Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources Important Questions
Very Short Answer Question s (VSA) 1 Mark
Question 1.
State some products/things we use that are made of metals.
Answer:
Railway lines, a tiny pin, machinery, cars etc. are all made of metals.
Question 2.
Name the minerals which do the cleaning work.
Answer:
Silica, oxide and phosphate minerals do the cleaning work.
Question 3.
Which rock consists of single mineral only?
Answer:
Limestone.
Question 4.
What is a mineral?
Answer:
Mineral is a “homogenous” naturally occurring substance with a definable
internal structure.
Question 5.
How do Geographers study minerals?
Answer:
Geographers study minerals as part of the earth’s crust for a better
understanding of landforms.
Question 6.
What is the interest of a geologists in minerals?
Answer:
A geologist is interested in the formation of minerals, their age and physical
and chemical composition.
Question 7.
State some of the non-metallic minerals.
Answer:
Non-metallic minerals are mica, salt, potash, sulphur, granite, limestone,
marble sand stone etc.
Question 8.
Give some examples of energy minerals.
Answer:
Coal, petroleum and natural gas are energy minerals.
Question 9.
What type of mineral is copper?
Answer:
Copper is a metallic mineral.
Question 10.
Where are minerals found?
Answer:
Minerals are found in ores.
Question 11.
What is an ‘ore’?
Answer:
The term ‘ore’ is used to describe an accumulation of any material mixed with
other elements.
Question 12.
Where are a number of minerals found in sedimentary rocks? Give example.
Answer:
In sedimentary rocks a number of minerals occur in beds or layers. Examples are
coal and some forms of iron ore.
Question 13.
Which minerals are formed as a result of evaporation? Name any two.
Answer:
Potash salt and sodium salt.
Question 14.
Placer deposits contain minerals which are not corroded by water. Which are
these minerals?
Answer:
Gold, silver, tin and platinum.
Question 15.
What do you understand by Rat-hole mining?
Answer:
In the tribal areas of the north-east India, minerals are owned by individuals
or communities. Thus, coal mining in Jowai and Cherapunjee is done by family
member in the form of a long narrow tunnel, known as ‘Rat-hole’ mining.
Question 16.
Which reserves of minerals are found in peninsular rocks?
Answer:
Peninsular rocks contain most of the reserves of coal, metallic minerals mica
and many other non-metallic minerals.
Question 17.
Where petroleum deposits are found in India?
Answer:
Sedimentary rocks on the western and eastern flanks of the peninsula, in Gujarat
and Assam have most of the petroleum deposits.
Question 18.
Which part of India has no minerals or is devoid of economic minerals?
Answer:
The vast alluvial plains of north India are almost devoid of economic minerals.
Question 19.
Which is the main reason for variations in distribution of minerals in India?
Answer:
The variations in distribution of minerals in India is due to differences in the
geological structure, processes and time involved in the formation of minerals.
Question 20.
Which is the finest iron ore and why?
Answer:
Magnetite is the finest ore with a very high content of iron up to 70 per cent.
It has excellent magnetic qualities.
Question 21.
From which belt iron ore is exported via Vishakhapatnam port and to which
countries?
Answer:
Iron ore from the mines of Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur belt is exported to Japan and
South Korea via Vishakhapatnam port.
Question 22.
Which are main non-ferrous minerals?
Answer:
Copper, lead, bauxite, zinc and gold are non-ferrous metals.
Question 23.
What is the advantage of copper’s use in electrical cables?
Answer:
The copper is malleable, ductile-‘and good conductor and therefore its use is
advantageous in electrical cables.
Question 24.
Which place in India produces more copper?
Answer:
The Balaghat mines in Madhya Pradesh produce 52 per cent of India’s copper.
Question 25.
How are bauxite deposits formed?
Answer:
Bauxite deposits are formed by the decomposition of a wide variety of rocks rich
in aluminium silicates.
Question 26.
Which state is the largest bauxite producing in India?
Answer:
Orrisa.
Question 27.
Why is mica the most indispensable mineral used in electric and electronic
industries?
Answer:
Due to its excellent di-electric strength, low power loss factor, insulating
properties and resistance to high voltage, mica is one of the most indispensable
mineral used in electric and electronic industries.
Question 28.
From which minerals energy can be generated?
Answer:
Energy can be generated from fuel minerals like coal, petroleum, natural gas,
uranium and from electricity.
Question 29.
Which are non-conventional source of energy? Mention any three.
Answer:
Non-conventional source of energy are solar, wind, biogas, tidal energy.
Question 30.
Which are different types of coal?
Answer:
Lignite, bituminous and anthracite.
Question 31.
State two types of electricity.
Answer:
1.
Hydro-electricity.
2.
Thermal electricity.
Question 32.
Where is Kaiga thermal power plant?
Answer:
Kaiga thermal power plant is in Karnataka.
Question 33.
In which state the largest solar power plant is located?
Answer:
The largest solar power plant of India is located at Madhapur, near Bhuj.
Question 34.
How hiogas is produced in rural areas?
Answer:
Shrubs, farm waste, animal and human waste are used to produce biogas for
domestic consumption in rural areas.
Question 35.
Which nuclear plant is situated in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Kalpakkam nuclear power plant is located in Tamil Nadu.
Question 36.
Which country is ranked as a ‘wind super power’ in the world?
Answer:
India is ranked as a ‘wind super power’ in the world.
Question 37.
In India which place provides ideal conditions for utilising tidal energy?
Answer:
Gulf of Kuchchh.
Question 38.
What is geothermal energy?
Answer:
Geothermal energy refers to the heat and electricity produced by using the heat
from the interior of the earth.
Question 39.
How you can contribute towards the conservation of energy resources? State one
way.
Answer:
We can contribute towards the conservation of energy by using public transport
systems instead of individual vehicles.
Question 40.
Which are the two planks of sustainable energy?
Answer:
Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy sources
are the twin planks of sustainable energy.
Question 41.
Define the term ‘mineral’.
Answer:
Geologists define mineral as a “homogeneous, naturally occurring substance with
a definable internal structure.” They have physical and chemical properties by
which they can be identified.
Question 42.
Define the term ‘rock’.
Answer:
Rocks are combinations or aggregates of minerals in varying proportions. Some
rocks consist of a single mineral, e.g., limestone while most rocks consist of
several minerals.
Question 43.
Define the term ‘ore’.
Answer:
The term ‘ore’ is used to describe an accumulation of any mineral mixed with
other elements.
Question 44.
Name the finest quality of iron ore.
Answer:
Magnetite is the finest quality of iron ore.
Question 45.
Orissa is the leading producer of which mineral?
Answer:
Manganese ore.
Question 46.
Name one fossil fuel which is considered environment friendly.
