CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set-4
Class 10thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set-4
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 4
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
Instructions
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective-type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based assessment units of 4 marks each with sub-parts.
Section A
Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20.
Question 1.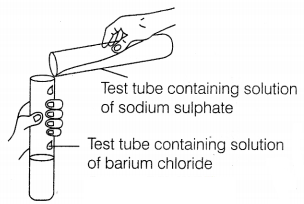
Identify the product that represents the solid state in the
above reaction.
(a) Barium chloride
(b) Barium sulphate
(c) Sodium
chloride
(d) Sodium sulphate
Answer:
(b) Barium sulphate
The
reaction involved is as follows.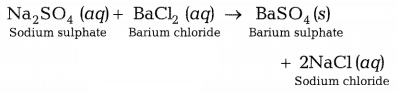
Question 2.
Which one of the following properties is not generally
exhibited by ionic compounds?
(A) Solubility in water.
(B) Electrical
conductivity in solid state.
(C) High melting and boiling points.
(D)
Electrical conductivity in molten state.
Answer:
(B) Electrical
conductivity in solid state.
Explanation: ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity because the movement of ions in the solid is not possible due to their rigid structure.
Question 3.
Mild non-corrosive basic salt is
(a) Ca(OH)2
(b) NaCl
(c) NaOH
(d) NaHCO3
Answer:
(d)
NaHCO3
Among the given options, mild to non-corrosive basic salt
is NaHCO3.
Question 4.
When sodium bicarbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid,
the gas evolved is:
(A) Hydrogen; it gives a pop sound with burning match
stick.
(B) Hydrogen; it turns lime water milky.
(C) Carbon dioxide; it
turns lime water milky.
(D) Carbon dioxide; it blows off a burning match
stick with a pop sound.
Answer:
(C) Carbon dioxide; it turns lime water
milky.
Explanation: When sodium hydrogen carbonate (sodium bicarbonate) is treated
with dil. hydrochloric acid, a brisk effervescence is observed.
This is due
to the release of carbon dioxide gas.
NaHCO3 (s) + HCl (aq) → NaCl
(aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
When carbon dioxide reacts
with lime water, lime water turns milky due to the formation of calcium
carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 → CaCO3 (s) +
H2O (l)
Question 5.
Which one of the following correctly represents sodium
oxide?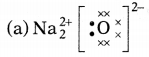
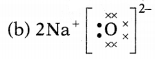
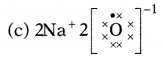
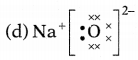
Answer: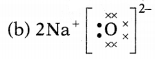
Among the given options, the correct representation of sodium
oxide is given as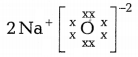
Question 6.
Identify the basic salt from the following salts:
(A)
Na2CO3
(B) NH4Cl
(C) NaNO3
(D) KCl
Answer:
(A) Na2CO3
Explanation: Na2CO3 is a basic salt. It is made up of a strong base (NaOH – sodium hydroxide) and weak acid (H2CO3 – carbonic acid).
Question 7.
An element M has 50% of the electrons filled in the 3rd shell
as in the 2nd shell. The atomic number of M is
(a) 10
(b) 12
(c) 14
(d) 18
Answer:
(c) The electronic configuration of an element with atomic
number 14 is
K L M
2 8 4
Thus, it contains 4 electrons in the M shell,
i.e. 3rd shell which is 50% of the electrons that are present in the 2nd shell
(i.e. 8 electrons)
Question 8.
Stomata are the tiny, kidney, or bean-shaped pores or openings
present in the epidermis of the cell. Opening and closing of stomata is due
to:
(A) high pressure of gases inside the cells.
(B) movement of water in
and out of the guard cells.
(C) stimulus of light in the guard cells.
(D)
diffusion of CO2 in and out of the guard cells.
Answer:
(B)
movement of water in and out of the guard cells.
Explanation: The opening and closing of the stomatal pore is the function of guard cells. They swell when water flows into them, causing the stomatal pore to open and on the loss of turgidity the guard cells become flaccid leading to the closure of the stomatal pore.
Question 9.
