CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-1
Class 10thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set-1
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 1 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
- Question paper comprises five Sections – A, B, C, D, and E. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Questions no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section C contains Q.25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section D – Questions no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions. carrying marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words
- Section-E – Questions no. from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F — Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section
A
Section A consists of 20
questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Identify the crop with the help of the clues given below.
(1)
This crop is used as both food and fodder. It requires temperature from
21°C to 27°C.
It is a Kharif crop which grows well in old Alluvial soil.
(a) Millets
(b) Maize
(c) Wheat
(d) Pulses
Answer:
(b) Maize
Question 2.
Which place in India has an artificial lake to conserve water
that dates to 11th century? (1)
(A) Delhi
(B) Bhopal
(C) Mumbai
(D)
Kolhapur
Answer:
(B) Bhopal
Explanation: Bhopal is known as the ‘City of Lakes’; it has artificial lakes that date to the 11th century.
Question 3.
According to the Human Development Report of UNDP, 2018, the
HDI ranking of countries is mentioned below. (1)
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Sri Lanka | 1. 76 |
| B. India | 2. 130 |
| C. Pakistan | 3. 150 |
| D. Nepal | 4. 149 |
Why does India rank low on the Human Development Index despite of its huge
size and population? Select the most suitable options from the following.
(a)
Less investment in social infrastructure.
(b) Gender inequality is still
prevalent.
(c) Increasing income inequalities among different sections of the
society.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 4.
Which of the following options represent potential measures
that can be taken to mitigate the threats posed by mining activities on the
Buxar tiger reserve’s ecosystem and biodiversity? (1)
(i) Banning hunting,
giving legal protection to their habitats and restricting wildlife trade.
(ii) Prohibiting the visit of public into forest area.
(iii) Establishing
wildlife sanctuaries and National Parks
(iv) Converting forests into Reserved
and Protected forests
Options:
(A) Statement i and ii are correct.
(B)
Statement ii, iii & iv are correct
(C) Statement ii is correct
(D)
Statement i, iii, & iv are correct
Answer:
(D) Statement i, iii, &
iv are correct
Explanation: Measures to be taken to mitigate the threats posed by mining
activities on the Buxar tiger reserve’s ecosystem and biodiversity:
i.
Implementing stricter regulations and monitoring mechanisms.
ii. Enforcing
buffer zones around protected areas.
iii. Promoting alternative livelihoods
and sustainable economic development in the surrounding communities
Question 5.
The activities involved in tourism like guides, hotels,
travel, food, etc are included in which sector of the economy? (1)
(a) Public
sector
(b) Tertiary sector
(c) Unorganised sector
(d) Primary
sector
Answer:
(b) Tertiary sector
Question 6.
Which of the following statements accurately distinguishes
between Majoritarianism and Power sharing? (1)
(A) Majoritarianism emphasizes
the dominance of the majority community, while Power sharing emphasizes the
sharing of power among different groups.
(B) Majoritarianism emphasizes the
need for consensus building, while Power sharing emphasizes the exclusion of
minority groups.
(C) Majoritarianism emphasizes the importance of
accommodating minority interests, while Power sharing emphasizes the need for
majority rule.
(D) Majoritarianism emphasizes the need for peaceful
resolution of conflicts, while Power sharing emphasizes the use of force to
impose the majority’s will.
Answer:
(A) Majoritarianism emphasizes the
dominance of the majority community, while Power sharing emphasizes the sharing
of power among different groups.
Explanation: Majoritarianhan emphasizes the dominance of the majority community, title Power sharing emphasizes the sharing of power among different groups.
Question 7.
Which of the following statements held that workers are
exploited in the unorganized sector? Identify the correct option.
I. There
are no fixed number of working hours.
II. They do not get other allowances
apart from the daily wages.
III. They can be asked to leave the job at any
time.
IV. Workers are registered by the government and have to follow its
rules and regulations.
Codes
(a) Both I and II
(b) Both H and III
(c) I, II and III
(d) Only IV
Answer:
(c) I, II, and III
Question 8.
Rahul has a sack of cotton but he needs wheat and Anush has a
sack of wheat and needs cotton, under this situation both will be able to
exchange their goods. In case of absence of such coincidence of wants, they may
not exchange their goods.
