwar district of Rajasthan have declared 1,200 hectares of forest as the Bhairodev Dakav ‘Sonchuri’, declaring their own set of rules and regulations which do not allow hunting, and are protecting the wildlife against any outside encroachments.
Question 36.1
How are forests related to Communities?
Answer:
These
local communities directly depend on various components of the forest and
wildlife for food, drink, medicine, culture, spirituality, etc.
Question 36.2
Explain the aim of ‘The Wildlife Protection Act.
Answer:
The main objective of the Wildlife Protection Act is to protect the
remaining population of endangered species by banning hunting. giving legal
protection to their habitats and restricting wildlife trade.
Section F
Section
F consists of Map based questions of 5 marks
Question 37.
(a) Two places A and B are marked on the given outline map of
India. Identify them and write their correct names on the
lines drawn near
them. (2)
A. The place associated with the cotton mill’s worker’s
satyagraha
B. The place where an incident occurred due to which Mahatma
Gandhi called off the Non-Cooperation Movement.
(b) On the same outline map
of India, locate and label any three of the following with suitable symbols.
(3)
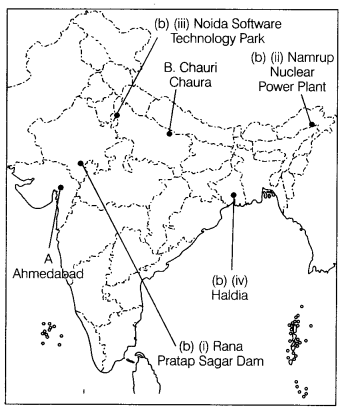
(i) A dam in Rajasthan
(ii) Namrup Nuclear Power Plant
(iii) A
Software Technology Park in Uttar Pradesh
(iv) A seaport in West
Bengal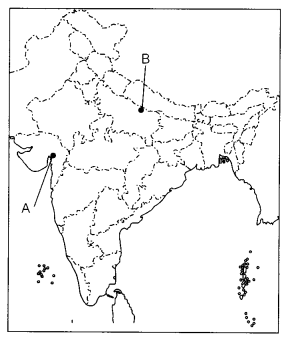
Answer: