Social Science Manufacturing Industries
Very Short Answer Question s (VSA) 1 Mark
Question 1.
How is economic strength of a country-measured?
Answer:
The economic strength of a country is measured by the development of
manufacturing industries.
Question 2.
What is NMCC?
Answer:
National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council.
Question 3.
What are the benefits of cities in industrialisation?
Answer:
Cities provide markets and provide services such as banking, insurance,
transport, labour, consultants and financial advice etc. to the industry.
Question 4.
Name the places where most manufacturing units were located before independence.
Answer:
Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai.
Question 5.
Which are the factors for the ideal location of industry? Mention any one.
Answer:
Availability of raw material.
Question 6.
Mention any two agro-based industries.
Answer:
Cotton and woolen textile industry.
Question 7.
How industries are divided on the basis of capital investment?
Answer:
- Small scale industry.
- Large scale industry.
Question 8.
Mention the industries on the basis of ownership.
Answer:
- Public sector owned and operated by the government
agencies – BHEL.
- Private sector owned and operated by individuals –
TISCO.
- Joint sector which are owned and run jointly by the
state and individuals – Oil India Ltd.
- Cooperative sector industries owned and operated by the
producers or suppliers of raw material, workers or both g. sugar industry in
Maharashtra.
Question 9.
In which state spinning continues to be centralised?
Answer:
Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
Question 10.
Mention two places of silk textile industries.
Answer:
Srinagar, Anantnag and Baramula in Jammu & Kashmir.
Question 11.
Where most of the jute mills are located?
Answer:
Most of the jute mills are located in West Bengal mainly along the banks of the
Hugh river.
Question 12.
State one reason for increase in internal demand for jute products.
Answer:
The internal demand has been on the increase due to government policy of
mandatory use of jute packaging.
Question 13.
In which year the National Jute Policy was formulated?
Answer:
2005.
Question 14.
What is the position of India in the production of sugar, gur and khandsari?
Answer:
India stands second as a world producer of sugar but occupies the first place in
the production of gur and khandsari.
Question 15.
In recent years why is there a tendency for the sugar mills to shift and
concentrate in the Southern and Western states? State any one reason.
Answer:
The sugarcane produced there has a higher sucrose content.
Question 16.
What are the challenges before sugar industry? Mention any one.
Answer:
Old and inefficient methods of production.
Question 17.
What do you mean by mineral based industries? Give one example.
Answer:
- Industries that use minerals and metals as raw materials
are called mineral based industries.
1. Iron and
steel
2. Cement.
Question 18.
State any one feature of iron and steel industry.
Answer:
Iron and steel is a heavy industry because all the raw materials as well as
finished goods are heavy and bulky entailing heavy transportation costs.
Question 19.
Name any one integrated steel plant.
Answer:
TISCO.
Question 20.
By which authority, the steel of all public sector undertaking is marketed?
Answer:
All public sector undertaking market their steel through, Steel Authority of
India Ltd.
Question 21.
Why the Chhotanagpur region has the maximum concentration of iron and steel
industries?
Answer:
The Chhotanagpur region has the maximum concentration of iron and steel
industries due to low cost of iron ore, high grade raw material in proximity,
cheap labour and vast growth potential in the home market.
Question 22.
State any one feature of aluminium smelting industry.
Answer:
Aluminium is light, resistant to corrosion, a good conductor of heat, malleable
and becomes strong when it is mixed with other metals.
Question 23.
What is the contribution of chemical industry in the GDP?
Answer:
The chemical industry contributes approximately 3 per cent of the GDP.
Question 24.
Which are organic chemicals? How are they used?
Answer:
Organic chemicals include petrochemicals which are used for manufacturing of
synthetic fibres, synthetic rubber, plastics, dye-stuffs, drugs, and
pharmaceuticals.
Question 25.
When the fertiliser industry has expanded significantly?
Answer:
After the Green Revolution the fertiliser industry has expanded significantly to
many parts of the country.
Question 26.
Which materials are required by the cement industry?
Answer:
The cement industry requires bulky and heavy raw materials like limestone,
silica, alumina and gypsum.
Question 27.
What is the main cause for rapid strides in the cement industry in 1980s and
1990s?
Answer:
Decontrol of price and distribution since 1989 and other policy reforms led the
cement industry to make rapid strides in capacity, process, technology and
production.
Question 28.
What is the use of automobiles?
Answer:
Automobiles provide vehicle for quick transport of good services and passengers.
Question 29.
Which city has emerged as the electronic capital of India?
Answer:
Bangalore.
,
Question 31.
What does the software technology park provide?
Answer:
The software technology parks provide single window service and high data
communication facility to software experts.
Question 32.
Which machine helps in reducing noise pollution?
Answer:
Silencers.
Question 33.
Name any two industries that are responsible for water pollution.
Answer:
Chemical, textile, dying and petroleum refineries.
Question 34.
What is manufacturing? To which sector of economy does it belong?
Or
“The economic strength of a country is measured by the development of
manufacturing industries”. Support the statement with arguments.
Answer:
Manufacturing. Production of goods in large quantities after processing from raw
materials to more valuable products is called manufacturing.
Manufacturing belongs to secondary sector in which the primary materials are
processed and converted into finished goods. The economic strength of a country
is measured by the development of manufacturing industries.
Question 35.
Write the importance of ‘manufacturing sector’ for our nation.
Or, “Manufacturing industry is considered the backbone of economic development
of India.” Give reasons.
Answer:
Importance of manufacturing industries for India:
1. It helps
in modernizing agriculture, which is the base of our economy.
2. It
reduces heavy dependence on agricultural income by providing jobs in
non-agricultural sectors.
3.
Industrial development is necessary for eradication of poverty and unemployment
because people get jobs and generate more income.
4. Export of
manufactured goods expands trade and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
5.
Industries bring riches faster to a nation because manufacturing changes raw
materials into finished goods of a higher value, so industrial development
brings prosperity to the country.
Question 36.
“Agriculture and industry are not exclusive of each other, but move hand in
hand.” Give arguments in favor of this statement.
Or,
Explain with examples how industries in India have given a major boost to
agriculture.
Answer:
Agriculture and industry in India are inseparable or interdependent on each
other:
1.
Agro-industries in India have boosted agriculture by raising its productivity.
2.
Industries depend on agriculture for their raw materials, e.g. cotton textile
industry.
3.
Industries provide many agricultural inputs like irrigation pumps, fertilisers,
insecticides, PVC pipes, machines and tools etc. to the farmers.
4.
Manufacturing industries have assisted agriculturists to increase their
production and also made the production processes very efficient.
5.
Development of different modes of transport by industrial sector has not only
helped farmers to obtain agricultural inputs but has also helped them trade
their products.
Question 37.
Write the contribution and present growth rate of manufacturing sector in
national economy. Suggest measures to increase the industrial growth rate.
Answer:
The share of manufacturing sector has stagnated at 17% of GDP. The trend of
growth rate over the last decade has been around 7% per annum. Since 2003, it
has shown an increased growth rate of 9-10% per annum. The desired growth rate
over the next decade is 12%. To attain this target, following steps can be
taken:
1.
Appropriate policy interventions by the government.
2. Renewed
efforts by the industries to improve productivity.
Question 38.
List the major factors which affect the location of an industry at a place. What
is the key to the decision of ‘factory location’?
Answer:
1. Raw
material. Cheap and abundant availability of raw material. Industries which use
heavy and perishable raw material have to be located close to the source of raw
material.
2. Labour.
Availability of cheap labour is necessary for keeping the cost of production
low.
3. Power.
Cheap and continuous supply of power is extremely necessary for continuity in
the production process.
4. Capital.
It is necessary for developing infrastructure, for the entire manufacturing
process and for meeting manufacturing expenditure.
5. Banking
and insurance facilities, favourable government policies are other factors which
affect location of an industry.
The ‘key’ to the decision of a factory location is least cost so that the
venture is profitable.
Question 39.
“Industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand.” Explain.
Answer:
After an industrial activity starts, urbanisation follows. Some industries are
located in and around the cities. Thus industrialisation and urbanisation go
hand in hand. Cities provide markets, services such as banking, insurance,
transport, labour, consultants and financial advice, etc. to industries.
Question 40.
What are ‘agglomeration economies’ in the industrial context?
Answer:
Many industries tend to come together to make use of the advantages offered by
the urban centres known as ‘agglomeration economies’. Gradually, a large
industrial agglomeration or clustering takes place around an urban centre.
Question 41.
State any five basis on which industries are classified.
Answer:
1. On the
basis of source of raw materials used — Agro-based and mineral-based.
2. According
to their main role — Basic and Consumer industries.
3. On the
basis of capital investment—Small-scale and large-scale industries.
4. On the
basis of ownership — Public Sector, Private Sector, Cooperative Sector, Joint
Sector.
5. Based on
the bulk and weight of raw material and finished goods—heavy industries, Light
industries.
Question 42.
Classify industries on the basis of capital investment. How are they different
from one another? Explain with examples.
Answer:
On the basis of capital investment industries can be classified as:
1.
Small-scale industry
2.
Large-scale industry
Difference:
If the investment is more than one crore rupees in any industry, it is
considered as a large scale industry.
For example, Iron and Steel industry, cement industry.
If the investment is less than one crore rupees in any industry, it is
considered as a small scale industry.
For example, Plastic industry, Toy industry.
Question 43.
Classify industries on the basis of source of raw material. How are they
different from each other?
Answer:
On the basis of sources of raw material industries are classified as:
(i) Agro based industries;
(ii) Mineral based industries
Difference between Agro-based industries and Mineral-based industries
|
Agro-based industries |
Mineral-based industries |
|
They obtain their raw materials from agricultural products.
Example: Textiles —cotton, jute, silk and woolen. Rubber, Sugar, Coffee,
Tea and Edible Oil, etc. |
They obtain their raw materials from minerals. Example: Iron and steel,
cement, machine tools, petro-chemicals, etc. |
Question 44.
Explain the types of industries on the basis of ownership and give one example
of each.
Answer:
Four types of industries based on ownership are:
1. Public
Sector industries. They are owned and operated by government agencies, e.g.
BHEL, SAIL, etc.
2. Private
Sector industries are owned and operated by an individual or a group of
individuals, e.g. TISCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd., Dabur Industries.
3. Joint
Sector industries are jointly run by the Public (government) and Private Sector
(individuals), e.g. Oil India Ltd.
4.
Cooperative Sector industries are owned and operated by the producers or
suppliers of raw materials, workers, or both. They pool in the resources and
share the profits or losses proportionately, e.g. sugar industry in Maharashtra
and coir industry in Kerala.
Question 45.
Name four agro-based and four mineral-based industries.
Answer:
Four Agro-based industries are cotton textile, jute textile, sugar industry and
edible oils industry.
Four Mineral-based industries are iron and steel industry, aluminium industry,
copper smelting industry and cement industry.
Question 46.
Explain the role of agro-based industries in Indian economy.
Answer:
Role of agro-based industries in Indian economy:
1. The
agro-based industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by
raising its productivity as they obtain their raw material from agriculture.
2.
Development and competitiveness of industries has not only assisted
agriculturists in increasing their production but also made the production
processes very efficient.
3. The
farmers are heading for commercial farming to produce high value crops for
industries. This may in turn help improve the economic status of the farmers.
4. These
agro-based industries, by creating demand, support the growth of many other
industries e.g., packaging materials and engineering works etc.
Question 47.
Explain the significance of textile industry in India.
Or
The textile industry is the only industry which is self-reliant and complete in
the value-chain? Justify this statement?
Or
“Textile industry occupies a unique position in the Indian economy”. Support the
statement with appropriate arguments.
The Textile industry occupies a unique position in the Indian Economy because:
1. It
contributes significantly to industrial production (14%).
2. It
employs largest number of people after agriculture, i.e. 35 million persons
directly.
3. Its share
in the foreign exchange earnings is significant at about 24.6%.
4. It
contributes 4% towards GDP.
5. It is the
only industry in the country which is self-reliant and complete in the value
chain, i.e., from raw material to the highest value added products.
Question 48.
Write the stages of the development of cotton textile industry in India from
ancient to modern times.
Answer:
Stages of development of Cotton Textile Industry in India:
1. In
ancient India, cotton textiles were produced with hand spinning and handloom
weaving techniques.
2. After the
18th century, powerlooms came into use.
3. Our
traditional industries suffered a setback during the colonial period because
they could not compete with the mill-made cloth from England.
4. Today,
there are nearly 1600 cotton and human-made fibre textile mills working at
various levels and owned by varied sectors. It is a decentralised industry
today.
Question 49.
List factors which favoured the location and concentration of cotton textile
industry in Maharashtra
and Gujarat in early years.
Answer:
1.
Availability of raw cotton was abundant and cheap because these are the
traditional cotton growing States.
2. Moist
climate in these coastal States also helped in the development of cotton textile
industry because humid conditions are required for weaving the cloth, else the
yarn breaks.
3.
Well-developed transportation system and accessible port facilities in
Maharashtra and Gujarat led to their concentration there.
4. Proximity
to the market is yet another factor as cotton clothes are ideal and comfortable
to wear in these warm and humid States.
5. Cheap
labour was abundantly available.
Question 50.
Write two major differences between the weaving and spinning sectors of cotton
textile industry.
Answer:
|
Spinning Sector |
Weaving Sector |
|
1. Spinning is a centralised activity mainly done in Maharashtra, Gujarat
and Tamil Nadu. |
1. Weaving is a highly decentralised activity. It provides scope for
incorporating traditional skills with modernity. So weaving is done at various
levels, example, handlooms, power- looms, etc. |
|
2. India has world class production in spinning. |
2. Weaving supplies low quality of fabric as it cannot use much of the
high quality yam. |
Question 51.
Name the main countries to which India exports its cotton yarn and cotton goods.
Answer:
The major countries are: Japan, USA, UK, Russia and France.
Question 52.
What are the problems faced by the cotton textile industry?
Answer:
Problems faced by the cotton textile industry:
1. Power
supply is erratic in our country.
2. Machinery
needs to be upgraded, especially in weaving and processing sectors.
3. Low
output of labour.
4. We still
need to import cotton in spite of the fact that the production of cotton in the
country has increased.
5. Stiff
competition from the synthetic fibre industry.
Question 53.
Explain the main factors which are responsible for the concentration of jute
mills along the banks of Hugli River.
Answer:
Factors responsible for the concentration of jute industry on the banks of
Hugli:
1. Proximity
of the jute producing areas to the Hugli Basin.
2.
Inexpensive water transport provided by the Hugli River.
3. It is
well connected by a good network of railways, waterways and roadways to
facilitate movement of raw materials to the mills.
4. Abundant
water for processing raw jute.
5.
Availability of cheap labour from West Bengal and the adjoining States of Bihar,
Orissa and Uttar Pradesh.
6. Kolkata
as a port and large urban centre, provides banking, insurance and port
facilities for export of jute goods.
Question 54.
Write down the major problems/challenges faced by the jute industry.
Answer:
The major challenges faced by the jute industry:
1. Stiff
competition in the international market from synthetic substitutes.
2. Stiff
competition from other competitors like Bangladesh, Brazil, Philippines, Egypt
and Thailand.
3. The
demand for jute products is declining both in international as well as domestic
markets.
4. The cost
of production is high and many jute mills still have obsolete machinery.
Question 55.
What are the objectives of formulating National Jute Policy? In which year was
this policy formulated?
Do you think that the demand for jute products will pick up at global level and
why?
Answer:
National Jute Policy was formulated in 2005 with the following objectives:
1. For
increasing productivity
2. For
improving quality
3. For
ensuring good prices to the jute farmers
4. For
enhancing the yield per hectare
Yes, the demand for jute products in the world market will grow. The
growing global concern for environment friendly, biodegradable material, also
led to the government policy of mandatory use of jute packing.
Question 56.
Name some countries which are the main buyers of Indian jute products.
Answer:
The main buyers of Indian jute products are:
1. USA
2. Canada
3. Russia
4. United
Arab Republic
5. UK
6. Australia
Question 57.
Why are the sugar mills located close to the sugarcane fields?
Or
Why are sugar mills concentrated in sugarcane producing areas?
Answer:
Reasons for location of sugar mills close to the fields:
1. The raw
material used, (i.e.,) sugarcane is bulky and perishable.
2. It cannot
be transported to long distances because its sucrose content dries up fast, so
it should be processed within 24 hours of its harvest.
Question 58.
Write the distribution of sugar industry in India.
Answer:
There are over 460 sugar mills in the country. Out of these, 60% mills are in
Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. Rest of the mills are spread over Maharashtra, Tamil
Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat and Punjab.
Question 59.
Why are sugar mills shifting and concentrating in southern and western State of
India? Give reasons.
Answer:
Sugar Industry is shifting towards southern and western States, because:
1. Cane
produced here has higher sucrose content.
2. The
favorable climatic conditions (cooler climate) ensure a longer growing and
crushing season.
3. The
Cooperatives are more successful in these States and sugar industry being
seasonal in nature, is ideally suited to cooperative sector.
4. Yield per
hectare is higher in southern States.
Question 60.
What are the major challenges faced by sugar industry?
Answer:
Challenges faced by the sugar industry:
1. Seasonal
nature of the industry.
2. Old and
inefficient methods of production.
3. Delays in
transportation of cane to the factories.
4. The need
to maximize the use of bio gas.
Question 61.
Why is iron and steel industry called the basic or key industry? Explain.
Answer:
1. Since all
the other industries—heavy, medium and light, depend on it for their machinery.
2. Steel is
needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods.
3. Steel is
needed for construction material, defense and medical equipment’s.
4. Steel is
needed for telephonic, scientific equipment and a variety of consumer goods.
5.
Production and consumption of steel is often regarded as the index of a
country’s development.
Question 62.
(a) Why is iron and steel industry called a heavy industry? Give reasons.
(b) Write four raw materials of iron and steel industry and the proportions in
which they are required.
Answer:
(a) Iron and steel industry is a heavy industry because:
1. All the
raw materials used are heavy and bulky.
2. The
finished goods are also very heavy and bulky entailing heavy transportation
costs.
3. Iron-ore,
coal, limestone are the major raw materials used in producing iron and steel and
they are heavy.
4.
Transportation costs of raw materials and finished goods of iron and steel
industry are heavy (costly).
5. Efficient
transport network is needed for its distribution.
(b) The raw materials of iron and steel industry are:
1. Iron ore,
coking coal and limestone are required in the ratio of 4 : 2 : 1.
2. Manganese
is required in some quantity to harden the steel.
Question 63.
Describe India’s position in the world regarding production of steel and its
consumption.
Answer:
1. India
produces 32.8 million tons of steel.
2. India
ranks 9th among the world’s crude steel producers.
3. It is the
largest producer of sponge iron.
4. However,
its per capita consumption per annum is only 32 kg.
Question 64.
Name the marketing body through which all public sector undertakings market
their steel.
Answer:
Steel Authority of India Limited. (SAIL)
Question 65.
What is the major difference between integrated steel plants and mini steel
plants?
Answer:
An integrated steel plant is large and handles everything in one complex—from
putting together raw materials in the blast furnace to steel making, rolling and
shaping. An integrated steel plant uses a blast furnace and iron-ore as raw
material.
Mini steel plants are smaller, have electric furnaces, use steel scrap and
sponge iron. They have re-rollers that use steel ingots also. They produce mild
and alloy steel of given specifications.
Question 66.
Why are most of the iron and steel industries concentrated in and around
Chotanagpur Plateau Region? Give reasons.
Answer:
Reasons:
1. Low cost
of iron-ore which is mined here.
2. High
grade raw materials in close proximity.
3.
Availability of cheap labor.
4. Vast
growth potential in the home market.
5. Efficient
transport network for their distribution to the markets and consumers.
6.
Availability of power because this region has many thermal and hydel power
plants.
7.
Liberalisation and FDI have also given boost to the industry with efforts of
private entrepreneurs.
Question 67.
What problems does the iron and steel industry in India face?
Or,
Why is India not able to perform to her full potential in iron and steel
production? Explain.
Answer:
In spite of being an important producer of iron and steel, India has not been
able to exploit her complete potential, because of:
1. High cost
of production and limited availability of coking coal.
2. Lower
productivity of labor.
3. Irregular
supply of energy.
4. Poor
infrastructure.
Question 68.
What recent developments have led to a rise in the production capacity of the
iron and steel industry?
Answer:
1. In recent
years, liberalisation policy of the government and increased Foreign Direct
Investment in the industry combined with the efforts of private entrepreneurs
and firms have increased production capacity.
2. Greater
allocation of funds and resources for research and development in the production
of steel will provide a boost to the industry.
Question 69.
Write four characteristics and four major uses of aluminum.
Answer:
Four characteristics of aluminum:
1. It is a
light metal.
2. It is
resistant to corrosion.
3. It is a
good conductor of heat.
4. It is
malleable and becomes strong when mixed with other metals.
Four uses (importance) of aluminum.
1. It is
used for manufacturing aircrafts.
2. It is
used for making utensils and packing material.
3. It is
used for making wires.
4. It has
gained popularity as a substitute of steel, copper, zinc and lead in a number of
industries.
Question 70.
How many aluminum smelting plants are set up in India? Write their distribution.
Answer:
There are eight aluminum smelting plants in the country. They are located in the
states of Orissa (Nalco and Balco), West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh,
Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu. Together they produced 600 metric tons
of aluminum in 2004.
Question 71.
(a) Name the mineral used for obtaining aluminum. Write its one important
characteristic by which it can be identified.
(b) List two prime factors required for the location of an aluminum smelting
plant.
Answer:
(a) Bauxite is the raw material used in aluminum industry. It can be identified
by its dark reddish colour and bulky nature.
(b) Two prime factors required for the location of aluminum melting plant are:
·
Regular and cheap supply of electricity.
·
An assured source of raw material at a minimum cost.
Question 72.
Give reasons to highlight the importance of chemical industry in Indian economy.
Answer:
Importance of chemical industry:
1. It
contributes approximately 3% of the GDP.
2. It is the
3rd largest in Asia and occupies 12th position in the world in terms of its
size.
3. It
comprises both large and small-scale manufacturing units producing a variety of
items, ranging from plastic, rubber, soaps, and chemical fertilizers to
pharmaceuticals.
4. The
chemical industry is its own largest consumer. Basic chemicals undergo
processing to further produce other chemicals that are used for industrial
application, agriculture or directly for consumer markets.
5. The
chemical industry in India is fast growing and diversifying in both organic and
inorganic chemicals, thereby generating lot of employment.
Question 73.
Name two groups into which the chemical industry is usually classified. What is
the main difference in their locations over space and why?
Answer:
The two groups are:
1. Inorganic
chemical industry
2. Organic
chemical industry.
Inorganic chemical industries are widely spread over the country because
they use inorganic chemicals like sulphuric acid, nitric acid, alkalies, soda
ash and caustic soda which can be transported anywhere.
Organic chemical plants are located near oil refineries or petrochemical plants
so these are located at specific locations.
Question 74.
List five products each of inorganic and organic chemical industry.
Answer:
Products of
|
Organic Chemical Industry |
Inorganic Chemical Industry |
|
1. Synthetic fibres |
1. Fertilisers |
|
2. Synthetic rubber |
2. Adhesives and paints |
|
3. Plastics |
3. Glass |
|
4. Dye-stuffs |
4. Soaps and detergents |
|
5. Drugs and pharmaceuticals |
5. Synthetic fibres and plastics |
Question 75.
Name four major groups of fertilizers produced in India.
Answer:
Main groups of fertilizers produced in India are:
1.
Nitrogenous fertilizers (mainly urea).
2.
Phosphatic fertilizers.
3. Ammonium
phosphate (DAP).
4. Complex
fertilizers which have a combination of nitrogen, phosphate and potash.
Question 76.
Name the fertilizers which India needs to import and why?
Answer:
Potash is entirely imported as India does not have any reserves of commercially
usable potash or potassium compounds in any form.
Question 77.
What is India’s position in the world with regard to the production of
nitrogenous fertilizers?
Answer:
India is the 3rd largest producer of nitrogenous fertilizers, because:
1. There are
57 fertilizer units manufacturing nitrogenous and complex nitrogenous
fertilizers — 29 for urea and 9 for producing ammonium sulphate as a by-product.
2. There are
68 other small units which produce single super-phosphate.
3. At
present there are 10 Public Sector undertakings.
4. One unit
is in the Cooperative Sector at Hazira in Gujarat under the Fertilizer
Corporation of India (FCI).
Question 78.
What is the main reason for the fertilizer industry to expand in several parts
of the country? Name the states which together produce about 50% of the
country’s fertilizers.
Answer:
After the Green Revolution, the fertilizer industry expanded to several parts
because natural gas could be transported by pipelines to any desired location.
States which produce about 50% of the fertilizers are:
1. Gujarat
2. Tamil
Nadu
3. Uttar
Pradesh
4. Punjab
and
5. Kerala.
Question 79.
Name the important raw materials used in the manufacturing of cement.
Answer:
Raw materials used in cement industry are:
1. limestone
2. silica
3. alumina
4. Gypsum.
Question 80.
Write down the locational factors of cement industry.
Answer:
Factors which affect location of cement industry are:
1.
Availability of raw materials which are heavy and bulky, e.g., limestone,
silica, etc.
2.
Availability of coal and electric power.
3. Rail
transportation.
Question 81.
What factors led to the rapid expansion of cement industry in India?
Answer:
Factors that led to rapid expansion of cement industry are:
1. Decontrol
of cement price since 1989.
2. Decontrol
of distribution of cement since 1989.
3. Many
other policy reforms led the cement industry to expand in capacity, process,
technology and production. Today, there are 128 large plants and 332 mini cement
plants in the country, producing variety of cement.
Question 82.
Why does Indian cement have a large demand in the international market and whom
do we export to?
Answer:
Because of the good quality cement being produced in India, it has found a
readily available market in South and East Asia, Middle East and Africa.
Question 83.
Why has the automobile industry of India witnessed fast growth? Give reasons.
Answer:
Reasons for fast growth in automobile industry:
1. After
liberalisation, the coming in of new and contemporary models stimulated the
demand for vehicles in the market.
2. This led
to the healthy growth of the industry including passenger cars, two and
three-wheelers.
3. Foreign
Direct Investment (FDI) brought in new technology and aligned the industry with
global developments.
4. Trucks,
buses, cars, motorcycles, scooters, three-wheelers and multi-utility vehicles
and commercial vehicles are manufactured in India at various centres such as
Delhi, Gurgaon, Mumbai, Jamshedpur etc.
This industry has experienced a quantum jump in less than 15 years.
Question 84.
“Electronic industry has revolutionized the life of the masses and the country’s
economy.” Justify the statement with suitable arguments.
Answer:
Electronic industry has revolutionized the life of the people and the country’s
economy because:
1. It
produces a wide range of products from transistor sets to televisions and
computers for the masses.
2. It has
helped us set up telephone exchanges, telephones, cellular telecom, radios and
many other equipments which have application in space technology, aviation,
defence, meteorological departments, etc.
3. It has
generated employment for a large number of people. It employed over one million
people by March 2005, out of these 30% are women employees.
4. This
industry has been a major foreign exchange earner because of its fast growing
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) Sector.
5. India is
one of the leading countries in software development. We have 18 software
technology parks which provide high data communication facility to software
experts.
Question 85.
Write the distribution of the electronics industry.
Answer:
Bangalore has emerged as the electronic capital of India. Other important
centres for electronic goods are the four mega cities of Hyderabad, Pune,
Lucknow and Coimbatore.
Question 86.
What is a software technology park? How many such parks do we have? Name the
technology park which is closest to Delhi.
Answer:
Software technology parks provide single window service and high data
communication facility to software experts.
We have 18 software technology parks. Noida Software Technology Park is the
closest to Delhi.
Question 87.
Explain how industries cause air pollution.
Answer:
Air pollution is caused by the industries in the following ways:
1. The
presence of high proportion of undesirable gases, such as sulphur dioxide and
carbon monoxide in the smoke emitted from the industries causes air pollution.
2. Smoke is
emitted by chemical and paper factories, brick kilns, refineries and smelting
plants, and burning of fossil fuels in factories that ignore pollution norms.
3. Air-borne
particulate materials contain both solid and liquid particles like dust, sprays,
mist and smoke.
4. Toxic gas
leaks can be very hazardous with long-term effects, e.g., Bhopal gas leak
tragedy.
Question 88.
Write down the adverse effects of air pollution.
Answer:
Air pollution adversely affects:
1. human
health,
2. animals
and plants,
3. buildings
and
4.
Atmosphere as a whole resulting in climate change.
Question 89.
Suggest measures to control air pollution caused by industries.
Answer:
Measures to control air pollution:
(i) Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to
factories with fabric filters, electrostatic precipitators etc.
(ii) Equipment’s to control aerosol emissions can be used in industries, e.g.,
electrostatic precipitators, scrubbers and inertial separators.
(iii) Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories.(a)
How are water bodies polluted by industries?
(b) Give examples of industries which cause a lot of water pollution.
(a)
1. Water
pollution is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and affluents
discharged
into rivers.
2. Major
water pollutants are dyes, detergents, acids and salts.
3. Heavy
metals like lead and mercury, pesticides and fertilizers and synthetic chemicals
with carbon, plastics and rubber etc. discharged in the water bodies without
treatment pollute these water bodies.
4. Solid
wastes, e.g., fly ash, phospo-gypsum and iron and steel slags, etc. and wastes
from nuclear power plants cause water pollution.
5. Dumping
of harmful chemicals and industrial effluents etc. on the land causes rain-water
to percolate. As a result, these pollutants contaminate ground water.
(b) Major water polluting industries are:
1. Paper and
pulp industries
2. Petroleum
refineries
3. Chemical
industry
4. Tanneries
5. Textile
and dyeing industries
6.
Electroplating industries.
Question 90.
Suggest measures to control water pollution caused by industries.
Answer:
1.
Minimising the use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or
more successive stages.
2.
Harvesting of rain-water to meet water requirements of industries and other
domestic purposes.
3. Treating
hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds in the
following ways:
1. Primary
treatment by mechanical means such as screening, grinding, flocculation and
sedimentation.
2. Secondary
treatment by biological process.
3. Tertiary
treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves
recycling of waste water.
Question 91.
What is noise pollution? Write its effects on human health and suggest ways to
reduce industrial noise pollution.
Answer:
Noise pollution: Unwanted loud noise is an irritant and a source of stress.
Effects of noise pollution on human health:
1. Noise
pollution results in irritation and anger.
2. It can
cause hearing impairment.
3. It can
increase heart rate.
4. It can
raise blood pressure.
5. There can
be physiological effects as well.
Ways to reduce industrial noise pollution:
1. Machinery
and equipment can be fitted with silencers.
2. Almost
all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise.
3. Noise
absorbing material may be used apart from personal use of earplugs and
earphones.
Question 92.
How do industries pollute environment? Explain with five examples.
Answer:
The five types of industrial pollution are:
1. Air
pollution. Smoke is emitted by chemical and paper factories, brick kilns,
refineries and smelting plants, and burning of fossil fuels in factories that
ignore pollution norms. Air-borne particulate materials contain both solid and
liquid particles like dust, sprays, mist and smoke.
2. Water
pollution. Major water pollutants are dyes, detergents, acids and salts. Heavy
metals like lead and mercury, pesticides and fertilizers and synthetic chemicals
with carbon, plastics and rubber etc. discharged in the water bodies without
treatment pollute these water bodies.
3. Noise
pollution. The generators, compressors, machines, furnaces, looms, exhaust fans,
etc. used by industries create a lot of noise. Noise can raise blood pressure
and can have physiological effects as well.
4. Land
pollution. Land and water pollution are closely related. Dumping of industrial
wastes especially glass, harmful chemicals, industrial effluents, packing, salts
and garbage renders the soil useless.
5. Thermal
pollution. Wastes from nuclear power plants, nuclear and weapon production
facilities cause cancer and birth defects.
Question 93.
Explain any five measures to control industrial pollution in India.
Answer:
Five measures to control industrial pollution:
1.
Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to
factories with fabric filters, electrostatic precipitators, etc.
2.
Equipments to control aerosol emissions can be used in industries, e.g.,
electrostatic precipitators, scrubbers and inertial separators. Smoke can be
reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories.
3.
Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements of industries and other
domestic purposes.
4. Treating
hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds.
5. Machinery
and equipment can be fitted with silencers.
6. Noise
absorbing material may be used apart from personal use of earplugs and
earphones.
Question 94.
Explain the pro-active approach adopted by the National Thermal Power
Corporation (NTPC) for preserving the natural environment and resources?
Answer:
NTPC is taking the following measures in places where it is setting up power
plants:
1. Optimum
utilisation of equipment by adopting latest techniques and upgrading existing
equipment.
2.
Minimising waste generation by maximising ash utilisation.
3. Providing
green belts for nurturing ecological balance.
4. Reducing
environmental pollution through ash pond management, ash water recycling system
and liquid waste management.
5.
Ecological monitoring, reviews and online data base management for all its power
stations.
Question 95.
Suggest any three steps to minimise the environmental degradation caused by the
industrial development in India.
Answer:
Steps to minimize the environmental degradation caused by industrial development
in India are:
1.
Minimizing use of water for processing by reusing and recycling in two or more
successive stages. Harvesting of rain water to meet water requirements of
industries and other domestic purposes.
2. Treating
hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds.
3.
Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke to factories with
electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators.
Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories.
4. Machinery
and equipments can be fitted with silencers to prevent noise pollution.
Question 96.
How manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of economic development of
the country? Explain any three points in this regard.
Or
The economic strength of a country is measured by the development of
manufacturing industries.
Explain.
Answer:
The economic strength of a country lies in the development of manufacturing
industries. It is the backbone of development in general and economic
development in particular due to the following reasons:
- Manufacturing industries help in modernising
agriculture.
- It reduces the heavy dependence of people on
agricultural sector. At present more than half of the workers in the country are
still working in the primary sector, mainly in agricultural activities. The
workers in this sector are under employed.
- It provides jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
- Industrial development or manufacturing industries are
necessary for the removal of unemployment and poverty in a country like India.
This was the main philosophy behind public sector ventures in India.
- It brings down regional disparities by establishing
industries in tribal and backward areas.
- Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce
and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
- The industries make a country rich and prosperous
because raw materials are transformed into a wide variety of finished goods of
higher value which increases the income.
Question 97.
“Agriculture and industry are complementary to each other.” Explain with
examples.
Or
How do industries give boost to the agriculture sector?
Answer:
It is true that agriculture and industry move hand in hand.
- There are agro-based industries such as cotton, woollen,
jute, edible oil that get their raw materials from agriculture.
- In return, these industries sell their products such as
irrigation pumps, fertilisers, insecticides, PVC pipes and many other things to
the farmers.
- Thus agro-industries has given boost to agriculture by
raising its productivity and has made the production processes very efficient as
well.
Question 98.
What is the contribution of industry to national economy in India? Compare it
with the East Asian Countries. What is the desired growth and present position
of industry in GDP?
Answer:
- The contribution of industry to national economy has
not been satisfactory for the last two decades. It has stagnated at 17 per cent
of GDP — out of a total of 27 per cent for the industry which includes 10 per
cent for mining, quarrying, electricity and gas.
- In comparison to India’s 17 per cent share in the GDP,
the East Asian Countries have contributed 25 to 35 per cent to their GDP.
- The trend of growth rate in manufacturing over the last
decade has been around 7 per cent per annum.
- The desired growth over the next decade is 12 percent.
- At present growth rate is about 9 to 10 per cent and it
is expected that we can achieve the growth rate of 12 per cent by some efforts
like setting up of the National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC).
Question 99.
Why are industries located in or near the cities?
Or
Why do the industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand? Explain.
Answer:
Industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand because sometimes
industries are set up in or near the cities. The reasons for this are as
mentioned below:
- Industries need different types of services such as
labour, banking, transport, insurance and financial consultants. Such services
are available in cities.
- In cities the manufactured products are sold. They
become markets for these products and people are able to buy them according to
their requirements.
Availability of products attracts people from other parts to settle there. Thus, industrialisation leads to urbanisation. - Sometimes many industries are set up together to make
use of the advantage offered by the urban centers known as agglomeration
economies. Gradually a large industrial agglomeration takes place. Thus, it is
correct to state that the industries are located in or near the cities.
Question 100.
Where the most manufacturing units were located in the pre-independence period?
What were the results?
Answer:
- In the pre-independence period, the manufacturing units
were located in places keeping in view the overseas trade. These places were
Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai.
- Result :
- The result of locating the manufacturing industries at
Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai and other places was the emergence of certain
pockets of industrially developed urban centers surrounded by a huge
agricultural rural hinterland.
- First cotton textile mill was set up at Mumbai in 1854.
- First jute mill was established at Rishra near Kolkata
in 1859.
- The result of locating the manufacturing industries at
Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai and other places was the emergence of certain
pockets of industrially developed urban centers surrounded by a huge
agricultural rural hinterland.
Question 101.
Classify industries on the basis of source of raw material. How are they
different from each other?
Answer:
(1) Industries on the basis of source of raw material are classified as given
below :
1.
Agro-based e., cotton, woolen, jute, silk, textile, rubber, sugar, tea, coffee,
edible oil.
2. Mineral
based e., iron and steel, cement, aluminum, machine tools and petrochemicals.
|
Agro-based industries |
Mineral based industries |
|
(1) These are not capital intensive and do not need large investment e.g.,
dairy products.
(2) Agro-based industries use plant and animal based products as their raw
material. These are based on agricultural raw material.
(3) Cotton textiles, dairy products are example of agro-based industries. |
(1) These are capital intensive industries as these involve large
investments.
(2) These industries use any kind of mineral such as iron ore, aluminum.
Example is iron and steel industry and chemical industry.
(3) These industries use raw material for the manufacture of a number of
other products such as heavy machinery, building material and railway coaches. |
Question 102.
Classify industries on the basis of their main role. How do they differ from
each other?
Answer:
- The industries on the basis of their role are classified
into basic industries and consumer industries.
- The difference between the two are as given below :
|
Basic Industries |
Mineral based industries |
|
(1) Basic industries produce primary raw materials for factories to work
for instance steel and iron industries.
(2) Basic industries do not depend on other industries to exist. Their raw
material is not the output of another industry but rather their raw material is
the stuff of nature itself.
(3) The basic industries are iron and steel, copper smelting etc. |
(1) These are capital intensive industries as these involve large
investments.
(2) These industries use any kind of mineral such as iron ore, aluminum.
Example is iron and steel industry and chemical industry.
(3) These industries use raw material for the manufacture of a number of
other products such as heavy machinery, building material and railway coaches. |
Question 103.
How industries are classified on the basis of ownership? Explain.
Answer:
(1) Industries are classified on the basis of ownership into various
categories as
mentioned below :
- Public sector
- Private sector
- Joint sector
- Cooperative sector.
(2) These are explained below:
- Public sector: These are owned and
operated by the government agencies. Examples are BHEL, SAIL etc.
- Private sector: These industries are
owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals. Their main object
is to earn profit. Examples are TISCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd., Dabur Industries.
- Joint sector: These industries are
jointly run by the state and individual or a group of individuals. Examples Oil
India Ltd. which is jointly owned by private and public sector.
- Cooperative sector: These industries
are owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers
or both. They pool in the resources and share the profits or losses
proportionately such as the sugar industry in Maharashtra, the coir industry in
Kerala.
Question 104.
Classify industries on the basis of capital investment. How are they different
from one another? Explain with examples.
Answer:
- On the basis of capital investment, industries are
classified into small scale and large scale industry.
- Small scale and large scale industries differ from
each other as mentioned below :
|
Small scale industry |
Large scale industry |
|
(1) A small scale industry is that in which maximum investment is? One
crore.
(2) These industries employ less number of persons.
(3) Most of the work is done by man power, small machines and tools.
(4) Raw material used are less and therefore, production is also less.
These are generally more labor intensive. |
(1) In large scale industry the investment is more than X one crore.
(2) These industries employ a large number of persons.
(3) Most of the work is done by machines.
(4) The production is on large scale as the raw materials used is more. |
Question 105.
Classify industry on the basis of the bulk and weight of raw material and
finished goods.
Answer:
On the basis of bulk and weight of raw material and finished goods the
industries are classified into heavy and light industries.
- Heavy industries are such as iron and steel.
- Light industries that use light raw materials and
produce light goods such as electrical industries.
Question 106.
“The textile industry is the only industry in the country which is self-reliant
and complete in the value chain.” Justify the statement.
Or
“The textile industry occupies unique position in the Indian economy.”
Explain with examples.
Answer:
The textile industry occupies unique position in the Indian economy due to
the facts mentioned below :
- It contributes 14 per cent to industrial production.
- It generates employment for 35 million persons.
- It earns foreign exchange which is 24.6 per cent of the
total earnings.
- It contributes 4 per cent towards GDP.
- It is self-reliant and complete in the value chain e.,
raw material to the highest value added products as shown in figure given below
:
Figure showing value addition in the textile industry:
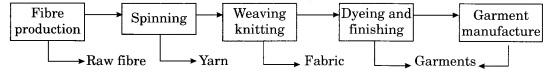
From above it is clear that value at each step is added in the textile
industry and one has to go step by step.
Question 107.
Describe the condition of cotton textile industry in India before and after
independence.
Answer:
(1) Before independence :
- In ancient India and even during the British rule our
textiles were produced with hand spinning and handloom weaving techniques.
- India remained the world’s main producer of cotton
textiles.
- Indian textiles were of top quality and other countries
could not compete with it.
- There was great demand for Indian textiles and India had
a substantial export trade to Britain as well.
(2) During British period after 18th century textile industry suffered a
setback due to coming of Manchester goods in India. The Indian weavers could not
compete due to various reasons.
(3) At present the condition of cotton textile industry in India is as
mentioned below:
- There are 1600 cotton and human made fibre textile mills
in the country.
- About 80 per cent are in the private sector and the rest
in public and cooperative sectors.
- There are thousands of small factories with four to ten
looms.
- In the early years, cotton textile industry was
concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat due to
availability of raw cotton, market, transport, labour and port facilities. But
now spinning is centralised in Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu but weaving
is highly decentralised to provide scope for incorporating traditional skills
and designs of weaving in cotton, silk, zari and embroidery.
- Cotton textiles industry is closely related to
agriculture. It provides a living to farmers, cotton boll pluckers and workers
engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring
and sewing.
- It supports many other industries, such as, chemicals
and dyes, mill stores, packaging materials and engineering works by creating
various types of demands.
- India has world class production in spinning, but
weaving supplies low quality of fabric.
- The handspun khadi provides large scale employment to
weavers in their homes as a cottage industry.
- India exports yam to Japan and cotton goods to USA, UK,
Russia, France, East European countries, Nepal, Singapore, Sri Lanka and African
countries.
Question 108.
Describe the production of fabric in India by various sectors. Why is it
important for us to keep the mill sector loomage lower than the power loom and
handloom?
Answer:
(1) The production of fabric in India by various sectors is as mentioned
below :
|
Sector |
Share of production |
Loomage |
|
Mills
Powerloom
Handloom |
G.OCUper cent
54.17 per cent
23.00 per cent |
1.33 lakh
14 lakh
NA |
From above figure it is clear that 90 percent of the weaving, cutting and
processing is in decentralised sector.
(2) It is important for us to keep the mill/sector loomage lower than
power loom and handloom due to facts as mentioned below:
- In our country many artisans and weavers work
independently along with the familly on handloom and powerlooms.
- Most of these people working on handlooms and power
looms are poor. It is the only source of income for them.
- If the mill production is increased to meet the demands
of the people then these weavers and artisans will suffer as their sales will be
affected.
- Increase in mill production will lead largely to rural
unemployment and decline in standard of living.
Thus in order to provide more employment opportunities and regular income to these weavers, the loomage or the production of the mills must be kept lower than power loom and handloom.
Question 109.
Why is it important for us to improve our weaving sector instead of exporting
yam in large quantities?
Answer:
We need to make improvement in the weaving sector for the reasons as
mentioned below :
- Weaving machinery is old and needs to be upgraded to
give more output.
- Power supply to powerlooms is erratic and power needs to
be available on continuous basis.
- Weavers can directly supply cloth to garment
manufacturers instead of garment makers importing the fabric.
- This will also increase employment and incomes of the
weavers.
- Increasing the weaving capacity will increase the GDP
of country and create opportunity for development of ancillary industries like
dyeing, processing and printing of woven fabrics, production of stitched
garments.
- This could also mean reduction in imports of fabrics
and readymade garments thus saving foreign exchange reserves and using it for
other important products.
Question 110.
Explain why many of our spinners export cotton yam while apparel/garment
manufacturers have to import fabric.
Answer:
India’s share in the world trade of cotton yarn accounts for one-fourth of the
total trade. However, our trade in garments is only 4 per cent of the world’s
total but in spite of these facts many of our spinners export cotton yarn while
apparel/garment manufacturers have to import fabric. The reasons for this state
of affairs are as mentioned below:
- The weaving, knitting and processing units cannot use
much of the high quality yam that we produce.
- There are some large and modern factories but most of
the production is done in fragmented small units. These units cater to the needs
of loqal market. This mismatch is a major drawback for the industry.
- Production of good quality long staple cotton has
increased but India still imports due to the following reasons :
- Erratic power supply.
- Old machinery that needs upgradation.
- Low output of labour.
- Stiff competition with the synthetic fiber industry.
- Erratic power supply.
Question 111.
Describe the factors responsible for the location of most of the jute mills
along the banks of the Hugli River in West Bengal.
Answer:
The factors for the location of most of the jute mills along the banks of the
Hugli river in a narrow belt i.e., 98 km long and 3 km wide in West Bengal are
as given below :
- Proximity of the jute producing areas.
- Inexpensive water transport.
- Good network of railways, roadways and waterways to
facilitate movement of raw material to the mills.
- Abundant water for processing raw jute.
- Cheap labour from West Bengal and adjoining states of
Bihar, Orissa and Uttar Pradesh.
- Availability of facilities such as banking, insurance
and port facilities for export of jute goods at Kolkata which is a large urban
center.
Question 112.
What are the challenges faced by the jute industry? How the internal demand has
been on the increase? Which are the main markets for jute products?
Answer:
(1) The challenges faced by the jute industry are as mentioned below :
- Stiff competition in the international market from
synthetic substitutes.
- Competition with other countries like Bangladesh,
Brazil, Philippines, Egypt and Thailand.
(2) However inspite of the challenges, there is increase in the
internal demand due to factors as mentioned below:
- The government has made mandatory use of jute packaging.
- The growing global concern for environment friendly
biodegradable materials has also increased the use of jute products.
- In 2005 National Jute Policy was formulated with the
objective of increasing productivity, improving quality, ensuring good prices to
the jute farmers and enhancing the yield per hectare.
- The growing global concern for environment friendly
biodegradable materials has also helped in use of more jute products.
(3) The main markets are USA, Canada, Russia, United
Arab Republic, UK and Australia.
Question 113.
Give a brief description of sugar industry with special reference to its raw
material, its nature, location of sugar mills and place in the world.
Answer:
(1) Raw material : The raw material, i.e., sugarcane, is bulky and in
haulage, its sucrose content reduces. It is weight losing and perishable.
(2) Nature: This industry is seasonal in nature and, therefore, it is
ideally suited to the cooperative sector because it needs large manual labour in
various processes of cultivation and production of sugar and other products that
can be provided by the cooperatives.
(3)
- Location of sugar mills: There are
about 460 sugar mills which are located in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra,
Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana and Madhya
Pradesh. Sixty per cent mills are in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- In recent years there has been a tendency for the
sugar mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states due to
following reasons :
1. The
sugarcane produced in the southern and western states has a higher sucrose
content.
2. The
cooler climate also ensures a longer crushing season.
3. The
industry is ideally suited to the cooperative sector and this sector has been
more successful in these states.
4. Place
in the world: India stands second as a producer of sugar. It,
however, occupies the first place in the production of gurand
5. The
challenges before the sugar industry are its seasonal nature, old and
inefficient methods of production, transport delay in reaching sugarcane to
factories, need to maximise the use of baggase.
Question 114.
Describe iron and steel industry with reference to its features, uses and method
of production.
Ans.
(1) Basic industry : Iron and steel industry is the basic industry
because all the other industries depend on it for their machinery.
(2) Production and heavy industry:
1. It is a
heavy industry because all the raw materials as well as finished goods are heavy
and bulky entailing heavy transportation costs.
2. Iron ore,
coking coal and limestone are required in the ratio of approximately 4:2:1. f
(3) Some quantities of manganese are also required to harden the steel.
3. Uses: Steel
is used to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction material,
defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment and consumer goods.
Question 115.
Which mineral’s production and consumption is regarded as the index of a
country’s development? What is the rank of India among the world crude steel
producers? Why is the per capital consumption of steel so low in India?
Answer:
(1) Production and consumption of steel is often regarded as the index of a
country’s development.
(2)
1. India
produces 32.8 millon tons of steel.
2. It ranks
ninth among the world crude steel producers.
3. It is the
largest producer of sponge iron.
(3) In spite of large quantity of production of steel, per capital
consumption per anum is only 32 kg. The reasons for the low consumption of steel
are as mentioned below:
- Lack of domestic market for steel in India.
- Most of the steel is produced for international market.
- High costs of steel because modern and cost effective
technologies for steel production are not utilised due to lack of
infrastructure.
- Nearly % of Indian population live in villages which
require very small quantities of steel.
- To carry steel to some areas is difficult because of
improper means of transport.
- Low developed remote areas are not in need of steel.
Question 116.
Why the Chhotanagpur plateau region has the maximum concentration of iron and
steel industries? Give reasons.
Answer:
The Chhotanagpur plateau region has the maximum concentration of iron and
steel industries due to the following reasons :
- Low cost of iron.
- High grade raw materials are available in proximity.
- Cheap labour is available.
- There is vast growth potential in the home market.
Question 117.
Which are the factors responsible for not performing to our full potential? What
is its present position?
Answer:
(1) We are not able to perform to our full potential energy due to the
reasons as mentioned below :
- High costs and limited availability of coking coal.
- Lower productivity of labour.
- Irregular supply of energy.
- Poor infrastructure.
(2) The present position is as mentioned below:
- The overall production of steel is sufficient to meet
our domestic demand.
- Liberalisation and Foreign Direct Investment have given
a boost to the industry with the efforts of private entrepreneurs.
- There is need to allocate resources for research and
development to produce steel more competitively.
Question 118.
Write a brief note on Aluminium smelting industry in India.
Answer:
(1) Qualities : It is light, resistant to corrosion, a good conductor of
heat and malleable. It becomes strong when it is mixed with other metals.
(2) Uses: It is used to manufacture aircraft, utensils and wires. It is
also used as a substitute of steel, copper, zinc and lead in a number of
industries.
(3)Position of Aluminum:
- Aluminium smelting is the second important metallurgical
industry in India. There are eight aluminium smelting plants in India. These are
located in Orissa (Nalco and Balco), West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh,
Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
- In 2004, India produced over 600 million tons of
aluminium.
- Factors for the location of the industry are regular
supply of electricity and an assured source of raw materials e., bauxite at the
minimum cost.
Question 119.
Describe the main features of chemical industry in India.
Ans.
The main features are as follows:
- It is fast growing and diversifying industry.
- Its contribution to GDP is approximately 3 per cent.
- It is the third largest in Asia and twelfth in the world
in size.
- It has both large and small scale manufacturing units.
- Rapid growth in both organic and inorganic sectors.
- It has its own consumer market because basic chemicals
are used for producing other chemicals that are used for industrial application,
agriculture or directly for consumer markets.
- Organic chemicals include petrochemicals, which are used
for manufacturing of synthetic fibres, synthetic rubber, plastics, dye stuffs,
drugs and pharmaceuticals.
- Organic chemical plants are located near oil refineries
and petrochemical plants because petrochemicals are heavy organic chemicals
which are difficult to transport to other places.
- The inorganic chemical industry manufactures
fertilisers, plastics, paints, adhesives, soaps, detergents and paper etc. These
products are used by people all over the country and can 1 be
produced by small inorganic chemical industries spread all over the country.
Question 120.
Write a short note on the main features of the fertiliser industry in India.
Answer:
Main features are :
- It produces nitrogenous fertilisers (mainly urea),
phosphatic fertilisers and ammonium phosphate (DAP) and complex fertilisers
i.e., combination of nitrogen (N), phosphate (P) | and potash (K).
- India is the third largest producer of nitrogenous
fertilisers.
- Number of fertiliser units in the country are as
follows :
1.
Nitrogenous and complex nitrogenous fertiliser — 57
2. Urea – 29
3. Ammonium
sulphate – 09
4. Single
superphosphate – 68
- There are 10 public sector undertakings and one in
cooperative sector at Hazira in Gujarat under the Fertiliser Corporation of
India.
