Electricity
Class 10th Science Chapter MCQs
Electricity Class 10 MCQs Questions
1.
Which of the following represents voltage?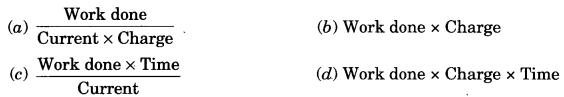
Answer
Answer: (a)
2.
Unit of electric power may also be expressed as
(a) volt
ampere
(b) kilowatt hour
(c) watt second
(d) Joule
second
Answer
Answer: (a) volt ampere
3.
Electrical resistivity of a given metallic wire depends
upon
(a) its length
(b) its thickness
(c) its shape
(d) nature of
the material
Answer
Answer: (d) nature of the material
4.
A cell, a resistor, a key and ammeter are arranged as shown in
the circuit diagrams of Figure (i), (ii) and (iii). The current recorded in the
ammeter will be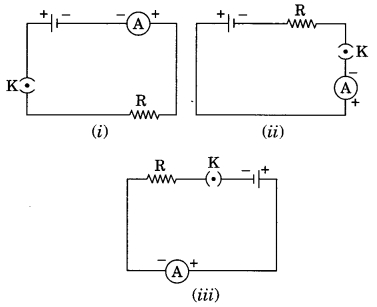
(a) maximum in (i)
(b) maximum in (ii)
(c) maximum in (iii)
(d) the
same in all the cases
Answer
Answer: (d) the same in all the cases
5.
The unit of e.m.f. of a cell is
(a) dyne
(b) volt
(c)
ampere
(d) joule
Answer
Answer: (b) volt
3.
Electrical resistivity of any given metallic wire depends
upon
(a) its thickness
(b) its shape
(c) nature of the material
(d)
its length
Answer
(c) nature of the material
4.
Two devices are connected between two points say A and B in
parallel. The physical quantity that will remain the same between the two points
is
(a) current
(b) voltage
(c) resistance
(d) None of
these
Answer
(b) voltage
5.
100 J of heat is produced each second in a 4Ω resistor. The
potential difference across the resistor will be:
(a) 30 V
(b) 10 V
(c)
20 V
(d) 25 V
Answer
(b) 10 V
6.
The resistivity of insulators is of the order of
(a) 10-8
Ω-m
(b) 101 Ω-m
(c) 10-6 Ω-m
(d) 106 Ω-m
Answer
(a) 10-8 Ω-m
7.
An electric bulb is connected to a 220V generator. The current
is 0.50 A. What is the power of the bulb?
(a) 440 W
(b) 110 W
(c) 55
W
(d) 0.0023 W
Answer
(b) 110 W
8.
The electrical resistance of insulators is
(a) high
(b)
low
(c) zero
(d) infinitely high
Answer
(d) infinitely high
9.
When electric current is passed, electrons move from:
(a)
high potential to low potential.
(b) low potential to high potential.
(c)
in the direction of the current.
(d) against the direction of the
current.
Answer
(b) low potential to high potential.
10.
The heating element of an electric iron is made up of:
(a)
copper
(b) nichrome
(c) aluminium
(d) iron
Answer
(b) nichrome
11.
Coulomb is the SI unit of:
(a) charge
(b) current
(c) potential difference
(d) resistance
Answer
(a) charge
12.
Work done to move 1coulomb charge from one point to another
point on a charged conductor having potential 10volt is
(a) 1 Joule
(b) 10
Joule
(c) zero
(d) 100 Joule
Answer
(c) zero
13.
A student says that the resistance of two wires of same
length and same area of cross section is same. This statement is correct if
(a) Both wires are of different materials
(b) Both wires are made of same
material and are at different temperature.
(c) Both wires are made of same
material and are at same temperature.
(d) Both wires are made of different
materials and are at the same temperature.
Answer
(c) Both wires are made of same material and are at same temperature.
14.
A cooler of 1500 W, 200 volt and a fan of 500 W, 200 volt are
to be used from a household supply. The rating of fuse to be used is
(a) 2.5
A
(b) 5.0 A
(c) 7.5 A
(d) 10 A
Answer
(d) 10 A
15.
If the current I through a resistor is increased by 100% the
increased in power dissipation will be (assume temperature remain unchanged)
(a)100%
(b) 200%
(c) 300%
(d) 400%
Answer
(c) 300%
16.
A coil in the heater consume power P on passing current. If
it is cut into halves and joined in parallel, it will consume power
(a) P
(b) P/2
(c) 2P
(d) 4P
Answer
(d) 4P
17.
If R1 and R2 be the resistance of the
filament of 40 W and 60 W respectively operating 220 V, then
(a)
R1 < R2
(b) R2 < R1
(c)
R1 = R2
(d) R1 ≥
R2
Answer
(b) R2 < R1
18.
A metallic conductor has loosely bound electrons called free
electrons. The metallic conductor is
(a) negatively charged
(b) positively
charged
(c) neutral
(d) Either positively charged or negatively
charged
Answer
(c) neutral
19.
To get 2 Ω resistance using only 6 Ω resistors, the number of
them required is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer
(b) 3
20.
Resistivity of a metallic wise depends on
(a) its
length
(b) its shape
(c) its thickness
(d) nature of
material
Answer
(d) nature of material
21.
Assertion: Conductors allow the current to flow through
themselves.
Reason: They have free charge carriers.
(a) Both A and R are
true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R
is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A
is false but R is true.
(e) Both A and R are
false.
Answer
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
22.
Assertion: Bending of wire decrease the resistance of
electric wire.
Reason: The resistance of a conductor depends on length,
thickness, nature of material and temperature of the conductor.
(a) Both A
and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are
true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is
false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
(e) Both A and R are
false.
Answer
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
23.
What is the commercial unit of electrical energy?
(a)
Joules
(b) Kilojoules
(c) Kilowatt-hour
(d)
Watt-hour
Answer
(c) Kilowatt-hour
24.
A boy records that 4000 joule of work is required to transfer
10 coulomb of charge between two points of a resistor of 50 Ω. The current
passing through it is
(a) 2 A
(b) 4 A
(c) 8 A
(d) 16
A
Answer
(c) 8 A
25.
A fuse wire repeatedly gets burnt when used with a good
heater. It is advised to use a fuse wire of
(a) more length
(b) less
radius
(c) less length
(d) more radius
Answer
(d) more radius
26.
Three resistors of 1 Ω, 2 ft and 3 Ω are connected in
parallel. The combined resistance of the three resistors should be
(a)
greater than 3 Ω
(b) less than 1 Ω
(c) equal to 2 Ω
(d) between 1 Ω and
3 Ω
Answer
(b) less than 1 Ω
27.
Which of the following gases are filled in electric
bulbs?
(a) Helium and Neon
(b) Neon and Argon
(c) Argon and
Hydrogen
(d) Argon and Nitrogen
Answer
(d) Argon and Nitrogen
28.
Electric power is inversely proportional to
(a)
resistance
(b) voltage
(c) current
(d)
temperature
Answer
(a) resistance
29.
An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is
operated on 110 V, the power consumed will be:
(a) 100 W
(b) 75 W
(c)
50 W
(d) 25 W
Answer
(d) 25 W
30.
1 mV is equal to:
(a) 10 volt
(b) 1000 volt
(c) 10-3
volt
(d) 10-6 volt
Answer
(c) 10-3 volt
31.
A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into five equal parts.
These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this
combination is R’, then the ratio R/R’ is:
(a) 1/25
(b) 1/5
(c) 5
(d) 25
Answer
(d) 25
32.
Electric potential is a:
(a) scalar quantity
(b) vector
quantity
(c) neither scalar nor vector
(d) sometimes scalar and sometimes
vector
Answer
(a) scalar quantity
33.
What is the maximum resistance which can be made using five
resistors each of 1/5 W?
(a) 1/5 Ω
(b) 10 Ω
(c) 5 Ω
(d) 1
Ω
Answer
(d) 1 Ω
34.
A current of 1 A is drawn by a filament of an electric bulb.
Number of electrons passing through a cross-section of the filament in 16
seconds would be roughly
(a) 1020
(b) 1016
(c) 1018
(d)
1023
Answer
(a) 1020
35.
The resistance of hot filament of the bulb is about 10 times
the cold resistance. What will be the resistance of 100 W-220 V lamp, when not
in use?
(a) 48 Ω
(b) 400 Ω
(c) 484 Ω
(d) 48.4
Ω
Answer
(c) 484 Ω
36.
The nature of the graph between potential difference and the
electric current flowing through a conductor is
(a)parabolic
(b)
circle
(c) straight line
(d) hyperbolic
Answer
(c) straight line
37.
Two resistors are connected in series gives an equivalent
resistance of 10 Ω. When connected in parallel, gives 2.4 Ω. Then the individual
resistance are
(a) each of 5 Ω
(b) 6 Ω and 4 Ω
(c) 7 Ω and 4 Ω
(d) 8
Ω and 2 Ω
Answer
(b) 6 Ω and 4 Ω
38.
Resistivity of a metallic wise depends on
(a) its
length
(b) its shape
(c) its thickness
(d) nature of
material
Answer
(d) nature of material
39.
The least resistance obtained by using 2 Ω, 4 Ω, 1 Ω and 100
Ω is
(a) < 100 Ω
(b) < 4 Ω
(c) < 1 Ω
(d) > 2
Ω
Answer
(c) < 1 Ω
40.
A battery of 10 volt carries 20,000 C of charge through a
resistance of 20 Ω. The work done in 10 seconds is
(a) 2 × 103 joule
(b) 2
× 105 joule
(c) 2 × 104 joule
(d) 2 × 102 joule
Answer
(b) 2 × 105 joule
41.
Kilowatt hour is the unit of
(a) power
(b) energy
(c)
impulse
(d) force
Answer
Answer: (b) energy
42.
1 kWh is equal to
(a) 3.6 × 106 MJ
(b) 3.6 ×
105 MJ
(c) 3.6 × 10² MJ
(d) 3.6 MJ
Answer
Answer: (d) 3.6 MJ
43.
Materials which allow larger currents to flow through them are
called
(a) insulators
(b) conductors
(c) semiconductors
(d)
alloys
Answer
Answer: (b) conductors
44.
Conventionally, the direction of the current is taken as
(a) the direction of flow of negative charge
(b) the direction of flow of
atoms
(c) the direction of flow of molecules
(d) the direction of flow of
positive charge
Answer
Answer: (d) the direction of flow of positive charge
45.
The unit of specific resistance is
(a) ohm
(b) ohm
(c) ohm-metre
(d) ohm per metre
Answer
Answer: (c) ohm-metre
46.
The slope of voltage (V) versus current (I) is called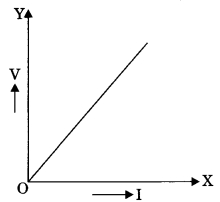
(a) resistance
(b) conductance
(c) resistivity
(d)
conductivity
Answer
Answer: (a) resistance
47.
The variable resistance is called
(a) resistor
(b)
rheostat
(c) open switch
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (b) rheostat
48.
The SI unit of resistance is
(a) ohm m
(b) ohm
m1
(c) ohm
(d) (ohm)-1
Answer
Answer: (c) ohm
49.
An electric iron draws a current 4 A when connected to a 220
V mains. Its resistance must be
(a) 1000 Ω
(b) 55 Ω
(c) 44 Ω
(d)
None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) 55 Ω
50.
The element used almost exclusively for filaments of
incandescent lamps
(a) copper
(b) gold
(c) silver
(d)
tungsten
Answer
Answer: (d) tungsten