Human Eye and Colourful World
Class 10th Science Chapter HOTs
HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
Question
1.
A person is able to see objects clearly only when these
are lying at distance between 50 cm and 300 cm from his eye.
- What kind of defect of vision he is suffering from ?
- What kind of lenses will he required to increase his range of vision from 25 cm to infinity ? Explain briefly.
Answer:
- For a normal eye, the near point is at 25 cm and the far point is at
infinity from the eye. The given
person cannot see object clearly either closer to the eye or far away from the eye. So, he is suffering horn both myopia and hypermetropia. - A bi-focal lens consisting of a concave lens and convex lens of suitable focal lengths will be required to correct the defects and to increase his range or vision from 25 cm to infinity. In a bi-focal lens, upper portion is concave which corrects distant vision and lower portion is convex which corrects near vision.
Question
2.
A student finds the writing on the black board as blurred
and unclear when sitting on the last desk in a classroom. He however, sees it
clearly when sitting on the front desk at an approximate distance of 2 m from
the black board.
(a) Draw ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of image
of the black board writing by his eye-lens when he is seated at the
- last desk,
- front desk.
(b) Name the kind of lens that would help him to see clearly even when he is
seated at the last desk. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate how this lens helps
him to see clearly.
Answer:
(a)
- Formation of image of the black board writing by the eye-lens of the
student sitting at the last desk is shown in figure.

- Formation of image of the black board writing by the eye-lens of the
student sitting at the front-desk is shown in figure.
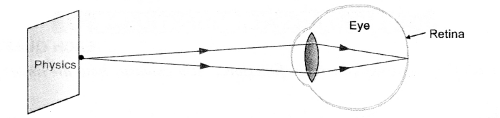
(b) Student is suffering from Myopia, so his eye defect can be corrected by
using a concave lens as shown in figure.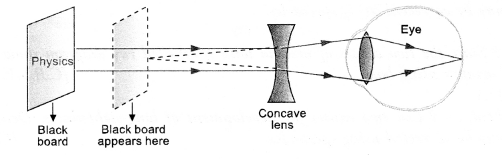
Question
3.
A student finds the writing on the black board as blurred
and unclear while sitting on the front desk in a classroom of a big size. He
however, sees it clearly while sitting on the last desk of the classroom.
(a)
Draw ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of image of the black board
writing by his eye-lens when he is seated at
- the front desk,
- last desk.
(b) Name the defect, the eye of the student is suffering from?
(c) Name
the type of lens that would enable him to see the black board writing clearly,
when seated on the front desk.
(d) Draw a ray diagram to illustrate how this
lens helps him to see clearly.
Answer:
(a)
- Formation of image of black board writing by the eye-lens of the student
sitting on the front desk is shown in figure.
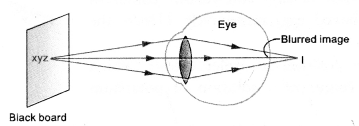
- Formation of the image of the black board writing by the eye-lens of the
student sitting on the last desk is shown in figure.
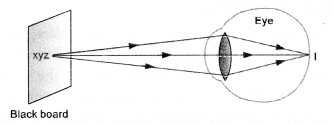
(b) Student’s eye suffers from hypermetropia or long sightedness as he is
able to see far off object clearly but unable to see near object clearly.
(c)
Convex lens of suitable focal length.
(d)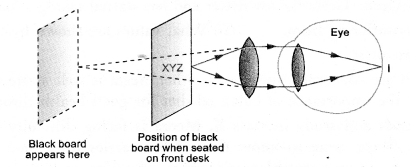
Question
4.
A person cannot see object farther than 10m from the eye
clearly. Name the defect of vision, he is suffering from. How can it be
corrected ? Draw ray diagrams for
- defective eye,
- its correction.
Answer:
He is
suffering from myopia or short-sightedness. The defect can be corrected using
spectacles having concave lens.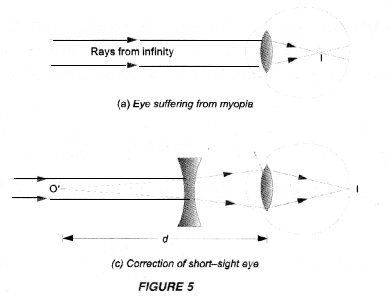
Question
5.
A 14-years old student is not able to see clearly the
questions written on a black board placed at a distance of 5 m from him.
(a)
Name the defect of vision, he is suffering from.
(b) With the help of
labelled ray diagram show how this defect can be corrected.
(c) Name the type
of lens used to correct this defect.
(d) State two causes of this defect.
Answer:
(a) Student is
suffering from Myopia or short-sightedness
(b) For ray diagram,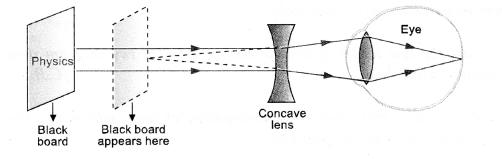
(c) Concave lens of suitable focal length is used to correct this defect.
(d)
It is due to
- elongation of the eye ball,
- excessive curvature of the cornea.
Question
6.
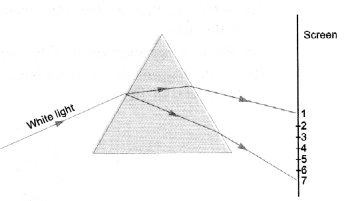
A beam of white light falling on a glass prism gets split
up into seven colours marked 1 to 7 as shown in the diagram. A student makes the
following statements about the spectrum observed on the screen.
(a) The
colours at position marked 3 and 5 are similar to the colour of the sky and the
core of a hard boiled egg respectively. Is the statement made by the student
correct or incorrect ? Justify.
(b) Which two positions correspond closely to
the colour of
- a solution of potassium permanganate ?
- Danger or stop signal lights ?
Answer:
(a)
(i) The colours at positions 3 and 5 are yellow and blue respectively. On the
other hand, student has identified them as blue (i.e colour of sky) and yellow
(colour of the core of a hard boiled egg) respectively. Hence, the statement is
incorrect.
(b)
- Position 7 is the position of violet colour, which corresponds to the colour of a solution of potassium permanganate.
- Position 1 is the position of red colour, which corresponds to the colour of ‘danger’ or stop signal lights.
Question
7.
A glass prims is able to produce a spectrum when white
light passes through it but a glass slab does not produce any spectrum. Explain.
Why is it so ?
Answer:
When white
light enters the glass slab, dispersion of light takes place. The angle of
refraction for violet colour is more than for red colour on entering the glass
slab. But all colours of light return to the original direction of propagation
while refracting from other side of the glass slab and thus white light emerges
out of the glass slab. Hence, glass slab does not produce any spectrum.