- Main fertiliser producing states are Gujarat, Tamil
Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Kerala where half of the fertiliser is
produced. Other states are Andhra Pradesh, Orissa, Rajasthan, Bihar,
Maharashtra, Assam, West Bengal, Goa, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka.
Question 120.
Describe the cement industry in India with special reference to the uses of
element and its expansion.
Answer:
The main facts about the cement industry in India are as given below :
- Uses: Cement is used for construction of buildings,
factories, dams, airports, roads and other commercial complexes.
- Raw materials: Bulky and heavy raw materials like
limestone, silica, alumina and gypsum are used in it. Besides this, it needs
coal, electric power and rail transportation.
- Location of plants :
- First cement plant was set up in Chennai in 1904.
However,decontrol of price and distribution and policy reforms since 1989 led to
its expansion.
- There are 128 large plants and 332 mini-cement plants in
the country.
- Some plants have been strategically located in Gujarat.
These plants have suitable access to the market in the Gulf countries.
- Present position of the industry: Good quality of cement
of India has great demand in Last Asia, Middle East, Africa and South Asia as
well as in the country. At present the cement industry is doing well in terms of
production as well as export. Efforts are being made
togenerate adequate domestic demand and supply in order to sustain the industry.
- First cement plant was set up in Chennai in 1904.
However,decontrol of price and distribution and policy reforms since 1989 led to
its expansion.
Question 121.
What are the advantages of automobiles? What are the factors responsible or the
healthy growth of automobile industry? Which are the main centers of automobile
industry?
Answer:
- Advantages: Automobiles provide
vehicles for quick transport of good services and passengers.
- Liberalisation, foreign direct investment, new and
contemporary models are factors responsible for the healthy growth of the
industry including passenger cars, two and three- wheelers.
- Manufacturing: Trucks, buses, cars,
motor cycles, scooters, three-wheelers and multiutility vehicles are
manufactured in India at various centers.
- Location of industry: Around Delhi,
Gurgaon, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Indore, Hyderabad, Jamshedpur
and Bangalore.
- Number of manufacturers : At present, the number of
manufacturers are as given below :
- Passenger cars and multi-utility vehicles – 15
- Commercial vehicles – 09
- Two and three-wheelers – 14
- Passenger cars and multi-utility vehicles – 15
Question 122.
Name the electronic capital of India. Write characteristics of IT and electronic
industry of India.
Answer:
- Bangalore is the electronic capital of India.
- The main characteristics of the electronic industry
are as mentioned below :
- Products of electronics industry: Transistor
sets, television, telephones, cellular telecom, pagers, radars, computers and
many other equipment required by the telecommunication industry.
- Centers: Bangalore, Mumbai, Delhi,
Hyderabad, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow and Coimbatore.
- Software Technology Parks: 18 parks
which provide single window service and high data communication facility to
software experts.
- Employment: Up to 31st March, 2005,
the IT industry employed over one million persons. It is likely to increase to 8
million in next three to four years. 30 per cent employees are women in this
industry.
- Foreign exchange: It earns lot of
foreign exchange due to fast growing Business Processes Outsourcing (BPO)
sector.
- Products of electronics industry: Transistor
sets, television, telephones, cellular telecom, pagers, radars, computers and
many other equipment required by the telecommunication industry.
Question 123.
Describe the method of treatment of industrial effluents.
Answer:
Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases as given below
:
1. Primary
treatment by mechanical means. This involves screening, grinding, flocculation
and sedimentation.
2. Secondary
treatment by biological process.
3. Tertiary
treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves
recycling of wastewater.
Question 124.
Describe the ways by which the NTPC has preserved the natural environment and
other resources like water.
Answer:
NTPC is a major power providing corporation in India. It has ISO certification
for EMS (Environment Management System) 14001. The Corporation has taken
following steps for preserving the natural environment and resources like water:
1. Optimum
utilisation of equipment adopting latest techniques and upgrading existing
equipment.
2.
Minimising waste generation by maximising ash utilisation.
3. Providing
green belts for nurturing ecological balance and addressing the question of
special purpose vehicles for afforestation.
4. Reducing
environmental pollution through ash pond management, ash water recycling system
and liquid waste management.
5.
Ecological monitoring, reviews and online database management for all its power
stations.
Thus, by taking above steps, the NTPC has shown the way to the people for
preserving the natural environment.
MAP QUESTIONS
Question 1.
On the outline map of India, show major places of following industries:
- Cotton textile
- Woollen textile
- Silk textile
- Synthetic textile.
Answer:
Major places of above industries are given below :
- Cotton Textile: Ahmedabad, Rajkot,
Porbandar, Vadodara, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, Coimbatore, Madurai, Moradabad,
Agra, Kanpur, Murshidabad, Haora and Hugli.
- Woollen Textile: Ahmedabad,
Jamnagar, Mumbai, Bangalore, Bikaner, Panipat, Gurgaon, Jaipur, Shahjahanpur,
Gwalior, Kanpur, Srinagar, Amritsar and Ludhiana.
- Silk Textile: Kolar, Bangalore,
Mysore, Belgaon, Murshidabad, Varanasi, Baramulla, Srinagar and Anantnag.
- Synthetic Textile : Amritsar,
Gwalior, Ahmedabad, Surat, and Murshidabad.
Question 2.
On the outline map of India show the major iron and steel plants.
Answer:
The major iron and steel plants are shown as given below :
- Bokaro
- Jamshedpur
- Raurkela
- Bhilai
- Durgapur
- Vijaynagar
- Bhadravati
- Salem
- Vishakhapatnam
- Burnpur
Question 3.
On the outline map of India show the major Software Technology Parks.
Answer:
There are 18 Software Technology Parks that provide single window service and
high data communication facility to software experts. They are at Mohali,
Srinagar, Noida, Jaipur, Gandhinagar, Indore, Mumbai, Pune, Mysore, Bangalore,
Thiruvananthapuram, Chennai, Coimbatore, Hyderabad, Vishakhapatnam,
Bhubaneshwar, Kolkata and Guwahati.See map given below :
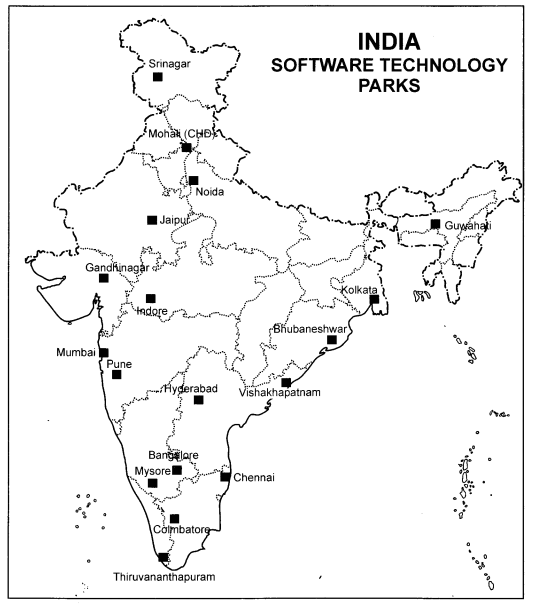
Question 4.
Six features with serial numbers (1) to (6) are marked in the given political
outline map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following
information and write their correct names on the lines marked in the map.
1. Woollen
textile
2. Silk
textile
3. Cotton
textile
4. Iron and
steel plant
5. Software
technology park
6. Iron and
steel plant.
Answer:
- Woollen textile — Ludhiana
- Silk textile — Srinagar
- Cotton textile — Ahmedabad
- Iron and steel plant — Salem
- Software technology park — Noida
- Iron and steel plant — Bumpur
See map given below: