Life Processes
Class 10th Science Chapter HOTs
HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Question
1.
What does the diagram depict ?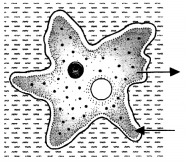
Answer:
Gaseous
exchange in Amoeba.
Question
2.
What does diagram depict ? What are A and B ?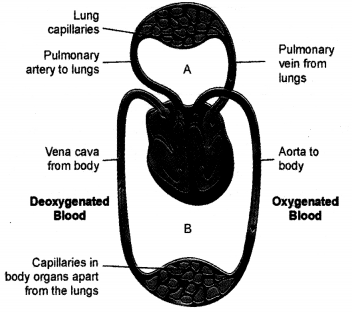
Answer:
Double
Circulation :
(A) Pulmonary
Circulation
(B) Systemic Circulation.
Question
3.
How are viruses living when they do not show movements
?
Answer:
Viruses do not show movements outside the host cells. They show movements at the
molecular level inside the living cells.
Question
4.
What is
(a) Primary reaction of photosynthesis
(b)
Calvin cycle
(c) Krebs cycle
(d) EMP
(e) Oxidative phosphorylation
?
Answer:
(a)
Primary Reaction of Photosynthesis: It is the conversion of light
energy into chemical energy by chlorophyll a molecules.
(b) Calvin
Cycle: It is a cycle of reactions that occur during reduction of
CO2 to carbohydrate with the help of ATP and NADPH2
produced during light reaction.
(c) Krebs Cycle: It is a
cycle of reactions that occur inside the mitochondria wherein an activated
acetyl group is completely oxidised to form CO2, NADH2 and
FADH2.
(d) EMP: Embden-Meyerhoff-Parnas pathway,
also called glycolysis, is the first step of respiratory breakdown of glucose
that occurs in the cytoplasm forming two molecules each of pyruvate, ATP and
NADH2.
(e) Oxidative Phosphorylation: It is the
process of ATP formation from ADP and inorganic phosphate with the help of
energy liberated during oxidation of reduced coenzymes (NADH2,
FADH2).
Question
5.
A girdled tree dies if the girdle is wide and is not
filled up. Comment.
Answer:
Girdling
removes bark containing phloem from the trunk region. Food manufactured by
foliage does not reach the roots which requires the same as they are always
growing. In the absence of food supply, roots starve and stop absorbing water.
The foliage wilts and the plant dies.
Question
6.
Study the diagram. Name the parts “A” and “B”. State one
function of each. (CBSE A.I. 2008)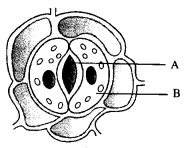
Answer:
A—Stomatal
pore or stoma Function: Pathway for exchange of gases or photosymthesis and
respiration and loss of water vapours in
transpiration.
B—Guard cell Function: Two guard cells
present in each stoma, create pore when they are turgid and close the same when
they are flaccid.
Question
7.
In the experiment “Light is essential for photosynthesis”
why does the uncovered part of the leaf turn blue-black after putting iodine
solution. (CBSE Foreign 2010)
Answer:
The uncovered
part of the leaf exposed to sunlight performs photosynthesis and accumulates
starch. Iodine reacts.with starch to give blue-black colouration.
Question
8.
Give one reason why multicellular organisms require
special organs for exchange of gases between their body and their environment.
(CBSE A.I. 2010)
Answer:
Multicellular
organisms require special organs for exchange of gases as most of their cells
are internal and are not in direct contact with environment.
Question
9.
Name the green dot like structures in some cells observed
by a student when a leaf peel was viewed under a microscope. What is the green
colour due to ? (CBSE Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Chloroplasts
with green colour due to chlorophyll.
Question
10.
Explain the process of breakdown of glucose in a cell
- In the presence of oxygen
- In the absence of oxygen.
Answer:
Glucose is
first broken down to pyruvic acid during glycolysis. Glycolysis occurs in cell
cytoplasm. It produces energy.
- Presence of Oxygen: It is aerobic respiration where pyruvic acid is completely oxidised to carbon dioxide and water inside mitochondria releasing a lot of energy.
- Absence of Oxygen: Pyruvic acid is metabolised
anaerobically in the cell cytoplasm forming either
- Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) and carbon dioxide or
- lactic acid: Very little energy is released.
Question
11.
Explain the process of digestion of food in mouth,
stomach and small intestine in human body. (CBSE Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Mouth: Food is moistened, crushed and acted upon by salivary amylase which
converts some starch into maltose and dextrins.
Stomach: Food is acidified,
churned and mixed with enzyme pepsin. Pepsin acts in acidic medium over proteins
to form soluble components, peptones and proteoses. Small quantities of
semi-liquified food called chyme is passed on the duodenum.
Small Intestine:
Acidity is neutralised and the food is made alkaline. Food is acted upon by
pancreatic juice and succus entericus. Pancreatic juice has trypsin, amylase and
lipase enzymes to digest proteins, carbohydrates and fats respectively. Succus
entericus has enzymes for breakdown of peptides and disaccharides into amino
acids and monosaccharides respectively.