Answer:
Natural gas.
Question 47.
Which is the main source of energy in India?
Answer:
The main source of energy in India is fossil fuels especially coal.
Question 48.
In which non-conventional source of energy is India referred to as a super
power?
Answer:
Wind Power.
Question 49.
Which mineral is formed by decomposition of rocks, leaving a residual mass of
weathered material?
Answer:
Bauxite
Question 50.
Name the state where the largest wind farm cluster is located?
Answer:
Tamil Nadu.
Question 51.
In which State are the ‘Balaghat’ Copper mines located?
Answer:
Madhya Pradesh.
Question 52.
Which is the most abundantly available fossil fuel in India? Name its four major
forms.
Answer:
Coal;
1.
Anthracite
2. Lignite
3.
bituminous
4. peat
Question 53.
Which rock consists of a single mineral only?
Answer:
Limestone consists of a single mineral only.
Question 54.
How do minerals occur in sedimentary rocks?
Answer:
In sedimentary rocks a numbers of minerals occur in beds or layers. They have
been formed as a result of deposition, accumulation and concentration in
horizontal strata.
For example, coal, iron ore.
Question 55.
Why are there a wide range of colours, hardness, crystal forms, lustre and
density found in minerals?
Answer:
A mineral that will be formed from a certain combination of elements depends
upon the physical and chemical conditions under which the mineral forms. It is
because of these physical and chemical conditions that minerals possess a wide
range of colours, crystal forms, lustre and density.
Question 56.
How do minerals occur in igneous and metamorphic rocks?
Answer:
In igneous and metamorphic rocks, minerals may occur in cracks, crevices, faults
and joints.
Question 57.
How do minerals occur in sedimentary rocks?
Answer:
In sedimentary rocks a number of minerals occur in beds or layers. They have
been formed as a result of deposition, accumulation and concentration in
horizontal stratas.
Question 58.
Why should the use of cattle cake as fuel be discouraged?
Answer:
Using dung cake or cattle cake as fuel is being discouraged because it consumes
most valuable manure which could be used in agriculture.
Question 59.
How are ‘Gobar gas plants’ beneficial to the farmers?
Answer:
“Gobar Gas Plants” are beneficial to the farmers in the form of energy and
improved quality of manure.
Question 60.
Where is the largest solar plant located in India?
Answer:
The largest solar plants located at Madhapur near Bhuj in Gujarat.
Question 61.
Name the industry which uses limestone as its main raw material.
Answer:
Cement industry.
Question 62.
How is energy an indispensable requirement of our modem life? Explain with three
examples.
Answer:
Modern life is highly governed by technology and revolves around it. Modem
technology is driven by energy and is highly automated. Every sector of National
economy — agriculture, industry, transport and commerce need greater inputs of
energy. In the domestic sector also, energy demands, in the form of electricity,
are growing because of increasing use of electric gadgets and appliances. Energy
is the basic requirement for economic development.
Question 63.
Mention any three characteristics of ferrous group of minerals found in India.
Answer:
Metallic minerals that have iron in them are called ferrous minerals. For
example, iron ore, manganese, nickel, cobalt etc.
Three characteristics of ferrous group of minerals found in India are:
1. Ferrous
minerals account for about three fourths of the total value of the production of
metallic minerals.
2. They
provide a strong base for the development of metallurgical industries.
3. India
exports substantial quantities of ferrous minerals to Japan and South Korea
after meeting her internal demands.
Question 64.
Why is there a pressing need to use non-conventional sources of energy in India?
Explain any three reasons.
Answer:
1. The
growing consumption of energy has resulted in India becoming increasingly
dependent on fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas which are found in limited
quantity on the earth.
2. Rising
prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainties
about the security of energy supply in future, which in turn has serious
repercussions on the growth of the national economy.
3.
Increasing use of fossil fuels also causes serious environmental degradation
like air pollution, water pollution etc.
So there is an urgent need to use sustainable energy resources like solar,
water, wind, tide biomass etc.
Question 65.
Make a distinction between hydroelectricity and thermal electricity stating
three points of distinction.
Or
What are the two main ways of generating electricity? How are they different
from each other? Explain.
Answer:
Electricity is generated mainly in two ways:
1. By
running water which drives hydro turbines to generate hydroelectricity.
2. By
burning other fuels such as coal, petroleum and natural gas to drive turbines to
produce thermal power.

Question 66.
“Minerals are an indispensable part of our lives.” Comment.
Answer:
Almost everything we use, from a tiny pin to a towering building or a ship, all
are made from minerals. All means of transport are manufactured from minerals
and run on power resources derived from the earth. Even the food that we eat
contains minerals. Human beings have used minerals for their livelihood,
decorations, festivities and in all stages of development.
Question 67.
Mention any three major iron-ore belts of India. Write any three characteristics
of the southern most iron-ore belt.
Answer:
The three major iron-ore belts of India are as follows:
1.
Orissa-Jharkhand belt.
2.
Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur belt in Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra.
3.
Bellary-Chitradurga-Chikmaglur-Tumkur belt in Karnataka.
4.
Maharashtra-Goa belt.
Bellary-Chitradurga-Chikmaglur-Tumkur belt is the southern most iron-ore
belt.
Characteristics:
·
This belt in Karnataka has large reserves of iron-ore.
·
Kudremukh mines in the Western Ghats are known to be one
of the largest in the world.
·
Kudremukh is a 100 per cent export unit and the ore is
transported as slurry through a pipeline to a port near Mangalore.
Question 68.
Classify energy resources into two categories. Give two examples of each.
Answer:
Energy resources can be classified as conventional and non-conventional sources.
Conventional sources include—firewood, cattle-dung cake, coal, petroleum,
natural gas, etc. Non-conventional sources include—solar, wind, tidal,
geothermal energy and biogas.
Question 69.
Differentiate between metallic and non-metallic minerals with examples.
Answer:
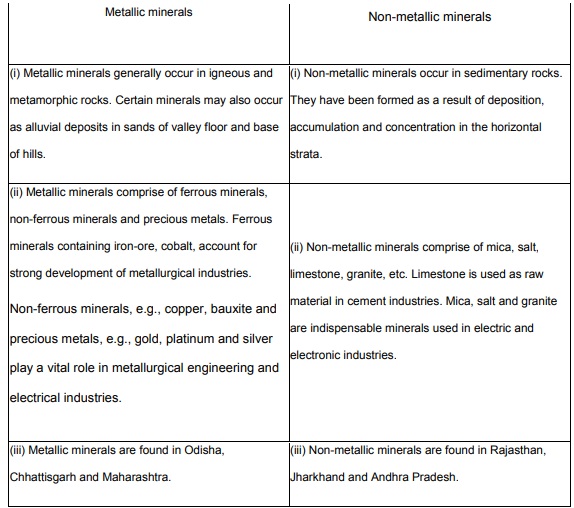
Question 70.
Differentiate between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals with examples.
Answer:
Ferrous minerals:
1. Ferrous
minerals account for about three fourths of the total value of the production of
metallic minerals.
2. They
provide a strong base for the development of metallurgical industries.
3. India
exports substantial quantities of ferrous minerals to Japan and South Korea
after meeting her internal demands.
Non-ferrous minerals:
1. India’s
reserves and production of non-ferrous minerals is not very satisfactory.
2.
Non-ferrous minerals include copper, bauxite, lead, zinc and gold.
3. They
provide a strong base for the development of metallurgical, engineering and
electrical industries.
4.
Non-ferrous minerals like copper and bauxite are mainly found in Madhya Pradesh
and Odisha respectively.
Question 71.
Explain the use of petroleum as an energy resource and as an industrial raw
material.
Answer:
The use of petroleum as a source of energy:
1. It is
used as a fuel for internal combustion engines in automobiles.
2. It is
used as a fuel for railways and aircrafts.
3. It
provides fuel for heat and lighting.
The use of petroleum as an industrial raw material:
1. It is
used as lubricant for machinery.
2. It is
used as raw material for a number of manufacturing industries, for example,
chemical industry.
3. Its
numerous by-products are used in petrochemical industries such as fertilizer,
synthetic rubber, synthetic fibre, medicines, vaseline wax, soap, cosmetics etc.
Question 72.
Distinguish between conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.
Or
Classify energy resources into two categories. Give two examples of each.
Answer:
Energy sources can be classified as conventional and non-conventional sources.
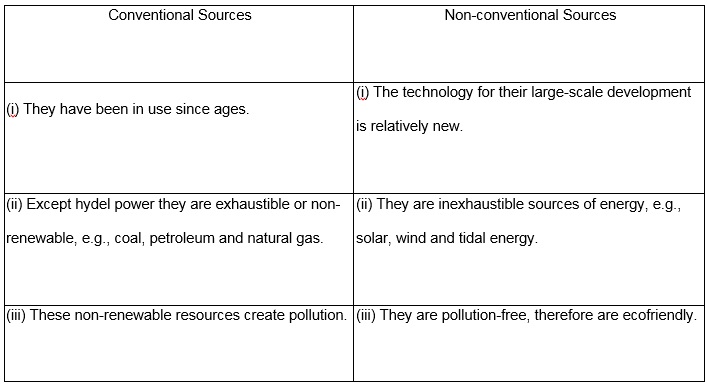
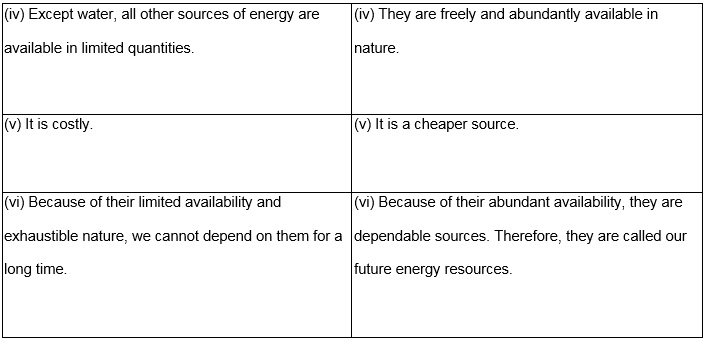
Question 73.
Explain any three steps to be taken to conserve the energy resources.
Answer:
1. We need
to develop a sustainable path of energy development, i.e., increased use of
renewable or non-conventional energy resources.
2. We have
to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy
resources.
3. As
concerned citizens we can do our bit by using public transport systems instead
of individual vehicles, switching off electricity when not in use, using power
saving devices etc.
Question 74.
What is the use of manganese? Name the largest manganese-ore producing state of
India.
Answer:
Manganese is mainly used in the manufacturing of the following items:
1. Steel
(nearly 10 kg of manganese is required to manufacture 1 tonne of steel).
2.
Ferro-manganese alloy
3. Bleaching
powder
4.
Insecticides and paints
Odisha (Orissa) is the largest producer of manganese-ore in India.
Question 75.
Why is energy required for all activities? How can energy be generated? Explain.
Answer:
Energy is needed to cook, to provide light and heat, to propel vehicles and to
drive machinery in industries. Energy is a basic requirement for economic
development. Every sector of the national economy—agriculture, industry and
transport—commercial and domestic needs inputs of energy.
Energy can be generated from fuel minerals like coal, petroleum, natural gas,
uranium and from electricity. Conventional sources like firewood and cattledung
cakes are most commonly used in rural India to generate energy.
Question 76.
‘Environmental degradation has been seen everywhere/ Explain any three values
that can help to prevent environment degradation.
Answer:
Three values that can help to prevent Environmental Degradation:
1. We must
ensure sustainable and equitable use of resources without degrading the
environment or risking health or safety.
2. We must
raise awareness and consciousness among people about the importance of judicious
use of resources to prevent degradation of land, water, vegetation and air.
3. The
following measures must be adopted to prevent environmental degradation:
·
Minimising use of water for processing by reusing and
recycling it.
·
Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal
in factories.
·
Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy
efficiency and reduce noise.
Question 77.
Which is the most abundantly available fossil fuel in India? Mention its
different forms.
Answer:
The most abundantly available fossil fuel is Coal.
There are four types of coal:
1.
Anthracite. It is the highest quality hard coal. It contains more than 80%
carbon content. It gives less smoke.
2.
Bituminous. It is the most popular coal in commercial use and has 60-80% carbon
content. Metallurgical coal is high grade bituminous coal and is of special
value for smelting iron in blast furnaces.
3. Lignite.
It is a low grade brown coal. It is soft with high moisture content.
4. Peat. It
has a low carbon and high moisture content. It has low heating capacity and
gives lot of smoke on burning.
Question 78.
How is the mining activity injurious to the health of the miners and
environment? Explain.
Answer:
Adverse effect on health: The dust and noxious fumes inhaled by miners make them
vulnerable to pulmonary diseases.
The risk of collapsing mine roofs, inundation and fires in coal mines are a
constant threat to miners.
Adverse effects on the environment:
The water sources in the region get contaminated due to mining.
Dumping of slurry and waste leads to degradation of land, soil and
increase in stream and river pollution. Stricter safety regulations and
implementation of environmental laws are essential to prevent mining from
becoming a ‘killer industry’.
Question 79.
In the present day energy crisis what steps will you like to take for saving
energy?
Or
Why is energy needed? How can we conserve energy resources? Explain.
