Science Chapter 4 - Carbon and its Compounds
Page No 61:
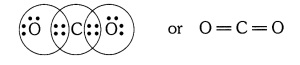
Question 1:-What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide
which has the formula CO2?
Answer:
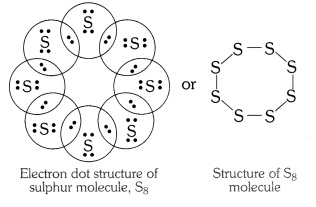
Question 2:-What would be electron dot structure of sulphur which is
made up of eight atoms of sulphur.
Answer:
Page Number: 68 – 69
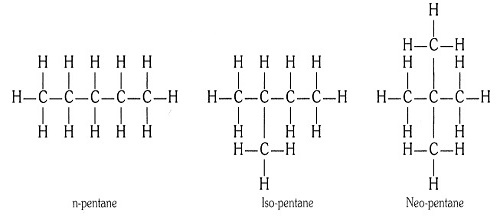
Question 1:-How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Answer: Three, these are n-pentane, iso-pentane and
neo-pentane.
Question 2:-What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the
huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Answer:
(i) Tetravalency
(ii) Catenation.
Two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds
we see around us are
1. Carbon has six valence electrons which are actually a high number of valency.
2. Covalent bonding happens easily with carbon atoms and numerous others such as oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen, Sulphur, hydrogen, etc.
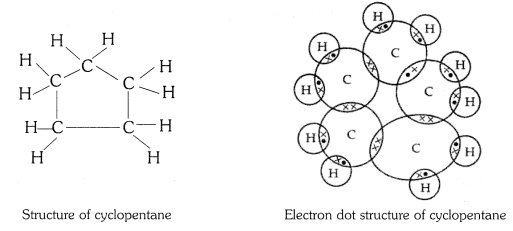
Question 3:-What will be the formula and electron dot structure of
cyclopentane?
Answer:
The molecular formula of cyclopentane is C5 H10 .
The electron dot structure of cyclopentane is given on the next page.
Question 4:-Draw the structures for the following compounds :
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Bromopentane
(iii) Butanone
(iv) Hexanal
Answer:
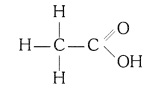
(i) Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH)
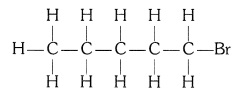
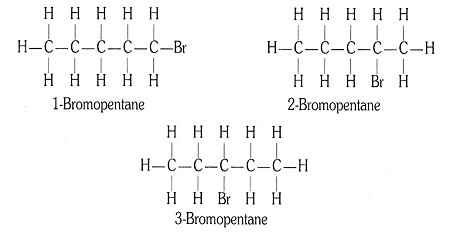
(ii) Bromopentane (C5H11Br)
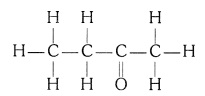
(iii) Butanone (CH3 — CH2 —
COCH3)
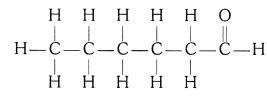
(iv) Hexanal (C5H11CHO)
Structural isomers for bromopentane: There are three structural isomers
for bromopentane depending on the position of Br at carbon 1, 2, 3.
Question 5:-How would you name the following compounds?
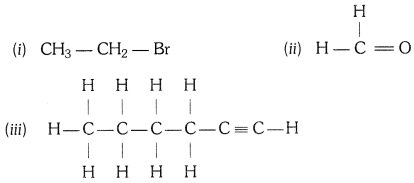
Answer:
(i) Bromoethane
(ii) Methanal
(iii) 1 – Hexyne
Page Number: 71
Question 1:-Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an
oxidation reaction?
Answer:
Conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid is an oxidation reaction because
addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation. Here, oxygen is added to
ethanol by oxidising agent like alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified
potassium dichromate and it is converted into acid.

Question 2:-A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can
you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Answer:
A mixture of ethyne and air is not used for welding because burning of ethyne in
air produces a sooty flame due to incomplete combustion, which is not enough to
melt metals for welding.
Page Number: 74
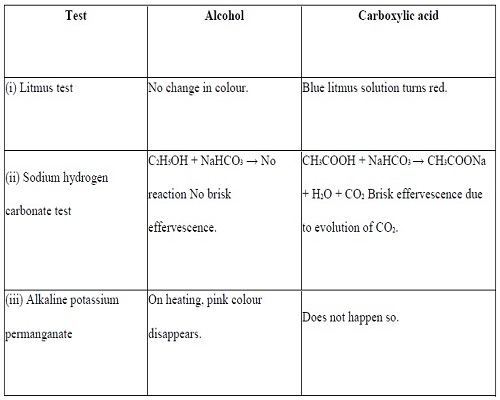
Question 1:-How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol
and a carboxylic acid?