Which one of the following would be the best option
that describes the mutual exchange of goods and eliminate the exchange of goods?
(1)
Identify the situation and choose the right option that will help “R” and
“S” to eliminate this situation.
(A) Double coincidence of want, Exchanging
commodity for commodity.
(B) Double Coincidence of want, Credit on
Commodity.
(C) Double coincidence of want, Loan on commodity.
(D) Double
coincidence of want, Money.
Answer:
(D) Double coincidence of want,
Money.
Explanation: The goods can be easily exchanged with the use of money and it negates the unnecessary requirement of the need of two individuals to need each other’s commodities.
Question 9.
Coalition Government is formed by the two or more political
parties. Which of the following options best signifies this image
related to
coalition? (1)
(a) Coalition government is a new form of Government in
India.
(b) The ruling party and the opposition party form a coalition
government.
(c) In the coalition government, the leader decides every
rule.
(d) The leader of the coalition keeps the partners of the government
satisfied.
Answer:
(c) In the coalition government, the leader decides
every rule.
Question 10.
Identify the painting from the options given below.
(1)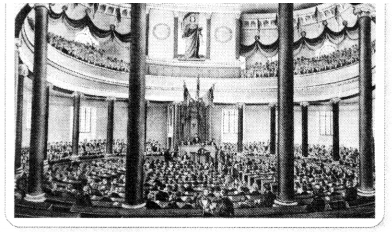
(A) Frankfurt Parliament
(B) Reichstag
(C) Duma
(D)
The House of Parliament
Answer:
(A) Frankfurt Parliament
Explanation: The picture is of the Frankfurt parliament.
Question 11.
Which among the following claimed that true German culture
was discovered among the common people? (1)
(a) Louis Philippe
(b) Johann
Gottfricd Herder
(c) Karol Karpinski
(d) Carl Welcker
Answer:
(b)
Johann Gottfred Herder
Question 12.
Choose the correction option to complete the statement.
(1)
If a government provides its citizens a right and means to examine the
process of decision, it is _______________.
(A) An accountable government
(B) A responsible government
(C) A transparent government
(D) A stable
government.
Answer:
(A) An accountable government
Explanation: If a government provides its citizens a right and means to examine the process of decision, it is called an Accountable government.
Question 13.
Which of the following two ports grew after the European
companies gained power in trade? (1)
(a) Surat and Hoogly
(b) Madras and
Masulipatnam
(c) Bombay and Calcutta
(d) Kandla and Vishakhapatnam
Answer:
(c) Bombay and Calcutta
Question 14.
If there is a disruption by transporters and lorries refuse
to transport vegetables, milk, etc. from rural areas to urban areas, food will
become scarce in urban areas, whereas farmers will be unable to sell their
products. Which of the following sectors will be affected due to the situation
stated above? (1)
(A) Primary and Secondary
(B) Secondary and Tertiary
(C) Tertiary, Primary and Secondary
(D) Tertiary and Primary.
Answer:
(C) Tertiary, Primary and Secondary
Explanation: Tertiary sector, primary sector, and secondary sector are affected due to the strike carried out by the Trade Union’.
Question 15.
Arrange the following events in a chronological order.
(1)
I. First spinning and weaving mill of Madras began production
II.
First jute mill cornes up in Bengal
III. James Watt patents the steam
engine
IV. Earliest factories started in England
Codes
(a) I, II, IV,
III
(b) IV, I, II, III
(c) IV, III, lI, I
(d) III, IV, II, I
Answer:
(c) IV, III, II, I
Question 16.
“M” gave his friend clues about a type of soil that suits for
growing cotton. Which of the following clues provided by “M” would be most
useful in identifying the ideal type of soil?
Clues:
i. It is well-known
for its capacity to hold moisture.
ii. It turns yellow when it is
hydrated.
iii. It is rich in kankur and bhangar nodules.
iv. It is a
well-drained loamy soil.
(A) Clue i
(C) Clue i and ii
(B) Clue i and
iii
(D) Clue iv
Answer:
(A) Clue i
Explanation: Black Soil is well known for its capacity to hold moisture.
Question 17.
Consider the following statements on the practice of
federalism in India. Identify those that hold for decentralization
after
1992. (1)
I. Local Governments did not have any power or resources of their
own.
II. It became constitutionally mandatory to hold regular elections to
Local Government bodies.
III. The State Governments are required to share
some powers and revenue with Local Government bodies.
IV. No seats are
reserved in the elected bodies for Scheduled Castes. Scheduled Tribes and other
backward classes.
Codes
(a) II and III
(b) I and III
(c) I and
IV
(d) II and IV
Answer:
(a) II and III
Question 18.
The process of integration between different countries is
called as _____________.
(A) Privatization
(B) Globalization
(C)
Liberalization
(D) Competition
Answer:
(B) Globalization
Explanation: The process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries through the movement of goods and services, investments and technology between countries is called Globalization
Question 19.
Identify the power-sharing system with the help of the
following information.
Power is shared among different organs of the
government.
All the organs of the government are placed at the same
level.
It specifies the concept of checks and balances.
(a) Community
Government
(b) Vertical Division of Power
(c) Horizontal Division of
Power
(d) Unitary form of Government
Answer:
(c) Horizontal Division of
Power
Question 20.
Miss “S” approached a bank nearby to avail loan for her own
business, as well as a Self-help group which is operating in her village, the
bank rejected her loan application whereas the Self-help group accepted to
support her by providing the loan. Which one of the following documents is
required by the bank, but not required by the self-help group to approve Miss
“S’s” loan application for her business? (1)
(A) Application for loans
(B)
Arrangement Letter
(C) Document on Collateral
(D) Demand promissory note
and take delivery letter.
Answer:
(C) Document on Collateral
Explanation: Document on Collateral is required by the bank, but not by the
self-help group to approve the loan application for business.
Section
B
Section B consists of 4
questions of 2 marks each
Question 21.
Study the map thoroughly and mention any one major irrigation
dam which is located in the highlighted Indian state. (2)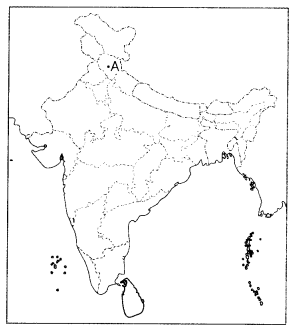
Answer:
Bhakra Nangal Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Satluj river in
Bhakra village in Bilaspur district of Himachal Pradesh.
Question 22.
The most powerful weapon of the Spanish conqueror was not a
conventional military weapon at all. Justify the above statement by giving two
reasons. (4)
(A) The Spanish conquerors won America with not conventional
military weapon but with germs like smallpox which spread deep into the
continent before any European could reach there.
OR
(B) “Traders and
travelers introduced new crops to lands they travelled. “Substantiate this
statement with illustrations
Answer:
- America’s original inhabitants had no immunity against these diseases that came from Europe. This disease erased the whole community, leading to conquest. This biological warfare in the mid-sixteenth century made it easy for the Spanish to overpower the Americans.
OR
- “Traders and travelers introduced new crops to lands they travelled”
- It is believed that noodles travelled West from China to become Spaghetti. Perhaps Arab Traders took Pasta to fifth century Cecily and Island now in Italy,
- Similar food was known in India and Japan, so that the truth about their origins may never be known.
- Many of our common foods such as potatoes, soya, groundnuts, maize, tomatoes, chilies, sweet potatoes, and so on were not known to our ancestors until about five centuries ago. These foods were only introduced in Europe and Asia after Christopher Columbus accidentally discovered the vast continent that would later become known as America. Many of our common foods came from America’s original inhabitants – the American Indians.
Question 23.
What do you understand by the term investment? Name a few
companies which make foreign investments. (1+1)
Answer:
The money that is
spent to buy assets such as land, buildings, machines and other equipment is
called investment.
The companies which make foreign investments in India are
Nike, Coca-Cola, Pepsi, Honda, Nokia, Tata Motors. Infosys, Ranbaxy. Asian
Paints, etc.
Question 24.
Mention any four reasons to prove that India is a federal
country.
Answer:
The following are the reasons which prove that India is a
federal country.
- Division of Powers: The Constitution of India demarcates the powers of the Central and State governments, and both have their separate areas of jurisdiction. The Seventh Schedule of the Indian Constitution lists the Union List, State List, and Concurrent List, which define the powers and responsibilities of the Central and State governments.
- Independent Judiciary: India has an independent judiciary with the power
of judicial review.
The Supreme Court of India is the highest judicial authority in the country and has the power to interpret the Constitution and resolve disputes between the Central and State governments. - Representation of States: The Rajya Sabha, the upper house of the Indian Parliament, represents the States and Union Territories of India. The members of the Rajya Sabha are elected by the elected members of the Legislative Assemblies of the States and Union Territories.
- Special Status to States: Some States in India enjoy special status and have been granted more autonomy than others. For example, Jammu and Kashmir have their own Constitution and a separate flag, and Nagaland has its own constitutions and a special status under Article 371A of the Indian Constitution. These factors contribute to India being a federal country where power is divided between the Central and State governments.
Section
C
Section C consists of 5
questions of 3 marks each
Question 25.
Raj is a student of Class X. He often gets confused about the
difference between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence
farming. Write three points of difference between primitive subsistence farming
and intensive subsistence farming. (3)
Answer:
Three points of difference
between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming are as
follows
| Primitive Subsistence Farming | Intensive Subsistence Farming |
| This type of farming is done on very small patches of land. | In this type of farming, the land holdings are comparatively bigger. |
| In this type of farming, primitive tools like hoe digging sticks are used for cultivation. | In this type of farming. modern agricultural inputs like chemical fertilisers, HYV seeds. machines are used wtierever suitable. |
| This agriculture is dependent on rainfall and natural fertility of the soil. | In this type of farming. means of irrigation like tubewells, canals are used Soil fertility is also increased by the use of fertilisers. |
Question 26.
(A): A worker in an urban area, who was working in a small
factory, was not paid his wages properly, he was forced to work extra hours
under poor working conditions, there was no job security, and recently he lost
his job and was found selling electrical items in a pushcart. (3)
Analyze the
role of the government in protecting the workers working in an Unorganized
sector.
OR
(B): Mr Pawan, a village head wanted to create more job
opportunities to increase the income of the people of his village under MNREGA
act, suggest any three activities, so that Mr Pawan could initiate in his
village.
Answer:
(A) The following are how the workers in the unorganized
sector can be protected by the government.
- The small factories must be registered by the government and have to follow its rules and regulations which are given in various laws such as the Factories Act, Minimum Wages Act, Payment of Gratuity Act, Shops and Establishments Act etc.
- The government can provide loans to help unemployed educated youth to start their own business.
- The workers are supposed to get medical benefits and, under the laws, the factory manager has to ensure facilities like drinking water and a safe working
OR
(B) Under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MNREGA), the Village Head, Mr. Pawan, can take several initiatives to increase the income of the people living in his village. MNREGA aims to employ rural households, and the following activities can be initiated to generate employment opportunities and increase income:
- Cleaning the lake/pond: Cleaning and maintaining water bodies such as lakes and ponds can help to improve the quality of water and make it suitable for irrigation purposes. This can lead to increased agricultural productivity, which, in turn, can increase the income of the farmers. Additionally, cleaning of the lake/ pond can provide employment opportunities for the local people.
- Village road construction: The construction of village roads can improve connectivity and accessibility within the village, making it easier for people to commute to work or transport goods. This can help to increase economic activity in the village, creating more job opportunities and boosting the income of the local people.
- Co-operative milk society/small scale industry: The formation of a co-operative milk society can provide a platform for the local dairy farmers to collectively sell their milk and other dairy products, increasing their income. Similarly, the establishment of a small-scale industry can generate employment opportunities.
- Construction work: The construction of houses, community centers, and other infrastructure projects can generate employment opportunities for the local people, helping to boost their income. This can also improve the living standards of the villagers, making it a sustainable solution for poverty reduction.
Question 27.
How can we say that globalization has been advantageous to
consumers as well as producers? Give reasons. (3)
Answer:
We can say that
globalization has been advantageous to both consumers as well as producers due
to the following reasons
Globalization has led to an intense increase in
industrial competition. As a result, producers are competing over each other to
provide better and cheaper services to the consumers. This has also resulted in
a reduction in the prices.
With the initiation of globalization, producers now have actively free access to international markets. Also. they can avail more easily of the credit facilities forwarded in terms of capita’ and technology. For instance in the case of the electronics goods and garments industry.
Consumers have more chances of goods and services as compared to earlier times, especially in modern digital technological equipment like cell phones, cameras, etc.
Question 28.
The Indian constitution provides 3 lists to distribute the
legislative power. State any two subjects that are included in the union list.
In which list the subject “Education” is included and why? (3)
Answer:
(i)
The Indian Constitution has a three-fold distribution of legislative power,
which contains three lists: The Union List, the State List, and the Concurrent
List. The subjects that are included in the Union List are those that are under
the exclusive jurisdiction of the Union Government. Some of the subjects that
are included in the Union List are:
- Defense of the country
- Foreign affairs and relations
- Banking, currency, and coinage
- Railways and air transport
- Posts and telegraphs
- Census and statistics
- Copyrights, patents, and trademarks
(ii) The subject “Education” comes under the Concurrent List, which means that both the Union Government and the State Governments have the power to make laws on this subject. The Concurrent List contains subjects that are of common interest to both the Union and the State Governments.
Question 29.
Evaluate the various impacts of First World War on the
economy of Britain. (3)
Or
Do you agree that agriculture in India takes
place in the unorganised sector? Give three points. (3)
Answer:
The impact
of First World War on Britain’s economy were as follows
(i) Britain which was
a leading economy of the world before the First World War faced a prolonged
crisis. While Britain was preoccupied with war, industries had developed in
Japan and India. After the war, Britain found it difficult to recapture its
earlier position.
(ii) Britain has borrowed liberal’y from the USA for its war time expenditure, thus at the end of the war, Britain was burdened with huge external debt.
(iii) After the war, production in Britain contracted which led to huge job losses. In 1921, one in every five British workers was out of work. Anxiety and uncertainty about work became an enduring part of the post-war time.
Or
Yes, Indian agriculture is mostly concentrated in the unorganized
sector. This is justified through the following points
(i) Agriculture in
India faces the problem of disguised unemployment which means more people are
employed than needed So this shows that agriculture is unorganized.
(ii) Farmers are employed during harvesting and sowing season while the rest of the time they are unemployed, So, the problem of underemployment shows that agriculture is unorganized.
(iii) Most of the farmers depend on moneylenders. rich farmers and relatives for taking loans instead of banks. Then they have to pay high interest, which means that agriculture in India is an unorganized sector.
Section
D
Section D consists of 4
questions of 5 marks each
Question 30.
(A) Analyze the impact of mining activities on the local
environment and the health of the surrounding communities. (5)
OR
(B)
“Non-conventional resources are the best option to conserve the natural
resources” Substantiate this statement with Examples.
Answer:
The hazards
of mining or the impacts of mining on the health of the miners and the
environment are given below:
- The dust and noxious fumes inhaled by miners make them vulnerable to pulmonary diseases.
- The risk of collapsing mine roofs.
- Inundation and fires in coal mines are a constant threat to miners.
The fact that mining is one of the most dangerous jobs, mining usually hurts the environment with the production of a lot of waste. - Disruption to the local flora and fauna, and contamination of local water sources.
- It could require the removal of massive amounts of topsoil, leading to erosion, loss of habitat and pollution.(Any other relevant points)
OR
“Non-conventional resources are the best option to conserve natural resources”
- Non-conventional sources are also known as renewable sources of energy.
Examples of non-conventional sources of energy include solar
energy, Bioenergy, tidal energy, wind energy, Geothermal energy, Natural gas etc. - They are inexhaustible and renewable. They are also considered as clean sources of energy.
- Optimal use of resources of energy minimizes environmental impact and
non-conventional resources produce minimum secondary waste
compared to use conventional sources. - The growing consumption of energy has resulted in the country becoming increasingly depend on fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas. Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainties about the security of energy supply in future., which in turn has serious repercussions on the growth of the national economy.
- Natural gas is considered an environmentally friendly fuel because of low carbon dioxide emissions. It does not cause air pollution or environmental degradation, thus, it is the fuel for present century.
- Renewable energy resources technologies provide an excellent opportunity
for mitigation of greenhouse gas emission and reducing global
warming through substituting conventional energy sources.
Question 31.
What are better public facilities? Explain any four public
facilities. (1+ 4)
Or
Elucidate the significance of secondary sector in
Indian economy. (5)
Answer:
Public facilities are the facilities provided
by the government either free of cost or at very low price for the welfare of
the people like schools, health centres, public transports, etc. The importance
of these facilities is to make these available for everyone to use.
Four major facilities are as follows
- Basic Education Government provides schools and other educational facilities like chairs, books, etc to be used by the public. But, their use and performance are depended on collective response and community cooperation.
- Basic Health Facilities Government provides hospitals and vaccine programmes to maintain proper health.
- Law and Order Facility/Security the government must ensure law and order and provide security to maintain peace in the country.
- Provide Public Distribution System (PDS) Government opens PDS shops or ration shops through which it supplies basic food items like rice, wheat, pulses, etc at very low prices/ subsidised rate to the tower income group or poor people
Or
The significance of secondary sector in Indian economy are as
follows
Secondary sector involves the industrial production. Industrial
activities utilise the materials produced in the primary sector. In the process,
it creates massive employment of various scales. It also induces service sector
like transport, market, etc to flourish. As all the sectors of economy are
interdependent, secondary sector has a great contribution for the sustainance
and growth of other sectors.
The secondary sector induces growth and productivity to primary sector and helps in flourishing of teiliary sector,
- It produces instruments and appliances that directly help primary sector for better production.
- It absorbs excess labour from the primary sector and reduces disguised unemployment.
- It also contributes significantly to the GDP of India and employment basket.
Question 32.
(A) Analyse the role of a multiparty system in a democratic
country like India. (5)
(OR)
(B) Evaluate the differences between the
national and regional parties and assess the requirements for a regional party
to become a national party.
Answer:
In a democratic system like India,
multiparty politics plays a crucial role in representing the diverse interests
and aspirations of the citizens.
- The multiparty system allows for a competitive and dynamic political environment, where parties with different ideologies and agendas can participate and compete for the support of the electorate.
- The presence of multiple parties also provides a check and balance against any one party becoming too powerful and dominant.
- This system allows a variety of interests and opinions to enjoy political representation. People can choose between several candidates.
- Through this system different and diverse parties could represent the sections of society and power does not absorb in the hands of one single party. India adopted this system because of the vast diversity and plurality in the nation.
OR
The differences between the National parties and the regional Parties are:
- National parties are powerful in the nation; it deals with national issues.
- Regional parties’ power is limited to a specific region or state, only the issues and demands of a specific region are discussed by regional parties.
- National parties’ actions offer preference to national issues over regional problems.
- Regional parties’ operations are confined to the state.
The regional parties must attain the following requirements to become a National Party: - A party must gain at least six percent of the total votes in Lok sabha or assembly elections in four states to be a national party and win at least four seats in Lok sabha.
- A party has to receive at least six percent of the total votes in the legislative election to become a regional party and win at least two seats. Examples of national parties are the BJE Congress and BSE The examples of regional parties are DMK and Telugu Desam.
Question 33.
Briefly discuss the resources based on ownership. (5)
Or
Write down the features of alluvial soil concerning its formation, area
classification, and inclusion of minerals. (5)
Answer:
Resources based on
ownership means who owns the resources. It can be a person, a group, a community
or a country.
The classification of resources is tabulated below
| Class of Resource | Explanation | Examples |
| individual | Resources owned by individuals | Plot of land, house. |
| Community | Resources accessible to all members of the community. | Public parks, burial grounds. |
| National | Resources owned by the government and its agencies within its political boundaries and territorial waters. | Roads, railways, water resources, forests, wildlife |
| International | Oceanic resources beyond the exclusive economic zone of countries and those in polar regions minerals are regulated by Antarctica’s international institutions. | Fisheries in international waters, minerals in Antractica |
Or
The features of alluvial soil are as follows
Formation Alluvial soil
is made-up of silt, sand and clay. It is deposited by three important Himalayan
river systems-the Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra. It is bigger and coarser
in the upper reaches of the river and becomes finer as the river
flows
down.
Distribution/Area This soil is prevalent in the river valleys of the Northern
plains (Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra), strips in Gujarat and Rajasthan. as well as
in the Eastern coastal plains in the deltas of rivers of the Peninsular plateau
(Mahanadi, Krishna,
Kaveri).
Classification According to their age, alluvial soil can be classified as (Bangar) old alluvial and Khadar (new alluvial). Khadar has higher concentration of Kankar and contains more tine particles than Bangar.
Nutrients/Minerals This soil is rich in nutrients like potash, phosphoric acid, and lime, which is suitable for growing paddy, wheat, sugarcane, and other cereal and pulse crops.
Section
E
Section E consists of 3
Case-based questions of 4 marks each
Question 34.
Read the given source below and answer the following
questions: (4)
It is said of “passive resistance” it is the weapon of the
weak, but the power which is the subject of this article can be used only by the
strong. This power is not passive resistance; indeed, it calls for intense
activity. The movement in South Africa was not passive but active … ‘Satyagraha
is not physical force. Satyagraha does not inflict pain on the adversary; he
does not seek his destruction … In the use of satyagraha, there is no ill will
whatever. ‘Satyagraha is pure soul force. Truth is the very substance of the
soul. That is why this force is called satyagraha. The soul is informed with
knowledge. In it burns the flame of love. … Nonviolence is the supreme dharma …’
It is certain that India cannot rival Britain or Europe in force of arms. The
British worship the war god and they can all of them become, as they are
becoming, bearers of arms. The hundreds of millions in India can never carry
arms. They have made the religion of non-violence their own.
In his famous
book Hind Swaraj (1909) Mahatma Gandhi declared that British rule was
established in India, with the cooperation of Indians, and had survived only
because of this cooperation. If Indians refused to cooperate, British rule would
collapse within a year.
(a) Why did Gandhiji say that passive resistance is not the weapon of the
weak?
Answer:
Gandhiji said” passive resistance is not the weapon of the
weak because it calls for intense activity with a lot of inner strength.
(b) “Satyagraha is pure soul-force”. Substantiate this statement in 20
words.
Answer:
(b) Truth is the very substance of the soul that is
informed with knowledge and thus this force is called satyagraha.
(c) What according to Mahatma Gandhi is the best weapon to use to collapse
British rule in India?
Answer:
Mahatma Gandhi in his book Hind Swaraj
declared that through noncooperation(Satyagraha) only British rule could
collapse in India as they could build their empire only with the cooperation of
Indians.
Question 35.
Read the given extract and answer the following
questions.
The distribution pattern of the Railway network in the country has
been largely influenced by Physiographic, economic, and administrative factors.
The Northern plains with their vast level land, high population density, and
rich agricultural resources provided the most favorable conditions for their
growth. However, a large number of rivers requiring construction of bridges
across their wide beds posed some obstacles, in the hills’ terrains of the
peninsular region, railway tracts arc laid through low hills, gaps or
tunnels.
The Himalayan mountainous regions too are unfavourable for the construction of railway lines due to high relief, sparse population and lack of economic opportunities. Likewise, it was difficult to lay railway lines on the sandy plain of Western Rajasthan, swamps of Gujarat, forested tracks of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and Jharkhand. The contiguous stretch of Sahyadri could be crossed only through gaps or passes (Ghats).
In recent times, the development of the Konkan railway along the West coast has facilitated the movement of passengers and goods in this most important economic region of India. It has also faced several problem such as sinking of track in some stretches and landslides.
Today, the railways have become more important in our National economy than
all other rncans of transport put together. However, rail transport suffers from
certain problems as well. Many passengers travel without tickets. Thefts and
damaging of railway property has not yet stopped completely. People stop the
trains, pull the chain unnecessarily and this causes heavy damage to the
railway.
(i) State the factors which influence the railway network in India.
(1)
(ii) Constructing the railways in the Peninsular region, Himalayan
region, Rajasthan and Gujarat is a diflicult task.
State any two reasons
which are responsible behind this. (2)
(iii) Railways are important part of
our national economy, but still it is facing several problems. State any two
reasons behind this.
Answer:
(i) Factors which are largely responsible to
influence the railway network in India are physiographic. economic and
administrative factors.
(ii) It is difficult to construct railway lines in
the Peninsular region, Himalayan region. Rajasthan and Gujarat. The reasons for
this are The Peninsular region and the Himalayan region are hilly and
mountainous regions. Peninsular region has undulating topography where railway
tracts are laid through low hills, gaps or tunnels. On the other hand, the
Himalayas have high relief, sparse population and lack of economic
opportunities. Rajasthan has sandy plains and Gujarat has swampy lands thus, to
construct railway lines there is a difficult task.
(iii) It is true that railways have become more important in our national economy, but still this transport is facing several problems.
The reasons for this are
- Many passengers travel by trains without tickets.
- This incurs heavy loss of rail budget.
- People stop the trains, pull the chain unnecessarily and this causes heavy damage to the railway.
Question 36.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that
follow: (4)
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of
the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed
than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more
income means more of all things that human beings need. Whatever people like,
and should have, they will be able to get with greater income. So, greater
income itself is considered to be one important goal. Now, what is the income of
a country? Intuitively, the income of the country is the income of all the
residents of the country. This gives us the total income of the country.
However, for comparison between countries, total income is not such a useful
measure. Since, countries have different populations, comparing total income
will not tell us what an average person is likely to earn. Are people in one
country better off than others in a different country? Hence, we compare the
average income which is the total income of the country divided by its total
population. The average income is also called per capita income. In World
Development Reports, brought out by the World Bank, this criterion is used in
classifying countries. Countries with per capita income of US$ 49,300 per annum
and above in 2019, are called high income or rich countries and those with per
capita income of US$ 2500 or less are called low-income countries. The rich
countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries
are generally called developed countries.
1. Explain the significance of per
capita Income.
Answer:
The Per capita income enables comparisons between
countries and provides insights into the relative economic performance and
living standards across different nations. Per capita income also serves as an
important indicator of the standard of living in a country.
2. What are the classifications of countries based on per capita income, and
which entity is responsible for determining these
classifications?”
Answer:
The courtiers are classified into “High-income
or Rich countries and low-income countries based on their per capita Income. If
it is US $ 49,300 per annum they will be classified as rich country and if the
per capita income is US$ 2500 per annum it will be called a poor country. World
Bank determines this classification.
Section
F
Section F consists of Map based
questions of 5 marks each
Question 37.
(a) Two places A and B have been marked on the given outline
map of India. Identify them on the map and write their correct names on the line
drawn near them. (2)
A. Jallianwala Bagh Incident
B. Calling of the
Non-Cooperation Movement.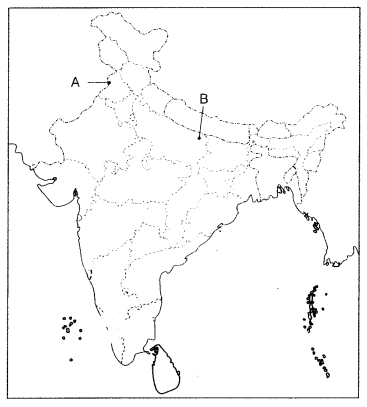
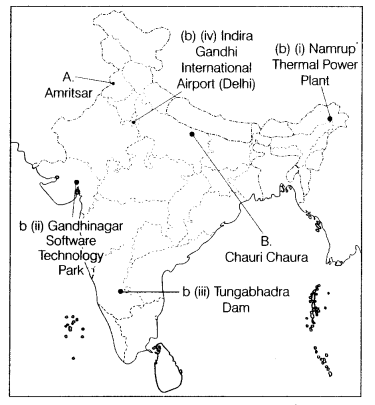
(b) On the same outline map of India, locate and label any three of the
following with suitable symbols. (3)
(i) Nanirup Thermal Power Plant
(ii)
Gandhinagar Software Technology Park
(iii) Tungabhadra dam
(iv) An
International Airport in Delhi NCR
Answer: