Carbon and its Compounds
Class 10th Science Chapter HOTs
HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
Question
1.
An organic compound A of molecular formula
C2H4 on reduction gives another compound B of molecular
formula C2H6. B on reaction with chlorine in the presence
of sunlight gives C of molecular formula C2H5Cl.
(a)
Name the compounds A, B and C.
(b) Write chemical equation for the conversion
of A to B and name the type of reaction.
Answer:
The compound A
of molecular formula C2H4 is an alkene. Upon reduction
with hydrogen, it gives ‘B’ of molecular formula C2H6. The
compound ‘B’ upon chlorinadon gives ‘C’ of molecular formula
C2H5Cl.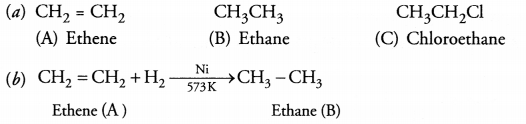
The reaction to called addition reaction.
Question
2.
Name the functional group of organic compounds that can be
hydrogenated. With the help of suitable example, explain the process of
hydrogenation mentioning the conditions of the reaction and any one change in
physical property with the formation of the product. Name any one natural source
of organic compounds that are hydrogenated.
Answer:
The functional group which can be easily hydrogenated is![]()
The family is known as alkenes. The hydrogenation reaction can be carried by
heating a member of the family (e.g. ethene) with hydrogen in the presence of a
catalyst like nickel (Ni) For example.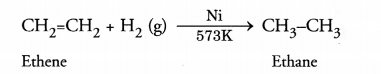
Ethene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon while ethane is of saturated nature.
Edible oils such as coconut oil, olive oil, peanut oil etc. contain atleast one
![]()
in their molecules. These are regarded as unsaturated compounds. Upon
hydrogenation, these get converted into fats which no longer contain any ![]()
Question
3.
An organic compound A’ of molecular formula
C2H6O on oxidation with dilute alkaline KMnO4
solution gives an acid ‘B’ with the same number of carbon atoms. Compound A’ is
often used for sterilization of skin by doctors. Name the compound. Write the
chemical equation involved in the formation of ‘B’ from A.
Answer:
The compound ‘B’ should contain a —COOH group as it is an acid. Since it has
only two carbon atoms, the other carbon atom must represent CH3
group. Thus, compound ‘B’ is ethanoic acid (CH3COOH). The compound A
used for the sterilization of skin by doctors is ethanol
C2H5OH (C2H6O). The chemical
reaction involved in the oxidation by dilute alkaline KMnO4 solution
also called Baeyers reagent is :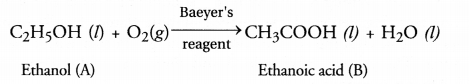
Question
4.
A to F are the structural formulae of some organic
compounds :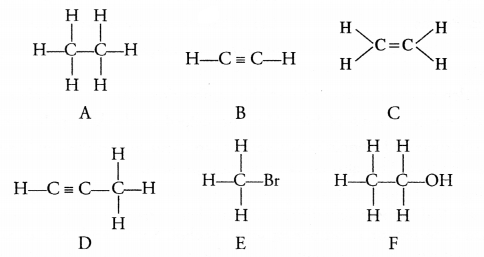
(i) Give the letters which represent the same family.
(ii) Give the letters
which do not represent hydrocarbons.
(iii) Flow can ‘C’ be converted into A
?
Answer:
(i)
Letters ‘B’ and ‘D’ represent the family of alkynes.
(ii) Letters ‘E’ and ‘F’
donot represent any hydrocarbon.
(iii) ‘C’ can be converted into ‘A’ by
passing hydrogen (H2) in the presence of Ni at 473 K.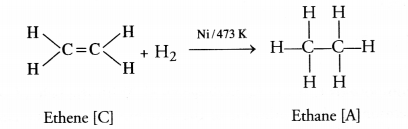
Question
5.
(a) A test tube contains a brown liquid in it. The colour
of the liquid remains the same when methane is passed through it but it
disappears when ethene is passed. Suggest the name of the liquid brown in
colour. Give the chemical equation involved.
(b) The formula of an ester is
C3H7COOC2H5. Write the formulae of
the acid and alcohol from which the ester is prepared.
Answer:
(a) The brown liquid seems to be bromine dissolved in water. Methane
(CH4) is a saturated hydrocarbon and does not react with bromine.
Ethene (C2H4) being unsaturated in nature, decolourises
bromine and its colour therefore, disappears.
(b) In an ester, the left side in the molecular formula containing
C3H7CO is derived from the acid while the right side
having OC2H5 is from the alcohol. This means that the acid
and alcohol participating in the ester are C3H7COOH and
C2H5OH respectively. The formation of ester may be shown
as follows :