CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-11
Class 10thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-11
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 11 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
- Question paper comprises five Sections — A B. C. D and E. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section C contains Q.25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions. carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words,
- Section E – Questions no. from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying S marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section
A
Section A consists of 20
questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Who ruled France in the 1830s and was forced to flee after
unemployment caused workers to revolt on roads? (1)
(a) King Emmanuel II
(b) King William I
(c) King Louis Philippe
(d) King Wilhelm
Answer:
(c) King Louis Philippe
Question 2.
Who among the following published ‘Kesari’?
(a)
Balgangadhar Tilak
(c) Jyotiba Phule
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) B.R.
Ambedkar
Answer:
(a) Balgangadhar Tilak
Question 3.
The following image is a caricature of which personality in
the German Reichstag (Parliament) from Figaro, Vienna. Identify. (1)
(a) King Victor Emmanuel II
(b) Otto von Bismarck
(c) Giuseppe
Mazzini
(d) Giuseppe Garibaldi
Answer:
(b) Otto von Bismarck
Question 4.
Arrange the following in chronological order and choose the
correct option:
(I) Napoleonic wars
(II) The Treaty of Vienna
(III)
Greek Struggle for Independence
(IV) Slav Nationalism Ottoman Empire
Options:
(a) III, II, I and IV
(b) I, II, III, and IV
(c) IV, Ill, II,
and I
(d) IV, II, III and I
Answer:
(b) I, II, III, and IV
Question 5.
Arrange the following events in a chronological order.
I.
First Malayalam book was printed.
II. Calcutta Supreme Court passed
regulations to control press freedom.
III. Fairy Tailes printed by Grime
Brother.
IV. Martin Luther wrote Nincty Five Thesis’.
Codes
(a) IV,
III, I, II
(b) II, III, I, IV
(c) IV, I, III, II
(d) II, IV, III, I
Answer:
(c) IV, I, III, II
Question 6.
Ruling party means:
(a) Political party that runs
government.
(b) Political party that competes in the election.
(c)
Opposition party.
(d) Non-Political party.
Answer:
(a) Political party
that runs government.
Question 7.
Find the connect statement regarding the Joint Forest
Management Programme. (1)
(a) Odisha passed the first resolution for Joint
Forest Management.
(b) This program was initiated in the year 1988.
(c) it
is a combined effort of local community with local committees.
(d) Members
are entitled to cash benefits from the forests.
Answer:
(d) Members are
entitled to cash benefits from the forests.
Question 8.
Consider the following statements regarding democracy and
identify the incorrect one from the following.
(a) Promotes equality among
citizens
(b) Enhances the dignity of the individual
(c) Provides a method
to resolve conflicts
(d) Does not provide room to correct mistakes
Answer:
(d) Does not provide room to correct mistakes
Question 9.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R).
Mark your answer as per the codes given below. (1)
Assertion (A)
Floodgate dams are built across rivers so that water flows into the inlet and
gets trapped during high tides.
Reason (R) Trapped water flows back via a
pipe that carries it through a power-generating turbine.
Codes
(a) Both A
and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are
true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is
false
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Answer:
(d) A is false, but R is
true.
Question 10.
Which of the following regions has the highest representation
of women in their national parliaments?
(a) Asian
(b) American
(c)
African
(d) Nordic
Answer:
(d) Nordic
Question 11.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R).
Mark your answer as per the codes given below. (1)
Assertion (A)
Community Government in Belgium is elected by one language community.
Reason
(R) Community Government helped in resolving conflict between different
linguistic groups.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct
explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct
explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is
true
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of
A
Question 12.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below:
Assertion (A):
Moneylenders can lend loans at whatever interest rate they choose.
Reason
(R): Moneylenders do not follow the rules and regulations set for them by the
RBI.
Options:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct
explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct
explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct, but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is
wrong, but (R) is correct.
Answer:
(c) (A) is correct, but (R) is
wrong.
Question 13.
Pokharan, the place where India conducted its nuclear tests,
lies in Rajasthan. Suppose the Government of Rajasthan was opposed to the
Central Government’s nuclear policy, could it prevent the Government of India
from conducting the nuclear tests? Identify the reason for the given
options.
(a) Yet, the State Government could prevent it as ‘Defence’ is a
subject of the State List.
(b) No, the State Government could not prevent the
Central Government from conducting the nuclear tests because ‘Defence’ is the
subject of the Union List and nuclear tests are part of the Defence.
(c) Yes,
the State Government could prevent it as conducting nuclear tests is a subject
of the Concurrent List.
(d) No, the State Government could not prevent the
Central Government as conducting nuclear tests in any state is legally
valid.
Answer:
(b) No, the State Government could not prevent the Central
Government from conducting the nuclear tests because ‘Defence’ is the subject of
the Union List and nuclear tests are part of the Defence.
Question 14.
Read the given data and find out the percentage of rural
girls attending school.
Education Achievement of Rural Population of Uttar
Pradesh
| Category | Male | Female |
| Literacy rate for rural population | 70% | 54% |
| Literacy rate for rural children in age group 10-14 years | 90% | 87% |
| Percentage of rural children aged 10-14 attending school | 85% | 82% |
(a) 85%
(b) 82%
(c) 81%
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) 82%
Question 15.
What kind of change took place in 1993 in Belgium? Identify
the correct option. (1)
(a) The constitutional powers were taken away from
Regional Governments and were given to the Central Government.
(b) The
Regional Governments were given constitutional powers that were no longer
dependent on the Central government.
(c) The Regional Governments were given
constitutional powers that were co-dependent with the Central Government.
(d)
The constitutional powers were completely taken away from the Central Government
and were given to the majority community.
Answer:
(b) The Regional
Governments were given constitutional powers that were no longer dependent on
the Central government.
Question 16.
Find the odd one out from the following:
(a) Bokaro,
Jamshedpur, Vadodara, Vijaynagar
(b) Mohali, Pune, Bengaluru, Indore
(c)
Kanpur, Rajkot, Chennai, Moradahad
(d) Kolkata, Delhi, Hyderabad,
Gurugram
Answer:
(a) Bokaro, Jamshedpur, Vadodara, Vijaynagar.
Question 17.
Analyze the table given below and answer the question that
follows. The source shows a database of workers employed in different sectors
(in millions). (1)
| Sector | Unorganised | Organized | Total |
| Primary | 200 | 2 | 202 |
| Secondary | 50 | 5 | 55 |
| Tertiary | 80 | 20 | 100 |
| Total | 330 | 27 | 357 |
| Total in % | – | – | 100% |
Calculate the percentage of people in an organized sector.
(a) 10%
(b)
9.6%
(c) 7.6%
(d) 8.4%
Answer:
(c) 7.6%
Question 18.
Assume there are four families in a country. The average per
capita income of these families is 6000. If the income of three families is ₹
5000, ₹ 8000, and ₹ 4000 respectively, what is the income of the fourth
family?
(a) ₹ 5500
(b) ₹ 2000
(c) ₹ 300
(d) ₹ 7000
Answer:
(d)
₹ 7000.
Question 19.
Which of the following provisions gives NREGA the Right to
Work? (1)
(a) An increase in land productivity has been given preference.
(b) If the government fails to provide employment, it will give unemployment
allowance.
(c) Thu act has been spread to all the districts in the
country.
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(b) If the government fails to
provide employment, it will give an unemployment allowance.
Question 20.
Identify the correct statement/s about globalization:
I.
Removal of barriers by the government
II. Foreign companies are allowed to
set up factories
III. Has enabled all companies to increase their
investments
IV. Has lessened foreign investment and foreign trade
Options:
(a) I & II
(b) II & III
(c) I & III
(d) II
& IV
Answer:
(a) I & II
Section
B
Section B consists of 4
questions of 2 marks each
Question 21.
State the order passed by the Supreme Court to reform the
Election Commission of India. (2)
Answer:
The Supreme Court passed an
order to reduce the influence of money and criminals. Now, it is mandatory for
every candidate who contests elections to file an affidavit giving details of
his property and criminal cases pending against him. The new system has made a
lot of information available to the public. But there is no system of checking
if the information given by the candidates is true.
Question 22.
How did the Non-Cooperation Movement unfold in the cities and
towns of India?
OR
Why was the Inland Emigration Act of 1859 troublesome
for plantation workers?
Answer:
The Non-Cooperation Movement was adopted
enthusiastically by the people in towns and cities. Some of the actions taken by
the people were:
- Thousands of students left government schools and colleges.
- Middle-class people participated enthusiastically iii the movement, and thousands of teachers and lawyers left their jobs and practices respectively.
OR
The Inland Emigration Act of 1859 was troublesome for plantation
workers because they were not permitted to leave the tea gardens without
official permission. People rarely got such permissions. They were also not
allowed to go to their homes.
Question 23.
Mention two factors responsible for the location of jute
mills in the Hugh basin.(2)
Or
Give two reasons for shifting sugar
industry from North to South India. (2)
Answer:
Factors responsible for
location of jute mills in the Hugh Basin are
- Inexpensive water transport, supported by a good network of railways and roadways.
- Availability of cheap ‘labour from nearby areas.
Or
The reasons for shifting of sugar industry from North to South India are
- The sucrose content of sugarcane grown is higher in South India i.e., Peninsular India.
- Thus, more sugar can be extracted from the same amount of sugarcane.
- The crushing season is longer in Peninsular India, as the summers are less hotter than the North India.
Question 24.
How do demand deposits share the essential features of
money?
Answer:
Demand deposits share the essential features of money
because:
- With demand deposits, we can directly settle payments without the use of cash. The facility of cheques helps in this manner.
- Along with currency, demand deposits are commonly accepted as a means of payment. Thus, they constitute money in the modern economy.
Section
C
Section C consists of 5
questions of 3 marks each
Question 25.
Table showing study of employment and income in Ahmedabad are
as follows. (1+2)
| Sector | Workers Employed | Income Generated |
| Organised | 400000 | ₹ 32000 million |
| Unorganised | 1100000 | ₹ 28000 million |
| Total | 1500000 | ₹ 60000 million |
(i) In the table given above, we can analyse that in the unorganised sector
more workers are employed as compared to organised sector. But still, the income
generated by the unorganised sector is far behind the organised sector. What is
the reason behind it?
(ii) What kind of ways should be thought for employment
in the city?
Answer:
(i) Generally, workers belonging to the unorganised
sector are given low wages as compared to organised sectors. This is the reason
why the total income of the unorganised sector is far behind the total income of
the organised sector,
(ii) The ways of generating more employment are To set
up industries that process vegetables an agricultural produce like potatoes,
rice, wheat, fruits, etc which can be sold in outside markets.
To promote and
locate industries and service in outside of the city where a large number people
can get employment.
Question 26.
What is resource planning? Give three phases of resource
planning.
OR
Describe any three main features of ‘Alluvial soil’ found in
India.
Answer:
Resource planning is proper and judicious planning of
resources.
The phases of resource planning are:
- Resource identification and inventory in different parts of the country. This includes the assessment, mapping, qualitative and quantitative estimation and resource measurement.
- Development of a planning structure with the necessary technical skills and institutional capacity to implement resource development plans.
- Matching the resource development with the overall plans of national development.
OR
Major characteristics of Alluvial Soil are:
- Alluvial soil is considered as one of the most fertile soils amongst all soil types. Alluvial soil covers the entire northern plains in India.
- Alluvial soil contains sand, silt, and clay mainly due to silt deposited by the Indo-Gangetic Brahmaputra rivers. According to age, it is classified into Bhangar (old alluvial) and Khadar (new alluvial).
- Alluvial soil contains an ample amount of potash, phosphoric acid, and lime. This soil is ideal for the growth of crops like sugarcane, wheat and rice, etc.
Question 27.
Why resource planning is essential for India? Explain.
(3)
Answer:
Resource planning is essential in India as resources are
limited and unevenly distributed over the country. Planning will help in
reducing wastage as well as taking care of the requirements of future
generations An example of uneven distribution of resources is Arunachal Pradesh
which has an abundance of water resources but lacks infrastructural development
to utilise the water resources. Irrational consumption and over-utilisation of
resources lead to socioeconomic and environmental problems in Punjab,
waterlogging has increased salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
Question 28.
Explain the majoritarianism in Sri Lanka.
Answer:
Majoritarianism is practiced in Sri Lanka in the following ways:
- In 1956, an Act was passed to recognize Sinhala as the only official language, thus disregarding Tamil.
- The governments followed preferential policies that favored Sinhala applicants for university positions and government jobs.
- A new constitution stipulated that the state shall protect and foster Buddhism.
Question 29.
What were the beliefs of plantation workers in Assam about
the notion of Swaraj? Explain. (3)
Answer:
The plantation workers in Assam
had understood the notion of Swaraj in the following ways:
For plantation
workers in Assarn, freedom meant the right to move freely in and out of the
confined space in which they were enclosed. Under the Inland Emigration Act of
1859. plantation workers were not permitted to leave the tea gardens without
permission.
Swaraj for plantation workers meant retaining a link to the village from where they had come. When plantation workers heard of the Non-Cooperation Movement thousands of workers refused to obey their authorities, left the plantations, and headed home. They believed that Gandhi Raj was corning and everyone would be given land in their village. The plantation worker, however never, reached their destination as they were caught by the police and brutally beaten up.
Section
D
Section D consists of 4
questions of 5 marks each
Question 30.
How did the amendment of 1992 help in strengthening the
three-tier system?
OR
The real success of federalism in India can be
attributed to the nature of democratic politics in India. Explain.
Answer:
- The rationale behind decentralization is that the regional issues can be better handled at the local level.
- The people of the area know better about the problems of their area.
- Elections are held regularly for the local government bodies at village, block, district, town, and city levels. For conducting municipal and panchayat elections, an independent institution called the State Election Commission has been established in every State.
- Some seats are reserved in the elected bodies for the Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and Other Backward Classes (OBCs). One-third of all positions are kept reserved for woman candidates.
- These local bodies generate their revenues on their own. The State governments must share some powers and revenues with the local government bodies and the nature of sharing differs from State to State.
OR
- Linguistic States after independence: In 1950, the boundaries of several old states were changed to create new states. This was done to ensure that the people who spoke the same language, and shared a common culture, ethnicity or geography could live in the same state.
- Language Policy: The Indian Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one of the languages. Though Hindi was identified as the optional language. but the central government has not imposed Hindi on states where people speak a different language. Besides Hindi, there are 22 other languages recognized as Scheduled Languages by the Indian Constitution.
- Center-state relations: Improving center-state relations is one more way in which federalism has been strengthened in practice. Though the Indian Constitution has demarcated the powers of the Union and the state governments but still the Union government can influence the state in many ways. In the past, the Central government has often misused the Constitution to dismiss the state governments that were controlled by rival parties. This undermined the spirit of federalism and that of democracy.
Question 31.
Explain five political outcomes of democracy. (5)
Or
Should democracy be judged by its outcome? Explain. (5)
Answer:
The five
political outcomes of democracy are as follows
- The most basic outcome of democracy is that it produces a government that is accountable to the citizens and responsive to the needs and expectations of the citizens.
- Democracy is based on the idea of deliberation and negotiation.
- A democratic government may take more time to follow procedures before arriving at a decision. But because it follows procedures, its decisions may be both more acceptable to the people and more effective. So. the cost of time that democracy pays is worth it.
- Democracy ensures that decision-making will be based on norms and procedures. So, a citizen has the right and the means to examine the process of decision-making. This is known as transparency.
- A democratic government is a legitimate government as it is the people’s own government.
Or
Democracy should be judged by its outcome because it opens the path of
expectations which is one of the criteria for judging any democratic
country.
The following points justify the above statement
- The examination procedure of democracy is eternal, it passes one test, it produces another test.
- It automatically gives rise to expectations as well as complaints by the people when they want to know about the functioning of democracy.
- The fact that people also complain about democracy indicates the awareness and the ability of people to expect and to look critically at power holders and the high and the mighty.
- It transforms people from the status of a subject into that of a citizen.
- Most individuals today believe that their vote makes a difference to the way the government is run and to their self-interest.
Question 32.
Write any two non-material things on which the quality of our
life depends. Define the following concepts:
(a) Infant Mortality Rate (or
¡MR)
(b) Literacy Rate
(c) Net Attendance Ratio
OR
Kerala with lower
per capita income has a better human development ranking than Maharashtra.
