Social Science Life Lines of National Economy Important Questions
Very Short Answer Questions (VSA) 1 Mark
Question 1.
Why is there the need for transport system? Mention any one reason.
Answer:
The movement of goods and products from the supply locations to demand locations
(markets) necessitates the need for transport.
Question 2.
Which are the different types of transport?
Answer:
The transport can be classified into land, water and, air transport.
Question 3.
Mention two types of airways.
Answer:
Domestic Airways and International Airways.
Question 4.
What are the factors for growing importance of the roadways? State two factors.
Answer:
1.
Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railway lines.
2. It
provides door-to-door service.
Question 5.
How are roads classified in India?
Answer:
In India roads are classified into six classes as mentioned below :
1.
Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways
2.
National Highways
3.
State Highways
4.
District Roads
5.
Other roads that link rural areas with towns
6.
Border Roads.
Question 6.
What is road density?
Answer:
The length of road per 100 sq. km of area is known as density of roads.
Question 7.
What was national average density of roads in 1996-97?
Answer:
The national average density of roads in India in 1996-97 was 75 km per 100 sq.
km.
Question 8.
Mention one drawback of roads in India.
Answer:
Most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow.
Question 9.
When and where the first train steamed off in India?
Answer:
In India, the first train steamed off from Mumbai to Thane in 1853, covering a
distance of 34 km.
Question 10.
The northern plains provide favourable conditions for the growth of the
railways. Mention any two.
Answer:
1.
Vast level land.
2.
High population density.
Question 11.
Why railway track are laid with difficulty in Rajasthan?
Answer:
It is difficult to lay railway lines on the sandy plain of Rajasthan.
Question 12.
In recent times which railway has been developed along the west coast?
Answer:
Konkan Railway.
Question 13.
The railways is facing many problems. Mention any two problems.
Answer:
1.
Many passengers travel without ticket.
2.
People pull the chain unnecessarily.
Question 14.
What is the use of pipelines transport?
Answer:
Pipelines are used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural
gas from oil and natural gas fields to refineries, fertilizer factories and big
thermal power plants.
Question 15.
There are three important networks of pipeline transportation in the country.
Mention any one.
Answer:
Gas pipeline from Hazira in Gujarat connects Jagdishpur in Uttar Pradesh via
Vijaipur in Madhya Pradesh. It has branches to Kota in Rajasthan, Shahjahanpur,
Babrala and other places in Uttar Pradesh.
Question 16.
Why are the waterways useful? State any two advantages.
Answer:
1.
Waterways are the cheapest means of transport.
2. It
is a fuel efficient and environment friendly mode of transport.
Question 17.
Which waterways have been declared as National Waterways by the government?
Answer:
1. The
Ganga River between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km) NW No. 1.
2. The
Brahmaputra River between Sadiya and Dhubri (891 km) NW No. 2.
3. The
West-Coast Canal in Kerala (205 km) NW No. 3.
Question 18.
What is the length of India’s coastline?
Answer:
7516.6 km.
Question 19.
Which port was the first port developed after independence and why?
Answer:
Kandla in Kuchchh was the first port developed after independence to ease the
volume of trade on Mumbai port in the wake of loss of Karachi port of Pakistan
after the Partition.
Question 20.
Which is the biggest port? State its one feature.
Answer:
1.
Mumbai is the biggest port.
2. It
has a spacious, natural and well-sheltered harbour.
Question 21.
Which is the premier iron ore exporting port of the country?
Answer:
Marmagao (Goa) is the premier iron ore exporting port of the country.
Question 22.
Which is one of the oldest artificial port in the country?
Answer:
Chennai is one of the oldest artificial ports of the country.
Question 23.
What type of port is Kolkata?
Answer:
Kolkata is an inland riverine port.
Question 24.
State one feature of Airways.
Answer:
Airways is the fastest, most comfortable and prestigious mode of transport.
Question 25.
Which is the extreme south-western port located at the entrance of a lagoon with
a natural harbour?
Answer:
Kochchi.
Question 26.
When was air transport nationalised?
Answer:
In 1953.
Question 27.
Which company provides helicopter services to ONGC and where?
Answer:
Pawanhans Helicopters Ltd. provides helicopter services to Oil and Natural Gas
Commission in its far off-shore operations.
Question 28.
In which states special provisions have been made to provide air services to the
common people?
Answer:
It is only in the north-eastern states that special provisions are made to
extend the air services to the common people.
Question 29.
How many telephone exchanges are there in India?
Answer:
About 37565.
Question 30.
How many villages are covered with STD telephone facility in India?
Answer:
More than two-thirds villages in India have already been covered with Subscriber
Trunk Dialing (STD) telephone facility.
Question 31.
What is trade?
Answer:
The exchange of goods among people, states and countries is referred to as
trade.
Question 32.
Which states are important destinations of foreign tourists in India?
Answer:
Rajasthan, Goa, Jammu and Kashmir and Temple towns of south India.
Question 33.
Why is transportation necessary?
Answer:
Transportation is necessary:
1. for the
movement of goods and services from their supply location to demand location,
i.e. to link production centers with consumption centers.
2. for the
movement of people from one region to the other.
3. for
carrying out trade at all levels.
4. to supply
goods, resources, etc. from the surplus regions to deficient regions.
5. for
supplying relief measures to the regions where some natural calamities strike.
6. for
transporting raw materials from mining regions and farms to the industries, etc.
Efficient means of transport are the prerequisites for economic development of a
nation.
Question 34.
What do you understand by means of transport? Write three important domains of
the earth which are covered by them.
Answer:
Means of transport include all kinds of vehicles, trains, aero planes and ships.
Means of transport are used for the movement of people, goods and services from
one place to another. These are developed on three important domains of the
earth, i.e., land, water and air. Based on these, transport can also be
classified into land, water and air transport.
Question 35.
Today the world has become a “global village”. Justify this statement.
Answer:
Today the world has become a “large village” because of:
1. efficient
and fast means of transport and
2.
Development of telecommunication and satellite communication systems.
These two functions, i.e. various means of transport and communication
have reduced time and distance, have brought the world closer and the physical
distances have become meaningless. For example, now trading from local levels
has been extended to the international level and even financial transactions can
take place round the world in no time. All this has been made possible because
of efficient and quick means of transport and communication.
Question 36.
“Modern means of transport and communication serve as lifelines of our nation.”
Justify this statement by giving supportive arguments.
Or
“Efficient means of transport are prerequisites for the fast development of the
country.” Express your views in favour of this statement.
Answer:
India is well linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size and
diversities because of efficient means of transport and communication. They are
rightly called the lifelines or arteries of a nation because:
1. Economic
development of a country depends on the well-developed and efficient means of
transport and communication.
2. They are
indispensable for movement of people, goods and services from one place to
another.
3. They have
contributed to socio-economic progress in many ways by connecting far flung
areas of the country.
4. They have
enriched all aspects of our lives — social, cultural, individual and economic.
5. They
promote trade, tourism and business thus adding value to the economy.
6. Transport
and communication have made possible international trade which is essential for
every economy as no country is self-sufficient in all resources.
7. They link
areas of production with consumption, i.e. agricultural farms are linked to the
markets and industries.
8. They help
in the balanced regional development of a country.
9. They play
a very important role at the time of natural calamities, i.e., for providing
relief measures.
10. Deficient areas can
obtain resources from the regions of surplus, thereby making the interdependence
among the regions possible.