Answer:
Energy is required for all activities. It is needed to cook, to provide light
and heat, to propel vehicles and to drive machinery in industries.
1. Energy is
the basic requirement for economic development.
2. Every
sector of national economy — agriculture, industry, transport and commerce needs
greater inputs of energy.
3. In the
domestic sector also, energy demands, in the form of electricity, are growing
because of increasing use of electrical gadgets and appliances.
We have to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited
energy resources. So conservation of energy should be done at all levels.
Increased use of renewable energy resources, e.g., solar energy, hydel power,
etc.
We, as concerned citizens can help conserve energy in the following ways:
1. Using
more of public transport system instead of individual vehicles.
2. Switching
off electrical devices when not in use.
3. Using
power saving devices.
4. Using
non-conventional sources of energy such as solar energy, wind energy etc.
5. Getting
the power equipment regularly checked to detect damages and leakages.
Question 80.
How can solar energy solve the energy problem to some extent in India? Give your
opinion.
Or
Why does solar energy have a bright future in India?
Answer:
Reasons:
1. India is
a tropical country and gets abundant sunshine.
2. It has
enormous possibilities of tapping solar energy.
3. It is an
inexhaustible source of energy which is freely available in nature.
4. It is a
cheaper source of energy and is fast becoming popular in rural and remote areas.
5.
Photovaltic technology is available which converts sunlight directly into
electricity.
6. Because
of its abundant and free availability in all parts of India in addition to its
ecofriendly nature, solar energy is called the energy of future.
Also use of solar energy will minimise the dependence of rural households
on firewood. It will contribute to environmental conservation and reduce
pressure on conventional sources of energy.
Question 81.
‘Consumption of energy in all forms has been rising all over the country. There
is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development and energy
saving/ Suggest and explain any three measures to solve this burning problem.
Answer:
Every sector of the national economy—agriculture, industry, transport,
(commercial and domestic), needs greater inputs of energy.
With increasing population and changing lifestyles energy consumption is
increasing very fast. We are not self-sufficient in energy according to demands.
Therefore we have to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our
limited resources. Conservation of energy should be done at all levels.
Three measures to reduce consumption of energy in all forms:
1. We can do
our bit by using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles.
2. Switching
off electricity when not in use.
3. Using
power saving devices or using non-conventional sources of energy such as solar
energy, wind energy etc.
4. Checking
the power equipments regularly can help in saving of energy.
Question 82.
What are the main types of formations in which minerals occur?
Answer:
Minerals generally occur in the following forms:
1. Veins and
lodes. In igneous and metamorphic rocks minerals may occur in the cracks, faults
or joints by getting solidified in them. The smaller occurrences are called
veins and the larger lodes, eg., metallic minerals like tin, copper, zinc and
lead etc. are found in lodes and veins.
2. In
sedimentary rocks minerals occur in beds or layers. They are formed as a result
of deposition, accumulation and concentration in horizontal strata. Some
sedimentary minerals are formed as a result of evaporation, especially in arid
regions eg., gypsum, potash and salt.
3. Another
mode of formation involves decomposition of surface rocks and the removal of
soluble contents, leaving a residual mass of weathered material containing ores.
Bauxite is formed this way.
4. Placer
deposits. Certain minerals occur as alluvial deposits in sands of valley floors
and the base of hills, eg., gold, silver, tin and platinum. These are called
placer deposits and contain minerals which are not corroded by water.
5. Ocean
waters contain vast quantities of minerals, eg., common salt, magnesium and
bromide are largely derived from the ocean waters. The ocean beds are rich in
manganese nodules.
Question 83.
Why is there a pressing need to use renewable energy resources in India? Explain
any five reasons.
Answer:
1. The
growing consumption of energy has resulted in India becoming increasingly
dependent on fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas which are found in limited
quantity on the earth. So there is an urgent need to use sustainable energy
resources like solar, water, wind etc.
2. Rising
prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainties
about the security of energy supply in future, which in turn has serious
repercussions on the growth of the national economy.
3.
Increasing use of fossil fuels also causes serious environmental degradation
like air pollution, water pollution etc.
4. Renewable
sources of energy are pollution free and do not cause harm to ozone, therefore
they are eco-friendly.
5. They are
a cheaper source and are freely and abundantly available in nature.
Question 84.
How is energy a basic requirement for the economic development of the country?
Explain with examples.
Answer:
Reasons:
·
Energy is the basic requirement for economic development.
·
Every sector of national economy—agriculture, industry,
transport and commerce needs greater inputs of energy.
·
In the domestic sector also, energy demands, in the form
of electricity, are growing because of increasing use of electric gadgets and
appliances.
·
The economic development plans implemented since
independence necessarily required increasing amounts of energy.
·
Because of all these, per capita consumption of energy is
continuously increasing.
Question 85.
Why is it necessary to conserve mineral resources? Suggest any four ways to
conserve mineral resources.
Or
Explain the importance of conversation of minerals. Highlight any three measures
to conserve them.
Answer:
Conservation of minerals is necessary because of the following reasons:
1. The
formation of minerals takes a long geological period of millions of years.
2. They are
finite, i.e., limited in nature.
3. Many of
them are non-renewable and exhaustible.
4. The rate
of replenishment of minerals is infinitely small in comparison to rate of
consumption.
5. They have
to be preserved for our future generations because they are very important for
industrial development of the nation.
Ways to mineral conservation:
1. We should
use minerals in a planned and sustainable manner.
2. Improved
technologies need to be evolved to allow use of low grade ores at low cost.
3. Recycling
of metals should be done.
4. Using
scrap metals and other substitutes should be promoted.
5. Wastages
in mining, processing and distribution should be minimized.
6.
Controlled export of minerals should be undertaken.
Question 86.
“There is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development.”
Give two broad measures for it. As concerned citizens, how can you help conserve
energy?
Answer:
Two broad measures to develop a sustainable path of energy development are:
1. We have
to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy
resources. So conservation of energy should be done at all levels.
2. Increased
use of renewable energy resources, e.g., solar energy, hydel power, etc.
Concerned citizens can help conserve energy in the following ways:
1. Using
more of public transport system instead of individual vehicles.
2. Switching
off electricity when not in use.
3. Using
power saving devices.
4. Using
non-conventional sources of energy such as solar energy, wind energy etc.
5. Getting
the power equipment regularly checked to detect damages and leakages.
Question 87.
Highlight the importance of petroleum. Explain the occurrence of petroleum in
India.
Or
Which is the next major source of energy after coal in India? Describe any three
advantages of it.
Answer:
Importance of Petroleum in India:
1. It is the
second most important energy source of India after coal. It can be easily
transported by pipelines and does not leave any residue. This property of
petroleum gives it an added advantage in its use over other fuels.
2. It
provides fuel for heat and light.
3. It
provides lubricants for machinery.
4. It
provides raw material for a number of manufacturing industries.
5. It is an
important fuel used in transportation sector.
6. Petroleum
refineries act as a ‘nodal industry’ for synthetic textiles, fertilizers and
many chemical industries.
Occurrence of Petroleum in India:
1. Most of
the petroleum occurrences in India are associated with anticlines and fault
traps in the rock formations of the tertiary age.
2. In
regions of folding anticlines it occurs where oil is trapped in the crest of the
upfold. The oil bearing layer is porous limestone or sandstone through which oil
may flow.
3. Petroleum
is also found in fault traps between porous and non-porous rocks.
Question 88.
‘Energy saved is energy produced.’ Assess the statement.
Answer:
Energy saved is energy produced. We cannot keep on producing non-renewable
resources like petrol, diesel and electricity. So the need of the hour is the
better utilization of existing resources. Energy depletion has become a global
phenomenon at present time. The biggest problem that man has to face in near
future is the energy crisis.
The demand of energy is growing manyfold in the form of coal, oil, gas or
electricity but the energy sources are becoming scarce and costlier. Nearly 97%
of the world’s consumed energy is coming from fossil fuels, coal, petroleum and
natural gas. Among the various strategies for meeting energy demand, the
efficient use of energy and its conservation is the best solution.
Following are some measures to conserve energy resources:
1. We should
try and use more and more public transport system instead of private vehicles.
2.
Electronic devices must be switched off when not in use.
3. Reducing
the consumption of non-renewable sources of energy.
4. Solar
Power should be used to the maximum to generate electricity.
5. Recycling
of goods and commodities can also help to conserve energy.
Question 89.
Describe the importance of minerals in human life.
Answer:
1.
Minerals are an indispensable part of human life. Almost all things we use are
made of minerals.
2.
Human beings use minerals for their livelihood, decoration, festivities,
religious and ceremonial rites.
3.
Buildings, ships, railway lines, cars, buses, aeroplanes, various implements
etc. are manufactured from minerals and run on power resources derived from the
earth.
4. Our
food too contains minerals. Life processes cannot occur without minerals.
5.
They are very important part of total food intake.
6. It
is only 0.3 per cent of the total intake of nutrients but they are so potent and
so important that without them we would not be able to utilise the other 99.7
per cent of the foodstuffs.
7. In
toothpaste, fluoride which is used to reduce cavities, comes from a mineral
fluorite.
Question 90.
“Minerals are found in varied forms in nature ranging from the hardest diamond
to the softest talc.” Why are they so varied?
Answer:
The reasons are as mentioned below :
1.
Rocks are combinations of homogenous substances called minerals.
2.
Majority of the rock consist of several minerals except limestone that consists
of a single mineral only.
3. A
particular mineral depends upon the physical and chemical conditions under which
the material forms.
4.
This in turn, results in a wide range of colours, hardness, crystal forms,
luster and density that a particular mineral possesses. Geologists use these
properties to classify the minerals.
Question 91.
Which are the ideal conditions under which minerals may be mined?
Answer:
The ideal conditions for mining of minerals are as given below :
1. The
mineral content of the ore must be in sufficient concentration to make its
extraction commercially viable.
2. The
type of formation determines the relative ease with which mineral ores may be
mined.
3.
This also determines the cost of extraction.
Question 92.
Describe the main types of formations in which minerals occur.
Answer:
The minerals occur in various types of formations as given below :
(1) Igneous and metamorphic rocks: See Textbook
Exercise Question 2(3).
(2) In sedimentary rocks: Minerals occur in beds or layers.
strata e.g., coal and some forms of iron ore have been concentrated as a result of long periods under heat and pressure.
2.Gypsum, potash, salt and sodium salt are formed as a result of evaporation, especially in arid regions.
(3) Some minerals like bauxite are formed due to
decomposition of surface rocks and the removal of soluble constituents, leaving
a residual mass of weathered material containing ores, e.g., bauxite is formed
this way.
(4) Certain minerals like gold, silver, tin and platinum occur as
alluvial deposits in sands of valley floors and the base of hills. These are
called ‘placer deposits’ and contain minerals, which are not corroded by water.
(5) Ocean waters: Some minerals like common salt, magnesium and bromine
are largely derived from ocean waters. The ocean beds too are rich in manganese
nodules.
Thus, minerals are found in various types of formations.
Question 93.
Describe the factors that play an important role in affecting the economic
viability of a reserve. How does reserve turns into a mine?
Answer:
(1) Important factors affecting the economic viability of reserve are as
mentioned below :
1.
Concentration of mineral in the ore must be sufficient.
2.
There should be ease of extraction.
3. It
must be close to the market.
(2) To meet the demand, a choice is made between a
number of possible options.
1.
When this is done a mineral ‘deposit’ or ‘reserve’ turns into a mine.
Question 94.
“India has fairly rich and varied mineral resources but they are unevenly
distributed.” Explain.
Answer:
(1) The above statement is correct. India is rich in mineral resources but
they are unevenly distributed as mentioned below :
1.
Peninsular rocks : These rocks contain most of the reserves of
coal, metallic minerals, mica and many other non-metallic minerals.
2.
Sedimentary rocks on the western and eastern flanks of the peninsula, in Gujarat
and Assam have most of the petroleum deposits.
3.
Rajasthan with the rock systems of the peninsula, has reserves of many
non-ferrous minerals.
4. The
vast alluvial plains of north India are almost devoid of economic minerals.
(2) Causes of these variations are differences in the
geological structure, processes and time involved in the formation of minerals.
Question 95.
Describe the different types of iron ores and their importance or uses.
Answer:
(1) There are four types of iron ores :
1.
Magnetite: It is the finest quality with a very high content of
iron up to 70 per cent. It has excellent magnetic qualities, especially valuable
in electrical industry.
2.
Haematite: It has content of iron between 50 to 60 per cent. It
is the most important
industrial iron that is used in industries. ,
3.
Limonite: It has iron content of about 40-60 per cent.
4.
Siderite: It has content of between 40 to 50 per cent.
(2) Iron ore is very important for the industrial
development of the country. It is a metal of universal use. It is used for
manufacturing of machines, agricultural implements and items of general use.
Question 96.
Describe the major iron ore belts in India.
Answer:
The major iron ore belts in India are given below :
(1) Orissa-Jharkhand belt :
(2) Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur belt:
(3) Bellary-Chitradurga-Chikmaglur-Tumkur belt:
(4) Maharashtra-Goa belt:
Iron ores are not of very high quality, but efficiently exploited and exported through Marmagao port.
Question 97.
Describe the uses of manganese. Where is it found in India?
Answer:
(1) Uses :
1.
Manganese is mainly used in the manufacturing of steel and ferro-manganese
alloy.
2. 10
kg of manganese is used to manufacture, one tonne of steel.
3. It
is also used in manufacturing bleaching powder, insecticides and paints.
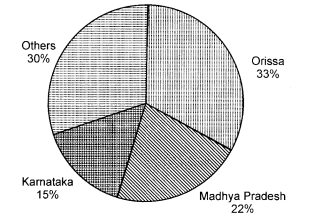
(2) Orissa is the largest producer of manganese ores.
It produced one-third of the country’s total production in 2000-01. Karnataka
produces 15%, Madhya Pradesh 22% and other states produce 30% manganese in the
country. See the figure given below:
Question 98.
Describe the distribution of copper in India. What are its uses and what is the
position of India regarding its availability?
Answer:
1.
Copper is found in the Balaghat mines (Madhya Pradesh), Singbhum district of
Jharkhand and Khetri mines in Rajasthan. The Balaghat mines produce 52 per cent
of India’s copper. However, India is critically deficient in the reserve and
production of copper.
2.
Copper is malleable, ductile and a good conductor and is, therefore, mainly used
in electrical cables, electronic and chemical industries.
Question 99.
Write a short note on bauxite, its formation, features and distribution in
India.
Answer:
(1) Type of mineral : Bauxite is a clay-like substance from which alumina
and later aluminium is obtained. Aluminium is an important metal because it
combines the strength of metals such as iron, with extreme lightness and also
with good conductivity and great malle-ability.
(2) Formation: Bauxite deposits are formed by the decomposition of a wide
variety of rocks rich in aluminium silicates.
(3) Distribution:
1. It
is found in the Amarkantak plateau, Maikal Hills and the plateau region of
Bilaspur-Katni. Orissa is the largest bauxite producing state in India with 45
per cent of the country’s total production in 2000-01.
2.
Panchpatmali deposits in Koraput district are the most important bauxite
deposits in the state.
Question 100.
Name the non-metallic mineral which can split easily into thin sheets? Mention
its uses.
Or
Describe the formation, distribution and uses of mica in India.
Answer:
1.
Mica is a non-metallic mineral which can be split easily into thin sheets that a
thousand can be layered into a mica sheet of a few centimeters height. It is
made up of a series of plates or leaves.
2.
Mica can be clear, black, green, red, yellow or brown.
3.
Uses: It has excellent di-electric strength, low power loss
factor, insulating properties and resistance to high voltage, and is, therefore,
very useful and indispensable mineral in electric and electronic industries.
4.
Distribution: It is found in the northern edge of the Chhota
Nagpur plateau, around Ajmer in Rajasthan and Nellore mica belt of Andhra
Pradesh. Koderma Gaya-Hazaribagh belt of Jharkhand is the leading producer of
mica.
Question 101.
Describe how limestone is found. What are its uses? Describe its distribu¬tion
in India.
Answer:
1.
Limestone is found in association with rocks composed of calcium carbonates or
calcium and magnesium carbonates. It is found in sedimentary rocks of most
geological formations.
2.
Uses: Limestone is the basic raw material for the cement
industry. It is essential for smelting iron ore in the blast furnace.
3.
Limestone is produced in Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat,
Tamil Nadu and some other states.
Question 102.
Describe the hazards of mining or describe the impact of mining on the health of
the miners and the environment. What is the position of miners in India?
Answer:
(1) The hazards of mining or the impacts of mining on the health of the
miners and the environment are given below :
1. The
dust and noxious fumes inhaled by miners make them vulnerable to pulmonary
diseases.
2. The
risk of collapsing mine roofs, inundation and fires in coalmines are a constant
threat to miners.
3. The
water sources in the area get contaminated due to mining.
4. It
leads to degradation of soil and land due to dumping of waste and slurry.
5. It
increases pollution in stream and river.
(2) The condition in coal mines in India are sometimes
not satisfactory. Underground fires start mostly from burning trash close to
coal pits. Over 50% of coal-belt mines are not safe in India. The companies
which own mines do not meet the basic safety standards. The safety status of
mines has been graded second and third degrees in the past. Lack of security
measures in the coal mines leads to disasters. It has, in practice, become a
‘killer industry’ because many miners are killed every year due to explosions or
other incidents in the mines.
Question 103.
Explain the importance of conservation of minerals. Highlight any three measures
to conserve them
Or
Why is conservation of minerals necessary? Explain three methods to conserve
them?
Answer:
See Textbook Question 2(4).
Question 104.
State another name of lignite coal and write any one feature and use of the
same.
Or
Describe qualities of different types of coal found in India. Describe its
formation, distribution and uses.
Answer:
(1) There are four types of coal. Their qualities are given below:
1.
Peat: It has low carbon and high moisture contents and low
heating capacity.
2.
Lignite: It is a low grade brown coal. It is soft with high
moisture content. It is used for generation of electricity.
3.
Bituminous: It is the most popular coal in commercial use.
Metallurgical coal, a high grade bituminous coal has a special value for
smelting iron in blast furnaces.
4.
Anthracite: It is the highest quality hard coal.
(2) Formation: It is formed due to the compression of
plant material over millions of years.
(3) Distribution : Coal is found in Damodar valley i.e., West Bengal,
Jharkhand, Jharia, Raniganj, Godavari, Mahanadi, Son and Wardha valleys,
Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
(4) Uses of coal:
1. It
is used for power generation, to supply energy to industry as well as for
domestic needs.
2. It
meets most of the commercial energy requirements in India.
Question 105.
Highlight the importance of petroleum. Explain the occurrence of petrolei ? in
India.
Answer:
(1) Importance : It is the second major energy source in India after coal.
Its uses are as given below:
1. It
provides fuel for heat and lighting.
2. It
provides lubricants for machinery.
3. It
provides raw materials for many manufacturing industries.
4.
Petroleum refineries act as a ‘nodal industry’ for synthetic, textile,
fertiliser an numerous chemical industries.
(2) Occurrences of petroleum is as mentioned below:
1.
Most of the petroleum occurrences in India are associated with anticlines and
fault traps in the rock formations of the tertiary age.
2. In
regions of folding, anticlines or domes, it occurs where oil is trapped in the
crest of the upfold.
3. The
oil bearing layer is a porous limestone or sandstone through which oil may flow.
4. The
oil is prevented from rising or sinking by intervening non-porous layers.
(3) Distribution of petroleum: Distribution of petroleum is given below
:
1. 63%
of India’s petroleum production is from Mumbai High, 18 per cent from Gujarat
and 16 per cent from Assam.
2.
Ankeleshwar is the most important field of Gujarat.
3.
Assam is the oldest oil producing state of India. Digboi, Naharkatiya and Mora a
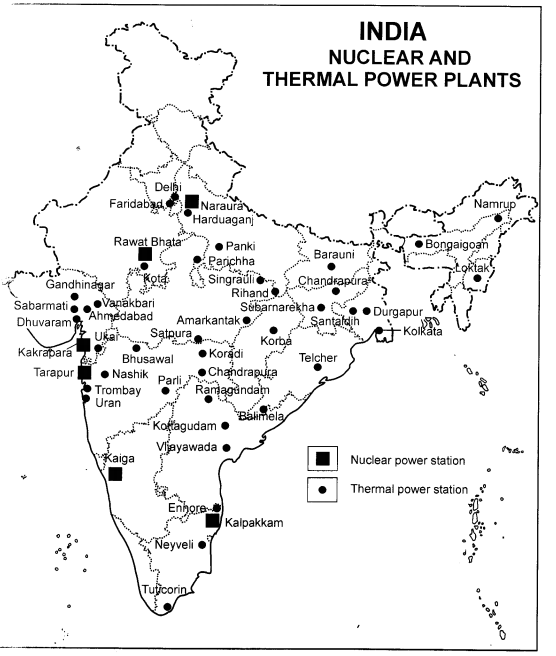
Hugrijan are the important oil fields in the state.
Question 106.
Write a short note on natural gas as a conventional source of energy with
special reference to its uses, features and distribution.
Answer:
1.
Uses: Natural gas is found in association with or without
petroleum. It is an important clean energy resource. It is used as a source of
energy and an industrial raw materia ; in the petrochemical industry. The power
and fertiliser industries are the main users of natural gas. CNG (Compressed
Natural Gas) is used in vehicles in place of liquid fuels.
2.
Features: It is environment friendly because of low carbon
dioxide emissions.
3.
Distribution: Large-reserves are in the Krishna-Godavari basin,
Mumbai High, Gulf of Cambay, Andaman and Nicobar islands.
4. The
1700 km long Hazira-Vijaipur-Jagdishpur cross country gas pipeline links Muml
High and Bassien with the fertiliser, power and industrial complexes in western
and northern India.
Question 107.
What are the two main ways of generating electricity? How are they different
from each other?
Or
Differentiate between hydroelectricity and thermal electricity.
Or
Why per capita consumption of electricity is considered as an index of
development?
Answer:
(1) Electricity is generated in two ways :
1.
Hydroelectricity: It is generated by fast flowing water which
is a renewable source. India is producing hydroelectricity through a number of
multi-purpose projects like the Bhakra Nangal, Damodar Valley Corporation, the
Ropili Hydel Project.
2.
Thermal electricity: It is generated by using coal, petroleum
and natural gas. The thermal power stations use non-renewable fossil fuels for
generating electricity. There are over 310 thermal power plants in India.
(2) For progress and prosperity of individuals and the
nation, electricity is an important requirement. It is used at homes as well as
in offices and in industries. It has a very wide range of applications in
today’s world. That is why its per capital consumption is considered as an index
of development.
Question 108.
How nuclear or atomic energy is obtained? Mention the nuclear power stations and
the states where they are located.
Answer:
(1) Nuclear or atomic energy is obtained by altering the structure of
atoms. When such an alteration is made, much energy is released in the form of
heat and this is used to generate electric power. It is produced by using
uranium and thorium. These are available in Jharkhand and the Aravalli ranges of
Rajasthan. Monazite sands of Kerala contain uranium. India has vast deposits of
thorium which is about 50 per cent of world’s deposits.
(2) Six nuclear power stations are located in the states as mentioned below:
1.
Naraura – Uttar Pradesh
2.
Rawat Bhata – Rajasthan
3.
Kakrapara – Gujarat
4.
Tarapur – Maharashtra
5.
Kaiga – Karnataka
6.
Kalpakkam — Tamil Nadu.
Question 109.
Why should non-conventional energy be used more? Explain.
Or
Why is there a pressing need for using renewable energy sources in India?
Explain.
Answer:
The reasons for using renewable energy sources or non-conventional energy
such as solar, wind, water are as mentioned below :
1. Use
of fossil fuels has caused serious environmental problems.
2.
Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised
uncertainties about energy resources in the future.
3.
India has abundance of sunlight, water, wind and biomass.
4.
Rising prices of oil etc. has serious repercussions on the growth of the
national economy as we have to make payment for import of oil in foreign
exchange.
Question 110.
Describe the importance of wind energy in India with special reference to its
uses.
Answer:
India has a wind power potential of 20,000 MW. This energy requires only initial
cost on the establishment of wind farm. The largest wind farm cluster is located
in Tamil Nadu from Nagarcoil to Madurai. Wind farms have been established in
Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Kerala, Maharashtra and Lakshadweep. India
now ranks as a “wind super power” in the world.
Question 111.
How is biogas produced? What are its uses?
Answer:
(1) Production : Shrubs, farm waste, animal and human waste are used to
produce biogas for domestic consumption in rural areas. Decomposition of organic
matter yields gas, which has higher thermal efficiency in comparison to
kerosene, dung cake and charcoal.
(2) Uses of biogas:
1.
Biogas plants are set up at municipal, cooperative and individual levels.
2. The
plants using cattle dung are known as ‘Gobar gas plants’ which are used in rural
India.
3.
Gobar gas plants are very beneficial for the farmers because they provide energy
to the farmers as well as improve quality of manure.
4. It
prevents the loss of trees and manure due to burning of fuel wood and cow dung
cakes.
Question 112.
What is tidal energy? How does it generate electricity? Which area provides
ideal conditions for utilising tidal energy in India?
Answer:
(1) Tidal energy means use of oceanic tides to generate electricity.
(2) Generation of electricity: To generate electricity, floodgate
dams are built across inlets. During high tide water flows into the inlet and
gets trapped when the gate is closed. After the tide falls outside the
floodgate, the water retained by the floodgate flows back to the sea via a pipe
that carries it through a power-generating turbine.
(3) Areas of ideal conditions for utilising tidal energy: The Gulf of
Kuchchh provides ideal conditions for utilising tidal energy. The National
Hydropower Corporation has set up a 900 MW tidal energy power plant in the Gulf
of Kuchchh.
Question 113.
What is Geothermal Energy? Name the places where experimental projects for
geothermal energy have been set up in India.
Answer:
(1) Geothermal Energy : It refers to the heat and electricity produced by
using the heat from the interior of the earth.
(2) In India, two experimental projects have been set up as mentioned below:
1. In
the Parvati Valley near Manikarn in Himachal Pradesh.
2. In
the Puga Valley, Ladakh.
Question 114.
Describe the steps that should be taken for conservation of energy re¬sources.
Answer:
The following steps should be taken for conservation of energy resources :
1. Use
more and more of public transport system and less of individual vehicles.
2.
Switch off electricity whenever not required.
3. Use
power-saving devices.
4.
Check the power equipment regularly.
5.
Greater use of non-conventional sources of energy.
These steps are necessary because “energy saved is energy produced”.
MAP QUESTIONS
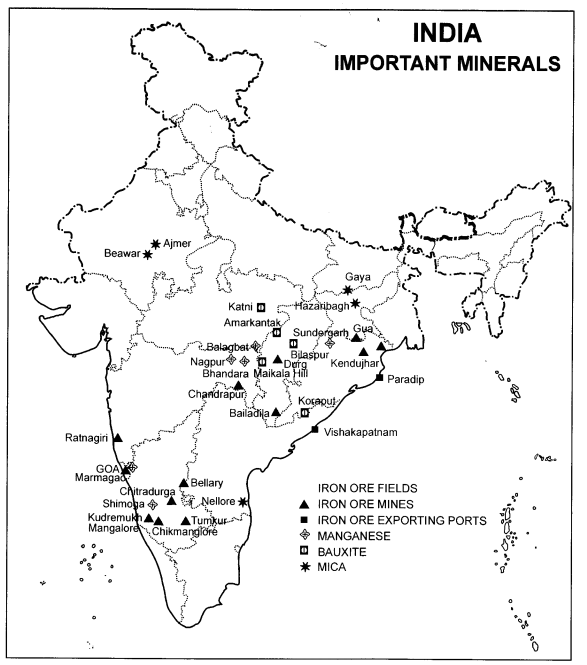
Question 1.
Show important places where the following minerals are found:
1.
Iron ore
2.
Manganese
3.
Bauxite
4.
Mica
Answer:
Question 2.
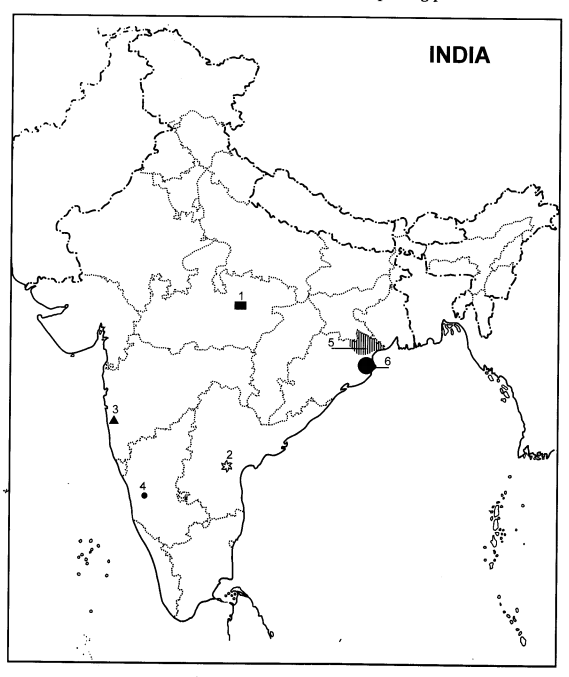
Six features with serial numbers (1) to (6) are marked in the given political
outline map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following
information and write their correct names on the lines marked in the map.
1.
A bauxite mine
2.
A mica mine
3.
Iron ore mines
4.
Manganese
5.
Iron ore fields
6.
Iron ore exporting port
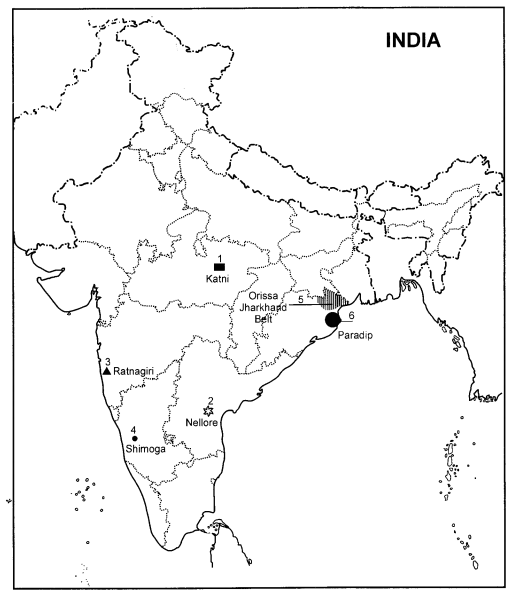
Answer:
The correct names are as given below :
1.
Katni
2.
Nellore
3.
Ratnagiri
4.
Shimoga
5.
Orissa-Jharkh and Belt
6.
Paradip
See map given below :
Question 3.
On the map of India, show the important places of conventional energy resources.
Answer:
Important places of conventional energy resources are given below :
(1) Coal mines: Neyvali, Singareni, Talcher, Korba, Sirfgarauli,
Bokaro, Jharia, Raniganj and Janji.
See the map given below :
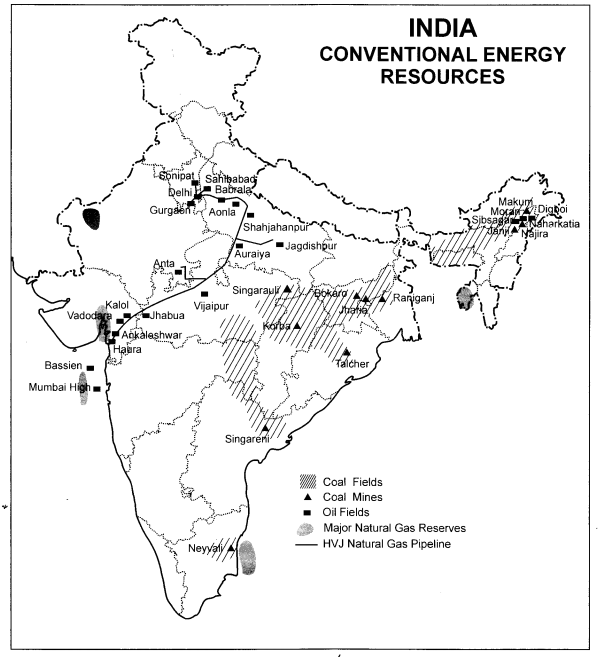
Question 4.
On the map of India show the nuclear and thermal power plants.
Answer:
1.
Nuclear power plants : Six power plants are at Kalpakkam, Kaiga,
Tarapur, Ki krapara, Rawat Bhata and Naraura.
2.
Hermal power plants : There are over Thermal power plants. The main
plants are at Delhi, Faridabad, Panki, Barauni, Loktak, Durgapur, Kolkata,
Singrauli, Bhusawal, ivawada. Sabarmati and other places.
see the map given below :