Hence, per capita income is not a useful criterion at all and should not be used
to compare states. Do you agree? Discuss.
Answer:
(i) A safe and secure
environment.
(ii) Quality friends and relatives.
Definitions:
- Infant Mortality Rate (or IMR) refers to the number of children that die before the age of one year as a proportion of 1000 live children born in that particular year.
- Literacy Rate is the measure of the proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group.
- Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group.
OR
The per capita income is a simple criterion that is easy to calculate
and understand the level of development in the society. So it is useful but it
is not a comprehensive measure of human development. It only reflects the
average income per person of the country but there are two limitations with this
criterion.
- The first limitation is that this criterion is very much influenced by the extreme upper and lower values and fails to represent the level of equality of income.
- Secondly, it does not represent the other indicators of quality of life like level of health and education which are equally or rather more important objectives for human development on which the magnitude of income depends. Kerala has a Low Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) and a better level of education than those of Maharashtra that is why Kerala, though with lower per capita income has a better human development ranking than Maharashtra.
Question 33.
Bank plays a significant in the economy of India. Analyse and
explain the statement in an elaborative manner. (3+2)
Or
Briefly describe
the functions of the Reserve Bank of India. (5)
Answer:
Banks play an
important role in the economy of India in the following ways
(i) Provide
Deposits Bank accept the deposits and also pay an amount as interest on the
deposits. In this way, people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an
amount as interest, People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and
when they
require, Since the deposits in the bank account can be withdrawn on
demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
(ii) Provide Loans Banks keep only a small portion of their deposits as cash with themselves Banks use the major position of the deposits to give loans. There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities. Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people, In this way, banks provide credit to set up industries and in agriculture. This generates more employment and raises income thereby bringing economic development.
Or
The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources
of loans in India Functions of the Reserve Bank of India are as follows The
Reserve Bank of India monitors that the banks maintain the cash balance and do
not give all the deposits as loans. The Reserve Bank of India ensures that the
banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and rich traders, but also
to small cultivators, small-scale industries, small borrowers, etc.
Periodically, banks have to submit information to the Reserve Bank of India on
how much they are lending, to whom, etc. The rate of interest charged on loans
given by the banks is decided by the Reserve Bank. In this way, the RBI keeps a
check on all the activities of banks and checks the flow of credit.
Section
E
Section E consists of 3
Case-based questions of 4 marks each
Question 34.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that
follow:
WHY NEWSPAPERS?
‘Krishnaji Trimbuck Ranade inhabitant of Poona
intends to publish a Newspaper in the Marathi Language with a view of affording
useful information on every topic of local interest. It will be open for free
discussion on subjects of general utility, scientific investigation, and the
speculations connected with the antiquities, statistics, curiosities, history,
and geography of the country and of the Deccan especially the patronage and
support of all interested in the diffusion of knowledge and Welfare of the
People is earnestly solicited.’ Bombay Telegraph and Courier, 6 January
1849.
The task of the native newspapers and political associations is identical to the role of the Opposition in the House of Commons in Parliament in England. That is of critically examining government policy to suggest improvements, by removing those parts that will not be to the benefit of the people, and also by ensuring speedy implementation. These associations ought to carefully study the particular issues, gather diverse relevant information on the nation as well as on what are the possible and desirable improvements, and this will surely earn it considerable influence.’ Native Opinion, 3 April, 1870.
Question 34.1
Explain the main reason of publishing the newspaper by
Krishnaji.
Answer:
Krishnaji wanted to publish important information
concerning political, scientific and other developments in society and wanted to
make the people aware of them.
Question 34.2
How was the task of native newspapers and political
associations seen as identical to the role of the opposition?
Answer:
The
native newspapers and the political associations were the media through which
the government policies were criticised and analysed. So in this way, both these
acted as the opposition to the government.
Question 34.3
Analyse the reasons of popularity of newspapers during 19th
century.
Answer:
Reasons for the popularity of newspapers in the
nineteenth century were:
- A large section of society started taking interest in the political developments taking place in the nation and this was presented efficiently in the newspapers.
- The newspapers became a source of social, cultural, and scientific developments as well in society.
Question 35.
Read the given extract and answer the following
questions.
Another way of classifying economic activities in sectors could be
based on who owns assets and is responsible for the delivery of services. In the
public sector, the government owns most of the assets and provides all the
services. In the private sector, ownership of assets and delivery of services is
in the hands of private individuals or companies.
Railways or post office is an example of the public sector whereas companies like Tata Iron and Steel Company Limited (TISCO) or Reliance Industries Limited (RIL.) are privately owned. Activities in the private sector are guided by the motive to earn profits. To get such services we have to pay money to these individuals and companies.
The purpose of the public sector is not just to earn profits. Governments
raise money through taxes and other ways to meet expenses on the services
rendered by it. Modern-day governments spend on a whole range of activities.
There are several things needed by the society as a whole but which the private
sector will not provide at a reasonable cost
(i) The bifurcation into the
public and private sector is on what basis? (1)
(ii) State one reason each as
to why railways and post offices are counted in the public sector. (1)
(iii)
State two reasons why the public sector is needed in a country like India.
(2)
Answer:
(i) The education into the public and private sector is based
on who owns the assets and is responsible for delivery of services.
(ii)
Railways and post offices are counted in the public sector due to railways being
owned by the government and not by any private individual. Government is
responsible for the delivery of various services through post offices.
(iii)
Public sector is needed in India due to Public sector spends on different
activities that are needed by the society which the private sector cannot
provide Private sector will not provide services at reasonable price, so public
sector is needed.
Question 36.
Read the given extract and answer the following
questions.
We have seen how crucial political parties are for the working of
democracy. Since parties are the most visible face of democracy, it is natural
that people blame parties for whatever is wrong with the working of democracy.
All over the world, people express strong dissatisfaction with the failure of
political parties to perform their functions well. This is the case in our
country too. Popular dissatisfaction and criticism have focused on four problem
areas in the working of political parties. Political parties need to face and
overcome these challenges to remain effective instruments of democracy.
To face these challenges, political parties need to be reformed. The question is: Are political parties willing to reform? If they are willing, what has prevented them from reforming so far? If the’ are not willing, is it possible to force them to reform? Citizens all over the world face this question. This is not a simple question to answer. In a democracy, the final decision is made by leaders who represent political parties. People can replace them, but only by another set of party leaders. If all of them do not wish to reform, how can anyone force them to change?
Question 36.1
How can you say that there is a lack of internal democracy
within political parties?
Answer:
- The concentration of power is in the hands of one or few leaders at the top.
- Ordinary members of the party do not get sufficient information about party decisions and those who disagree with the decisions find it difficult to continue in the party.
Question 36.2
“Defection makes democracy weak” Explain the steps taken by
our leaders to end defection.
Answer:
The Constitution was amended to
prevent elected MLAs and MPs from changing parties. This was done because many
elected representatives were indulging in defection to become ministers or for
cash rewards. Now the law states that if any MLA or MP changes parties, he or
she will lose the seat in the legislature. This new law has helped bring
defection down.
Section
F
Section F consists of Map based
questions of 5 marks
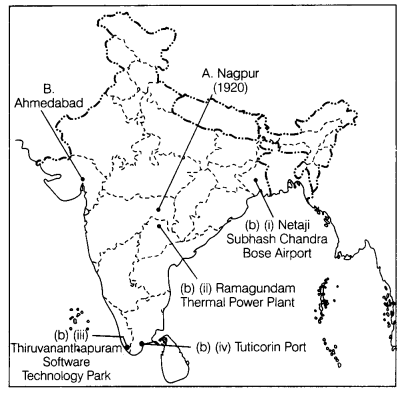
Question 37.
(a) Two places A and B are marked on the given outline map of
India. Identify them and write their correct names on the
lines drawn near
them. (2)
A. The place where the Indian National Congress Session was held in
December 1920.
B. The place where the Cotton Mill Workers Satyagraha was
conducted.
(b) On the same outline map of India, locate any three features of
the following with suitable symbols. (3)
(i) An airport in West Bengal
(ii) Ramagundam Thermal Power Plant
(iii) Thiruvananthapuram Software
Technology Park
(iv) Tuticorin Port
Answer: