CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set-5
Class 10thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set-5
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 5
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
Instructions
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective-type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based assessment units of 4 marks each with sub-parts.
Section A
Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20.
Question 1.
Consider the following figure,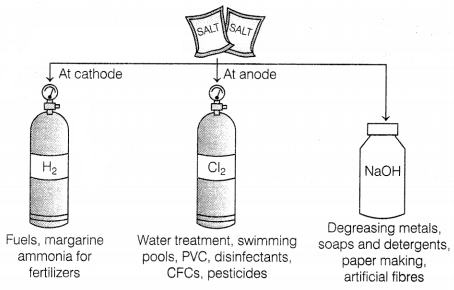
Which of the following two products are obtained from the
process shown in the given figure?
(i) HCl
(ii) Bleach
(iii) Litmus
(iv) H2SO4
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c)
(i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii)
Hydrochloric
acid and bleach are important products that are obtained from the chlor-alkali
process.
Question 2.
Which of the following is not observed in a homologous series?
Give a reason for your choice.
(A) Change in chemical properties.
(B)
Difference in -CH2, and 14u molecular mass.
(C) Gradation in
physical properties.
(D) Same functional group.
Answer:
(A) Change in
chemical properties.
Explanation: Change in chemical properties is not
observed in a homologous series. The chemical properties of all compounds in a
series remain the same.
Question 3.
Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of
acid strength?
(a) Water < acetic acid < hydrochloric acid
(b) Water
< hydrochloric acid < acetic acid
(c) Acetic acid < water <
hydrochloric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid < water < acetic acid
Answer:
(a) Water < acetic acid < hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric
acid is a mineral acid and ionizes completely in water, that’s why it is a
strong acid. Acetic acid is an organic acid and ionizes only partially in the
water, hence, it is a weak acid. Water is neutral. Thus, the order of acidity is
water < acetic acid < hydrochloric acid.
Question 4.
Metal oxides generally react with acids, but few oxides of
metal also react with bases. Such metallic oxides are:
(i) MgO
(ii)
ZnO
(iii) Al2O3
(iv) CaO
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B)
(ii) and (iii)
(C) (iii) and (iv)
(D) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(B) (ii)
and (iii)
Explanation: Some metal oxides, such as aluminum oxide, zinc oxide,
etc., show both addict as well as basic behavior. Such metal oxides can react
with both adds as well as bases to produce salts and water. Metal oxides of this
category are known as amphoteric oxides.
Question 5.
Which of the following is not the use of graphite?
(a) It
is used as a lubricant
(b) It is used in the manufacturing of
lead-pencils
(c) It is used in the manufacturing of artificial diamond
(d)
It is used for making insulated plates
Answer:
(d) It is used for making
insulated plates
Graphite can not be used for making insulated plates, as it
is a good conductor of electricity.
Question 6.
When you add a few drops of acetic acid to a test-tube
containing sodium bicarbonate powder, which one of the following is your
observation?
(A) No reaction takes place.
(B) Acolourless gas with a
pungent smell is released with brisk effervescence.
(C) A brown-colored gas
is released with brisk effervescence.
(D) Formation of bubbles of a colorless
and odorless gas.
Answer:
(D) Formation of bubbles of a colorless and
odorless gas.
Explanation: When a few drops of acetic add are added toa
test-tube containing sodium bicarbonate powder, it leads to the formation of
sodium acetate along with the release of carbon dioxide gas, which is a
colourless and odorless gas.
Question 7.
The structural formula of benzene is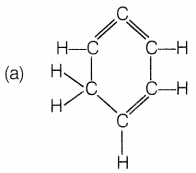
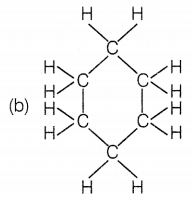
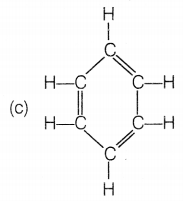
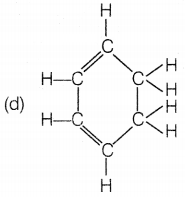
Answer:
Benzene molecules contain alternate single and double bonds.
Its formula is C6H6. In structure (a), double bonds are
not at alternate positions. In structure (b), the formula is
C6H12 and in structure (d), the formula is
C6H8.
Question 8.
The number of chromosomes in parents and offsprings of a
particular species undergoing sexual reproduction remains constant due to:
(A) doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation.
(B) halving of
chromosomes after zygote formation.
(C) doubling of chromosomes before gamete
formation.
(D) halving of chromosomes at the time of gamete formation.
Answer:
(D) halving of chromosomes at the time of gamete formation.
Explanation: The number of chromosomes in parents and offspring of a particular
species undergoing sexual reproduction remains constant due to the halving of
chromosomes through the process of meiosis at the time of gamete formation.
Question 9.
Identify the option that indicates the correct substrate for
the enzyme that is secreted in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine
respectively.
(a) Proteins, Proteins, Lipids
(b) Starch, Proteins,
Lipids
(c) Starch, Lipids, Starch
(d) Starch, Lipids, Proteins
Answer:
(b) Starch, Proteins, Lipids
The mouth secretes salivary amylase
which breaks down starch into sugars. Stomach secretes pepsin enzyme which
breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. In the small
intestine, bile juice emulsifies fats while lipase breaks them.
Question 10.
Given below are two columns, Column I shows enzymes secreted
by the glands in the alimentary canal of human beings and Column II indicates
the components of food on which enzymes act. Choose the options showing correct
matching.
| Column I(Enzymes) | Column II(Component) |
| (a) Pepsin | Starch |
| (b) Trypsin | Proteins |
| (c) Lipase | Proteins |
| (d) Amylase | Emulsified fat |
Answer:
(B) is correct
Explanation: Trypsin breaks down proteins into
smaller peptides in the duodenum of the small intestine. Pepsin is a stomach
enzyme that serves to digest proteins found in ingested food. Lipase is an
enzyme the body uses to break down fats in food so they can be absorbed in the
intestines. Amylase helps your body break down starches.
Question 11.
Select the correct option regarding the movement shown by
Mimosa Pudica.
(a) The movement is non-directional and occurs due to turgor
changes.
(b) The movement is an immediate response to a stimulus.
(c) The
movement is in response to touch and is called xyctinasty.
(d) The movement
is non-directional and involves growth.
Answer:
(a) The movement is
non-directional and occurs due to turgor changes.
The leaves of Mimosa pudica
respond to stimuli such as touch, blow or mechanical shack by folding their
leaflets and lowering their leaves. This effect is caused by a change in the
turgidity of the leaflets brought about by the movement of water into and out of
the parenchymatous cells of the swollen leaf base.
Question 12.
During pollination, plants ensure that the pollen grain from
a species germinates on the stigma of the same species. Which of the following
ensures this?
(A) Hydrotropism
(B) Chemotropism
(C) Phototropism
(D)
Geotropism
Answer:
(B) Chemotropism
Explanation: Chemotropism in plants
leads to the growth of pollen tubes towards the ovules and thus helps in the
fertilization process.
Question 13.
Which of the following phenomena of light are involved in the
formation of a rainbow?
(a) Reflection, refraction and dispersion
(b)
Refraction, dispersion, and total internal reflection
(c) Refraction,
dispersion, and internal reflection
(d) Dispersion, scattering, and total
internal reflection
Answer:
(c) Refraction, dispersion and internal
reflection
A rainbow is caused by dispersion, refraction, and internal
reflection of sunlight by tiny water droplets, present in the atmosphere and
always formed in a direction opposite to that of the sun. The water droplets act
like small prisms. They refract and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflect
it internally, and finally refract it again when it comes out of the
raindrop.
Question 14.
When we enter a dark room coming from outside, immediately,
the things inside the room do not appear clear to our eyes. This is because:
(A) pupils do not open at all in the dark.
(B) pupils take time to
adjust.
(C) light travels slower in a dark room.
(D) pupils open very
quickly in the dark.
Answer:
(B) pupils take time to adjust.
Explanation: When we enter a dark room coming from outside, immediately, the
things inside the room do not appear clear to our eyes. This is because pupils
take time to adjust.
Question 15.
The development of a seedling from an embryo under
appropriate conditions is called
(a) regeneration
(b) germination
(c)
vegetative propagation
(d) pollination
Answer:
(b) germination
Germination is a process occurring in plants in which the embryo develops into a
seedling under appropriate conditions.
Question 16.
Excessive exposure of humans to UV rays results in
(i)
damage to immune system.
(ii) damage to lungs.
(iii) skin cancer.
(iv)
peptic ulcers.
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (ii) and (iv)
(C) (i) and (iii)
(D) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(C) (i) and (iii)
Explanation: Excessive
exposure of humans to ultraviolet (UV)-rays results in:
(i) Skin cancer.
(ii) Damage to the immune system of the body.
Directions (Q.Nos. 17-20) consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both
A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true,
but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): Carbon shows maximum catenation property in
the periodic table.
Reason (R): Carbon has a small size and thus, forms a
strong C—C bond.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct
explanation of A.
Catenation is the bonding of atoms of the same element into
a series called a chain. Catenation occurs more readily with carbon, which forms
strong covalent bonds with other C-atoms to form long chains and structures.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): Amoeba takes in food using finger like
extensions of the cell surface.
Reason (R): In all unicellular organisms, the
food is taken in by the entire cell surface.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R
is false.
Explanation: Amoeba takes in food using temporary finger-like
extensions of the cell surface, called pseudopodia, which extend and fuse over
the food particle forming a food vacuole. Inside the food vacuole, complex
substances are broken down into simpler ones which then diffuse into the
cytoplasm. A unicellular organism does not need a specific organ for taking in
food, because the entire surface of the organism is in contact with the
environment.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): Amoeba an omnivore organisms.
Reason (R): A
lion is a carnivore organism.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is
not the correct explanation of A.
Amoeba is an omnivore organism, It feeds
upon both plant and animal matter. Its mode of nutrition is holozoic. Lion is a
carnivore organism because it eats other animals (meat eaters).
Question 20.
Assertion (A): Greater number of individuals is present in
lower trophic levels.
Reason (R): The flow of energy is unidirectional.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of
A.
Explanation: There are generally a greater number of individuals at the
lower trophic levels of an ecosystem; the greatest number is of the producers.
The flow of energy in an ecosystem is always linear or unidirectional. The
energy captured from producers does not revert solar input. Also, the energy
that passes to the herbivores does not come back to autotrophs.
Section B
Questions No. 21 to 26 are Very Short Answer Questions.
Question 21.
A metal taken does not react with cold as well as hot water,
but it reacts with steam. Identify the metal and write the chemical equations
involved.
Answer:
Aluminium only reacts with steam but does not react with
hot or cold water. The chemical equations involved are as follows: (2)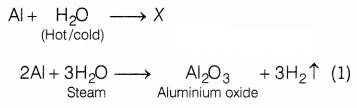
Question 22.
In the experimental set up on CO2 is released
during respiration’, if one forgets to keep the vial with KOH in the conical
flask, how will the result vary? Give details.
Answer:
In the absence of
KOH, CO2 released by germinating seeds is not absorbed, a partial
vacuum is not created in the conical flask, air pressure in the flask is not
reduced, and the water level does not rise in the delivery
tube.
Detailed Answer:
The rise in the level of water
indicates that CO2 is produced by germinating seeds during
respiration. The germinating seeds respire and produce C02, which is absorbed by
KOH solution. This creates a vacuum in the conical flask. The air present in the
bent glass tube moves into the conical flask. This pulls the water in the bent
tube further up.
So, if one forgets to keep the vial with KOH solution in a
conical flask during an experiment, then the released CO2 will not be
absorbed due to which the level of water will not rise in the tube and the
process of respiration will get very slow.
Question 23.
List the components and functions of transport systems in
highly organized plants.
Or
Explain, why the transportation of materials
is necessary for animals.
Answer:
The main components of the transport
system in highly organized plants are the xylem and phloem. These can be
explained as
- The xylem consists of tracheids and vessels. It conducts water and minerals (obtained from the soil) to the leaves. (1)
- Phloem consists of sieve tubes and companion cells. It helps to transport food materials, etc. from leaves to various parts of the plant. (1)
Or
The distribution of all essential substances such as food, oxygen, and
water throughout the body is carried out through the system of transportation.
It also displaces excretory wastes collected from the cells of the body to the
excretory organs from where they are expelled from the body. Thus,
transportation of materials is necessary to carry out various life processes.
(2)
Question 24.
A lens made of material with refractive index 1.5 is immersed
in a liquid with refractive index 1.5. The diagram shows two rays incident on
the lens when it is immersed in the liquid.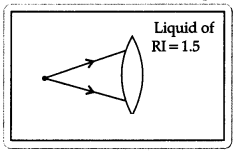
Copy the diagram and draw the light rays after they pass
through the lens. Justify your diagram.
Answer: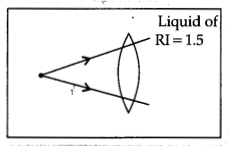
Since the refractive index of the liquid is equal to that of
the material of the lens, the light rays do not undergo refraction as they pass
from the liquid to the lens and back into the liquid.
Question 25.
A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at
a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle placed in front of a convex
lens, if the image is equal to the size of the object? Also, find the power of
the lens.
Or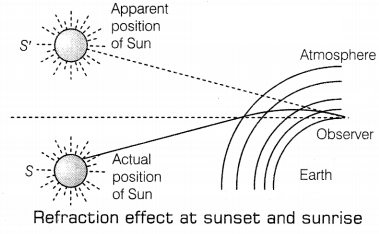
From the figure given above, explain the phenomena of
advanced sunrise and delayed sunset.
Answer:
Given, image distance, v =
+50 cm
Magnification, m = -1 [∵ image is inverted]
m = \(\frac{v}{u}\)
⇒ u = \(\frac{v}{m}=\frac{50}{-1}\) = -50 cm (1)
So, the needle is placed 50
cm in front of the lens.
By lens formula,
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}\)
⇒
\(\frac{1}{50}-\frac{1}{(-50)}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{25}\)
⇒ f = 25
cm = 0.25 m
∴ Power of convex lens, P = \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{0.25}\) = 4 D
(1)
Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset: The figure shows the actual position of the Sun S at the time of sunrise and S’ the apparent position of the Sun. The advanced sunrise and delayed sunset are because of atmospheric refraction. The light rays starting from the Sun travel from rarer to denser layers. They bend more and more towards the normal. (1)
However, an observer on the Earth sees an object in the direction of the rays reaching his eyes. The Sun which is actually in a position below the horizon, appears in the position S’ above the horizon for him. Thus, the Sun appears to rise early by about 2 minutes and set late by about 2 minutes. This increases the length of the day by about 4 minutes. (1)
Question 26.
(a) From the following groups of organisms, create a food
chain that is the most advantageous for human beings in terms of energy.
(b)
State the possible disadvantage if the cereal plant is growing in soil rich in
pesticides.
(Hawk, Rat, cereal plant, Goat, Snake, Human Beings)
Answer:
(a) Cereal Plant → Human beings
(b) Pesticides being
non-biodegradable accumulate progressively at each trophic level/leading to
biomagnification.
Section C
Questions No. 27 to 33 are Short Answer Questions.
Question 27.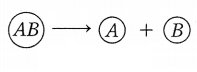
These given reactions require energy either in the form of
heat light or electricity to break down the reactants. Identify and define the
type of reaction. Write one equation each for this type of reaction where energy
is supplied in the form of heat, light, and electricity.
Or
What is
observed when sulphur dioxide is passed through (i) water and (ii) lime water?
Also, write chemical equations for the reactions that take place.
Answer:
Decomposition reaction: A reaction in which a single reactant breaks down to
form two or more products is known as a decomposition reaction.
(a) When a
decomposition reaction is carried out by heating then it is known as a thermal
decomposition reaction. (1)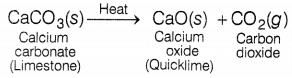
(b) A decomposition reaction in which energy is supplied in
the form of light, is known as photochemical decomposition reaction. (1)
(c) A decomposition reaction in which energy is supplied in
the form of electricity is known as an electrolytic decomposition reaction.
(1)
Or
(a) When SO2 is passed through water, sulphurous acid
is formed. Due to the formation of acid, the blue litmus is turned red.
(1)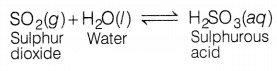
(b) When SO2 is passed through lime water, calcium
sulphite (white ppt.) is formed, which reacts with excess SO2 to form
calcium hydrogen sulphite. The chemical equation for the reactions are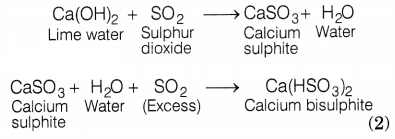
Question 28.
When ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in the presence of
conc. H2SO4, a substance with a fruity smell is
produced.
Answer the following:
(a) State the class of compounds to which
the fruity-smelling compounds belong. Write the chemical equation for the
reaction and write the chemical name of the product formed.
(b) State the
role of conc. H2SO4.
Answer:
(a) Esters.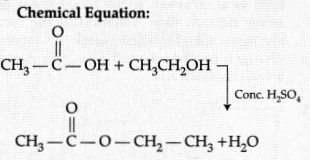
Product’s chemical name – Ethyl ethanoate
(b) Conc.
H2SO4 acts as a dehydrating agent. (Helps in the removal
of water formed in the reaction.)
C4H8, it is an
unsaturated hydrocarbon due to the presence of a double bond.
OR
Two carbon compounds X and Y have the molecular formula
C4H8, and C5H12, respectively. Which
one of these is most likely to show an additional reaction? Justify your answer.
iso, give the chemical equation to explain the process of addition reaction in
this case.
Answer:
C4H8, it is an unsaturated
hydrocarbon due to the presence of a double bond.
Question 29.
How is the sex of a child determined in human beings?
Answer:
A male germ cell that forms gametes carries one X and one Y
chromosome, while a female germ cell carries two X chromosomes. Therefore, the
sex of the child depends upon what happens during fertilization. (1)
(a) If a
sperm carrying an X-chromosome fertilizes the egg, the child born will be a
female (XX). (1/2)
(b) If a sperm carrying a Y-chromosome fertilizes the egg,
the child born will be a male (XY). (1/2)
Thus, the sperm (the male gamete)
determines the sex of the child. (1)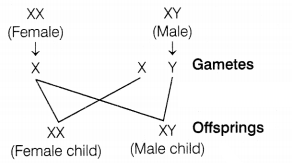
Question 30.
State briefly the changes that take place in a fertilised egg
till the birth of the child in the human female reproductive system. What
happens to the egg when it is not fertilised?
Answer:
Changes in the
fertilised egg:
(i) Zygote/fertilised egg start dividing.
(ii)
Implantation of the zygote in the inner uterine wall.
(iii) Embryo starts
growing with the help of the placenta which results in the development of the
child.
(iv) Birth of a child as a result of rhythmic contraction of the
muscles in the uterus.
When an egg is not fertilized, the inner lining of the
uterus slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous
(Menstruation).
Question 31.
A 6 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal
axis of a convex lens of focal length 25 cm. The distance of the object from the
lens is 40 cm. Then, determine (a) the position (b) and the size of the image
formed.
Answer:
Given, the height of the object, h0 = 6 cm
The focal length of the lens, f = 25 cm
Distance of the object, u = -40
cm
Question 32.
(a) What is the heating effect of electric current?
(b)
Write an expression for the amount of heat produced in a resistor when an
electric current is passed through it stating the meanings of the symbols
used.
(c) Name two appliances based on the heating effect of electric
current,
Answer:
(a) When electricity is supplied to a purely resistive
conductor, the energy of electric current gets dissipated entirely in the form
of heat. As a result, the resistor gets heated. The heating of a resistor
because of the dissipation of electrical energy is known as the heating effect
of electric current.
(b) When an electric current I passes through the
conductor, the amount of heat produced in time t is:
H = Vlt
Since, V =
IR
So, H = l2Rt
(c) Two appliances based on the heating effect
of electric current are electric iron and electric geyser.
Question 33.
Some modern insecticides have been introduced each having
different properties like accumulation in the bodies of predators, broken down
by soil bacteria, easily washed into lakes and rivers, and taken up by plant
roots. Among all these insecticides, which one will help in reducing or keeping
the level of environmental pollution to the lowest?
Answer:
Insecticides
are non-biodegradable chemicals added to crop fields to stop the growth of
insects infecting the crops. Modern insecticides are being developed keeping in
mind, the harm they cause to the environment and its components. (1)
Biodegradable insecticides can be decomposed into harmless substances, which will subsequently be dispersed in their specific pathways and cause no pollution. Non-biodegradable insecticides build up in the fat tissues of the body and pass on to organisms that feed on them. (1)
Hence, they accumulate along the food chain resulting in significant amounts in the tissues of consumers at the highest trophic level. This is called biomagnification. The property of newly developed insecticides which includes that they can easily get decomposed into simpler components by soil bacteria, will help in reducing or keeping the level of environmental pollution to the lowest. (1)
Section D
Questions No. 34 to 36 are long answer questions.
Question 34.
Write the chemical equation for the following:
(a)
Combustion of methane
(b) Oxidation of ethanol
(c) Hydrogenation of
ethene
(d) Esterification reaction
(e) Saponification reaction
Answer: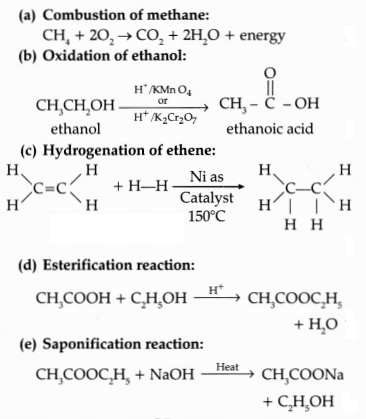
OR
(a) Draw two structural isomers of butane.
(b) Draw the structures of
propanol and propanone
(c) Name the third homologue of (a) alcohols (b)
aldehydes
(d) Name the following: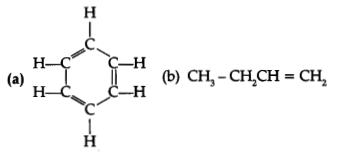
(e) Show the covalent bond formation in nitrogen
molecules.
Answer:
(a) Structural formulae of isomers of Butane are
n-butane and isobutane.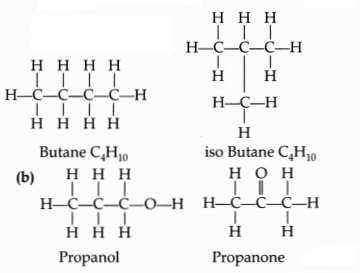
(c) (i) 3rd homologue of alcohol is propanol
(C3H7OH).
(ii) 3rd homologue of aldehyde is
propanal (CH3CH2CHO)
(d) (i) Benzene
(C6H6)
(ii) 1- Butene
(e) Covalent bond formation in
Nitrogen molecule: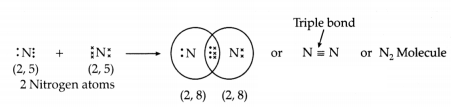
Question 35.
(a) Write differences between pollination and
fertilization
(b) ‘Reproduction helps in providing stability to the
population of a species’. Justify this statement.
Or
(a) Name the plant,
different characteristics, and contrasting pairs, Mendel used for his
experiments. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 and
F2 generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write
the ratio he obtained in F2-generation plants.
(b) How do Mendel’s
experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive? Also, explain how
gametes maintain their purity during reproduction.
Answer:
(a) Differences
between pollination and fertilization are as follows: (\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 6)
| Pollination | Fertilisation |
| (i) It is the transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of the same or different flower. | (i) It is the fusion of a male and a female gamete. |
| (ii) It carries male gamete-producing pollen grain to the female sex organs. | (ii) It leads to the formation of a zygote. |
| (iii) It is a physical process. | (iii) It is a biological process. |
| (iv) It occurs in seed plants only. | (iv) It occurs in both plants and animals. |
| (v) It is an external process. | (v) It can either be internal or external. |
| (vi) It leads to the formation of seeds. | (vi) This process leads to fertilization. |
(b) Reproduction is the process of producing new individuals of the same
species by existing organisms of a species. It ensures the transfer of genetic
materials from the first generation to the next generation. (1)
It is
important for the continuity of the generation of an organism or species as DNA
copying during reproduction helps to produce similar individuals as their
parents to maintain the stability of a species. (1)
Or
(a) Mendel used the
pea plant for his experiments. Seven pairs of contrasting characters in pea
plants were studied by Mendel. (1)
| Character | Dominant trait | Recessive trait |
| Seed shape | Round | Wrinkled |
| Seed colour | Yellow | Green |
| Flower colour | Violet | White |
| Pod shape | Full | Constricted |
| Pod colour | Green | Yellow |
| Flower position | Axial | Terminal |
| Stem height | Tall | Dwarf |
The progeny produced from them, F1-generation plants were all tall. (1)
Then Mendel allowed F1 progeny plants to undergo self-pollination. In the
F2 generation, he found that all plants were not tall, three quarters
were tall and one-quarter of them were short. The ratio he obtained in
F2-generation plants is 3 : 1. (1)
(b) When plants with two contrasting characters (e.g. tall and dwarf) are
crossed, only one character is visible in F1-generation and the other
character is suppressed. It shows the dominance of one character over another.
The F1 hybrid when selfed, produced plants with both dominant and
recessive phenotypes. (1)
It showed that the two unit factors of a character
that remain together in an individual do not get mixed up, or get contaminated
and keep their distinct identity. They separate or segregate during gamete
formation. (1)
Question 36.
Analyse the following observation table showing the variation
of image distance (v) with object distance (u) in the case of a convex lens and
answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations:
| S. No | Object-Distance u(cm) | Image-Distance v(cm) |
| 1 | -100 | +25 |
| 2 | -60 | +30 |
| 3 | -40 | +40 |
| 4 | -30 | +60 |
| 5 | -25 | +100 |
| 6 | -15 | +120 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give a reason to justify
your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of the observation, which is not
correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c) Select an
appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No. 2. Also
find the approximate value of magnification.
Answer:
(a) The focal length
of the convex lens can be calculated from S.No. 3 as when an object is placed at
a distance from the convex lens, its image is formed on the other side of the
lens at the same distance from the lens. So, the focal length is + 20 cm.
(b)
S.No. 6 is incorrect as the object distance is between the focus and pole and
here the real image is formed as the image distance is positive. But in such
situation, virtual image should form.
(c) Approximate value of magnification
for object distance – 60 cm and image distance +30 cm is -0.5.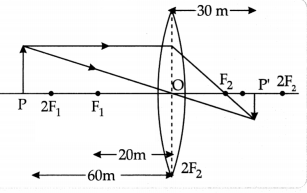
u = -60 cm; v = + 30 cm,/ = – 20 cm m = v/u = 30/-60= 1/2 =
-0.5
OR
(a) A security mirror used in a big showroom has a radius of curvature 5 m.
If the customer is standing at a distance of 20 m from the cash counter, find
the position, nature and size of the image formed in the security mirror.
(b)
Neha visited a dentist in his clinic. She observed that the dentist was holding
an instrument fitted with a mirror. State the nature of this mirror and the
reason for its use in the instrument used by dentist.
Answer:
(a) It is a
convex mirror. So focal length should be positive.
Radius of curvature R = +
5 m
∴ Focal length f = 5/2 + 2.5 m
Object distance u =- 20 m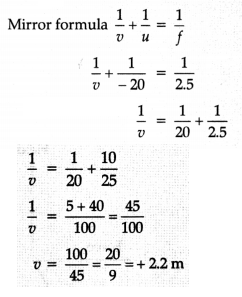
- Nature of image = virtual and erect image1
- Size of image: diminished image
(b) Concave Mirror – Reason: to obtain an erect and enlarged image of teeth
Section E
Questions No. 37 to 39 are case-based/data-based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
The table given below shows the hints given by the quiz
master in a quiz.
| Hints |
| (i) Substance ‘A’ is used as a refrigerant and food additive. |
| (ii) ‘A’ on reduction gives ‘B’. |
| (iii) ‘B’ is mainly used to produce ethylene. |
| (iv) ‘B’ on reaction with chlorine in the presence of sunlight gives ‘C’. |
| (v) ‘C’ is a colorless gas with a pungent odour. |
Based on the above hints answer the following questions.
(a) Name the
compounds A and C.
(b) Write the chemical equation for the conversion of A to
B and B to C.
Or
What is the industrial name of ‘A’? Give its industrial
uses.
Answer:
(a) A – Ethene, C – Chloroethane (2)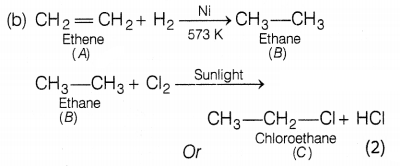
The industrial name of ethyne is acetylene.
Uses of ethyne
are
(i) It is used in the manufacture of polythene.
(ii) It is used as an
illuminant. (2)
Question 38.
Mendel blended his knowledge of science and mathematics to
keep the count of the individuals exhibiting a particular trait in each
generation. He observed several contrasting visible characters controlled in pea
plants in the field. He conducted many experiments to arrive at the laws of
inheritance.
(a) What do the F1 progeny of tall plants with round
seeds and short plants with wrinkled seeds look like?
(b) Name the recessive
traits in the above case.
(c) Mention the type of the new combinations of
plants obtained in F2 progeny along with their ratio, if F1
progeny was allowed to self-pollinate.
Answer:
(a)
F1 progeny of tall plants with round seeds and short plants with
wrinkled seeds will be a heterozygous tall plant with round seeds (TtRr) as tall
and round is the dominant traits.
(b) The recessive traits are short plants
and wrinkled seeds.
(c) The different types of combinations obtained in
F2 progeny are: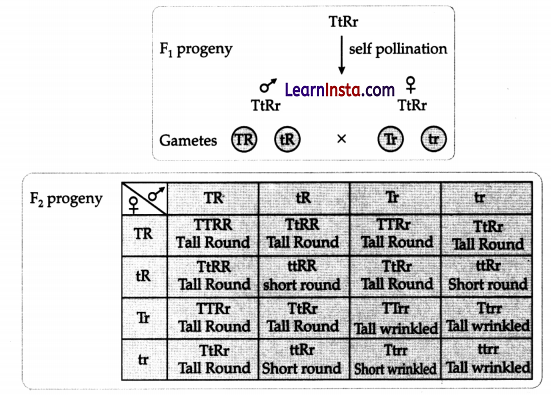
Tall plants with round seeds = 9 Short plants with round
seeds = 3 Tall plants with wrinkled seeds = 3 Short plants with wrinkled seeds =
1 Phenotypic ratio = Tall round: short round: tall wrinkled: short wrinkled:
9:3:3:1.
OR
(c) If 1600 plants were obtained in F2 progeny, write the number
of plants having traits:
(i) Tall with round seeds.
(ii) Short with
wrinkled seeds.
Write the conclusion of the above experiment.
Answer:
If 1600 plants were obtained in F2 progeny, the number of plants having traits
will be:
(i) Tall plants with round seeds = 9/16 × 1600 = 900
(ii) Short
plants with wrinkled seeds = 1/16 × 1600 = 100
The conclusion of the above
experiment states the “Law of independent assortment”. This law states that the
alleles of two (or more) different genes get sorted into gametes independently
of one another.
Question 39.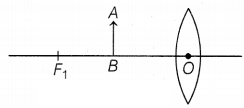
In an experiment, the formation of an image for an object AB
placed in front of a convex lens is shown above in the figure, with an
incomplete ray diagram.
(a) Based on text data given in the above paragraph,
if the object is placed at infinity, then where is the position of the image
formed by the lens?
(b) What is the nature and size of the image formed by
the convex lens?
(c) For the given position of an object in the figure, where
will be the image formed?
Or
If the focal length of the lens is 8 cm and
an object is placed at 12 cm from the optical center, then find the position of
the image formed.
Answer:
(a) The convex lens has the property to converge
the parallel beam of light rays at 4 points, i.e., the focus of the lens. Hence,
the image will be formed at the focus. (1)
(b) In this case, the nature of
the image formed by a convex lens is virtual and erect. The size of the image is
larger than that of the object, i.e. magnified image will be formed. (1)
(c)
The formation of the image is as shown below: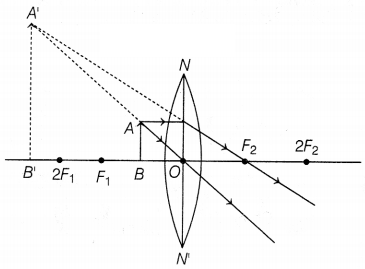
Hence, the position of the image is beyond 2F1 on the same
side of the object. (2)
Or
Given, the focal length of the lens, f = 8
cm
Object distance, u = -12 cm
Using lens formula,
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}\)
⇒
\(\frac{1}{8}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{-12}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{24}\)
⇒
v = 24 cm
Hence, the image will be formed at a distance of 24 cm from the
optical centre. (2)