11. They have added
substantially to growing amenities and facilities for the comforts of life.
Question 37.
Why do the movement of goods and services form one place to another require fast
and efficient means of transport? Explain with examples.
Answer:
Transport plays an important role in the economy. Because of transport raw
materials reach the factory and finished products reach to the consumer. The
pace of development of a country depends upon the production of goods and
services as well as their movement over space. Today the world has converted
into a large village with the help of efficient and fast moving transport:
1. Good
transport helps in quick carrying of raw materials from remote areas to the
production centre and allows distribution of goods efficiently.
2. Transport
helps in the development of communication. Various means of communication help
us in interacting with other people in all the parts of the world. It has
brought the world closer.
3. Transport
like railways helps us in conducting various activities like business,
sightseeing, pilgrimages, etc.
4. Pipelines
are used for transporting crude oil and natural gas to refineries and factories.
5. Water
provides the cheapest means of transport and is useful for international trade.
6. Air
transport provides the fastest, most comfortable mode of transport.
7. Thus, it
is clear that there are many advantages of transportation and communication.
These means help in the development of the country. So they are rightly called
the lifelines of a nation and its economy.
Question 38.
How are means of transport and communication complementary to each other?
Explain with three examples.
Answer:
1. Transport
and communication establish links between producing centres and consuming
centres. Trade or the exchange of such commodities relies on transportation and
communication. Transport provides the network of links and carriers through
which trade takes place.
2. Dense
network of roads, railways and airways connect the remote areas of the country
hence help in production and distribution of goods and services.
3.
Advancement in communication system has accelerated trade by carrying
information all over the world quickly.
4. Good
transport helps in quick carrying of raw material from remote areas to the
production centre and allows distribution of goods efficiently.
5. With
expansion of rail, ocean and air transport, better means of refrigeration and
preservation, trade has experienced spatial expansion.
Question 39.
Examine with examples the role of means of transport and communication in making
our life prosperous and comfortable.
Answer:
Transport and communication have a major role to play in making our lives
prosperous and comfortable:
1. Means of
transport provide seamless movement of goods and people and thus facilitate
various economic activities.
2. Means of
communication help in flow of information which is necessary for proper
management of supply chain and financial transactions. Today, we are living in
the age of communication, using telephone, television, films and Internet. Even
books, magazines and newspapers are important means of communication.
3. Various
means of transport and communication have reduced distances, bringing the world
closer. Modern life is so complex that one has to depend on others. The same is
true of the countries as well. No country today can prosper without the
co-operation and assistance of others. This requires movement of goods and
materials between countries. Trade provides us with our necessities and also
adds to the amenities and comfort of our life.
4. Transport
like railways help us in conducting various activities like business,
sightseeing, pilgrimage and transportation of goods over longer distances.
5. Water
provide the cheapest means of transport and is useful for international trade.
Air transport provides the fastest, most comfortable mode of transport.
Pipelines are used for transporting crude oil and natural gas to refineries and
factories.
Thus, means of transport and communication put life into a nation and its
economy. Hence, they are called the lifelines of a nation and its economy.
Question 40.
Name three means of land transport and write one advantage of each.
Answer:
Three means of land transport:
1. Roadways.
They can be laid in any type of terrain and provide door to door service.
2. Railways.
They can carry huge loads to long distances, therefore they are of great
significance in the national economy.
3.
Pipelines. These can be used for transporting liquid, gaseous and solid material
to great distances at low cost.
Roadways
Question 41.
Why is road transport more useful than rail transport in India? Give reasons.
Or, “Roadways still have an edge over railways in India”. Give reasons.
Answer:
Roadways score over railways:
1.
Construction of roads is easier and cheaper as compared to railways.
2. Roads
provide door to door service, thus the cost of loading and unloading is much
lower as compared to railways which generally leave the people and goods at the
destined railway stations.
3. Roads can
negotiate higher gradients of slope and, as such, can traverse through
mountainous terrain. But railways cannot negotiate steep gradients.
4. Road
transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller
amount of goods over short distances.
5. Road
transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport. They provide
links between railway stations, airports and sea ports.
6. They link
agricultural farms with markets and industries, thus linking rural and urban
areas.
Question 42.
Name six types of roads according to their capacity.
Answer:
Six types of roads:
1. Super
Highways —Golden Quadrilateral, North-South Corridor and East-West Corridor.
2. National
Highways
3. State
Highways
4. District
Roads
5. Other
Rural Roads
6. Border
Roads.
Question 43.
Write the characteristics of Super Highways, National Highways and State
Highways.
Answer:
Super Highways:
1. These are
6-lane roads built by National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) under the Road
Development Project launched by the government.
2. The major
objective of these roads is to reduce time and distance between the mega cities
of India, especially the Golden Quadrilateral, which links
Mumbai-Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai.
3. Other
important roads developed by NHAI are:
- North-South Corridor linking Srinagar in the North and
Kanyakumari in the South and
- East-West Corridor linking Porbander in Gujarat to
Silcher in Assam.
National Highways:
1. These are
the primary’ road systems which run in the North-South and East-West directions
connecting all the states and link extreme parts of the country.
2. These
roads are laid and maintained by the Central Government, i.e., Central Public
Works Department (CPWD) as they are of national importance.
3. The
historical Shershah Suri Marg, now called National Highway No. 1, links Delhi
and Amritsar and the longest highway in the country is National Highway No. 7
which links Varanasi and Kanyakumari.
State Highways:
1. Roads
linking state capitals with different district headquarters are known as State
Highways.
2. These
roads are constructed and maintained by State Public Works Department (PWD) in
states and union territories.
3. The
expenditure or cost and maintenance of these roads is the responsibility of the
respective state governments.
Question 44.
Differentiate between District Roads and Other Rural Roads?
Answer:
District Roads:
- District Roads connect the district headquarters with
other places of the district.
- These roads are maintained by the Zila Parishad.
Other Rural Roads:
- Rural roads which link rural areas and villages with
towns come under this category.
- These roads received special impetus under the ‘Pradhan
Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojna’. Under this scheme, special provisions are made so
that every village is linked to a major town in the country by an all season
motorable road.
Question 45.
What are ‘Border Roads’? What is their significance?
Answer:
1. Border
roads run along the land frontiers of our country in the northern and
north-eastern border areas.
2. The
Border Road Organisation (BRO) — a department of the Central Government was
established in 1960 for the development of border roads.
3. Their
construction and maintenance is the responsibility of the Central Government.
Importance of Border Roads:
1. These
roads are of strategic importance.
2. They have
increased the accessibility in areas of difficult terrain and have helped in the
economic development of these areas.
3. They are
the supply lines for our jawans (soldiers) who guard our land frontiers.
Question 46.
Classify roads on the basis of the type of material used for their construction.
Answer:
Roads can be classified into two categories on the basis of material used:
Metalled roads may be made of cement, concrete or bitumen. These are all-weather
roads.
Unmetalled roads are dusty and muddy tracks which go out of use in the rainy
season.
Question 47.
Define ‘road density’. What is the average road density in India? Name the
states having the highest and lowest densities respectively. What is the main
reason for this difference in their densities?
Answer:
Road density is defined as the length of road per 100 sq km, of area.
Average road density of India is 75 kms / 100 sq kms of area (1996-97).
Highest road density is in Kerala — It is 375 km / 100 sq kms.
Least road density is in Jammu & Kashmir—It is 10 km / 100 sq kms.
In Jammu & Kashmir, road density is less because of mountainous terrain, whereas
Kerala has levelled nature of land coupled with agricultural development which
supports a lot of population, therefore road density is higher.
Question 48.
What are the problems faced by road transportation in India?
Answer:
Problems faced by road transportation:
1. The road
network is inadequate in proportion to the volume of traffic and passengers.
2. About
half of the roads are unmetalled which makes them useless during rainy season.
3. The
National Highways are inadequate and lack roadside amenities.
4. The
roadways are highly congested in cities.
5. Most of
the bridges and culverts are old and narrow.
Question 49.
Why is the distribution of roads not uniform in India? Explain with examples.
Answer:
1.
Distribution of roads is not uniform in India due to different types of
geographical features.
2. Moreover,
the volume of traffic as well as passengers also affects road networking in
India. Roads are highly congested in cities. Most of the bridges and culverts
have become narrow, old and broken.
3. Some
roads are metalled, that is well built with brick and cement and about half of
the roads are unmetalled especially in rural areas which makes them unaccessible
during rainy seasons.
4. The
regions with rugged terrain have steep roads with lots of hairpin bends.
Railways
Question 50.
Railways play an important role in Indian economy. Give supportive arguments.
Or
Explain the importance of railways as the principle mode of transportation for
freight and passengers in India.
Answer:
1. Railways
are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India, as
they link different parts of the country.
2. They
carry huge loads and bulky goods to long distances.
3. Railways
make it possible to conduct multiple activities like business, tourism,
pilgrimage along with goods transportation over longer distances.
4. Railways
have been a great integrating force for the nation, for more than 150 years now.
5. They have
been helpful in binding the economic life of the country and also promoted
cultural fusion.
6. They have
accelerated the development of the industry and agriculture.
Question 51.
Describe the distribution of railway network in India.
Answer:
1. The
Indian railways have a network of 7,031 stations spread over the country.
2. The route
length is 63,221 kms.
3. It has a
fleet of 7,817 locomotives.
4. There are
5,321 passenger service vehicles.
5. The
number of coach vehicles is 4904.
6. We have
2,28,170 wagons which run on the total rail track of 1,08,486 kms.
Question 52.
Which factors affect the distribution pattern of the railway network in the
country?
Answer:
Factors that affect the distribution pattern of railway network in India:
1. Physical
factors: The nature of terrain and the number of rivers running through the
region will determine the density of railway network in that region.
For example, mountains, marshy, sandy and forested areas have sparse network
whereas plain areas have dense network of the railways.
2. Economic
factors: Regions which have rich resources and are economically more developed
have denser network of railways in comparison to the regions with low economic
development.
3.
Administrative factors: The administrative and political decisions also affect
the distribution of railway network in a region.
Question 53.
Analyse the physiographic and economic factors that have influenced the
distribution pattern of the railway network in our country.
Or,
‘The distribution pattern of Indian Railway network is influenced by the
physiographic factors. Examine the statement.
Answer:
Factors that affect the distribution pattern of railway network in India:
(i) Physiographic factors. The Northern plains with vast level land, high
population density and rich agricultural resources provide most favourable
conditions for railway network. The nature of terrain and the number of rivers
running through the region determine the density of railway network in that
region. Mountains, marshy, sandy and forested areas have sparse network whereas
plain areas have dense network of the railways. It was difficult to lay railway
lines on the sandy plains of Western Rajasthan, swamps of Gujarat and forested
tracks of Madhya Pradesh.
(ii) Economic factors. Regions which have rich resources and are
economically more developed have denser network of railways in comparison to the
regions with low economic development.
(iii) Administrative factors. The administrative and political decisions
also affect the distribution of railway network in a region.
Question 54.
List four factors which favoured the development of dense network of railways in
the northern plains.
Answer:
Four reasons for dense network of railways in northern plains are:
1. The vast
level land provided the most favourable conditions for their growth. It is
cheaper and easier to construct railway tracks here.
2. The
agricultural and industrial development in this region necessitated the
development of railway lines.
3. High
population density in this region further required the development of railway
lines.
4. Resources
such as iron and steel, fuels, etc., required for the development of railways
are available in abundance in the northern plains.
Question 55.
State reasons for the sparse railway network in Himalayan region.
Answer:
Reasons for sparse railway network in Himalayas:
1. High
relief and rugged terrain pose difficulty in construction.
2. Sparse
population.
3. Lack of
economic opportunities because of low economic development.
4. These are
also thickly forested areas.
Question 56.
Where is Konkan Railway Line developed in India and what problems are faced by
it?
Answer:
Konkan Railway Line is developed along the western coast of India through the
states of Maharashtra, Goa and Karnataka. This railway line has facilitated the
movement of passengers and goods in this most important economic region of
India.
Problems faced during its construction:
- Sinking of track in some stretches.
- Landslides were another hinderance.
Question 57.
What are the problems faced by Indian Railways?
Answer:
Problems faced by the Indian Railways:
- Many passengers travel without tickets.
- Thefts and damaging of railway property by miscreants.
- People stop the trains and pull chains unnecessarily
that cause’s heavy damage to the railways and also causes delays.
Question 58.
Explain the improvements made by the Indian Railways in its functioning.
Answer:
1. Railways
make it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business, sight-seeing,
pilgrimage, transportation of goods and passengers.
2. It
accelerated the deployment of industrial and agricultural sector.
3. Konkan
Railways along the west coast has facilitated the movement of passengers and
goods.
4. Metro
Rail, Mono Rail and Rapid metro systems are helping lakhs of people to commute
every day. These have helped in easing the traffic situation in cities like
Delhi, Mumbai and Gurgaon.
5. The
railways provide effective container service.
Pipelines
Question 59.
What are the advantages of pipeline transportation?
Answer:
Advantages of pipeline transportation:
1. Pipelines
can transport liquids, gases and solids (in slurry form) to any distance.
2. Pipelines
are used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil
and natural gas fields to refineries, fertilizer factories and big thermal power
plants.
3. Initial
cost of laying pipelines is high but subsequent running costs are minimal.
4. It
reduces trans-shipment losses and delays.
5. They can
be laid in any terrain and even through the water-bodies.
Question 60.
What made the location of inland oil refineries possible? Name any two inland
oil refineries.
Answer:
Location of inland oil refineries was made possible because of pipeline
transportation which links them with oilfields.
Inland oil refineries are:
1. Barauni
2. Mathura
3. Panipat.
Question 60.a.
Write about three most important networks of pipeline transportation.
Answer:
Important networks are:
1. From
oilfield in Upper Assam to Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh) via Guwahati, Barauni and
Allahabad.
2. From
Salaya (Gujarat) to Jalandhar (Punjab) via Viramgam, Mathura, Delhi and Sonepat.
3. Gas
pipeline from Hazira (Gujarat) via Bijaipur (Madhya Pradesh) to Jagdishpur
(Uttar Pradesh), called HBJ gas pipeline.
Waterways
Question 61.
Write four merits of waterways in India.
Answer:
1. Waterways
are the cheapest means of transport.
2. Waterways
are a fuel efficient and environment friendly mode of transport.
3. They are
most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
4. India’s
trade with foreign countries is carried from the ports located along the coast,
and more than 95% of the country’s trade volume is moved by the sea.
Question 62.
Mention any two inland waterways of India. Write three characteristics of each.
Answer:
Two inland water ways are:
(A) The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia:
Characteristics:
- The Inland Waterways Authority has declared this
waterway as National Waterway No. 1.
- Its total length is 1620 km.
- It is one of the most important waterway of India which
is navigable by mechanical boats upto Patna.
(B) The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri:
Characteristics:
- The total length is 891 km.
- It is declared as National Waterway No. 2.
- It is navigable by steamers upto Dibrugarh.
Major Seaports
Question 63.
What are major seaports?
Answer:
Seaports which handle our foreign trade are called major seaports. These ports
handle 95 per cent of India’s foreign trade.
Question 64.
Name the northernmost and southernmost ports of eastern and western coast
respectively.
Answer:
The northernmost port: of eastern coast — Kolkata
of western coast — Kandla
The southernmost port: of eastern coast — Tuticorin
of western coast — Kochi
Question 65.
Give an account of the major sea ports of India and their importance.
Answer:
1. Kandla
port in Kuchchh.
- It was developed after independence to reduce the load
on the Mumbai port as the Karachi port had gone to Pakistan after partition.
- It is a tidal port and caters to exports and imports of
the granary and industrial belts of Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab,
Haryana, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- Kandla port is located in Kuchchh in Gujarat.
- It caters to the convenient handling of exports and
imports for northern and western states of India.
2. Mumbai
port. It is the biggest port with a spacious natural and well-sheltered harbour.
3. Jawahar
Lai Nehru port. Planned as a subordinate and hub-port of the Mumbai port.
4. Marmagao
port (Goa).
- It is a premium iron ore exporting port.
- It accounts for about fifty per cent of India’s iron ore
exports.
5. New
Mangalore port (Karnataka). Caters to the export of iron-ore from Kudremukh
mines.
6. Kochchi.
Extreme south-western port located at the entrance of a lagoon with a natural
harbour.
7. Tuticorin
(Tamil Nadu).
- It has a natural harbour and rich hinterland.
- It engages in flourishing trade with neighbouring
countries like Sri Lanka, Maldives etc.
8. Chennai
port.
- Oldest artificial port in the country.
- It is second only to Mumbai in terms of volume of trade
and cargo.
9.
Vishakhapatnam port. Deepest land locked and well protected port catering mainly
to iron ore exports.
10. Paradip (Orissa)
specialises in iron ore export.
11. Kolkata port.
- It is an inland riverine port.
- It serves as a large and rich hinterland of
Ganga-Brahmaputra basin.
- It is a tidal port which requires constant dredging of
the Hugli River.
12. Haldia port. It was
developed to reduce pressure on Kolkata port.
Airways
Question 66.
Write four merits of air travel. Also mention any two demerits of air transport.
Answer:
Merits of air travel.
1. Air
travel is the fastest, most comfortable and prestigious mode of transport.
2. India is
a vast country with wide variation in relief. Air transport can cover difficult
terrains like high mountains of the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, dreary deserts
of Rajasthan, dense forests and long coastlines with great ease.
3. Air
travel has made access easier in the north-eastern part of the country, which is
marked with the presence of big rivers like Brahmaputra, dissected relief, dense
forests, frequent floods and international frontiers.
4. At the
time of natural calamities, relief measure and relief operations can be carried
out quickly with the help of air transport.
5. High
value perishable goods can easily be exported or imported by airways.
Demerits of air transport.
- Air travel is very expensive and not within the reach of
the common people. Air travel is very luxurious.
- It is adversely affected by bad weather conditions.
Question 67.
Why is air travel preferred in the north-eastern states? Give reasons.
Answer:
The north-eastern part of the country is marked with:
1. Dissected
relief,
2. dense
forests,
3. Frequent
floods
4. Big
rivers.
Under these difficult conditions, the road and rail transport is not well
developed. Journey through land transport is very tiresome and time-consuming.
So, for all these reasons, air travel is preferred in this part of the country,
where special provisions are made to extend the services to common people at
cheaper rates.
Question 68.
Name four airline services which cater to the domestic air traffic.
Answer:
Domestic air services are:
- Indian Airlines which extends its services to
neighbouring countries also.
- Alliance Air (Subsidiary of Indian Airlines).
- Private scheduled airlines, e.g., Jet, Sahara,
Kingfisher, Indigo, Go Air etc.
- Private non-scheduled operators provide air-taxi
service.
Question 69.
What are ‘Pawan Hans’ services? Write two purposes for which these services are
used.
Answer:
The Pawan Hans Helicopter Ltd., a public sector undertaking, provides helicopter
services to:
- Oil and Natural Gas Commission (ONGC) in its offshore
operations.
- Inaccessible areas and difficult terrains like the
north-eastern states, the interior parts of Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh
and Uttrakhand.
- They are also pressed into service at the time of
emergencies and for providing relief measures at the time of natural calamities.
Question 70.
Which is the ‘International Airline’ of India?
Answer:
‘Air India’ handles our international traffic. It is a public sector
undertaking. Jet and Kingfisher are examples of private airlines that fly to
other countries as well.
Question 71.
Name four cities where international airports are located and name these
airports.
Answer:
Cities where international airports are located:
1. Delhi —
Indira Gandhi International Airport
2. Mumbai —
Chhatrapati Shivaji Airport
3. Chennai —
Meenambakkam Airport
4. Kolkata —
Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Airport
Question 72.
Name the northernmost and southernmost international airport of India.
Answer:
Northern most international airport is Raja Sansi at Amritsar. Southern most
international airport of India is situated in Tiruvanantapuram and is called
Nedimbacherry Airport.
Communication
Question 73.
What is the main difference between means of transport and means of
communication?
Answer:
Means of transport: These are used for the movement of people, goods and
services from one place to another, e.g. roadways, airways, etc.
Means of communication: These are used for interchanging messages and ideas
between people without physical movement of the communicator or receiver, e.g.
letters, telephone, television, etc.
Question 74.
Write two types of means of communication and give two examples of each.
Answer:
Two types of means of communication are:
(i) Personal communication
(ii) Mass communication.
(i) Personal communication includes sending and receiving of messages between
two individuals at a personal level. The important means in this category are
telephone, post & telegraph services, fax, etc.
(ii) Mass communication means communicating with several people (masses) at the
same time. These are of two types:
- Print media. It includes printed material, e.g.
newspapers and magazines.
- Electronic media, e.g. Radio and T.V. This is an
important media, especially for illiterate masses of the country.
Question 75.
What are the functions performed by means of mass communication?
Answer:
Functions performed by means of mass communication:
1. It
provides entertainment to masses.
2. It
creates awareness among people about various national programmes and policies.
3. We come
to know the world happenings, weather bulletins and important international
phenomena, developments and researches, etc. through the means of mass
communication.
4. They help
in creating public opinion.
Question 76.
Explain the importance of ‘Radio’ and ‘Television’ as an effective means of mass
communication in India.
Answer:
Because a large part of the population of our country is illiterate, the
electronic media of mass communication i.e., Radio and T.V. play a very crucial
role in:
- providing entertainment
- increasing awareness among people about various national
programmes and policies.
Radio. It broadcasts —
- a variety of programmes in national, regional and local
languages.
- varied programmes for various categories of people in
rural, urban and remote areas through a number of radio
stations and transmitters.
T.V. It telecasts —
- a variety of entertainment, educational and informative
programmes.
- T.V. is a better means of mass communication as it gives
a visual report of world happenings; live telecast of sports and literacy
programmes etc., which become more entertaining and meaningful.
Question 77.
Name the mail channels which were introduced by the Indian postal network to
facilitate quick delivery of mails. What was the main purpose of this decision?
Answer:
Mail channels introduced by the Indian postal network are:
1. Rajdhani
Channel
2. Business
Channel
3. Metro
Channel
4. Bulk Mail
Channel
5. Green
Channel
6.
Periodical Channel
The main purpose is to facilitate quick delivery of mail to large towns
and cities.
Question 78.
“India has one of the largest telecom networks in Asia.” Justify this statement.
Answer:
1. Most of
the urban centres are connected by STD (Subscriber Trunk Dialling) telephone
facility.
2. More than
2/3rd of the villages in India have already been covered with STD telephone
facility, through many telephone exchanges.
3. In order
to strengthen the flow of information from the grass-root level to the higher
level, the government has made special provision to extend 24 hours STD service
facility to every village in the country.
4. There
have been uniform rates of STD facilities all over India. Even ISD services are
available in most of the cities of the country.
All this has been made possible by integrating the developments in space
technology with communication technology and development of computers and
internet. Recently a number of private companies have also entered into
telecommunication area.
Question 79.
Distinguish between first class mail and second class mail.
Answer:
Difference between Class mail and Second Class mail
|
Class mail |
Second Class mail |
|
1. Cards and envelopes make first class mail. |
1. This includes book packets, registered newspapers and periodicals. |
|
2. They are airlifted between stations covering both land and air. |
2. They are carried by surface mail, covering land and water transport. |
Question 80.
Write in brief about A.I.R. and Doordarshan.
Answer:
All India Radio (A.I.R. or Akashwani):
1. It
broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages.
2. It
broadcasts programmes for various categories of people in rural, urban and
remote areas.
3. It is
spread over different parts of the country through a number of radio stations
and transmitters.
Doordarshan:
1. It is the
national television channel of India.
2. It is one
of the largest terrestrial networks in the world.
3. It
telecasts a variety of programmes ranging from educational, entertainment to
sports, etc. for people of different age groups.
Question 81.
Approximately in how many languages are newspapers published in India?
Answer:
Newspapers are published in about 100 languages and dialects. Largest number of
newspapers published in India are in Hindi followed by English and Urdu.
Question 82.
What is the status of feature film production in India?
Answer:
1. India is
the largest producer of feature films in the world.
2. It
produces short, video feature films and video short films.
3. The
Central Board of Film Certification is the authority to certify both Indian and
foreign films.
International Trade
Question 83.
What is meant by trade? What is the difference between Local and State level
trade?
Answer:
The exchange of goods and services among people, states and countries, through
market channels, is referred to as trade.
Local trade is carried in cities, towns and villages.
State level trade is carried between two or more states.
Question 84.
What is ‘international trade’?
Answer:
Exchange of goods (buying and selling of goods) between two countries is called
international trade. It may take place through sea, air or land routes.
Two components of international trade are — export and import.
Question 85.
Why is international trade considered as an ‘economic barometer’ for a country?
Or
“Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its prosperity.”
Support the statement with suitable examples.
Answer:
Exchange of goods (buying and selling of goods) between two countries is called
international trade. It may take place through sea, air or land routes. It has
two components—export and import.
1.
Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its economic
prosperity.
2. As no
country is self-sufficient in all resources, it cannot survive without
international trade.
3. If the
balance of international trade is favourable that is value of export is more
than the value of import, a country will be able to earn more foreign exchange.
4.
International trade encourages a country to develop secondary and tertiary
sectors for exporting goods which can fetch more foreign exchange. In this day
and age of globalization exchange of goods and commodities has also been
overtaken by the exchange of information and knowledge as well.
5. A
country’s economic prosperity can be gauged by the health of its international
trade.
Question 86.
What is ‘balance of trade’? Explain its two types.
Answer:
The balance of trade of a country is the difference between its export and
import value. Balance of trade is of two types:
1.
Favourable balance of trade. When the value of export exceeds the value of
imports, it is called favourable balance of trade.
2.
Unfavourable balance of trade. If the value of imports exceeds the value of
exports, it is called unfavourable balance of trade.
Question 87.
Write a note on the changing nature of international trade in India.
Answer:
International trade in India has undergone a substantial change in the last
fifteen years. Liberalisation policies of government and lifting of barriers on
trade has made it truly global in nature. India has trading relations with all
major trading blocks and geographical regions of the world. In this day and age
of globalisation, exchange of goods and commodities has been overtaken by the
exchange of information and knowledge. India has proved to be a world leader in
software technology and is earning large amounts of foreign exchange through the
export of software technology.
Tourism As A Trade
Question 88.
Why is ‘tourism’ considered as a trade and industry in India? Give reasons in
support of your answer.
Answer:
1. With
increase in the number of foreign tourists visiting India, we earned foreign
exchange worth Rs. 21,828 crore in 2004 which is further increasing year by year
making tourism an important trade.
2. Over 2.6
million foreign tourists visit India every year for appreciating our heritage,
our culture for medical purposes or for business purposes, etc.
3. Over 15
million people are directly engaged in the tourism industry.
4. Tourism
promotes national integration, provides support to local handicrafts and
cultural pursuits.
5. Tourism
also helps in the development of international understanding about our culture
and heritage.
6.
Rajasthan, Goa, Jammu & Kashmir and temple towns of south India are the most
popular tourist destinations. These states earn huge sums of money from tourism
trade.
Question 90.
Give reasons for which foreign tourists visit India.
Answer:
Foreigners visit India for various purposes. These are:
1. Heritage
tourism
2.
Eco-tourism
3. Adventure
tourism
4. Cultural
tourism
5. Medical
tourism
6. Business
tourism
- Broadened cultural awareness of each other’s tradition.
- It is economically viable. India is a great value
destination as tourists can travel cheaply and lavishly.
- Indian hospitality is famous worldwide — ‘Atithi devo
bhava’.
- India is an avenue to explore spirituality through yoga,
meditation.
- Indian cuisine predominantly, North Indian is world
famous.
India has several historical and architectural attractions. Regional
handicrafts and ethnic designs of traditional products attract tourists
Question 91.
“Efficient means of transport are pre-requisites for the fast development.”
Express your views in favour of this statement.
Answer:
I agree with the above statement. Without efficient means of transport, no
development can be made in a country. The arguments in favour of the statement
are as mentioned below:
- The goods and services do not move from supply locales
to demand locales on their
own. - The movement of goods and services from supply locations
to demand locations necessitates the need for transport.
- A large number of workers are engaged in doing this work
so that the needs of people may be fulfilled.
- Traders too use transport facilities for sending and
receiving goods for selling to the consumers.
- If no transport facility is available, they may not be
able to send their goods and products to different places. Their trade will,
thus, be concentrated to one place only. The pace of development of a country,
thus, depends upon the production and movement of goods and services to all the
parts.
Question 92.
Do you agree with the view that transport, communication and trade are
complementary to each other? Explain you views.
Answer:
Yes, means of transport, communication and trade are complementary to each
other as mentioned below :
- Transport and communication provide the infrastructural
basis for conducting trade.
- The growth in trade also leads to creation of more
infrastructure to match the volume of trade because increase in the volume of
trade may need more means of transport.
- More trade creates avenue for investment in
infrastructure through the revenue generated by trade.
- The growth in trade means more transport like roads,
railways, air, water and pipelines to be developed to keep the wheels of economy
moving.
- Communication helps in commercial transactions to be
completed across different places all over the world. It helps to cross the
geographical barriers and keeps the traders informed about their business
instantly. The modern means of communication such as e-mail, mobile etc. are of
great help for the traders all over the world. The world has become a village.
Thus it can be said that progress in science, technology, means of transport and communication are responsible for increase in trade and commerce.
Question 93.
“Roadways still have an edge over railways in India.” Support the statement with
arguments.
Answer:
See Textbook Question 2(1) and (2).
Question 94.
Describe different kinds of roads according to their capacity.
Answer:
The roads are classified into six classes according to their capacity as
mentioned below :
(1) Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways :
- It is a major road development project linking
Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai and Delhi by six-lane Super Highways.
- The object of these Super Highways is to meet the
requirements of fast movement of traffic in the country and to reduce the time
and distance between the mega cities of India.
- North-South corridor connects Srinagar (JK) to
Kanniyakumari (Tamil Nadu).
- East-West corridor connects Silchsr, (Assam) to
Porbandar (Gujarat).
- These highway projects are being implemented by the
National Highway Authority of
India (NHAI). ”
(2) National Highways:
- National Highways link extreme parts of the country
including one state with another.
- These are primary road systems of national importance.
Therefore, these are con¬structed and maintained by the Central Public Works
Department (CPWD) of the central government.
The historical Sher Shah Suri Marg is called National Highway No. 1 between Delhi and Amritsar. - A number of major National Highways run in North-South
and East-West directions.
(3) State Highways:
- These roads link a state capital with different district
headquarters.
- These roads are constructed and maintained by the State
Public Works Department in State and Union Territories.
(4) District Roads:
- These roads connect the district headquarters with other
places of the district.
- These roads are maintained by the Zila Parishad.
(5) Rural Roads:
- Rural roads or village roads link rural areas and
villages with towns.
- Under Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana provisions
have been made to link every village in the country to a major town by an all
season motorable road. Thus, it is hoped that the condition of rural roads will
improve in future.
(6) Border Roads:
- These roads are in the border areas of the country.
- Border Roads Organisation which is a Government of India
undertaking constructs and maintains these roads.
- These roads are of strategic importance in the northern
and north-eastern border areas.
- These roads have improved accessibility in areas of
difficult terrain.
- These roads have also helped in the economic development
of these areas.
Question 95.
How roads are classified on the basis of the type of material used for their
construction?
Answer:
On the basis of type of material use for their construction, roads are
classified into two types as mentioned below :
(1) Metalled roads :
- These roads are made of cement concrete or even bitumen
or coal tar.
- One can go fast on metalled roads.
- These are all weather roads.
- These are maintained by the government.
(2) Unmetalled roads:
- These are not all weather roads.
- These are made of mud and gravel which are generally
found in the rural areas.
- These are sometimes made even of sand and laid as
extended roads.
- These may not be fit for use in rainy season.
- The unmetalled roads are maintained by common people.
- One cannot go fast on these roads.
Question 96.
Describe the problems that are being faced in road transportation in India.
Answer:
The problems that are being faced in road transportation in India are as
given below :
- Inadequate network in view of the volume of traffic and
passengers.
- Half of the roads are unmetalled that cannot be used
during rainy season.
- National highways are inadequate to meet the rush of
traffic.
- Roads in the cities are highly congested.
- Most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow.
- Roadside amenities like emergency health services,
police protection on the highways are not adequate.
The above problems need immediate attention of the government to make road transport more popular and useful in the country.
Question 97.
“Railways are the principal mode of transportation in India.” Explain.
Answer:
The railways are the main artery of inland transport in India. It is the
lifeline of the country as mentioned below:
- Railways are the principal mode of transportation for
freight and passengers.
- The Indian Railways have a network of 7,031 stations,
7,817 locomotives, 5,321 passenger service vehicles, 4,904 other coach vehicles
and 228,170 wagons as on 31st March, 2004.
- The total length of railways is 63,221 km.
- Railways are useful in conducting business, sightseeing,
and pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances.
- It is the largest public undertaking in the country.
Thus, it is clear that the railways are playing an important role in our
economy. It has played an important role in the integration of the country as
people can go from one region to another easily.
- It is the largest public undertaking in the country.
Thus, it is clear that the railways are playing an important role in our
economy. It has played an important role in the integration of the country as
people can go from one region to another easily.
Question 98.
Give brief description of the Indian Railway’s gauge operations.
Answer:
A table showing Indian Railway’s Track on multiple gauge operations is given
below
(Source : India Year Book, 2006)
|
Gauge in metres |
Route (km) |
Running Track (km) |
Total Track (km) |
|
(1) Broad Gauge (1.676)
(2) Meter Gauge (1.000)
(3) Narrow Gauge (0.762 & 0.610) |
46,807
13,209
3,124 |
66,754
13,976
3,129 |
88,517
16,489
3,450 |
|
Total |
63,221 |
83,859 |
1,08,486 |
Question 99.
Analyse the physiographic and economic factors that have influenced the
distribution pattern of railway network in our country.
Answer:
Physical and economic factors have influenced the distribution pattern of the
Indian Railway network in the following ways :
(1) Northern plains :
- Level land, high population density and rich
agricultural re¬sources has favoured development of railways in these plains,
- However, a large number of rivers requiring construction
of bridges across their wide river beds posed some obstacles
(2) Peninsular region and the Himalayan region:
- It is a hilly terrain. The railway tracks are laid
through low hills, gaps or tunnels. So, it is very difficult to lay the railway
lines.
- The Him alayan mountainous regions too are not
favourable for the construction of railway lines due to high relief, sparse
population and. lack of economic opportunities.
(3) Desert of Rajasthan: On the sandy plain of western
Rajasthan too, it is very difficult to lay railway lines which has hindered the
development of railways.
(4) Swamps of Gujarat, forested tracts of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh,
Orissa and Jharkhand : These are also not suitable for the development of
the railways.
(5) The contiguous stretch of Sahyadri could be crossed only through gaps
or passes (ghats). Although the Konkan railway along the west coast has been
developed but it has also faced a number of problems such as sinking of track in
some stretches and landslides.
Question 100.
Describe the problems being faced by the railways.
Answer:
The problems being faced by the railways are as mentioned below :
- Old track and poor state rolling stock: The
major problem faced by Indian railways is that the tracks are old and outdated.
These old tracks cause many serious railway accidents. This has also resulted in
speed restrictions.
- Travel without tickets: A large
number of passengers travel without purchasing tickets. Indian railways have to
bear extra loss of about? 5 crore every year on account of travelling without
tickets.
- Railway accidents: The incidence of
railway accidents in our country is greater as compared to other countries of
the world. Accidents occur due to the errors and negligence of the employees.
- Attack on railways: During
disturbances or strikes, people attack railway stations. This leads to loss of
railway property. For instance, there was heavy loss of railways in the
movements of West Bengal, Telangana and Assam and other places in the past.
- Lack of modern management: There is
lack of modern management as railway failed to attract suitable talent. It also
could not make economic analysis for perspective planning tariff.
- Outmoded technology: The rolling
stock technology is outmoded. This has made railways incapable of coping with
increasing transport demand and of raising and imporving the traffic volume and
flows at lower unit cost of operation.
- Problem of laying double lines: Most
of the railway lines are single lines which create great inconvenience to the
railway organisation and passengers.
- Competition with road transport: The
competition with road transport is harming the railways. The lack of
coordination between railways and road transport has lowered the earning
capacity of the railways.
Question 101.
What is pipeline transportation? Give any two points of importance of pipeline
transportation.
Or
Explain uses and advantages of pipeline transportation.
Answer:
(1) Under pipeline transportation now pipelines are
used to transport crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil and
natural gas fields to oil refineries, fertiliser factories and big thermal power
plants.
(2) Advantages:
- Crude oil and other petroleum products can be
transported to far away inland locations like Barauni and Panipat.
- Pipelines have proved beneficial for gas based
fertiliser plants.
- Solids can also be transported through a pipeline when
converted into slurry.
- Running cost of pipelines is minimal but initial cost of
laying pipeline is high.
- There are no trans-shipment losses or delays.
(3) Networks of pipelines: There are three networks
of pipeline transportation as given below:
- From oil field in upper Assam to Kanpur iJJttar Pradesh)
via Guwahati, Barauni and Allahabad. It has branches from Barauni to Haldia via
Rajbandh, Rajbandh to Maurigram and Guwahati to Siliguri.
- From Salaya in Gujarat to Jalandhar in Punjab via
Viramgam, Mathura, Delhi and Sonipat. It has branches to connect Koyali (near
Vadodara, Gujarat), Chakshu and other places.
- Gas pipeline from Hazira in Gujarat connects Jagdishpur
in Uttar Pradesh via Vijaipur in Madhya Pradesh. It has branches to Kota in
Rajasthan, Shahjahanpur, Babrala and other places in Uttar Pradesh.
Question 102.
Describe the inland navigation waterways in India. What are its advan¬tages?
Answer:
(1)
- India has inland navigation waterways of 14,500 km in
length. Out of these only 3,700 km are navigable by mechanised boats.
- National waterways : The
following waterways have been declared as the National Waterways by the
government:
- The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia (1,620 km)
— N.W. No. 1.
- The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri (891 km)
— N.W. No. 2.
- The West-Coast Canal in Kerala (Kottapurma-Komman,
Udyogamandal and Champakkara canals – 205 km) — N.W. No. 3.
- The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia (1,620 km)
— N.W. No. 1.
- The other inland waterways include the Godavari,
Krishna, Barak, Sunderbans, Buckingham canal, Brahmani. East-West canal and
Damodar Valley Corporation Canal.
(2) The advantages of waterways are as given below:
- Waterways are the cheapest means of transport.
- They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky
goods.
- It is a fuel-efficient transport.
- It is environment friendly mode of transport.
Question 103.
Describe the major sea ports of India.
Answer:
India has a long coastline of 7,516.6 km. There are 12 major and 181 medium and
minor ports. These major ports handle 95 per cent of India’s foreign trade.
The major sea ports of India are as given below:
- Kandla in Kuchchh (Gujarat): Kandla is a tidal port. It
caters to the needs of handling of exports and imports of highly productive
granary and industrial belt stretching across the states of Jammu and Kashmir,
Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- Mumbai port (Maharashtra) : It is the biggest port with
natural and well-sheltered harbdhr. Jawaharlal Nehru port was planned with a
view to decongest the Mumbai port and serve as a support for this region.
- Marmagao port (Goa): It is the premier iron ore
exporting port. This port accounts for about 50% of India’s iron ore export.
- New Mangalore port (Karnataka): It exports iron ore from
Kudremukh mines.
- Kochchi port: It is the extreme south-western port which
is located at the entrance of a lagoon with a natural harbour.
- Tuticorin port (Tamil Nadu): It has a natural harbour
and rich hinterland. It handles cargoes to Sri Lanka and Maldives too.
- Chennai port (Tamil Nadu): It is one of the oldest
artificial ports of India. It is next to Mumbai in volume of trade and cargo.
- Vishakhapatnam port (Andhra Pradesh) : It is the deepest
landlocked and well-protected port.
- Paradip port (Orissa): It specialises in the export of
iron ore.
- Kolkata port (West Bengal): It is ar»-inland riverine
port. It is a tidal port and requires constant dredging of Hoogly.
- Haldia port: It was developed as a subsidiary port in
order to relieve growing pressure
on the Kolkata port.
Question 104.
Describe the air transport in India. What are the advantages of airways?
Answer:
(1)
- In India, air transport was nationalised in 1953.
- Domestic air services: These
services are provided by Indian Airlines, Alliance Air, private scheduled
airlines and non-scheduled air operators.
- International air services: These
are provided by Air India.
- Helicopter services: These services are provided
by Pawanhans Helicopters Ltd. to Oil and Natural Gas Commission in its off-shore
operations, to inaccessible areas and difficult areas like north-eastern states
and the interior parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- Neighbouring countries: Indian
Airlines provides services to the neighbouring countries of South and south-east
Asia and the Middle East.
(2) The advantages of airways are as given below:
- It is the fastest and most comfortable mode of
transport. One can reach his destination at faraway places within a short
period.
- It can cover very difficult areas like high mountains,
dreary deserts, dense forests and
long oceanic stretches easily. - It is very useful in hostile areas and natural and
human-made calamities like floods, famines and earthquakes.
Question 105.
Explain why is air transport preferred in north-eastern states of India?
Answer:
The north-eastern states are full of big rivers, dissected relief, dense
forests, frequent
floods. It has international frontiers with Myanmar, Bangladesh and China. Under
these conditions, air transport is preferred in these hilly areas of
north-eastern states because air transport can cover very difficult areas like
high mountains and dense forests. It is also useful t in hostile areas and
natural and human-made calamities like floods. It is only in the north¬ eastern
states that special provisions are made to extend the air services to the common
people. As such air travel is within their reach and preferred.
Question 106.
Describe the main features of the Indian postal network.
Answer:
Main features of the Indian postal network are as given below :
- The Indian postal network is the largest network in the
world.
- Types of mail: There are two types of mail :
- First-class mail: Cards and envelops
fall in this category.
- Second-class mail: It includes book
packets, registered newspapers and periodicals.
- Mail channels: For quick delivery of
mails, six channels have been introduced. These are – Rajdhani Channel, Metro
Channel, Green Channel, Business Channel, Bulk Mail Channel and Periodical
Channel.
Question 107.
Write a short note on the telecom networks in India.
Answer:
- India’s telecom network is one of the largest networks
in Asia.
- All urban places and two-thirds of the villages have
Subscriber Trunk Dialling (STD) telephone facility. Special provisions have been
made to extend twenty-four hours STD facility to all villages. ‘
- There is a uniform STD rate in the country. It has been
made possible by integrating the development in space technology with
communication technology.
Question 108.
Which are the main means of mass communication? Explain the importance of
‘Radio’ and ‘Television’ as an effective mere of mass communication in India.
Answer:
- Radio, television, newspapers, magazines, books and
films are the main means of mass communication.
- The importance of‘ Radio’ and ‘Television’ as an
effective means of communication in India is due to the factors as mentioned
below :
- Radio and television provide entertainment to the
people.
- These create awareness among people about various
national programmes and policies as debates are conducted on television and
radio.
- Programmes are broadcasted in different languages for
all types of people.
- Doordarshan, the national television channel of India
and one of the largest terres¬trial networks in the world, broadcasts various
types of programmes from entertainment, educational to sports etc., for
different age groups.
- Radio and television provide entertainment to the
people.
Question 109.
What is the position of India in the production of films? What type of Rims are
produced and which authority certifies them?
Answer:
- India is the largest producer of feature films in the
world.
- Various types of films are produced – such as short
films, video feature films and video short films.
- The Central Board of Film Certification certifies both
Indian and foreign films.
Question 110.
Why international trade is considered the economic barometer for a country?
Answer:
The progress in international trade leads to economic prosperity. If the value
of
exports exceeds the value of imports, the country is considered to have made
advancement in international trade. It is called favourable balance of trade.
Developed countries come in this category. On the other hand, if the value of
imports exceeds the value of exports, it is termed as unfavourable balance of
trade. Thus, advancement of international trade is an index to its economic
prosperity and considered the economic barometer for a country.
Question 111.
Write a short note on how tourism as a trade has flourished in India.
Answer:
The tourism as a trade has flourished in India as mentioned below :
- There has been increase of 23.5 per cent during the year
2004 as against the year 2003 and contributed? 21,828 crore of foreign exchange.
- Over 2.6 million foreign tourists visit India every
year.
- Over 15 million people are directly employed in the
tourism industry in the country.
- It promotes national integration because people from
India also go from one place to another place.
- It helps- in the development of international
understanding. Foreign tourists are attracted by Indian culture and traditions.
- It supports local handicrafts and cultural pursuits
because tourists purchase many products during their visits.
- Foreign tourists visit India for visiting places of
heritage or to have adventure in hilly region or to have business with India.
- Rajasthan, Goa, Jammu and Kashmir and temple towns of
south India have attracted many tourists from all over the world.
MAP QUESTIONS
Question 1.
On the map of India show the following:
(1) Golden Quadrilateral
(2) North-South corridor
(3) East-West corridor
(4) National Highways with number.
Answer:
- Golden Quadrilateral will connect Delhi, Mumbai,
Chennai, Kolkata and Delhi. Its length will be 5,846 km.
- North-South corridor: It will
connect Srinagar and Kanniyakumari.
- East-West corridor will connect Silchar and Porbandar.
- National Highways connect one state with another. They
are of national importance. These roads are maintained by the Central
Government.
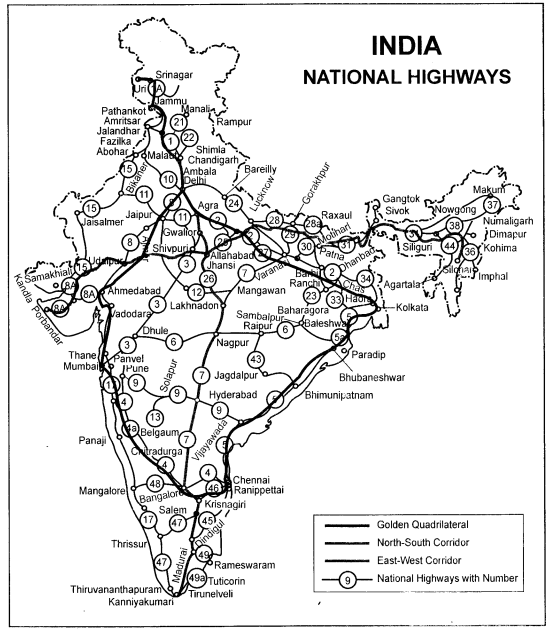
Question 2.
On the outline map of India show the following:
- Sea ports
- International Airports.
Answer:
Major sea ports and airports are as given below :
- Sea ports: Kandla, Mumbai, Marmagao, New Mangalore,
Kochchi, Tuticorin, Paradip, Vishakhapatnam, Chennai and Haldia.
- International Airports: Amritsar (Raja Sansi), Delhi,
Mumbai, Hyderabad, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Kolkata. See map given below :
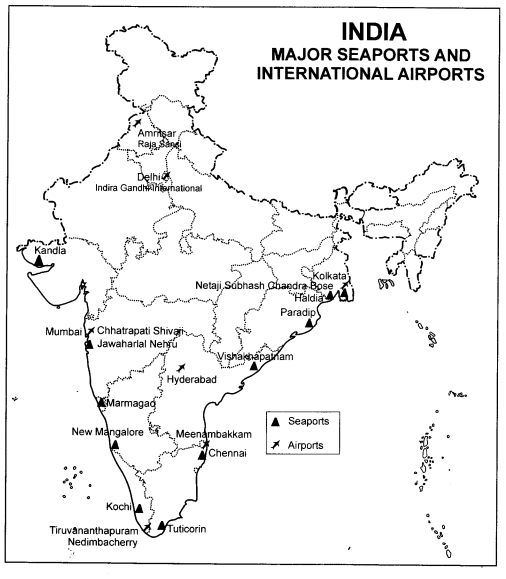
Question 3.
On the map of India locate headquarters of the railway zones in India.
Answer:
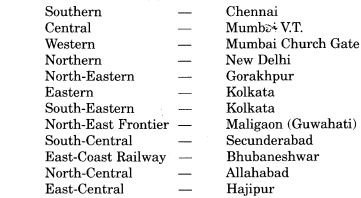
The headquarters of the sixteen zones are as given below :

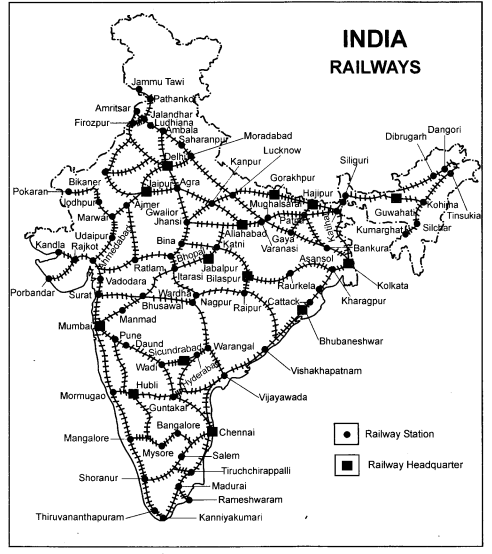
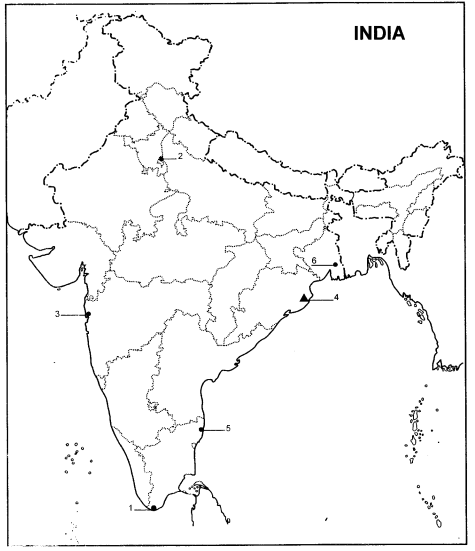
Question 4.
Six features with serial numbers (1) to (6) are marked in the given political
outline map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following
information and write their correct names on the lines marked in the map.
(1) Southern point of North-South corridor.
(2) A point in Golden Quadrilateral.
(3) An International Airport.
(4) A major sea port.
(5) Headquarter of Eastern Railways.
Answer:
- Kaniyakumari
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Paradip
- chinnai
- Kolkata