Receptors are usually located in sense organs. Gustatory
receptors are present in
(a) tongue
(b) nose
(c) eye
(d) ear
Answer:
(a) tongue
Question 10.
Which one of the given statements is incorrect?
(A) DNA
has the complete information for a particular characteristic.
(B) DNA is the
molecule responsible for the inheritance of characteristics from parents to
offspring.
(C) Change in information will produce a different protein.
(D)
Characteristics will remain the same even if protein changes.
Answer:
(D)
Characteristics will remain the same even if protein changes.
Explanation: Changes in protein structure can cause changes in the characteristic of an organism, as proteins are the molecules responsible for carrying out various functions in the cell.
Question 11.
The height of a plant is regulated by
(a) DNA which is
directly influenced by the growth hormone
(b) Genes which regulate the
proteins directly
(c) Growth hormones under the influence of the enzymes
coded by a gene
(d) Growth hormones directly under the influence of a
gene
Answer:
(c) Growth hormones under the influence of the enzymes coded
by a gene
Question 12.
Which pair of sex chromosomes will determine a male?
(A)
XO
(B) XX
(C) XY
(D) YY
Answer:
(C) XY
Explanation: In humans, all eggs of female carry X chromosome while sperm may have X or Y chromosome. The sex of the child depends on the type of sperm that fuses with the egg. If the egg fuses with the sperm carrying X chromosome, it results in a girl (XX) and if it fuses with the sperm carrying Y chromosome, it results in a boy (XY).
Question 13.
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror. Its image is
formed
(a) at a distance equal to the object distance in front of the
mirror
(b) at twice the distance of the object in front of the mirror
(c)
half the distance of the object in front of the mirror
(d) behind the mirror
and its position varies according to the object’s distance
Answer:
(d) The
image is formed behind the mirror and its position varies according to the
object’s distance.
Question 14.
The change in the focal length of an eye lens in human beings
is caused by the action of:
(A) optic nerves
(B) ciliary muscles
(C)
retina
(D) cornea
Answer:
(B) ciliary muscles
Explanation: The relaxation or contraction of ciliary muscles changes the curvature of the eye lens. The change in curvature of the eye lens changes the focal length of the eyes. Hence, the change in the focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of ciliary muscles.
Question 15.
In 1987, an agreement was formulated by the United Nations
Environment Programme (UNEP) to freeze the production of X to prevent depletion
of Y. X and Y respectively referred to here are
(a) Ozone, CFCs
(b) CFCs,
UV rays
(c) CFCs, Ozone
(d) UV rays, Diatomic Oxygen
Answer:
(c)
CFCs, Ozone
Question 16.
Select the mismatched pair in the following and correct
it.
(A) Bio-magnification — Accumulation of chemicals at the successive
trophic levels of a food chain.
(B) Ecosystem — Biotic components of the
environment.
(C) Aquarium — A man-made ecosystem.
(D) Parasites —
Organisms that obtain food from other living organisms.
Answer:
(D)
Parasites — Organisms that obtain food from other living organisms.
Explanation: Both biotic and abiotic components of the environment constitute an ecosystem.
Direction (Q.Nos. 17-20) consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both
A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but
R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): Rusting of iron is endothermic.
Reason (R):
As the reaction is slow, the release of heat is barely evident.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
The correct form of (A) statement is The
rusting of iron is exothermic.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): In humans, if gene (B) is responsible for
black eyes and gene (b) is responsible for brown eyes, then the colour of the
eyes of the progeny having gene combination Bb, bb or BB will be black only.
Reason (R): The black colour of the eyes is a dominant trait.
Answer:
(D)
A is false but R is true.
Explanation: In humans, if gene (B) is responsible for black eyes and gene (b) is responsible for brown eyes, then the colour of the eyes of the progeny having gene combination Bb and BB will be black only. The gene combination bb will be brown. It is because the black colour of the eyes is a dominant trait and the brown eye is a recessive trait.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): A compass needle is placed near a
current-carrying wire. The deflection of the compass needle decreases when the
magnitude of the current in the wire is increased.
Reason (R): The strength
of a magnetic field at a point near the conductor increases by increasing the
current.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
A compass needle is
placed near a current-carrying wire. The deflection of the compass needle
increases when the magnitude of the current in the wire is increased. Because
the strength of a magnetic field at a point near the conductor increases with
increasing the current.
Question 20.
Assertion (A): The energy that passes to the herbivores does
not come back to autotrophs.
Reason (R): The flow of energy in a food chain
is unidirectional.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct
explanation of A.
Explanation: The flow of energy is unidirectional. The energy that is captured by the autotrophs does not revert to the Sun and the energy which Passes to the herbivores does not come back to autotrophs. As it moves progressively through the various trophic levels, it is no longer available to the previous level.
Section B
Questions No. 21 to 26 are Very Short Answer Questions.
Question 21.
Dil. HCl is added to Zn granules. How will you prove that
chemical change has taken place here? Support your response with two
arguments.
Answer:
When zinc granules are added to dil. HC1, it leads to
the formation of zinc chloride salt with the evolution of hydrogen gas. The
evolved gas is colourless and odourless. Its chemical change can be detected by
measuring the temperature change, by observing the change in colour of zinc from
silver-grey to black, or by bubbles of gas.
Question 22.
Give the name of the enzyme present in the fluid in our mouth
cavity.
State the gland that produces it. What would happen to the digestion
process if this gland stops secreting this enzyme?
Answer:
- Ptyalin or salivary amylase is the starch hydrolyzing enzyme secreted by salivary glands in human beings.
- Amylase is a digestive enzyme that acts on starch in food, breaking it down into smaller carbohydrate molecules. Without amylase, a person will be unable to digest starch and sugars in the mouth.
Question 23.
What is the purpose of making urine in the human body? Name
the organs that store and release the urine.
Or
Why do arteries have thick
and elastic walls, whereas veins have valves?
Answer:
The main purpose of
making urine in the body is to filter out nitrogenous waste products like urea
and uric acid from the blood. The urinary bladder and urethra are the organs
that store and release the urine, respectively.
Or
The blood emerges from
the heart under high pressure and flows through arteries. Therefore, to resist
this pressure, the arteries have thick and elastic walls. Veins have valves,
which ensure that the blood flow occurs in one direction only.
Question 24.
Observe the following diagram and answer the questions that
follow: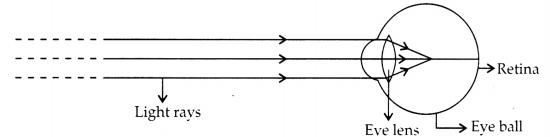
(a) Identify the defect of vision shown.
(b) List its two
causes.
(c) Name the type of lens used for the correction of this defect.
Answer:
(a) Myopia, as the image is formed before the retina for far away
objects.
(b) Possible causes are:
1. Elongation of eyeballs.
2.
Excessive curvature of the eye lens. we
(c) Correction: Using a concave lens
of suitable focal length.
Question 25.
A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into three equal
parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance
of this parallel combination is R1, what is the value of the ratio
R1 : R?
Or
Refer to the image below and state how the magnetic
field pattern indicates regions, where the magnetic field is stronger outside
the magnet. What happens to the magnetic field, when the current in the circuit
is reversed?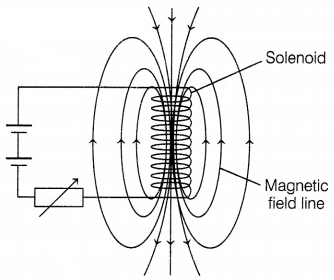
Answer:
According to the question,
Resistance of each
part = (R/3) Ω
Now, these parts are connected parallelly. So,
\(\frac{1}{R_1}=\frac{3}{R}+\frac{3}{R}+\frac{3}{R}=\frac{9}{R}\)
\(R_1=\frac{R}{9}\)
Hence, the ratio of \(\frac{R_1}{R}=\frac{1}{9}\) or
R1 : R = 1 : 9.
Or
The magnetic field strength is more in the
region, where the field lines are crowded. This means that the field strength is
maximum near the poles and it reduces as we go away from the poles.
Question 26.
(a) State the essential function performed by layer P at the
higher levels of the atmosphere.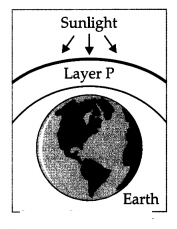
Answer:
The function of the ozone layer in the upper
atmosphere is to prevent harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from reaching the Earth’s
surface, as these UV rays cause various types of diseases including skin
cancer.
(b) Why was there a sharp drop in the amount of ozone in the atmosphere in
the 1980s?
Answer:
The amount of ozone in the atmosphere began to drop
sharply in the 1980s. This decrease is due to synthetic chemicals like
chlorofluorocarbons which are used as refrigerants and in fire
extinguishers.
Section C
Questions No. 27 to 33 are Short Answer Questions.
Question 27.
The given reaction shows one of the processes to extract the
metals like iron and manganese.
MnO2 (s) + Al (s) → Mn (l) +
Al2O3 (s) + Heat
(i) Give a reason why the above
reaction is known as a thermite reaction.
(ii) Identify the substance
oxidized and reduced in the above reaction.
(iii) Give a reason why aluminium
is preferably used in thermite reactions.
Answer:
(i) A thermite reaction
is an exothermic redox reaction. It is known for its ability to produce extreme
heat upon ignition accompanied by light. That’s why it is known as a thermite
reaction. The product obtained in this reaction is in a molten/ liquid
state.
(ii)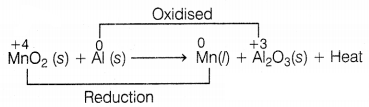
The substance oxidized = Al (s)
The substance reduced = Mn
in MnO2 (s)
(iii) Aluminium is preferably used in thermite
reactions, as it is placed above Fe and Mn in the reactivity series of metals or
we can say that, it is more reactive than Fe and Mn.
Question 28.
“Two different forms of carbon – diamond and graphite have
different structures and very different physical properties even though their
chemical properties are same.” Explain why.
Answer:
Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon. Allotropes are the different forms of the element having different physical properties. The element carbon occurs in various forms in nature with different physical properties but nearly same chemical properties. Diamond is a giant molecule of carbon atoms in which each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms forming a rigid three-dimensional structure, which is responsible for its hardness. Graphite crystal consists of a layer of carbon atoms in which each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms in the same plane giving a hexagonal array. Graphite structure is formed by hexagonal array being placed in layer one above the other.
OR
Shown below are the structural formulae of four carbon compounds.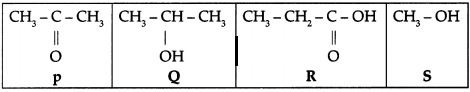
(a) Two of these compounds are more likely to have similar
chemical properties. Identify these two compounds. Give a reason for your
answer.
(b) Identify which of these compounds are likely to have the same
boiling point. Justify your answer.
Answer:
(a) Q and S
They have the
same functional group.
(b) None of them.
They are all different chemical substances.
Question 29.
We are advised to take iodized salt in our diet by doctors.
Justify its importance in our body.
Answer:
Iodine is required for the
synthesis of thyroxine hormone. This hormone regulates fat, protein, and
carbohydrate metabolism in our body. Deficiency of thyroxine leads to the
enlargement of the thyroid gland. This deficiency disease is known as goiter.
Therefore, we are advised to take iodized salt in our diet by doctors.
Question 30.
Some plants like pea plants have tendrils which help them to
climb up other plants. Explain how it is done. Name the plant hormone
responsible for this movement.
Answer:
Tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in
contact with any support, the part of the tendril in contact with the object
does not grow as rapidly as the part of the tendril away from the object. This
causes the tendril to circle the object and thus cling to it.
Auxin is the hormone that promotes the growth of the tendril around the support as it is synthesized in the tip of the shoot and stimulates the growth of the cells on the opposite side which causes the coiling of the tendril around the support.
Question 31.
(i) Explain why the refractive index of any material
concerning air is always greater than 1.
(ii) In the figure below, a light
ray travels from the air into the semi-circular plastic block. Give a reason why
the ray does not deviate at the semi-circular boundary of the plastic
block.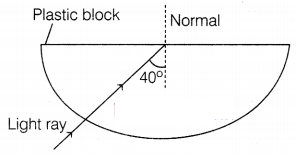
(iii) Complete the ray diagram of the above scenario, when
the light ray comes out of the plastic block from the top flat end.
Answer:
(i) The refractive index of a medium concerning air is given by
n
= \(\frac{Speed of light in air}{Speed of light in the medium}\)
Since the
speed of light in the medium is always less than the speed of light in air, the
refractive index of any material concerning air is always greater than 1.
(ii) The ray of light is undergoing normal incidence at the air-plastic block interface and for normal incidence, there is no deviation.
(iii) As the light comes out of the plastic block from the top flat end, it
moves away from the normal.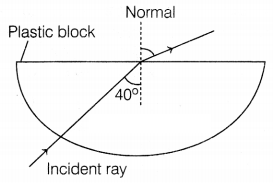
Question 32.
An electric motor rated 1100 W is connected to 220 V mains.
Find:
(a) The current drawn from the mains.
(b) Electric energy consumed
if the motor is used for 5 hours daily for 6 days.
(c) Total cost of energy
consumed if the rate of one unit is ₹ 5.
Answer:
Given,
Voltage (V) =
220 V
Power (P) = 1100 W
(a) Power (P) is given by the expression,
P =
V × I
1100 = 220 × I
I = \(\frac{1100}{220}\)
= 5A
(b) Electrical energy (E)
\(\begin{aligned}
& =\frac{P(\text { in
watt }) \times t(\text { in hour per day })}{1000} \times \text { No.of days }
\\
& =\frac{1100 \mathrm{~W} \times(5 \mathrm{~h} / \text { day })}{1000}
\times 6 \text { days }
\end{aligned}\)
= 33 units
(c) Total cost = Energy × Rate
= 33 units × \(\frac{\text { Rs. } 5}{\text
{ unit }}\) = Rs. 165
Question 33.
Anannya responded to the question: Why are electrical
appliances with metallic bodies connected to the mains through a three-pin plug,
whereas an electric bulb can be connected with a two-pin plug?
She wrote:
Three-pin connections reduce heating of connecting wires.
(i) Is her answer
correct or incorrect? Justify.
(ii) What is the function of a fuse in a
domestic circuit?
Answer:
(i) Anannya’s answer is incorrect. Electrical
appliances with metallic bodies need an earth wire that provides a
low-resistance conducting path to the flow of current. In case, there is an
accidental leakage of current through the conducting body of the appliances.
(ii) An electrical fuse is a safety device that operates to protect against the overflow of current in an electrical circuit. An important component of an electrical fuse is a metal wire or strip that melts when excess current flows through it.
Section D
Questions No. 34 to 36 are Long Answer Questions.
Question 34.
(a) Draw the structure of the following components.
(i)
Butanoic acid
(ii) Chloropentane
Answer:
(i) The structure of butanoic
acid is:
(ii) The structure of chloropentane is:
(b) How are structure (i) and structure (ii) given below related to one
another? Give a reason to justify your answer.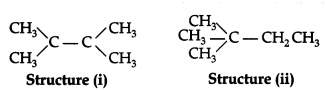
Draw one more possible structure for the above case.
Answer:
Structures (i) and (ii) are structural isomers of each other as
they have different structures but same molecular formula
(C6H14).
Another structural isomer is n-Hexane.
(c) Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated compounds based on their
general formula.
Answer:
Differences between saturated and unsaturated
compounds are:
| Saturated compounds | Unsaturated compounds |
| They have single bonds between carbon atoms. | They have at least one double or triple bond between carbon atoms. |
| Their general formula is CnH2n+2. | Alkenes (which have double bond) have general formula as
CnH2n. Alkynes (which have triple bond) have general formula as CnH2n-2. |
OR
(a) What happens when a small piece of sodium is dropped on ethanol? Write
the equation for this reaction.
(b) Why glacial acetic acid is called so?
(c) What happens when ethanol is heated at 443 K in the presence of conc.
H2SO4? Write the role of conc. H2SO4
in this case.
(d) Write an equation showing saponification.
Answer:
(a)
Ethanol reacts with sodium to produce hydrogen gas and sodium ethoxide.
2CH3CH2OH (Ethanol) + 2Na (Sodium) →
2CH3CH2O–Na+ (Sodium ethoxide) +
H2 (Hydrogen gas)
(b) The freezing point of pure ethanoic acid is 290 K and hence, it freezes during winter in cold climates. That is why it is called glacial acetic acid.
(c) When ethanol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K, it
loses one water molecule and forms ethene.
Role of H2SO4:
It acts as a dehydrating agent and removes water molecules from ethanol.
(d) Equation for saponification reaction: Heat
Question 35.
Given below are certain situations. Analyse and describe its
possible impact on a person
(i) Testes of a male boy are not able to descend
into the scrotum during his embryonic development.
(ii) The vas deferens of a
man is plugged.
(iii) Prostate and seminal vesicles are not functional.
(iv) Egg is not fertilized in a human female.
(v) The placenta does not
attach to the uterus optimally.
Or
(i) A doctor has advised Sameer to
reduce sugar intake in his diet and do regular exercise after checking his blood
test reports. Which disease do you think Sameer is suffering from? Name the
hormone responsible for this disease and the organ producing the hormone.
(ii) Which hormone is present in the areas of rapid cell division in a plant and
which hormone inhibits the growth?
Answer:
(i) Formation of the sperm will
be adversely affected because this process requires a lower temperature than the
body temperature.
(ii) If the vas deferens of a man is plugged, sperms will
not be transferred further because it is a passage for the transfer of
sperms.
(iii) When prostate and seminal vesicles are not functional, they
will not secrete fluid for nourishment and medium for the transport of
sperms.
(iv) When an egg is not fertilized in a human female, it lives for
about one day. Then, menstruation occurs in which the thickened lining of the
uterus breaks leading to the discharge of blood and mucus along with the run
fertilised egg.
(v) When the placenta does not attach to the uterus
optimally, nutrition and oxygen will not be provided to the growing embryo
affecting its growth.
Or
(i) Sameer is suffering from diabetes. Insulin is
the hormone responsible for this disease and it is produced by the pancreas.
(ii) Cytokinins are present in the areas of rapid cell divisions in a plant and
abscisic acid inhibits the growth.
Question 36.
(a) A lens produces a magnification of -0.5. Is this a
converging or diverging lens? If the focal length of the lens is 6 cm; draw a
ray diagram showing the image formation in this case.
Answer:
The image
will be real and inverted since the magnification has a negative value. The lens
that can produce a real and inverted image is a converging/ convex lens.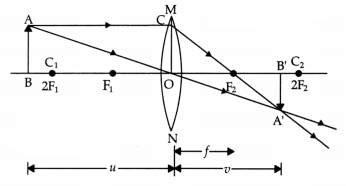
In the figure OF1 = OF2 = 6 cm.
(Marks will be deducted if arrows are not shown)
(b) A girl was playing with a thin beam of light from a laser torch by
directing it from different directions on a convex lens held vertically. She was
surprised to see that in a particular direction, the beam of light continued to
move along the same direction after passing through the lens. State the reason
for her observation. Draw a ray diagram to support your answer.
Answer:
The girl must have directed the ray of light along the direction of the optical
centre of the lens because the ray of light passes straight through the optical
centre of the lens.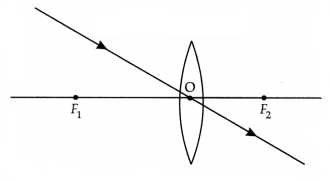
Section E
Questions No. 37 to 39 are case-based/data-based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
The table below shows the hints given by the quiz master in a
quiz.
| Hints |
| (i) Substance C is used as a preservative. |
| (ii) C has two carbon atoms; C is obtained by the reaction of A in the presence of alkaline potassium permanganate followed by acidification. |
| (iii) Misuse of A in industries is prevented by adding methanol, benzene, and pyridine to A. |
| (iv) F is formed on heating A in the presence of cone, sulphuric acid. |
| (v) F reacts with hydrogen gas in the presence of nickel and palladium catalysts. |
Based on the above hints, answer the following questions.
(a) Give the
IUPAC names of A and F.
(b) Illustrate with the help of chemical equations,
the changes taking place. (A → C and A → F)
Or
Name the chemical reactions
which occur in steps 2 and 5. Identify the compounds formed in these steps, if A
is replaced with its next homologue.
Answer:
(a) The IUPAC name of A is
ethanol and that of F is ethene.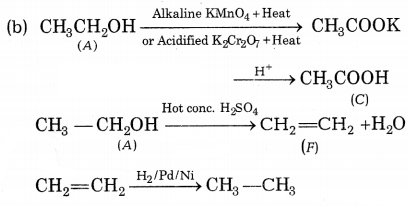
Or
The name reactions involved in steps 2 and 5 are
oxidation and addition (hydrogenation), respectively. The next homologue of (A)
is propanol, Thus, propanol on heating with alkaline KMnO4 is
propanoic acid. While Propanol reacts with hot concentrated form propene.
Question 38.
A plant with red flower (Rw) is cross bred with a plant with
white flower (ww). There are two variations of the gene controlling the colour
of the flower. The gene for red flower (R) is dominant over that for white
flower (w).
The Punnett square shows the result of the cross.
| w | w | |
| R | Rw | Rw |
| w | ww | ww |
(a) What percentage of the plants is likely to produce white flowers?
(b)
A red flower plant (RR) was crossed with a white flower plant (ww). What will be
the colour of the flower of the next generation of plants?
(c) What would
have caused the variation in the gene for flower colour?
Answer:
(a) In a
cross between a plant with a red flower (Rw) and a plant with a white flower
(ww), 50% of plants is likely to produce red flower and 50% white flowers.
(b) All flowers in the next generation would be red as R is the dominant trait.
The flowers will inherit Rw set of genes.
(c) Mutation caused variation in
the gene for flower colour. A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of an
organism. It can result from errors in DNA replication during cell division,
exposure to mutagens or a viral infection.
OR
(c) What is the name given to the above cross? Define it.
Answer:
A
cross between two plants, which differ in only one pair of contrasting
characters, is called monohybrid cross. In this cross, F2 phenotypic
ratio is 3:1 and genotypic ratio is 1:2:1.
Question 39.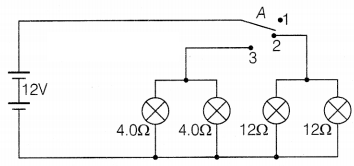
Vinita and Ahmed demonstrated a circuit that operates the two
headlights and the two sidelights of a car, in their school exhibition. Based on
their demonstrated circuit, answer the following questions.
(i) State what
happens, when switch A is connected to
(a) Position 2
(b) Position 3
(ii) Find the potential difference across each lamp, when lit.
(iii)
Calculate the current
(a) in each 12 Ω lamp, when lit.
(b) in each 4 Ω
lamp, when lit.
Or
Show with calculations, which type of lamp, 4.0 Ω or 12
Ω has the higher power.
Answer:
(i) (a) When switch A is connected to
position 2, then 12 Ω lamps will switch ON only.
(b) When switch A is
connected to position 3, then 4 Ω lamps will switch ON.
(ii) All the lamps
are connected parallel to each other, hence the potential difference will be 12V
for all the lamps.
(a) 12 Ω lamps are ON when the wire is connected to
position 2.
The voltage across both 12 Ω lamps = 12V
From V = IR (Ohm’s
law),
I = \(\frac{V}{R}=\frac{12}{12}\) = 1A
(b) 4 Ω lamps are ON when the
wire is connected to position 3.
The voltage across both 4 Ω lamps = 12 V
Hence, I = \(\frac{V}{R}=\frac{12}{4}\) = 3A
(iii) The power is given by P =
\(\frac{V^2}{R}\)
All lamps are in parallel and hence V for all lamps are
same.
For 4 Ω lamps, P = \(\frac{12 \times 12}{4}\) = 36 W
For 12 Ω lamps,
P = \(\frac{12 \times 12}{12}\) = 12 W
Hence, 4 Ω lamps will have higher
power.