CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set-2
Class 10thCBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set-2
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 2
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
Instructions
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective-type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 4 marks each with sub-parts.
Section A
Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20.
Question 1.
The graph given below depicts a number of electrons in an atom
of different elements A, B, C, and D.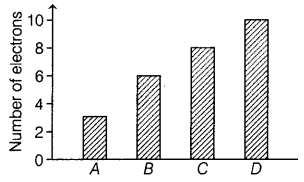
Which of the following element is a metal?
(a) A
(b)
B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer:
(a) A
The number of electrons in an atom of
element A is 3.
∴ Its electronic configuration is 2, 1, which means it can
easily lose its outermost electron and act as a metal. The number of outermost
electrons in an atom of elements B, C, and D are 4, 6, and 8 respectively.
Therefore, they cannot lose electrons. Hence, they are not considered as
metals.
Question 2.
Methane gas released from wastewater treatment plants can
be used as a source of fuel. Which chemical equation represents the combustion
of methane to produce heat energy?
(A) CH4 + CO2 →
2O2 + 2H2O
(B) CH4 + 2O2 →
CO2 + 2H2O
(C) 2O2 + 2H2O →
CO2 + CH4
(D) CO2 + 2O2 →
CH4 + 2H2O
Answer:
(B) CH4 +
2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Explanation: The reaction of methane is:
CH4 (Methane) +
2O2 (Oxygen) → CO2 (Carbon dioxide) + 2H2O
(Water) + 890 KJ (Heat)
Question 3.
Which three allotropes of carbon, do the given figures
represent?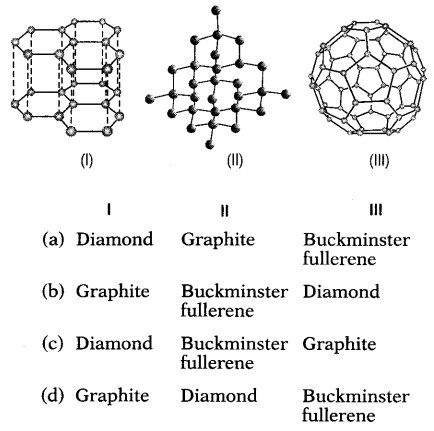
Answer:
(d) I – Graphite, II – Diamond, III – Buckminster
fullerene
(I) Is the structure of graphite crystal which consists of layers
of carbon atoms or sheets of carbon atoms.
(II) Is the structure of a
diamond.
(Ill) The structure of Buckminsterfullerene as their structure
resembles geodesic domes.
Question 4.
Builders use Plaster of Paris to make the surface layer
of the inner walls of a building. Which property of Plaster of Paris powder
makes it a suitable building material?
(A) It is lightweight.
(B) It is
white.
(C) It is found readily in nature.
(D) It gets hard when mixed with
water.
Answer:
(D) It gets hard when mixed with water.
Explanation: Plaster of Paris is a powder made of calcium sulphate hemihydrate. It forms a paste that hardens as it dries when mixed with water.
Question 5.
Alkalis are generally soluble in water, based on this which
among the following hydroxides is not an alkali?
(a) Ammonium hydroxide
(b) Calcium hydroxide
(c) Copper hydroxide
(d) Sodium hydroxide
Answer:
(c) Copper hydroxide is not an alkali because it is insoluble in
water. Hence, it is a base but not an alkali.
Question 6.
A part of a homologous series is shown below.
C3H4, C4H6,
C5H8
Which of these compounds is a part of the series shown above?
(A)
C2H2
(B) C2H4
(C)
C8H6
(D) C6H14
Answer:
(A)
C2H2
Explanation: The next homologous of the above series is C2H2. This is the homologous series of alkyne with general formula (CnH2n-2)
Question 7.
Ajay took calcium oxide in an iron container. He slowly added
some water to it. What would he observe?
(a) The container becomes cold
(b) The container becomes hot
(c) Green coloured solution is formed
(d)
White precipitate is formed
Answer:
(b) The reaction between calcium oxide
and water is highly exothermic, thus during the reaction between calcium oxide
and water, the container becomes hot as heat is released.
Question 8.
