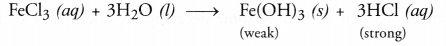Acids,Bases and Salts
Class 10th Science Chapter HOTs
HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
Question
1.
A student working in the laboratory added some water to a
syrupy liquid taken in a tube. The tube immediately cracked and the liquid which
escaped out of it, produced blisters on the skin of the student. What actually
happened ?
Answer:
The syrupy
liquid in the tube was concentrated sulphuric acid. Since it has great affinity
for water, the energy released was in the form of heat. That is why the tube
cracked and the vapours of the escaping acid produced blisters on the skin.
Question
2.
A baker found that the cake prepared by him is hard and
small in size. Which ingredient has he forgotten to add that would have made the
cake fluffy ? Give reason.
Answer:
The baker has
forgotten to add baking powder while making the dough for the cake. Actually,
sodium hydrogen carbonate present in baking powder releases carbon dioxide on
baking. The bubbles of the gas evolved leave behind pores which make the cake
soft and fluffy.![]()
Question
3.
A substance X is used as a building material and is
insoluble in water. When reacted with dilute HCl, it produces a gas which turns
lime water milky. Predict the substance. Write the chemical equations
involved.
Answer:
The substance
is probably calcium carbonate (CaCO3). also called lime stone or
marble. It is used as a building material. On reacting with dilute HCl, it
evolves CO2 gas which turns lime water milky.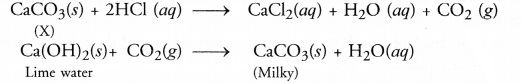
Question
4.
Dry pellets of base ‘X’ when kept in open absorb moisture
and turn sticky. The compound is also formed by chlor-alkali process. Write
chemical name and formula of X. Describe chlor-alkali process with balanced
chemical equation. Name the type of reaction that occurs when X is treated with
dilute hydrochloric acid. Write the chemical equation. While diluting an acid,
why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to
the acid ?
Answer:
The base ‘X’
is NaOH. It is of deliquescent nature and absorbs moisture from air and becomes
wet. It is manufactured by chlor-alkali process. The reaction of NaOH with
dilute HCl is known as neutralisation reaction.![]()
Pure HCl is highly concentrated. In case, it is to be diluted, the acid should
be added drop-by-drop to water taken in a glass beaker with constant stirring.
Actually, the acid has a strong affinity for water and the process of
dissolution is highly exothermic. If water is added to acid so much heat is
evolved that the glass beaker is likely to crack and the acid will spill.
Question
5.
What will you observe when :
- Red litmus paper is introduced into a solution of sodium carbonate.
- A methyl orange drop is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
- A drop of phenolphthalein is added to the solution of lime water.
- Blue litmus is introduced into a solution of ferric chloride.
Answer:
- The colour of the litmus paper will change to blue. Sodium carbonate
(Na2CO3) dissolves in water to form sodium hydroxide and
carbonic acid (H2O and CO2). The solution is of basic
nature since sodium hydroxide is a strong bases and carbonic acid is a weak
acid.
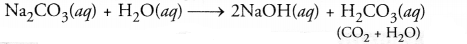
- In the acidic solution, the colour of methyl orange will change to reddish.
- Lime water contains traces of calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. It is therefore, basic in nature. The colour of phenolphthalein will become pink.
- Ferric chloride (FeCl3) solution on reacting with water will
form ferric hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. Since the acid is strong, the
solution will be acidic. Therefore, the colour of blue litmus will change to
red.