Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
Class 10th Maths Chapter MCQs
Class 10 Maths MCQs Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
1. Which of the following is not a quadratic equation
(a) x² + 3x – 5 =
0
(b) x² + x3 + 2 = 0
(c) 3 + x + x² = 0
(d) x² – 9 =
0
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:Reason: Since it has degree 3.
2. The quadratic equation has degree
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d)
3
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:Reason: A quadratic equation has degree
2.
3. The cubic equation has degree
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:Reason: A cubic equation has degree
3.
4. A bi-quadratic equation has degree
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d)
4
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:Reason: A bi-quadratic equation has degree 4.
5. The polynomial equation x (x + 1) + 8 = (x + 2) {x – 2) is
(a) linear
equation
(b) quadratic equation
(c) cubic equation
(d) bi-quadratic
equation
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:Reason: We have x(x + 1) + 8 = (x + 2) (x – 2)
⇒
x² + x + 8 = x² – 4
⇒ x² + x + 8- x² + 4 = 0
⇒ x + 12 = 0, which is a
linear equation.
6. The equation (x – 2)² + 1 = 2x – 3 is a
(a) linear equation
(b)
quadratic equation
(c) cubic equation
(d) bi-quadratic
equation
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:Reason: We have (x – 2)² + 1 = 2x – 3
⇒ x² + 4 –
2 × x × 2 + 1 = 2x – 3
⇒ x² – 4x + 5 – 2x + 3 = 0
∴ x² – 6x + 8 = 0, which
is a quadratic equation.
7. The roots of the quadratic equation 6x² – x – 2 = 0 are
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:Reason: We have 6×2 – x – 2 = 0
⇒ 6x² + 3x-4x-2
= 0
⇒ 3x(2x + 1) -2(2x + 1) = 0
⇒ (2x + 1) (3x – 2) = 0
⇒ 2x + 1 = 0 or
3x – 2 = 0
∴ x =\(-\frac{1}{2}\), x = \(\frac{2}{3}\)
8. The quadratic equation whose roots are 1 and
(a) 2x² + x – 1 = 0
(b)
2x² – x – 1 = 0
(c) 2x² + x + 1 = 0
(d) 2x² – x + 1 =
0
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:Reason: Required quadratic equation is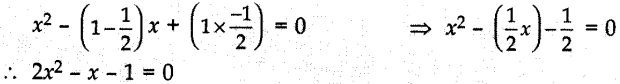
9. The quadratic equation whose one rational root is 3 + √2 is
(a) x² – 7x
+ 5 = 0
(b) x² + 7x + 6 = 0
(c) x² – 7x + 6 = 0
(d) x² – 6x + 7 =
0
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:Reason: ∵ one root is 3 + √2
∴ other root is 3 –
√2
∴ Sum of roots = 3 + √2 + 3 – √2 = 6
Product of roots = (3 + √2)(3 –
√2) = (3)² – (√2)² = 9 – 2 = 7
∴ Required quadratic equation is x² – 6x + 7 =
0
10. The equation 2x² + kx + 3 = 0 has two equal roots, then the value of k
is
(a) ±√6
(b) ± 4
(c) ±3√2
(d) ±2√6
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:Reason: Here a = 2, b = k, c = 3
Since the
equation has two equal roots
∴ b² – 4AC = 0
⇒ (k)² – 4 × 2 × 3 = 0
⇒ k²
= 24
⇒ k = ± √24
∴ k= ± \(\pm \sqrt{4 \times 6}\) = ± 2√6
11. The roots of the quadratic equation \(x+\frac{1}{x}=3\), x ≠ 0
are.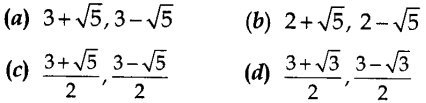
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:Reason: We have \(x+\frac{1}{x}=3\)
⇒
\(\frac{x^{2}+1}{x}=3\)
⇒ x² + 1 = 3x
On comparing with ax² + bx + c =
0
∴ a = 1, b = – 3, c = 1
⇒ D = b² – 4ac = (-3)² – 4 × (1) × (1) = 9 – 4 =
5
12. The roots of the quadratic equation 2x² – 2√2x + 1 = 0 are
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:Reason: Here a = 2, b = -2√2 , c = 1
∴ D = b² –
4ac = (-2√2 )² – 4 × 2 × 1 = 8 – 8 = 0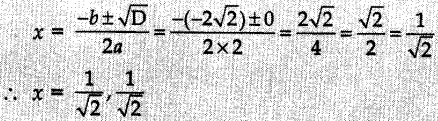
13. The sum of the roots of the quadratic equation 3×2 – 9x + 5 = 0 is
(a)
3
(b) 6
(c) -3
(d) 2
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:Reason: Here a = 3, b = -9, c = 5
∴ Sum of the
roots \(=\frac{-b}{a}=-\frac{(-9)}{3}=3\)
14. If the roots of ax2 + bx + c = 0 are in the ratio m : n, then
(a) mna²
= (m + n) c²
(b) mnb² = (m + n) ac
(c) mn b² = (m + n)² ac
(d) mnb² =
(m – n)² ac
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: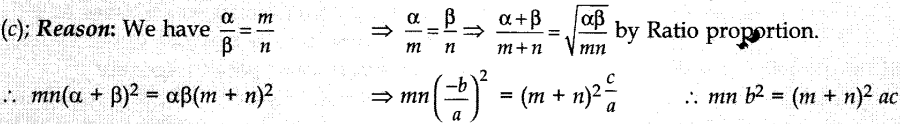
15. If one root of the equation x² + px + 12 = 0 is 4, while the equation x²
+ px + q = 0 has equal roots, the value of q is
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:Reason: Since 4 is a root of x² + px + 12 = 0
∴
(4)² + p(4) + 12 = 0
⇒ p = -7
Also the roots of x² + px + q = 0 are equal,
we have p² – 4 x 1 x q = 0
⇒ (-7)² -4q = 0
\(\therefore
q=\frac{49}{4}\)
16. a and p are the roots of 4x² + 3x + 7 = 0, then the value of
\(\frac{1}{\alpha}+\frac{1}{\beta}\) is
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: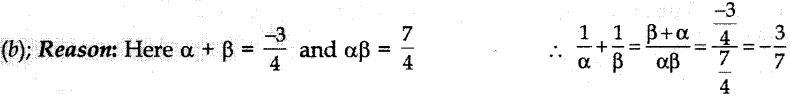
17. If a, p are the roots of the equation (x – a) (x – b) + c = 0, then the
roots of the equation (x – a) (x – P) = c are
(a) a, b
(b) a, c
(c) b,
c
(d) none of these
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:Reason: By given condition, (x – a) (x – b) + c =
(x – α) (x – β)
⇒ (x – α) (x – β) – c = (x – a) (x – b)
This shows that
roots of (x – α) (x – β) – c are a and b
18. Mohan and Sohan solve an equation. In solving Mohan commits a mistake in
constant term and finds the roots 8 and 2. Sohan commits a mistake in the
coefficient of x. The correct roots are
(a) 9,1
(b) -9,1
(c) 9, -1
(d) -9, -1
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:Reason: Correct sum = 8 + 2 = 10 from Mohan
Correct product = -9 x -1 = 9 from Sohan
∴ x² – (10)x + 9 = 0
⇒ x² – 10x +
9 = 0
⇒ x² – 9x – x + 9
⇒ x(x – 9) – 1(x – 9) = 0
⇒ (x-9) (x-l) = 0
.
⇒ Correct roots are 9 and 1.
19. If a and p are the roots of the equation 2x² – 3x – 6 = 0. The equation
whose roots are \(\frac{1}{\alpha}\) and \(\frac{1}{\beta}\) is
(a) 6x² – 3x
+ 2 = 0
(b) 6x² + 3x – 2 = 0
(c) 6x² – 3x – 2 = 0
(d) x² + 3x-2 =
0
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: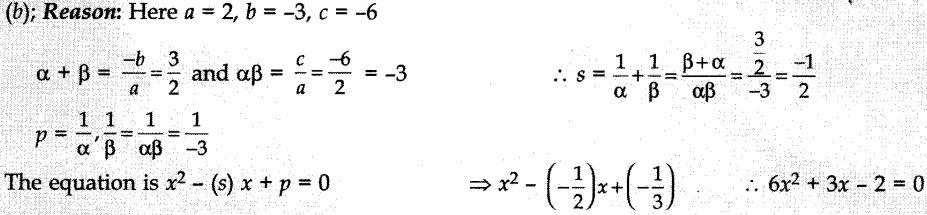
20. If the roots of px2 + qx + 2 = 0 are reciprocal of each other, then
(a) P = 0
(b) p = -2
(c) p = ±2
(d) p = 2
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:Reason: here α = \(\frac{1}{β}\)
∴ αβ = 1
⇒
\(\frac{2}{p}\) = 1
∴ p = 2
21. If one root of the quadratic equation 2x² + kx – 6 = 0 is 2, the value of
k is
(a) 1
(b) -1
(c) 2
(d) -2
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:Reason: Scice x = 2 is a root of the equation 2x² +
kx -6 = 0
∴ 2(2)² +k(2) – 6 = 0
⇒ 8 + 2k – 6 = 0
⇒ 2k = -2
∴ k =
-1
22. The roots of the quadratic equation![]()
(a) a, b
(b) -a, b
(c) a, -b
(d) -a,
-b
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: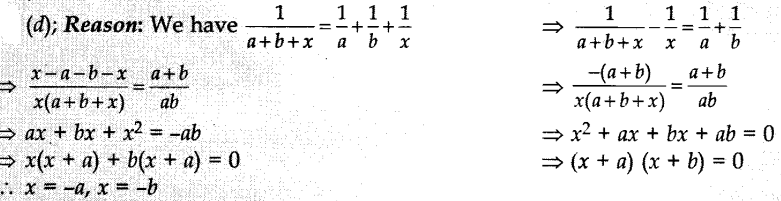
23. The roots of the equation 7x² + x – 1 = 0 are
(a) real and
distinct
(b) real and equal
(c) not real
(d) none of
these
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:Reason: Here a = 2, b = 1, c = -1
∴ D = b² – 4ac
= (1)² – 4 × 2 × (-1) = 1 + 8 = 9 > 0
∴ Roots of the given equation are
real and distinct.
24. The equation 12x² + 4kx + 3 = 0 has real and equal roots, if
(a) k =
±3
(b) k = ±9
(c) k = 4
(d) k = ±2
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:Reason: Here a = 12, b = 4k, c = 3
Since the
given equation has real and equal roots
∴ b² – 4ac = 0
⇒ (4k)² – 4 × 12 ×
3 = 0
⇒ 16k² – 144 = 0
⇒ k² = 9
⇒ k = ±3
25. If -5 is a root of the quadratic equation 2x² + px – 15 = 0, then
(a)
p = 3
(b) p = 5
(c) p = 7
(d) p = 1
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:Reason: Since – 5 is a root of the equation 2x² +
px -15 = 0
∴ 2(-5)² + p (-5) – 15 = 0
⇒ 50 – 5p -15 = 0
⇒ 5p = 35
⇒
p = 7
26. If the roots of the equations ax² + 2bx + c = 0 and bx² – 2√ac x + b = 0
are simultaneously real, then
(a) b = ac
(b) b2 = ac
(c) a2 = be
(d)
c2 = ab
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:Reason: Given equations have real roots, then
D1 ≥ 0 and D2 ≥ 0
(2b)² – 4ac > 0 and (-2√ac)² –
4b.b ≥ 0
4b² – 4ac ≥ 0 and 4ac – 4b2 > 0
b² ≥ ac and ac ≥ b²
⇒ b² =
ac
27. The roots of the equation (b – c) x² + (c – a) x + (a – b) = 0 are equal,
then
(a) 2a = b + c
(b) 2c = a + b
(c) b = a + c
(d) 2b = a +
c
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:Reason: Since roots are equal
∴ D = 0 => b² –
4ac = 0
⇒ (c – a)² -4(b – c) (a – b) = 0
⇒ c² – b² – 2ac -4(ab -b² + bc) =
0 =>c + a-2b = 0 => c + a = 2b
⇒ c² + a² – 2ca – 4ab + 4b² + 4ac – 4bc
= 0
⇒ c² + a² + 4b² + 2ca – 4ab – 4bc = 0
⇒ (c + a – 2b)² = 0
⇒ c + a –
2b = 0
⇒ c + a = 2b
28. A chess board contains 64 equal squares and the area of each square is
6.25 cm². A border round the board is 2 cm wide. The length of the side of the
chess board is
(a) 8 cm
(b) 12 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 36
cm
Answer
Answer: c
29. One year ago, a man was 8 times as old as his son. Now his age is equal
to the square of his son’s age. Their present ages are
(a) 7 years, 49
years
(b) 5 years, 25 years
(c) 1 years, 50 years
(d) 6 years, 49
years
Answer
Answer: a
30. The sum of the squares of two consecutive natural numbers is 313. The
numbers are
(a) 12, 13
(b) 13,14
(c) 11,12
(d)
14,15
Answer
Answer: a