Small hair-like structures line the upper part of the human
respiratory tract. These structures trap the dust particles, germs and chemicals
entering the human body during breathing. Smoking is likely to cause infections
in the respiratory tract. Which statement best explains the fact?
(A) Smoking
destroys the hair-like structures.
(B) Smoking causes excessive growth of the
hair-like structures.
(C) Smoking stimulates the hair-like structures to
release harmful chemicals.
(D) Smoking makes the hair-like structures wet and
they fail to trap dust particles.
Answer:
(A) Smoking destroys the
hair-like structures.
Explanation: Cilia are tiny hair-like projections that protect the airways by sweeping away mucus and dust particles and keeping the lungs clear. Smoking damages and eventually destroys these cilia.
Question 9.
Select the correct option.
(a) Liver – It stores bile
(b) Small intestine – Maximum absorption of water occurs
(c) Stomach –
Digestion of proteins begins here
(d) Large intestine – Absorption of
digested food takes place
Answer:
(c) Stomach – Digestion of proteins
begins here.
All the other options are incorrect, except (c) they can be
corrected as
Liver – It synthesizes bile.
Small intestine – Absorption of
digested food takes place.
Large intestine – Maximum absorption of water
occurs.
Question 10.
A student while observing an embryo of a gram seed listed
various parts of the embryo as listed below: Testa, Micropyle, Cotyledon,
Tegmen, Plumule, Radicle.
On examining the list, the teacher commented that
only three parts are correct. Select these three correct parts:
(A)
Cotyledon, Testa, Plumule
(B) Cotyledon, Plumule, Radicle
(C) Cotyledon,
Tegmen, Radicle
(D) Cotyledon, Micropyle, Plumule
Answer:
(B)
Cotyledon, Plumule, Radicle
Explanation: When a plant produces a seed, it has 3 basic parts: plumule (the future shoot), radicle (the future root), and cotyledons which may be 2 or 1 based on the type of plant being it dicot or monocot, respectively.
Question 11.
Which phytohormone is responsible for the growth of the plant
when light is shown from one side?
(a) Gibberellins
(b) Ethylene
(c)
ABA
(d) Auxin
Answer:
(d) Auxin
When growing plants detect light, a
hormone called auxin is synthesized at the shoot tip. When light shows from one
side of the plant, auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. The
concentration of auxin stimulates more growth on one side of the shoot which is
away from the light. Thus, the plant appears to bend towards light.
Question 12.
A student wants to obtain an erect image of an object using a
concave mirror of 10 cm focal length. What will be the distance of the object
from mirror?
(A) Less than 10 cm
(B) 10 cm
(C) Between 10 cm and 20
cm
(D) More than 20 cm
Answer:
(A) Less than 10 cm
Explanation: Object distance should be less than the focal length for the formation of an erect image. Hence, the range of distance of an object from the mirror should be less than 10 cm, i.e., from 0 to 10 cm in the front of the mirror from the pole. The nature of the image so formed will be virtual and erect.
Question 13.
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a
plane mirror, then the distance of the image from the mirror will be
(a) 5
cm
(b) 10 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 0
Answer:
(b) 10 cm
The distance of
the image is equal to the distance of the object from the mirror. Therefore, the
distance of the image from the mirror is 10 cm.
Question 14.
Choose the option giving correct matching the items given in
Column I & Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Physical environment | (i) Ozone depletion |
| (b) Exposure to UV radiation | (ii) Bacteria and fungi |
| (c) Chlorofluoro carbon compounds | (iii) Abiotic components |
| (d) Decomposers | (iv) Skin cancer |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
| (A) | (iii) | (i) | (iv) | (ii) |
| (B) | (iii) | (iv) | (i) | (ii) |
| (C) | (iii) | (iv) | (ii) | (i) |
| (D) | (iii) | (i) | (ii) | (iv) |
Answer:
(B) (iii) (iv) (i) (ii)
Explanation: The correct matching is:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Physical environment | (iii) Abiotic components |
| (b) Exposure to UV radiation | (iv) Skin cancer |
| (c) Chlorofluoro carbon compounds | (i) Ozone depletion |
| (d) Decomposers | (ii) Bacteria and fungi |
Question 15.
The arrangement of organisms into a series of groups based on
physiological, biochemical, anatomical, and other relationships is
(a)
hierarchy
(b) categorization
(c) taxonomy
(d) classification
Answer:
(d) classification
Classification involves the hierarchical
arrangement of living organisms into different categories based on common
inter-relationships between them.
Question 16.
Which of these statements is incorrect about a balanced
ecosystem?
(A) It is made up of interconnected food chains.
(B) It
involves interdependence among living organisms and the environment.
(C)
Animals are dependent on plants but plants are not dependent on animals.
(D)
It involves communities made up of different populations of organisms.
Answer:
(C) Animals are dependent on plants but plants are not dependent on
animals.
Explanation: The components of an ecosystem depend on each other to maintain the ecological balance. Plants are dependent on animals for carbon dioxide and other processes like pollination and dispersal of seeds.
Direction (Q. Nos. 17-20): These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both
A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but
R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): HCl produces hydronium ions
(H3O+) and chloride ions (Cl–) in aqueous
solution.
Reason (R): In the presence of water, bases give H+
ions.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false.
HCl produces H+
ions in an aqueous solution because, in the presence of water, acids give
H+ ions. As H+ ions cannot exist alone, they combine with
water molecules and form H3O+.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): Characteristics of parental plants can be
preserved through vegetative reproduction.
Reason (R): Asexual reproduction
involves only mitosis.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the
correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction involves a single individual, which gives rise to new individuals that are genetically identical to. their parents. It is because, when organisms reproduce asexually, only mitotic divisions are involved.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): The uterus prepares itself every month to
receive a fertilized egg.
Reason (R): The ovary releases one egg every
month.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation
of A.
It can be explained that Since the ovary releases one egg every month,
the uterus also prepares itself every month to receive a fertilized egg. Its
lining becomes thick and spongy to nourish the developing embryo.
Question 20.
Assertion (A): An ecosystem consists of biotic components and
abiotic components.
Reason (R): Biotic and abiotic components play important
roles in the sustenance of life and work independently in all ecosystems.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation: An ecosystem is a unit of biosphere in which biotic and abiotic components interact with each other. Biotic components depend on abiotic factors for survival.
Section B
Questions No. 21 to 26 are Very Short Answer Questions.
Question 21.
Give a test that can be used to differentiate between butter
and cooking oil.
Answer:
Butter contains saturated compounds while cooking
oil contains unsaturated compounds. Since unsaturated compounds are oxidized by
alk. KMnO4 with the disappearance of its pink colour. Therefore, when
cooking oil is treated with a few drops of alk. KMnO4, the pink
colour of KMnO4 disappears. With butter, however, the pink colour of
KMnO4 does not disappear. (2)
Question 22.
Two green plants are kept separately in oxygen-free
containers, one in the dark and the other in sunlight- It was observed that
plant kept in the dark could not survive longer. Give a reason for this
observation.
Answer:
Plants release oxygen during photosynthesis, which
can be utilized by the plant for respiration. The plant kept in the dark was not
able to perform photosynthesis to generate some oxygen for respiration.
The carbon dioxide released by the plant after respiration was utilized by the plants to photosynthesize food, hence, the plant was able to survive.
Question 23.
Draw a diagram showing the correct positions of the pancreas,
thyroid gland, pituitary gland, and adrenal gland in human beings.
Answer:
(a) The pituitary gland (master gland) is present at the base of the
brain.
(b) The thyroid gland is present just below the neck.
(c) The
Pancreas Is found just below the stomach.
(d) Adrenal glands are present on
the top of each kidney. (\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 4)
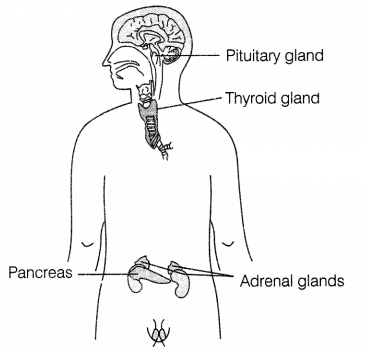
Question 24.
A light ray enters from medium A to medium B as shown in the
figure.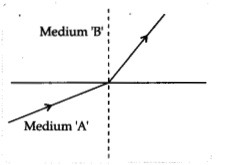
(a) Which one of the two media is denser w.r.t. the other
medium? Justify your answer.
Answer:
As it is clear from the figure, when
the light ray travelled from medium A to medium B, then it bends towards the
normal which means that medium B is optically denser than medium A.
(b) If the speed of light in medium A is VA and B is VB, what is the
refractive index of B concerning A?
Answer:
The refractive index of medium
A
Question 25.
What is meant by electric current? Write its SI unit.
Calculate the amount of charge that flows through a conductor when a current of
5A flows through it for 2 min.
Or
AB is a current-carrying conductor in
the plane of the paper as shown in the figure. What are the directions of
magnetic fields produced by it at points P and Q?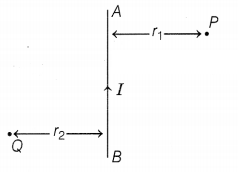
Given r1 > r2, when will the
strength of the magnetic field be larger?
Answer:
Electric current is
defined as the rate of flow of electric charge through any cross-section of a
conductor.
SI unit of electric current is ampere (A).
Given, I = 5 A, t =
2 min = 2 × 60 s = 120 s, q =?
We know that, charge, q = I × t = 5 × 120 =
600 C
Thus, the amount of charge flowing through the conductor is 600 C.
(2)
Or
According to the right-hand thumb rule, the magnetic field at P is
into the plane of the paper, and at Q, it is out of the plane of the paper.
The strength of the magnetic field at Q will be larger as
strength of the
field ∝ \(\frac{1}{r \text { (distance) }}\) (2)
Question 26.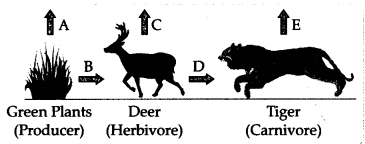
In the following food chain, vertical arrows indicate the
energy lost to the environment, and horizontal arrows indicate energy
transferred to the next trophic level. Which one of the three vertical arrows
(A, C, and E) and which one of the two horizontal arrows (B and D) will
represent more energy transfer? Give a reason for your answer.
Answer:
- Arrow A will represent more energy transfer as compared to C and E.
- Arrow B will represent more energy transfer as compared to D.
- When green plants are eaten by primary consumers, a great amount of energy is lost as heat to the environment. Some amount goes into digestion and in doing work and the rest goes towards growth and reproduction. An average of 10% of the food eaten is made available for the next level of consumers. This loss of energy takes place at every trophic level.
- Alternatively, By the 10% law of transfer of energy in a food chain, only 10% of energy available at one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level.
Section C
Questions No. 27 to 33 are Short Answer Questions.
Question 27.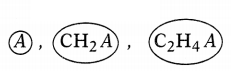
Define the given series. State any two characteristics of
this series.
Or
Choose the kind of chemical bonding (ionic bond, covalent
bond, both ionic and covalent bonds) present in the following compounds.
Potassium chloride, magnesium oxide, sulphuric acid, ammonium hydroxide, zinc
sulphide, and phosphorus trichloride (PCl3).
Answer:
A series
of similarly constituted compounds in which the members present have the same
functional group and similar chemical properties and any two successive members
in a particular series differ in their molecular formula by a -CH2
unit, is called a homologous series. (1)
Characteristics of homologous series:
(a) The molecular formulae of any
two successive members of a homologous series differ by -CH2–
unit.
(b) There is a regular gradation in the physical properties of members
of a homologous series. (2)
Or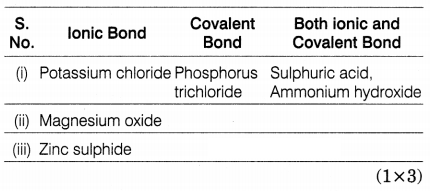
Question 28.
A reddish-brown metal used in electrical wires when powdered
and heated strongly turns black. When hydrogen gas is passed over this black
substance, it regains its original colour. Based on this information answer the
following questions:
(a) Name the metal and the black substance formed.
(b) Write balanced chemical equations for the two reactions involved in the
above information.
Answer:
(a) The brown colour metal is copper (Cu) and
black coloured substance is copper oxide (CuO).
(b) (i) When Cu metal is heated in an open china dish then Cu metal gets
oxidised.
Cu + O2 → 2CuO
(ii) When hydrogen gas is passed
over the black substance then CuO gets reduced.
CuO + H2 → Cu
+ H2O
OR
A metal ‘M’ on reacting with dilute acid liberates a gas ‘G’. The same metal
also liberates gas ‘G’ when reacts with a base.
(a) Write the name of gas
‘G’.
(b) How will you test the presence of this gas?
(c) Write chemical
equations for the reactions of the metal with (1) an acid and (2) a base.
Answer:
(a) Hydrogen gas
(b) On bringing a burning match stick near the mouth of the test tube, a pop sound is heard.
(c) Reaction with acid:
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2 +
H2(g)
Reaction with base:
2NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2(aq)
+ H2(g)
Question 29.
How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s
body?
Answer:
The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the
help of a special tissue called the placenta. This is a disc-like tissue that
develops between the uterine wall and the embryo. As the mother eats, the food
passes through the digestive system where the food breaks down into small
absorbable forms. These nutrients travel through the mother’s bloodstream and
get exchanged with the bloodstream of the fetus through the placenta. (3)
Question 30.
What are chromosomes? Explain how the stability of the DNA of
the species is ensured in sexually reproducing organisms.
Answer:
Chromosomes are thread-like structures which are made up of proteins and DNA.
DNA contains the information of traits which are passed from parents to
offspring from one generation to another. In sexually reproducing organisms, the
stability of DNA is ensured by the DNA copying mechanism. The DNA replication
process is very efficient and error free which in turn maintains the stability
of the DNA. The chromosome number is also maintained during reproduction by the
process of meiosis during gamete formation.
Question 31.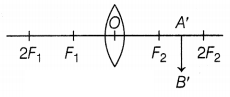
The above figure shows an incomplete ray diagram of an
object, where the image A’ B’ is formed after refraction. All the rays parallel
to the principal axis pass through the principal focus of the lens. O is the
optical center of the lens.
(a) Based on the text and the data given in the
above paragraph, what is the position of the object AB in front of the lens?
(b) What will be the size of image A B’ concerning the size of the object
AB?
(c) What is the sign of linear magnification produced by the lens?
Answer:
(a)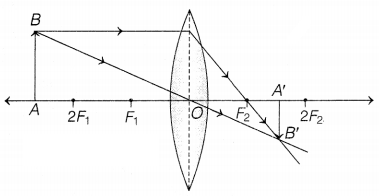
The position of object AB would have been beyond
2F1. (1)
(b) The size of the image would have been smaller than
the size of the object. (1)
(c) Magnification (M) = \(=\frac{\text { Height
of image }\left(h_1\right)}{\text { Height of object }\left(h_0\right)}\)
∴
Sign = \(\frac{-v e}{+v e}\) = -ve
(∵ Height of image below the principal
axis = -ve and height of object above the principal axis = +ve)
Hence, the
magnification produced by the above lens is negative. (1)
Question 32.
(a) List the factors on which the resistance of a uniform
cylindrical conductor of a given material depends.
Answer:
Factors
on which the resistance of a conductor depends:
- Length of conductor Resistance is directly proportional to the length of the conductor. This means resistance increases with an increase in the length of the conductor. This is why long wires create more resistance to the electric current.
- Area of cross-section: Resistance is inversely proportional to the area of
the cross-section of the conductor. This means
resistance decreases with an increase in the area of the cross-section of the conductor and vice versa. This is why, a thick copper wire creates less resistance to electric current. - Temperature: Resistance is directly proportional to the temperature.
- Nature of material: Resistance depends on the nature of the material. Some materials like silver are good conductors of electricity while some like plastic are bad conductors of electricity.
(b) The resistance of a wire of 0.01 cm radius is 10 Ω. If the resistivity of
the wire is 50 × 10-8 Ω m, find the length of this wire.
Answer:
Given, Radius, r = 0.01 cm = 0.0001 m
Resistance, R = 10
Ω
Resistivity, ρ = 50 × 10-8 Ω m
\(\begin{aligned}
R
& =\rho \frac{L}{A} \\
L & =\frac{R A}{\rho} \\
& =\frac{10
\times 314 \times(0.0001)^2}{50 \times 10^{-8}}
\end{aligned}\)
= 0.628 m
(Area, A = πr²)
Hence, the length of the wire is 0.628 m.
Question 33.
Justify.
(a) Two circular coils A and B are placed close
to each other. If the current in coil A is changed, will some current be induced
in the coil B? Give a reason.
(b) When magnetic field lines are drawn around
a current-carrying circular loop, it has been observed that they are close to
its axis. But these lines keep on diverging as we move away from the center.
Explain this observation.
Answer:
(a) When current in coil A is changed, a
changing magnetic field is set up around it. This changing magnetic field also
links with coil 6 and hence, some current will be induced in coil 6.
(1\(\frac{1}{2}\))
(b) We know that the magnetic field is stronger near the
current-carrying conductor and weaker as we move away from the conductor. In the
case of a current-carrying circular loop, the magnetic field is stronger near
the periphery but weaker near the center of the loop. Due to this, the magnetic
field lines appear as straight lines near the center. As we move towards the
periphery of the circular loop, the magnetic field lines appear to be diverging,
so that they can be circular around the wire of the loop. (1\(\frac{1}{2}\))
Section D
Questions No. 34 to 36 are Long Answer Questions.
Question 34.
(a) A compound “A” with a molecular formula of
C2H4O2 reacts with a base to give salt and
water. Identify ‘A’, state its nature and the name of the functional group it
possesses. Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer:
Compound A – Acetic add/ CH3COOH
Nature: Its nature is acidic.
Name of the functional group: COOH
Chemical equation:
CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) → CH3COONa(aq) +
H2O(l)
(b) When the above-stated compound A reacts with another compound ‘B’ having
molecular formula C2H6O in the presence of an add, a
sweet-smelling compound ‘C’ is formed.
(i) Identify ‘B’ and
‘C’.
Answer:
B- Ethanol (C2H5OH)
C- Ethyl
acetate
(ii) State the role of add in this reaction.
Answer:
Role of acid: It
is a catalyst which will speed up the process and esterification will proceed
speedily and complete on time.
(iii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer:
Chemical equation: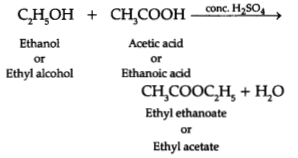
OR
(a) Match the following pH values 1, 7, 10, and 13 to the solutions given
below:
(i) Milk of magnesia
(ii) Gastric juices
(iii) Brine
(iv)
Aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Answer:
(i) Milk of magnesia: 10
(ii) Gastric
juices: 1
(iii) Brine: 7
(iv) Aqueous sodium hydroxide: 13
(b) Amit and Rita decided to bake a cake and added baking soda to the cake
batter. Explain with a balanced reaction, the role of the baking soda. Mention
any other use of baking soda.
Answer:
Baking soda undergoes thermal
decomposition to form Na2CO3 C02 and
H2O. CO2 makes the cake fluffy & soft.
\({NaHCO}_3
\stackrel{\text { heat }}{\longrightarrow} {Na}_2 {CO}_3+{CO}_2+{H}_2 {O}\)
Uses:
Used in fire extinguishers/antacids to neutralize excess add in the
stomach /to neutralize the effect of add-in insect sting.
Question 35.
(a) Write the equations and steps involved in photosynthesis.
In which way are the steps of photosynthesis different in desert plants?
(b)
What is ‘translocation’? Why is it essential for plants? Where in plants are the
following synthesized?
(i) Sugar
(ii) Hormones
Or
Give reasons:
(a) The placenta is essential for fetal development.
(b) Blocking of vas
deferens prevents pregnancy.
(c) Wind acts as a pollinating agent.
(d) Use
of condoms prevents pregnancy.
(e) Blocking of Fallopian tubes prevents
pregnancy.
Answer:
Three events that occur during photosynthesis are as
follows.
(i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of
light energy into chemical energy and splitting of water into hydrogen and
oxygen.
(iii) Reduction of CO2 into carbohydrates.
Desert
plants take up CO2 at night and prepare intermediate molecule, which
is absorbed by the chlorophyll during the day to make carbohydrates.
(2\(\frac{1}{2}\))
(b) Translocation: The transport of food prepared in the leaves to other
parts of the plants is known as translocation. The plants need to supply food to
all parts of the plants. Food is needed for producing energy, which in turn is
required by all parts of the plants to perform their activities.
(i) Sugars
are synthesized in leaves and then transported to storage organs like roots,
fruits, and seeds.
(ii) Plant hormones are synthesized at the tips of the
stems and roots. (2\(\frac{1}{2}\))
Or
(a) Placenta is essential for
foetal development because it helps in the nutrition, respiration, excretion,
etc., of the fetus through the maternal supply.
(b) Blocking of vas deferens
prevents the passage of sperm, hence, there is no fertilization so it prevents
pregnancy.
(c) Wind acts as a pollinating agent because it helps in the
transfer of light-weighted pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a
flower.
(d) Condoms prevent the entry of sperm into the vagina, hence
preventing pregnancy.
(e) If the Fallopian tube is blocked, sperm and egg do
not meet and fuse and fertilization does not take place. (5)
Question 36.
(a) Define the following terms in the context of spherical
mirrors:
(i) Pole
(ii) Centre of curvature
(iii) Principal axis
(iv)
Principal focus
Answer:
(i) Pole: Centre of the reflecting surface of the
mirror.
(ii) Centre of curvature: The centre of the hollow sphere of which
the reflecting surface is a part.
(iii) Principal axis: Straight line passing
through the pole and the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror.
(iv)
Principal focus: Incident rays parallel to the principal axis, after reflection,
either converge or appear to diverge from a fixed point on the principal axis
called the principal focus of the spherical mirror.
(b) Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a:
(i) Concave
mirror
Answer: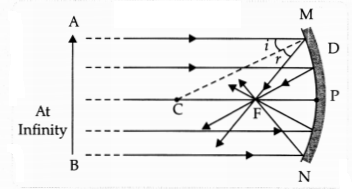
(ii) Convex mirror
Answer: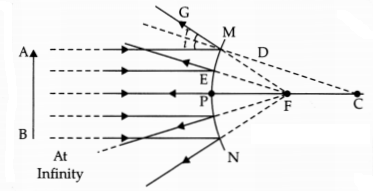
(c) Consider the given diagram in which Mis a mirror and P is an objed and Q
is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
State the type of the mirror M
and one Characteristic property of the image Q.
Answer:
Concave mirror
Image formed is virtual
(a) u =- 60 cm, f = -30 cm, v = ?
\(\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{f} & =\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u} \\
\frac{1}{v} & =\frac{1}{f}+\frac{1}{u} \\
\frac{1}{v} &
=\frac{1}{(-30 \mathrm{~cm})}+\frac{1}{(-60 \mathrm{~cm})}=\frac{-3}{60} \\
∴
\quad v & =-20 \mathrm{~cm} \\
m & =\frac{v}{u}=\frac{-20
\mathrm{~cm}}{-60 \mathrm{~cm}}=\frac{1}{3}
\end{aligned}\)
Distance of
the image will be 20 cm in front of lens.
(b) Nature: Virtual
Position: 20 cm from the lens on the same side as the
object.
Size: Diminished
Erect/Inverted: Erect
Section E
Questions No. 37 to 39 are case-based/data-based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
A student decided to observe the conductive nature of ionic
compounds in, different physical states. He took two samples of compounds. In
the first case, solid common salt was taken to make a circuit in which the bulb
did not glow. Secondly, he dissolved the same salt in water and completed the
circuit as given in the figure. In this case, the bulb glows.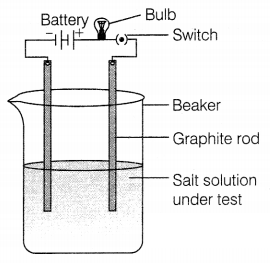
(a) What conclusion can you draw from this activity?
(b)
Why does salt conduct electricity in an aqueous solution but not in the solid
state?
