Control and Coordination
Class 10th Science Chapter HOTs
HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
Question
1.
What type of plant movement is seen in the diagram of
coiling of tendril ?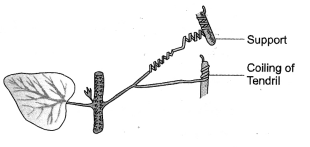
Or
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support? Describe in
brief.
Answer:
Thigmotropism
or curvature movement that occurs in response to contact. Less auxin is present
in the region of contact. The free side having more auxin shows more growth.
This causes the tendril to coil over the support.
Question
2.
Identify and label the parts shown as A and B in the
accompanying figure.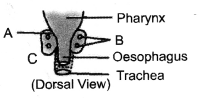
Answer:
Dorsal view of
thyroid an parathyroid.
A – Thyroid,
B- Parathyroid.
Question
3.
What are the hormones involved in providing milk to the
suckling infant ?
Answer:
1. Prolactin
(Maternity Hormone). Production of milk.
2. Oxytocin Ejection of milk.
Question
4.
How does pancreas control glucose level of blood
?
Answer:
Pancreas produces two hormones
- Insulin from P-cells of islet of Langerhans and
- Glucagon from a- cells of islets of langerhans.
Insulin is produced when glucose level of blood rises. Insulin helps the cells to withdraw glucose from blood. It also converts glucose into glycogen in liver and muscles.
Question
5.
Glucagon is secreted when glucose level of blood falls. It
mobilises reserve food like glycogen into glucose. What is pregnancy hormone ?
Why is it known so ?
Answer:
Progesterone
is called pregnancy hormone. It helps in maintaining pregnancy by non-formation
of new ova, promoting thickening and secretory activity of uterine wall and
attachment of embryo to the uterine wall.
Question
6.
What is dormin ?
Answer:
Dormin is the
other name of plant hormone abscisic acid. The hormne induces dormancy in buds
and seeds. So it has been called dormin.
Question
7.
(a)
- Name the parts labelled A and B in the neuron drawn above.
- Which part acquires the information in the neuron ?
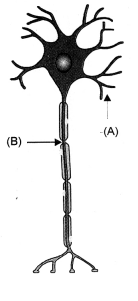
- Through which part does the information travel ?
- In what form does this information travel ?
- Where is the impulse converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission ?
(b) Name the hormone secreted by thyroid. What is the function ?
(c) Why
is the use of iodised salt advisable ?
(CBSE A.I. 2008 Compt.)
Answer:
(a)
- A-Dendrite, B-Axon
- Dandrite.
- Dandrite to cell body or cyton to axon.
- Electrical impulse
- In the region of synapse.
Impulse stimulates the release of chemical neurotransmitter from the surface of presynaptic knob or bouton of axon terminal. Neurotransmitter (e.g. acetylcholine) comes in contact with chemoreceptor sites of post-synaptic membrane of the next neuron and generates a fresh impulse.
(b) Thyroxine:
Function of Thyroxine. It controls
- Basal metabolic rate
- Metabalism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins
- Consumption of energy in physical activity and body temperature
- Development and differentiation.
(c) Iodised Salt: Salt is iodised to provide iodine to thyroid for synthesis of thyroxine which is iodine containing hormone.
Question
8.
(a) What are plant hormones ? Give one example each of a
plant hormone that
- promotes growth
- inhibits growth.
- promotes cell division
- promotes the growth of a tendril around a support.
(b) Name the parts labelled A, B and C in the diagram given below. Write one
function of each part. 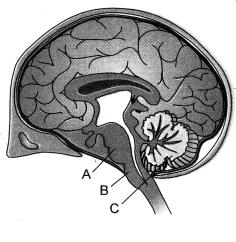
Answer:
(a) Plant
Hormones:
Phytohormones are chemical substances other than nutrients produced
naturally in plants which regulate growth, development, differentiation and a
number of physiological processes, e.g., auxin,
gibberellins, abscisic acid, cytokinins.
- Hormone That Promotes Growth. Auxin/Gibberellin.
- Hormone That Inhibits Growth. Abscisic acid or ABA
- Hormone That Promotes Cell Division. Cytokinin.
- Hormone That Promotes Growth of a Tendril Around a Support. Auxin.
(b) A-Pons Function: Relay centre, pneumotaxic area of respiratory
centre.
B-Medulla Function: Reflex centre, cardiac centre, respiratory
centre.
C-Cerebellum Function: Maintains equilibrium and coordinates muscular
activities