Money and Credit
Class 10th Social Science- Money and Credit
MONEY AND CREDIT
NCERT TEXTBOOK
QUESTIONS
Q.1. List the various sources of credit in Sonpur.
Ans.
There are various sources of credit which are available in Sonpur.
These are as follows :
(i) agricultural
traders (ii) moneylenders (iii) commercial banks
(iv) cooperative
societies (v) relative and friends etc.
Q.2. Look at a 10-rupee note. What is written on the top? Can you explain this?
Ans.
Reserve Bank of India (Guaranteed by the Central Government) is
written on a 10-rupee note.
This statement
means that the Central government has authorised the Reserve Bank of India
to issue this
note on behalf of the Central government.
Q.3. Write the functions of money.
Ans.
Money acts as a common medium of exchange, a common measure of value,
a standard of
deferred
payments and a store of value.
Q.4. How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who
need
money?
Ans.
Banks collect surplus money with people, as deposits. Banks use a
major portion of these
deposits to
extend loans. There is a huge demand for loans by businessmen and industrial
houses for
various economic activities. Banks may use the deposits to meet the loan
requirements of
the people. In this way, banks mediate between those who have surplus funds
(the depositors)
and those who are in need of these funds (the borrowers) and banks charge
a higher interest rate on loans
than what they offer on deposits.
Q.5. Modern currency is without any use of its own as a commodity. Why is it
accepted as
money?
Ans.
Modern forms of money include paper notes and coins. Modern currency
is neither made of
precious metals
such as gold, silver and copper nor consists of daily use commodities. The
modern currency
is without any use of its own.
It is accepted
as a medium of exchange because the currency is authorised by the government
of a country.
Q.6. Why are banks willing to lend to women organised in self-help groups
(SHGs)?
Ans.
Non-payment of loan by any member of the group is followed up
seriously by other members
in a group.
Because of this feature, banks are willing to lend to the poor women of SHGs,
even
though they have
no collateral as such.
Q.7. Why do you think that the share of formal sector credit is higher for the
richer
households, compared to the poorer households?
Ans.
The share of formal sector credit is higher for the richer households
because they can deposit
the collaterals
(security) such as land, building, livestock etc. while it is difficult for the
poorer
households
because of non-availability of such collaterals.
Q.8. Compare the terms of credit for the small farmer, the medium farmer and the
landless
agricultural worker in Sonpur.
Ans.
|
Small farmer |
Medium farmer |
Lendless agricultural worker |
|
Small farmers
generally take loan either from
moneylenders or from agricultural
traders. The rate of interest is very
high but neither collateral nor documentation is required for taking loan. |
For medium farmers
credit facilities are also available from banks at a very reasonable rate of interest. Repayment terms are flexible but in the process of getting credit, documentation and collateral is required. |
Being a landless
agricultural worker he remains idle
several months in a year. To meet his
contingent requirements (in case
of illness, or festivals) he
has to borrow credit form moneylender at a very high rate.
These workers are exploited by these moneylenders. |
Q.9. In India, about 80% of farmers are small farmers who need credit for
cultivation.
(a) Why might
banks be unwilling to lend to small farmers?
(b) What are the
other sources from which the small farmers can borrow?
(c) Explain with
an example how the terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmers.
(d) Suggest some
ways by which small farmers can get cheap credit.
Ans.
(a) As the small farmers find it difficult to provide necessary
documents / formalities and
collateral
security required for loan, so these banks might be unwilling to lend to small
farmers.
(b) Informal
sources of credit like moneylenders, employers, relatives, friends etc. are the
sources from
which small farmers borrow the credit.
(c) If higher
rate of interest is carried as terms of credit from informal sources, then it
would
be unfavourable
for the small farmers.
(d) Farmers can get cheap credit
through cooperatives and SHGs
Questions in the Exercise
Q.1. Self-help groups also discuss the following social problems.
(a) Health (b)
Nutrition (c) Domestic violence (d) All the above
Ans.
(d)
Q.2. In SHG most of the decision regarding savings and loan activities are taken
by
(a) Bank (b)
Members
(c)
Non-government organisations (d) Government.
Ans.
(b)
Q.3. Fill in the blanks :
(i) Majority of
the credit needs of the _______________ households are met from informal
sources.
(ii)
_____________ cost of borrowing increases the debt burden.
(iii)
_____________ issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government.
(iv) Banks
charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on _______________
(v)
______________ is an asset that the borrower owns and uses as a guarantee until
the loan
is repaid to the
lender.
Ans.
(i) rural (ii) higher (iii) RBI (iv) deposits (v) collateral
Q.4. In situations with high risks, credit might create further problems for the
borrower.
Explain.
Ans.
The areas like farming, where high risks are involved, crop failure
make loan repayment
impossible. To
repay the loan amount, farmers have to sell a portion of their land. In such a
situation credit
pushes the person into a debt-trap from which recovery is very painful.
Q.5. Why do lenders ask for collateral while lending?
Ans.
Generally lenders ask for collateral, which is an asset that the
borrower owns (such as land,
building,
vehicle, livestock etc.) and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan
is repaid. If
borrower fails
to repay the loan, the lender has the right to sell the collateral to obtain
payments.
Q.6. In what ways does the Reserve Bank of India supervise the functioning of
banks? Why
is it necessary?
Ans.
The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal
sources of loan. For example,
we have seen
that the banks maintain a minimum cash balance out of the deposits they receive.
The RBI monitors
that the banks actually maintain the cash balance. Similarly, the RBI sees
that the banks
give loans not just to profit making businesses but also to small cultivators,
small scale
industries etc.
Q.7. Manav needs a loan to set up a small business. On what basis will Manav
decide whether
to borrow from a bank or a moneylender? Discuss.
Ans.
If Manav has all the necessary documents showing his paying capacity
and collateral security
then he will go
in for a formal source of credit, i.e. bank. Bank will charge a reasonable rate
of interest. If
he cannot provide necessary documents required for loan from the bank, then he
has to opt for
an informal source of credit who sometimes lends at higher rate of interest and
uses unfair means to get back the
money.
PREVIOUS YEARS’
QUESTIONS
Q.1. Which are two major sources of formal sector credit in India? Why do we
need to expand
the formal sources of credit?
Ans.
Formal sector credit in India includes loans from banks and
cooperatives. RBI supervises their
functions of
giving loans. Lower rate of interest is charged as compared to informal sources
of credit on
these loans.
Need to expand formal sources of credit :
Formal sector credit
needs to be expanded in India
so as to save
people and especially poor farmers and workers from exploitation of the informal
sector credit.
Formal sector lends at a reasonable rate of interest which is very cheap. Formal
credit can fulfil various needs of
the people through providing cheap and affordable credit.
MULTIPLE CHOICE
QUESTIONS
Q.1. System of exchanging goods for goods is called :
(a) monetary
system
(b) credit
system
(c) barter
system
(d) exchange
system
Ans.
(c)
Q.2. Money
(a) eliminates
double-coincidence of wants
(b) acts as a
common measure of value
(c) acts as a
standard of deferred payments
(d) all the
above
Ans.
(d)
Q.3. At present which form of money is increasingly used apart from paper money?
(a) Commodity
money
(b) Metallic
money
(c) Plastic
money
(d) All the
above
Ans.
(c)
Q.4. What are the modern forms of money?
(a) Currency
(b) Plastic
money
(c) Demand
deposits (d) All the above
Ans.
(d)
Q.5. Terms of credit are with respect to :
(a) interest
rate (b) collateral
(c)
documentation (d) all the above
Ans.
(d)
Q.6. Credit or loan refers to an agreement
between :
(a) lender and
borrower
(b) consumer and
producer
(c) government
and tax payer
(d) all the
above
Ans.
(c)
Q.7. The formal sector meets only about _______ of the credit needs of rural
people :
(a) 25% (b) 52%
(c) 75% (d) 15%
Ans.
(b)
Q.8. The part of the total deposits which a bank keeps with itself in cash is
(a) zero
(b) a small
proportion
(c) a big
proportion
(d) 100 percent
Ans.
(b)
Q.9. An asset that the borrower uses as a repayment guarantee to a lender is
termed as a :
(a) deposit (b)
collateral
(c) advance (d)
all the above
Ans.
(b)
Q.10. Currency is issued in India by :
(a) commercial
banks
(b) regional
rural banks
(c) nationalised
banks
(d) Reserve Bank
of India
Ans.
(d)
Q.11. Who supervises the credit activities of lenders in the informal sector?
(a) Central Bank
of India
(b) Commercial
banks
(c) Moneylenders
(d) None
Ans.
(d)
Q.12. Rich households in urban areas avail cheap credit from
(a) formal
sources (b) informal sources
(c) government
(d) all the above
Ans.
(a)
Q.13. Productive loans by farmers are taken
(a) to buy
seeds, fertilisers, implements
etc.
(b) for
celebration of marriages
(c) for storage
of foodgrains in godowns
(d) none of the
above
Ans.
(a)
Q.14. Which of the following is not a source of rural credit?
(a) Regional
rural banks
(b) Moneylenders
(c) Traders
(d) Government
Ans.
(d)
Q.15. Rate of interest charged by moneylenders as compared to that charged by
banks is :
(a) lower (b)
same
(c) slightly
higher (d) much higher
Ans.
(d)
Q.16. Regional Rural Banks were set up in
________.
(a) 1969 (b)
1979
(c) 1989 (d)
1999
Ans.
(a)
Q.17. A Self-Help Group usually has :
(a) 5-10 members
(b) 10-15 members
(c) 15-20
members (d) 20-25 members
Ans.
(c)
Q.18. When was the KCC (Kisan Credit Card) scheme introduced?
(a) 1969 (b)
1979
(c) 1987-88 (d)
1998-99
Ans.
(d)
Q.19. Which state accounts for maximum percentage of SHGs (self-help groups) in
bank credit?
(a) Andhra
Pradesh (b) Tamil Nadu
(c) Kerala (d)
Karnataka
Ans.
(a)
Q.20.
_________ are widely accepted as a medium of exchange.
(a) Rupee notes
(b) Gold coins
(c) Silver coins
(d) All the above
Ans.
(a)
Q.21. Majority of the credit needs of the poor households are met from
(a) formal
sources
(b) informal
sources
(c) self-help
groups
(d) none of the
above
Ans.
(b)
Q.22. Who supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans?
(a) RBI (Reserve
Bank of India)
(b) Central
government
(c) State
government
(d) None
Ans.
(a)
Q.23. Which of the following is a major reason which prevents the poor from
getting bank loans?
(a) Absence of
collateral (security)
(b)
Non-repayment of loans
(c) Higher
interest rates
(d)
Documentation
Ans.
(a)
Q.24. Who helps the borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral?
(a) Self-help
group (SHG)
(b) State
government
(c) Employers
(d) Moneylenders
Ans.
(a)
Q.25. Formal sources of credit include
(a) banks (b)
moneylenders
(c) employers
(d) all the above
Ans.
(a)
Q.26. Which of the following is not a modern form of money?
(a) Paper notes
(b) Demand deposits
(c) Silver coins
(d) None of the
above
Ans.
(c)
PREVIOUS YEARS’
QUESTIONS
Q.1. Which of the following is not an advantage of self-help group?
(a) Grant of timely loans
(b) Reasonable
interests
(c) A platform
to discuss various issues
(d) Does not
help women to become self-reliant.
Ans.
(d)
Q.2. What do you mean by collateral?
(a) It is the total sum of money with a
person
(b) It is the
things kept in the locker
(c) It is the
guarantee given by the lender to the borrower.
(d) It is the
security to a lender until the loan is repaid
Ans.
(c)
Q.3. Identify the formal source of credit.
(a) Cooperative societies
(b) Moneylenders
(c) Traders
(d) Landlords
Ans.
(a)
Q.4. Which one of the following is not a modern form of money?
(a) Demand
Deposits
(b) Paper
currency
(c) Coins
(d) Precious
metals
Ans.
(d)
Q.5. Which one of the following authorizes money as a medium of exchange?
(a) Reserve Bank of India
(b) Self Help
Groups
(c) The Central
Government
(d) The
President of India.
Ans.
(a)
Q.6. Which of the following is not true regarding the in convenience of Barter
Exchange ?
(a) Lack of
double coincidence of want
(b) Absence of
divisibility
(c) Difficulty
in storing wealth
(d) Availability
of money as a medium of
exchange.
Ans.
(d)
Q.7. Which one of the following is NOT an informal sector loans for poor rural
household in India ?
(a) Commercial
Banks
(b) Moneylenders
(c) Traders
(d) Landlords
Ans.
(a)
Q.8. Which one of the following is the important characteristic of modern form
of currency?
(a) It is made
from precious metal
(b) It is made
from thing of everyday use
(c) It is
authorized by the commercial banks
(d) It is
authorized by the Government of the country
Ans.
(d)
Q.9. Which one of the following constitutes money in modern day economy?
(a) Gold (b) Silver
(c) Interest (d)
Demand Deposits
Ans.
(d)
Q.10. In a SHG most of the decisions regarding loan activities are taken by
(a) Banks (b) Member
(c)
Non-government organizations
(d) Cooperatives
Ans.
(b)
Q.11. Which one of the following is a major reason that prevents the poor from
getting loans from the banks?
(a) Lack of capital
(b) Not
affordable due to high rate of interest
(c) Absence of
collateral security
(d) Absence of
mediators
Ans.
(c)
Q.12. Which one of the following agencies issues currency notes on behalf of the
government of India ?
(a) Ministry of
Finance
(b) Reserve Bank
of India
(c) State Bank
of India
(d) World Bank
Ans.
(c)
Q.13. Formal Sources of credit include :
(a) money lenders (b) co-operatives
(c) Employers
(d) Finance
companies
Ans.
(b)
Q.14. Anything which is generally accepted by the people in exchange of goods
and services is called :
(a) money (b)
barter
(c) credit (d)
loans
Ans.
(b)
Q.15. Terms of credit does not include :
(a) interest
rate (b) collateral
(c) cheque (d)
mode of repayment
Ans.
(c)
Q.16. Banks do not give loans :
(a) to small
farmers
(b) to marginal
farmers
(c) to
industries
(d) without
proper collateral and
documents
Ans.
(d)
Q.17. The functioning of the formal sources of credit are supervised by :
(a) Government
of India
(b) Reserve Bank
of India
(c) Ministry of
finance
(d) State Bank
of India
Ans.
(b)
Q.18. Which one of the following is NOT a formal source of credit?
(a) Commercial
Banks
(b) State Bank
of India
(c) Employers
(d)
Co-operatives
Ans.
(c)
Q.19. Which one of the following is not included in the terms of credit?
(a) Rate of
Interest
(b) Mode of
payment
(c) Rate of
saving
(d) Collateral
Ans.
(c)
Q.20. Which is not the main source of credit from the following for rural
households in India ?
(a) Traders
(b) Relatives
and friends
(c) Commercial
Banks
(d) Money
landers
Ans.
(a)
Q.21. Cheap and affordable credit results in which one of the following ?
(a) Slow
economic growth
(b) Creating a
debt trap
(c) Poverty
(d) Good
economic growth
Ans.
(d)
Q.22. Deposits in bank accounts withdrawn on demand are called :
(a) Fixed
deposit
(b) Recurring
deposit
(c) Demand
deposit
(d) None of
these
Ans.
(c)
Q.23. Banks use the major portion of the deposit to :
(a) Keep reserve
so that people may withdraw
(b) Meet their
routine expenses
(c) Extend loans
(d) Meet
renovation of the bank
Ans.
(c)
Q.24. When both parties agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities it is
known as :
(a) measure of
value
(b) double
coincidence of wants
(c) store of
value (d) credit
Ans.
(b)
Q.25. Which among these is an essential feature of barter system ?
(a) Money can
easily exchange any commodity
(b) It is based
on double co-incidence of wants
(c) It is
generally accepted as a medium of exchange of goods with money
(d) It acts as a
measure and store of value
Ans.
(b)
Q.26. Which one of the following is the main source of credit for the rich
households?
(a) Informal
(b) Formal
(c) Both formal
and informal
(d) Neither
Formal nor informal
Ans.
(b)
Q.27. Why bank deposits are known as demand deposits ?
(a) Deposits
with the banks
(b) People have
the provision to withdraw the money when they require.
(c) Deposits
with the banks cannot be withdrawn.
(d) People have
the provision to withdraw the money only by cash.
Ans.
(b)
Q.28. Which households take more loans from the formal sector ?
(a) Poor
households and rich household.
(b) Well off
households and households with few assets.
(c) Poor
households and well off households
(d) Well off
households and rich households.
Ans.
(d)
Q.29. What portion of deposits are kept by the banks for their day to day
transaction ?
(a) 10% (b) 15%
(c) 20% (d) 25%
Ans.
(b)
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. Can everyone in Sonpur get credit at cheap rate? Who are the people who
can?
Ans.
No, not everyone in Sonpur can get credit at cheap rates.
Generally some
medium farmers, who are literate and have their own land for cultivation, get
credit at cheap
rates from banks.
Q.2. Write two main functions of a commercial bank.
Ans.
Accepting deposits from the individuals and providing loans to the
entrepreneurs are the two
main functions
of a commercial bank.
Q.3. Why should credit at reasonable rates be available for all?
Ans.
If credit is available at reasonable rate, this would lead to higher
income and many people
could then
borrow for a variety of needs such as for growing crops, for setting small scale
industries, for
business etc. Thus credit at reasonable rate will be helpful in the development
process of a
country.
Q.4. What do you understand by “terms of credit”?
Ans.
Interest rate, collateral and documentation requirement, and the mode
of repayment together
are called the
terms of credit.
Q.5. How is credit helpful for the country’s development?
Ans.
Large numbers of transactions in our day to day activities involve
credit in some form or the
other. Credit
helps people to meet the ongoing expenses of production, complete production
on time and
thereby increase their earnings. Hence, it plays a vital and positive role in a
country’s
development.
Q.6. What is the basic idea behind the SHG’s for the poor? Explain in your
words.
Ans.
The basic idea behind the SHG’s for the poor is to provide credit
facilities at a cheaper rate
and also without
much documentation process.
An SHG has 15-20
members, usually from the neighborhood, who meet and save regularly
in the range of
Rs 25 to Rs 100 or more. The amount which is collected by an SHG is utlised
to give loan to
a member of the group. Now the group decides as regards the loans to be
granted, the
purpose, amount, interest to be charged, and its repayment schedule.
Q.7. Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India?
Ans.
Formal sources of credit in India provide loans to individuals at far
cheaper rates than informal
sources of
credit. This helps to increase their income and they are able to repay the
principal
amount as well
as interest by parting with a small part of their higher income. It will lead to
more production.
This helps in the economic development of a country.
Q.8.
What is the main source of income for banks?
Ans.
The main source of income for banks is the difference between
interest rate charged from
borrowers and
what is paid to depositors. After keeping a portion of deposits as reserves
banks
lend to people
who demand money as loan and bank charges interest from them.
PREVIOUS YEARS’ QUESTIONS
Q.1. What do the banks do with the 'Public Deposits'? Describe their working
mechanism.
Ans.
Banks accept deposits from the Public and use the major portion of
these deposits to
extend loans.
There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities. Banks
make use of
these deposits to meet the loan requirement of the people and thereby earn
interest. This
is, infact, the main source of income of the bank. In this way, bank acts as
a mediator
between those who have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in
need of these
funds (the borrowers). Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what
they offer on
deposits.
Q.2. What are demand deposits? Describe any three salient features of demand
deposits.
Ans.
People with surplus money or extra amount deposit it in banks. The
banks keep the money safe
and give an
interest on it. The deposits can be drawn at any time on demand by the
depositors.
That is why they
are called 'demand deposits'.
(i) The demand
deposits encashable by issuing cheques have the essential features of money.
(ii) They make
it possible to directly settle payments without the use of cash.
(iii) Since
demand drafts/cheques are widely accepted as a means of payment along with
currency, they
constitute money in the modern economy.
Q.3. Mention any three points of distinction between formal sector loan and
informal sector loan.
Ans.
Formal Sources of Credit
Informal sources of
Credit
1. Formal
sources of credit are generally
1. Informal sources of credit are
generally
provided by
banks and cooperatives.
provided by moneylenders,
traders,
employers, relatives and friends.
2. Interest rate
for repaying loans is lower.
2. Interest rate for repaying loans is
costlier.
3. RBI
supervises the functioning of formal
3. In informal sector no such organisation
sources of loan
and also ensures that these
is there to supervise the credit
activities
facilities
should also be given to small
of lenders that they used to
charge higher
cultivators and
small borrowers.
rate of interest on loans.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. Differentiate between Reserve Bank of India RBI and Commercial Bank.
Ans.
Reserve Bank of India
Commercial Bank
1. It has the
sole monopoly right to issue
1. No such thing is done by commercial bank.
currency notes.
2. It is the
apex bank in the money market
2. It is a unit in the banking structure of the
country.
of a country.
3. It does not
deal with the public.
3. It directly deals with the public and
business firms.
4. It acts as a
banker to the government.
4. It has no such responsibility towards the state.
PREVIOUS YEARS’ QUESTIONS
Q.1. Explain any two
features each of formal sector loans and informal sector loans.
Ans. Formal Sector Loans :
Formal sector
loans include loans from banks and cooperatives. Features of formal sector
loans are :
(i) Formal
sectors provide cheap and affordable loans and their rate of interest is
monitered
by RBI.
(ii) Formal
sector strictly follows the terms of credit which includes interest rate,
collateral,
documentation
and the mode of repayment.
Informal Sector Loans :
Informal sector
loans include loans from moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends
etc. Features
for informal sector loans are :
(i) Their credit
activities are not governed by any organisation, therefore they charge higher
rate of
interest.
(ii) Informal
sector loan providers know the borrowers personally, and hence they provide
loans on easy
terms without collateral and documentation.
Q.2. What are the two main reasons for formal credit not being available to the
rural
poor ? Why is there a need to expand rural credit ?
Ans.
The two main reasons for formal credit not being available to rural
poor are :
(i) Absence of
collateral and documentation is the main reason which prevents rural poor from
getting bank
loans.
(ii) The
arrangements of informal sector loans are flexible in terms of timelines,
procedural
requirements,
interest rates etc. They are adjustable according to the needs and
convenience of
the borrower.
There is a need
to expand rural credit from the side of formal sector because :
(i) Informal
sectors exploit rural poors by putting them in debt-traps.
(ii) Cheap and
affordable credit for rural poors is important for the country’s overall
development.
Q.3. Why do the rural borrowers depend on the informal sector for credit? What
steps can
be taken to encourage them to take loans from the formal sources ? Explain any
two.
Ans.
The rural borrowers depend on the informal sector for credit because
:
(i) Absense of
collateral and documentation with rural borrowers.
(ii) Flexible
loans in term of timelines, interest rates, procedural requirements etc. are
provided
to rural
borrowers by informal sectors.
Steps that can
be adopted to encourage them to take loans from the formal sources are :
(i) Awareness
among rural borrowers against the exploitation of informal sectors. Need to
aware them
regarding high rate of interest and debt traps made by such moneylenders.
(ii) Promotion
to self-help groups. These groups collect their savings as per their own ability
to save. Members
can take small loans from the groups to meet their requirements. If the
group is regular
in savings for year or two, it can avail loan from the bank.
Q.4. ‘Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development’.
Explain the
statement with four points.
OR
Why do we need to expand formal source of credit in India ? Explain any four
reasons.
Ans.
If the loans are cheap and affordable, this can lead to countries
development in the following
ways :
(i) Cheap loans
results in higher incomes and higher profits which can help in the expansion
of business.
(ii) More and
more people can be benefitted by the loans in their businesses.
(iii) This can
help in making more and more agricultural activities, small-scale industries
etc.
Credit can be
distributed more equally which helps in benefitting the poor’s by the help of
cheaper loans.
Q.5. Answers the following questions :
(a) Why are
banks unwilling to lend loans to small farmers ?
(b) Besides
banks, what are the other sources of credit from which the small farmers can
borrow.
(c) Explain how
terms of credit can be unfavorable for the small farmers.
(d) From where
can small farmers get cheap loans ?
Ans.
(a) Banks provide loans after collateral and documentation
securities, which generally the
small farmers
failed to comply with. Therefore, banks are unwilling to lend loans to small
farmers.
(b) There are
several informal sources of credit like landlords, moneylenders, traders,
relatives and
friends etc.
(c) Terms of
informal credit can put the small farmers into debt-traps. Higher rate of
interest
and unfavorable
conditions exit farmers by the situation of multiple loans.
(d) Farmers can
get cheap and safe loans from formal credit providers i.e., banks and
cooperative
societies.
Q.6. Which are the two major sources of formal sector credit in India ? Why do
we need to
expand formal sources of credit ?
Ans.
The two major sources of formal sector credit in India are —
commercial banks and
cooperative
societies.
We need to
expand formal sources of credit due to following reasons :
(a) Informal
sources of credit exploit the poor’s resulting in putting them into debt-traps.
(b) Formal
sources of credit are cheaper and thus they help in country’s development.
Q.7. What is meant by term of credit ? What does it include ?
Ans.
Terms of credit are the requirements need to be satisfied for any
credit arrangements. It
includes
interest rate, collateral, documentation and mode of repayment. However the
terms of
credit vary
depending upon the nature of lender, borrower and loan.
Q.8. How does the Reserve Bank of India supervise the functioning of banks? Why
is this
necessary?
Ans.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) supervised the banks in the following
ways :
(i) It monitors
the balance kept by banks for day-to-day transactions.
(ii) It checks
that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but
also
to small
borrowers.
(iii)
Periodically banks have to give details about lending, borrowers and interest
rate to RBI.
It is necessary
for securing public welfare. It avoids the bank to run the business with profit
motive only. It
also keeps a check on interest rate of credit facilities provided by bank. RBI
makes sure that
the loans from the banks are affordable and cheap.
Q.9. Describe four features of Self-Help Group (SHG).
Ans.
The features of Self-Help Group (SHG) are :
(i) People form
their personal groups for the purpose of savings and also lend money among
themselves.
(ii) Rate of
interest is lower than informal service providers.
(iii) They can
also avail loans from banks if their savings are regular.
(iv) Decisions
regarding the savings and loan activities are taken by group members.
Q.11. What is double coincidence of want? How has money solved this problem?
Ans.
Things exchanged for other things without the use of money is known
as barter system. The
barter system
laid the foundation of trade but trade was limited to the bounds of a village or
town. Hence, in
a barter system when both the parties agree to sell and buy each other’s
commodities, it
is known as double coincidence of wants. Whatever commodity a person
desires to sell
is exactly what commodity the other wishes to buy. Without double coincidence
of wants
exchange of goods is not possible. Therefore, it is an essential feature.
Money eliminates
the need of double coincidence of wants. One can easily exchange their
goods in
exchange of money and later on pay money for the desired commodities. Money acts
as a
intermediate in the process of exchange, it is called as medium of exchange.
Q.12. How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who
need
money?
Ans.
People keep their surplus money in banks for safety and interest
which is provided by banks
to them. Banks
again keep only a small proportion of their cash with themselves. These days
banks keep only
15% of the total deposits with them. Rest of the money banks keep to extend
loans. Banks
charge interest on loans which is higher than the interest on deposits. This
surplus
interest becomes
the source of income for the banks. The 15% of cash deposits which banks
keep with
themselves helps to carry on with, day-to-day transactions. Like every day,
depositors
come to withdraw some of their
cash.
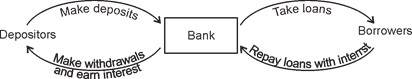
Q.13. Differentiate
between formal and informal sources of credit.
Q.11.
Ans.
|
Formal Sources |
Informal Sources |
|
1.
Formal sources of
credit are loans from banks and
cooperative societies.
2.
Functioning of formal sources of credit is governed by Reserve Bank of India.
Their interest rate and money lending
details are periodically checked by
RBI.
3.
Rate of interest is common and
fixed for all
formal sources and
borrowers.
4.
Formal sources of
credit needs to
satisfy all the terms of
credit before credit, activities.
5.
They provide cheap and
affordable credit for
both urban and
rural borrowers interest. |
1.
Informal sources of
credit are money-
lenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends etc.
2.
There is no organisation that manages or check the credit activities performed
by informal sources.
3.
Rate of interest depends upon the
choice of moneylenders.
4.
Informal sources of
credit are flexible in
terms of credit.
5.
They generally charge higher rate of |
Q.14. Mention four characteristics each of the formal and informal sources of
credit in India.
Ans. Features of formal sources of credit are :
(a) Formal
sources of credit are provided by banks and cooperative societies to the
borrowers.
(b) Reserve Bank
of India (RBI) governs the functioning of formal source of credit. RBI
periodically
checks the interest rate and other details of these sources.
(c) They follow
proper terms of credit which includes collateral, documentation, rate of
interest and
mode of repayment.
(d) They provide
cheap and affordable credits with common terms of credit for all.
Features of informal sources of credit are :
(a) Informal
sources of credit are moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends etc.
(b) There is no
government or private organization that manages or check the credit activities
performed by
informal sources.
(c) Their terms
of credit are flexible for the personal benefit of the lenders and condition of
borrowers.
(d) They
generally charge higher rates of interest and exploit the borrowers for their
own
benefits.
Q.15. Study the table given below and answer the questions that follow :
PEOPLE DEPENDING ON FORMAL SECTOR CREDIT IN URBAN AREAS
Category
Percentage of people
Poor households
15%
Households with
few assets
47%
Well-off
households
72%
Rich households
90%
(i) Poor
households share of formal credit in the urban areas is low as compared to that
of
rich households.
Why is it so ?
(ii) Mention two
difficulties faced by poor households in taking loan from a formal sector.
Ans.
(i) Poor households share of formal credit in urban areas is low as
compared to that of rich
households due
to the following reasons :
(a) Poor’s
generally lack in collateral guarantors and do not have proper mode of
repayment.
(b) Informal
sources of credit are generally flexible in timings, rate of interest, repayment
schedule etc.
Therefore, it is
easier for poor’s to approach moneylenders as they know them
personally.
(ii) (a) Poor’s
are not able to satisfy general terms of credit mostly collateral guarantees.
(b) Informal
moneylenders know the boor borrowers personally and therefore flexible in
terms of repayment schedule, amount
and interest etc.
Q.16. What are the modern forms of money currency in India? Why is it accepted
as a medium
of exchange? How is it executed?
Ans.
Modern forms of money include currency (paper notes) and coins.
It is accepted
as a medium of exchange because the currency is authorized by the government
of India. No
individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupee.
Any person
holding money can easily exchange it with any commodity or service that he
desires. It acts
as intermediate in the exchange process of different countries.
Q.17. Why are transactions made in money? Explain with suitable examples.
Ans.
Money is accepted as a medium of exchange because the currency is
authorized by the
government of
India. In money transactions, money can be paid for any goods or services one
desires. For
example : the producer of shoes may want wheat in exchange for his shoes. But
he may find it
difficult to find a person who is also willing to exchange his wheat for shoes.
So simultaneous
fulfilment of mutual wants is the first and foremost condition to buy and sell
the commodity.
In money transaction one can buy a commodity whenever one wants it. One
does not have to
wait for another person to agree to an exchange of goods.
Q.18. Study the diagram
given below and answer the questions that follow :
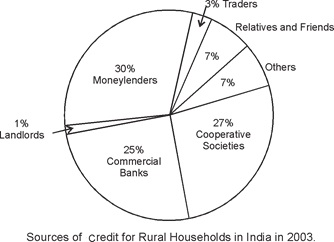
(a) Which are
the two major sources of credit for rural households in India?
(b) Which one of
them is the most dominant source of credit for rural households?
(c) What is the
most dominant source of credit? Give two reasons.
Ans.
(a) Moneylenders and cooperative societies.
(b) Moneylenders
(c) (i)
Moneylenders do not ask for a collateral.
(ii) Complicated
paper work or documentation is not involved.
Q.19. What are the various sources of credit in rural areas? Which one of them
is the most
convenient source of credit? Why is it most convenient? Give two reasons
Ans.
Various sources of credit in rural areas are : (i) Agricultural
traders, (ii) Moneylenders,
(iii) Commercial banks, (iv)
Cooperative societies and (v) Relatives and friends.
The most
convenient source of credit is a moneylender.
It is most
convenient because of the following two reasons :
(i) There is no
need of documentation process while taking loan from informal sources
(moneylenders).
(ii) No
collateral is required. Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (such as
land,
building, livestock etc.) and uses
this as a guarantee to the lender until the loan is repaid.