Or
If we take the sugar solution in water and test the
conductivity, will the bulb glow?
Answer:
(a) We can conclude that ionic
compounds such as common salt conducts electricity in aqueous solution only.
(2)
(b) Common salt (sodium chloride) conducts electricity in a molten state
because of the presence of free ions in the solution while in the solid state,
there are no free ions. (2)
Or
No, the bulbs will not glow. Sugar solution
is not an ionic compound because it does not give free ions in the solution.
Hence, there will be no electrical conductivity. (2)
Question 38.
The most obvious outcome of the reproductive process is the
generation of individuals of similar design, but in ‘ sexual reproduction they
may not be exactly alike. The resemblances as well as differences are marked.
The rules of heredity determine the process by which traits and characteristics
are reliably inherited. Many experiments have been done to study the rules of
inheritance
(a) Why an offspring of a human being is not a true copy of his
parents in sexual reproduction?
Answer:
An offspring is not a true copy of
his parents in sexual reproduction because of variations due to the
recombination of genetic material from two different parents.
(b) While performing experiments on inheritance in plants, what is the
difference between F1 and F2 generation?
Answer:
All
the F1 offspring are genetically identical and exhibit the dominant
trait.
F2 offspring can exhibit a range of dominant to recessive
traits.
(c) Why do we say that variations are useful for the survival of a species
over time?
Answer:
Variations help the organism to become more adapted to
the changing environmental conditions. This helps the organisms to overcome the
adverse conditions.
OR
(c) Study Mendel’s cross between two plants with a pair of contrasting
characters.
RRYY (Round Yellow) × rryy (Wrinkled Green)
He observed 4 types of combinations in F2 generation. Which of
these were new combinations? Why do new features which are not present in the
parents, appear in F2 generation?
Answer:
Round Green and
Wrinkled Yellow are the new combinations in the F2 generation.
New
features which are not present in parents appear in F2 generation due
to the segregation of different combinations of alleles of different characters
independently during gamete formation and fertilization.
Question 39.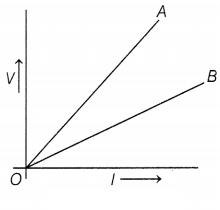
The V-I graphs for two wires A and B are shown in the figure
above. This graph is based on Ohm’s law. The slope of the V-I graph gives
resistance to the conductor.
(a) If wires A and B are of the same materials
having equal length, then which wire is thicker?
(b) If wires A and B are of
the same materials and have the same diameter, then which wire is shorter?
(c) If both wires are of the same length and the same diameter, then which wire
has maximum resistivity?
Or
If the temperature of wire A is more than the
temperature of wire B, then which one has the least resistance?
Answer:
(a) As wires A and B are of the same material, then ρA =
ρB
Also, IA = IB
Now, the slope of the
V-I graph = R = ρ.\(\frac{1}{A}\)
⇒ A = ρ.\(\frac{1}{R}\)
⇒ A ∝
\(\frac{1}{R}\)
⇒ d ∝ \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{R}}\)
As, the slope of A > slope
of B
∴ RA > RB ⇒ dA < dB
Hence, wire B is thicker wire. (1)
(b) Given, wires A and B are of the same material,
∴ ρA =
ρB
Also, dA = dB
As, I = \(A \cdot
\frac{R}{\rho}\)
⇒ I ∝ R
∵ RA > RBB
⇒
IA > IB
Hence, wire B is a shorter wire. (1)
(c) The greater the slope of the V-I graph, the greater the resistance of a
given metallic wire. In the given graph, wire A has a greater slope than B.
Hence, wire A has greater resistance.
For the wires of same length and
thickness, resistance depends on the nature of the material of the wire,
i.e.
RA = ρA \(\frac{l}{A}\) and RB = ρB
\(\frac{l}{A}\)
⇒ \(\frac{R_A}{R_B}=\frac{\rho_A}{\rho_B}\)
⇒ R ∝
ρ
Hence, the wire A is made of a material of high resistivity. (2)
Or
Given, TA > TB
As, the resistance of a wire is
directly proportional to the temperature, i.e. R ∝ T
Hence, wire B has the
least resistance. (2)