Answer:
Differences between alcohol and carboxylic acid
Question 2:-What are oxidising agents?
Answer:
Oxidising agents are the substances which give oxygen to another substances or
which remove hydrogen from a substance.
For example, acidic K2Cr2O7 is
an oxidising agent that converts (oxidises) ethanol into ethanoic acid.
Page Number: 76
Question 1:-Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a
detergent?
Answer:
No, because detergents can lather well even in hard water. They do not form
insoluble calcium or magnesium salts (scum). On reacting with the calcium ions
and magnesium ions present in the hard water.
Question 2:-People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually
after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a
paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why
is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Answer:
It is necessary to agitate to get clean clothes because the soap micelles which
entrap oily or greasy particles on the surface of dirty cloth have to be removed
from its surface. When the cloth wetted in soap solution is agitated or beaten,
the micelles containing oily or greasy dirt get removed from the surface of
dirty cloth and go into water and the dirty cloth gets cleaned.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
Chapter 4
Textbook Chapter End Questions
Question 1:-Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has
(a) 6 covalent bonds
(b) 7 covalent bonds
(c) 8 covalent bonds
(d) 9 covalent bonds
Answer:
(b) 7 covalent bonds.
Question 2:-Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional
group
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol
Answer:
(c) Ketone.
Question 3:-While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting
blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.
(c) the fuel is wet.
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Answer:
(b) The fuel is not burning completely.
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the
outside indicates that the fuel is not burning completely.
Question 4:-Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond
formation in CH3Cl.
Answer:
Covalent bond is formed by sharing of electrons so that the combining atoms
complete their outermost shell.
In CH3Cl : C = 6, H = 1 and Cl = 17
And their electronic configuration is C – 2,4, H – 1 and Cl – 2, 8, 7
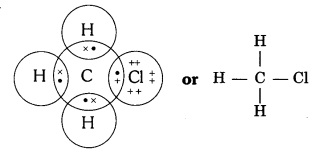
Three hydrogen atoms complete their shells by sharing three electrons (one
electron each) of carbon atom.
Chlorine completes its outer shell by sharing its one out of seven electrons
with one electron of carbon atom.
Thus carbon atom shares all its four electrons with three hydrogen atoms and one
of chlorine atom and completes its outermost shell and single covalent bonds are
formed in CH3Cl.
Question 5:-Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid (b) propanone (c) H2S
(d) F2.
Answer:
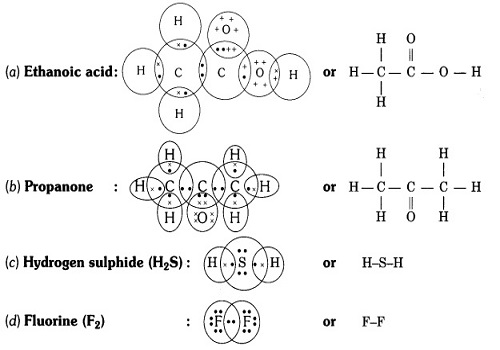
Question 6:-What is a homologous series? Explain with an example.
Answer:
Homologous series : A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having
similar structures and similar chemical properties in which the successive
compounds differ by -CH2 group.
Characteristics of homologous series:
(i) All members of a homologous series can be represented by the same general
formula. For example, the general formula of the homologous series of alkanes is
CnH2n+2,
in which ‘n’ denotes number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in one molecule of
alkane.
(ii) Any two adjacent homologues differ by one carbon atom and two hydrogen
atoms in their molecular formulae.
(iii) The difference in the molecular masses of any two adjacent homologues is
14u.
(iv) All the compounds of a homologous series show similar chemical properties.
(v) The members of a homologous series show a gradual change in their physical
properties with increase in molecular mass.
For example, general formula of the homologous series of alkanes is CnH2n+2,
in which ‘n’ denotes number of carbon atoms in one molecule of alkane. Following
are the first five members of the homologous series of alkanes (general formula
CnH2n+2).
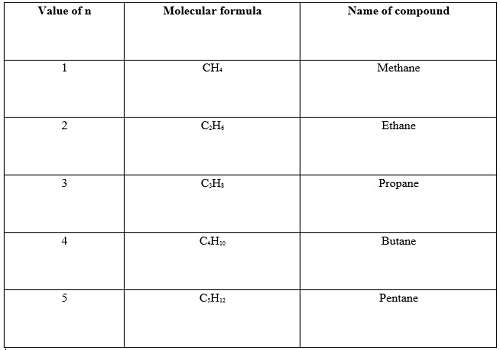
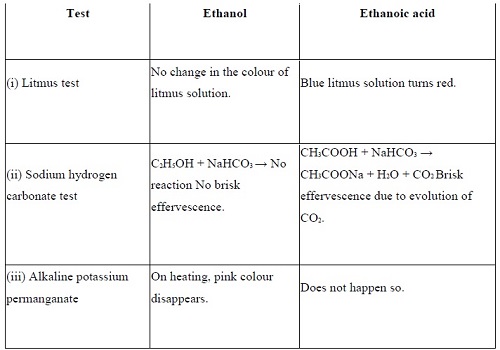
Question 7:-How can ethanol and ethanoic acid he differentiated on the
basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Answer:
Difference on the basis of physical properties
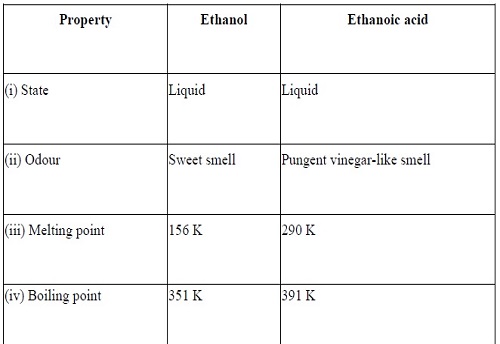
Difference on the basis of chemical properties
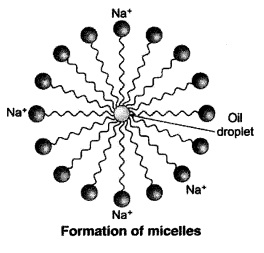
Question 8:-Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to
water? Will a micell be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Answer:
Micelle formation takes place when soap is added to water because the
hydrocarbon chains of soap molecules are hydrophobic (water repelling) which are
insoluble in water, but the ionic ends of soap molecules are hydrophilic (water
attracting) and hence soluble in water.
Such micelle formation will not be possible in other solvents like ethanol in
which sodium salt of fatty acids do not dissolve.
Question 9:-Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most
applications?
Answer:
Carbon and its compounds give a large amount of heat per unit weight and are
therefore, used as fuels for most applications.
Question 10:-Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated
with soap.
Answer:
Hard water contains salts of calcium and magnesium. Calcium and magnesium on
reacting with soap form insoluble precipitate called scum. The scum formation
lessens the cleansing property of soaps in hard water.
Question 11:-What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus
paper (red and blue)?
Answer:
Red litmus will turn blue because soap is alkaline in nature. Blue litmus
remains blue in soap solution.
Question 12:-What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Answer:
The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated
hydro-carbon is called hydrogenation. The process of hydrogenation takes place
in the presence of nickel (Ni) or palladium (Pd) metals as catalyst.
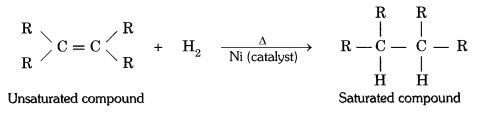
Application : The process of hydrogenation has an important industrial
application. It is used to prepare vegetable ghee (or vanaspati ghee) from
vegetable oils.
Question 13:-Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition
reactions :
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6,
C2H2 and CH4
Answer:
Addition reactions take place only in unsaturated hydrocarbons. So addition
reaction take place only in C3H6 and
C2H2.
Question 14:-Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically
between butter and cooking oil.
Answer:
Butter is a saturated carbon compound while cooking oil is an unsaturated carbon
compound. An unsaturated compound decolourises bromine water, while a saturated
compound cannot decolourise it. So we can distinguish chemically between a
cooking oil and butter by the bromine water. Add bromine water to a little of
cooking oil and butter taken in separate test-tubes.
·
Cooking oil decolourises bromine water showing that it is
an unsaturated compound.
·
Butter does not decolourise bromine water showing that it
is a saturated compound.
Question 15:-Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
OR
Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Answer:
When a dirty cloth is put in water containing dissolved soap, then the
hydrocarbon end of the soap molecules in micelle attach to the oil or grease
particles present on the surface of dirty cloth. In this way the soap micelle
entraps the oily or greasy particles by using its hydrocarbon ends. The ionic
ends of the soap molecules in the micelles, however, remain attached to water.
When the dirty cloth is agitated in soap solution, the oily and greasy particles
present on its surface and entrapped by soap micelles get dispersed in water due
to which the soap water becomes dirty but the cloth gets cleaned. The cloth is
cleaned thoroughly by rinsing in clean water a number of times.