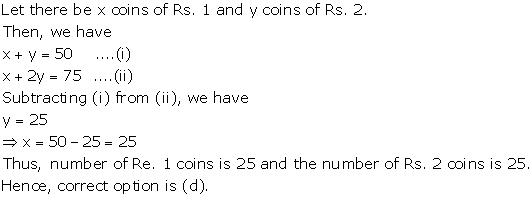Chapter 3 Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Class 10th R. D. Sharma Maths Solution
CBSE Class 10 Maths
R. D. Sharma Solution
Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.1
Solution 1
Solution 2
Seven years ago,
Age of Aftab = x - 7
Age of his daughter = y - 7
According to the given condition,
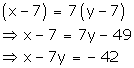
Three years hence,
Age of Aftab = x + 3
Age of his daughter = y + 3
According to the given condition,
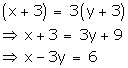
Thus, the given conditions can be algebraically represented as:
x - 7y = -42
x - 3y = 6
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
| x | -7 | 0 | 7 |
| y | 5 | 6 | 7 |
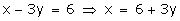
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
| x | 6 | 3 | 0 |
| y | 0 | -1 | -2 |
The graphical representation is as follows:
Concept insight: In order to represent a given situation mathematically, first see what we need to find out in the problem. Here, Aftab and his daughter's present age needs to be found so, so the ages will be represented by variables x and y. The problem talks about their ages seven years ago and three years from now. Here, the words 'seven years ago' means we have to subtract 7 from their present ages, and 'three years from now' or 'three years hence' means we have to add 3 to their present ages. Remember in order to represent the algebraic equations graphically the solution set of equations must be taken as whole numbers only for the accuracy. Graph of the two linear equations will be represented by a straight line.
Solution 3

Solution 4
Solution 5(i)
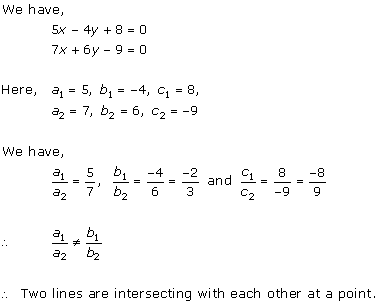
Solution 5(ii)
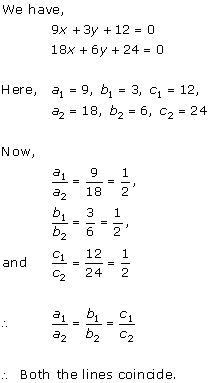
Solution 5(iii)
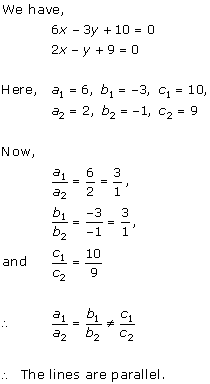
Solution 6(i)

Solution 6(ii)
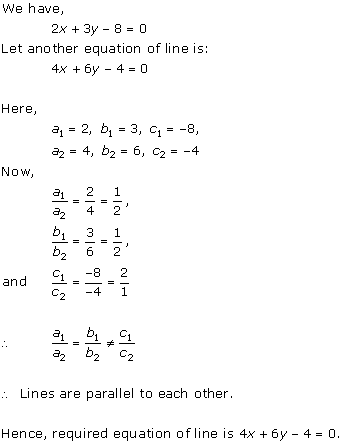
Solution 6(iii)
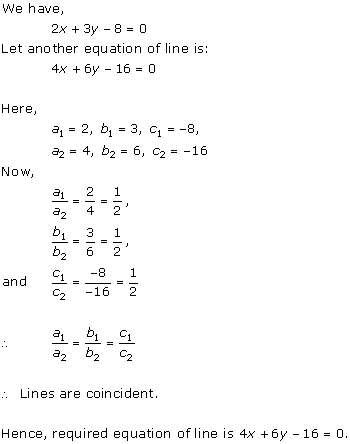
Solution 7
The given conditions can be algebraically represented as:
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
x |
50 | 60 | 70 |
| y | 60 | 40 | 20 |
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
x |
70 | 80 | 75 |
| y | 10 |
-10 |
0 |
The graphical representation is as follows:
Concept insight: cost of apples and grapes needs to be found so the cost of 1 kg apples and 1 kg grapes will be taken as the variables. From the given conditions of collective cost of apples and grapes, a pair of linear equations in two variables will be obtained. Then, in order to represent the obtained equations graphically, take the values of variables as whole numbers only. Since these values are large so take the suitable scale.
Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.2
Solution 1


Solution 2
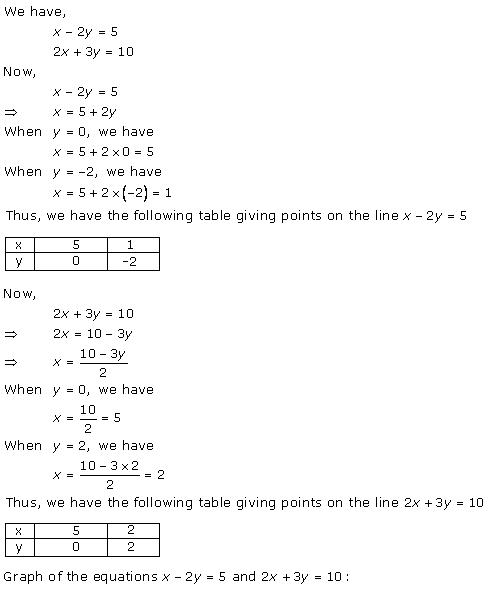
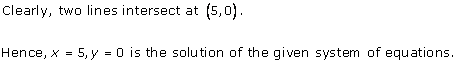
Solution 3

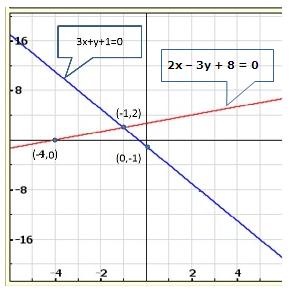
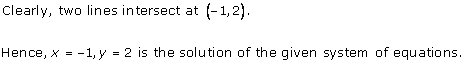
Solution 4
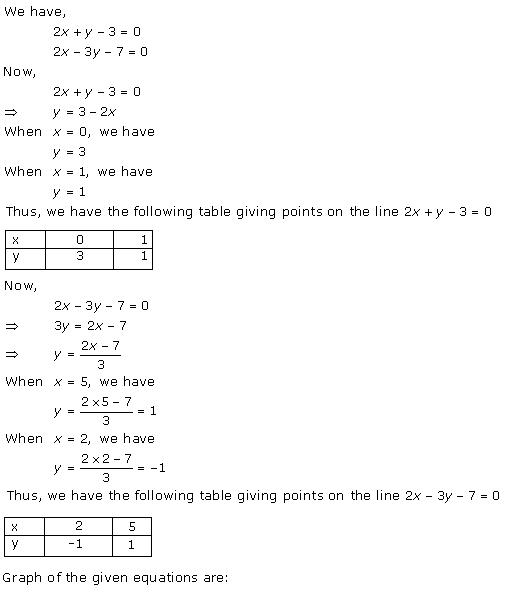
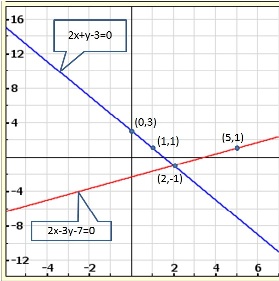
Solution 5
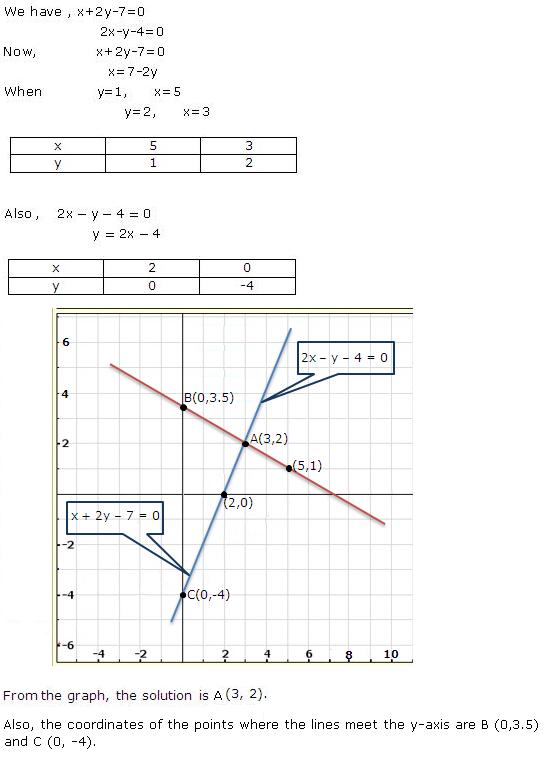
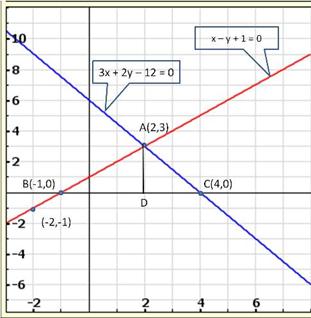
Given equations are:
x - y + 1 = 0 … (i)
3x + 2y - 12 = 0 … (ii)
From (i) we get, x = y - 1
When x = 0, y = 1
When x = -1, y = 0
When x = 1, y = 2
We have the following table:
|
x |
0 |
-1 |
1 |
|
y |
1 |
0 |
2 |
From (ii) we get, 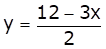
When x = 0, y = 6
When x = 4, y = 0
When x = 2, y = 3
We have the following table:
|
x |
0 |
4 |
2 |
|
y |
6 |
0 |
3 |
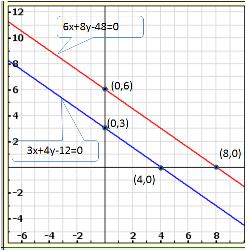
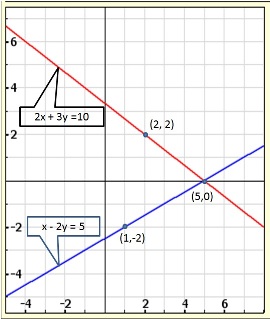
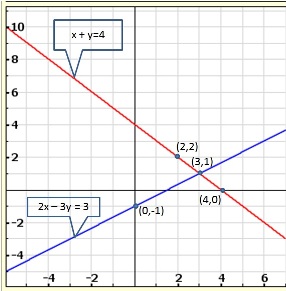
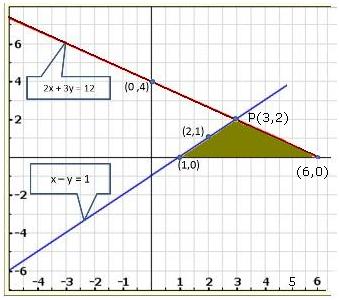
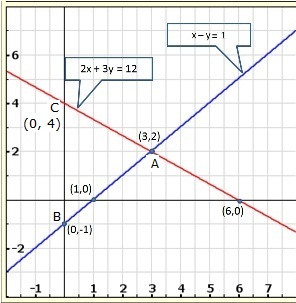
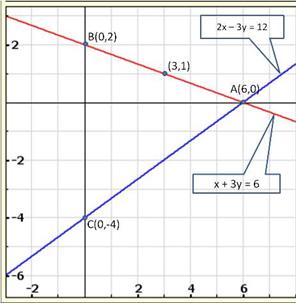
Graph of the given equations is:
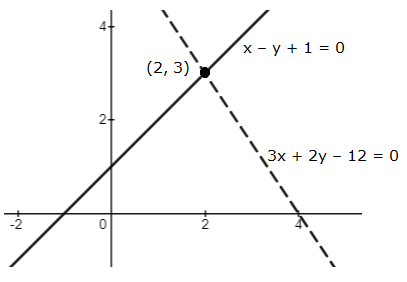
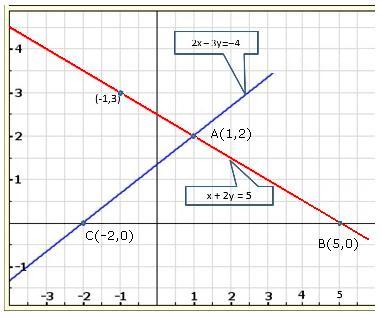
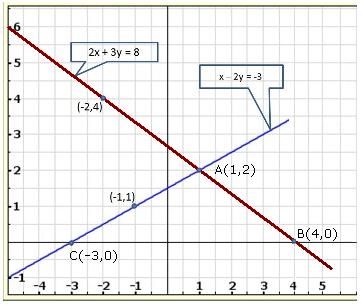
As the two lines intersect at (2, 3).
Hence, x = 2, y = 3 is the solution of the given equations.
Solution 6

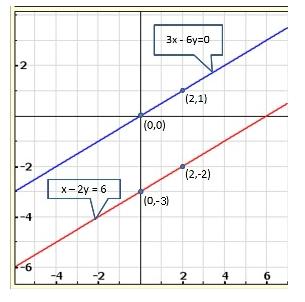

Solution 7

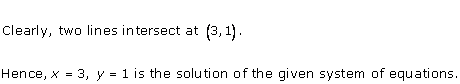
Solution 8

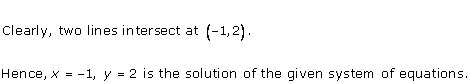
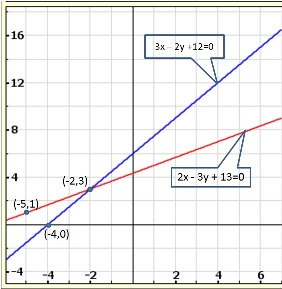
Solution 9

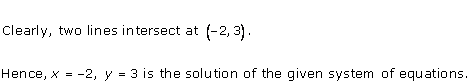
Solution 10

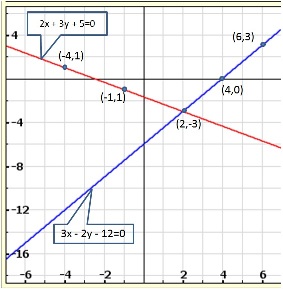
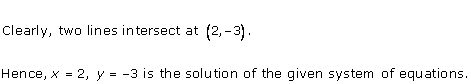
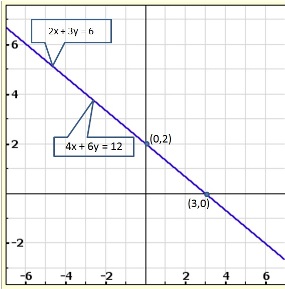
Solution 11

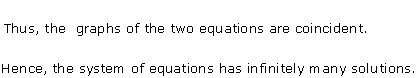
Solution 12

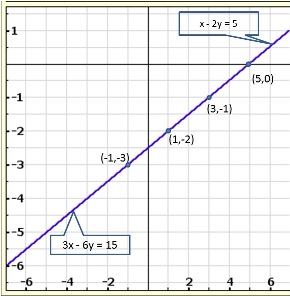
Solution 13

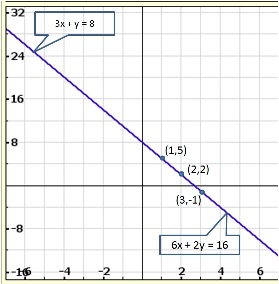
Solution 14

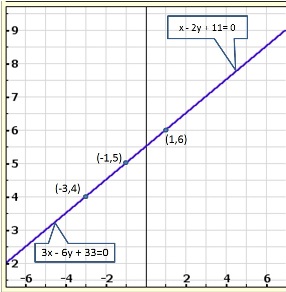
Solution 15

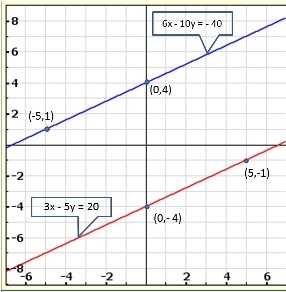

Solution 16

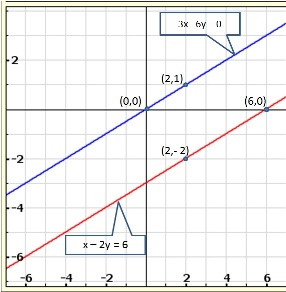

Solution 17

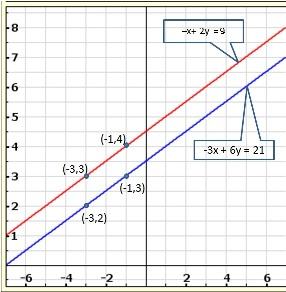

Solution 18

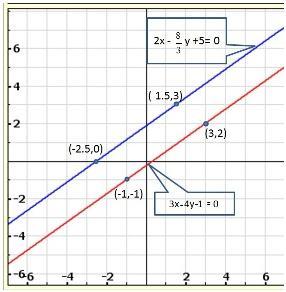

Solution 19(i)

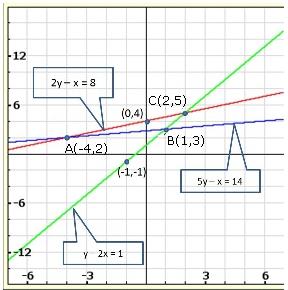

Solution 19(ii)

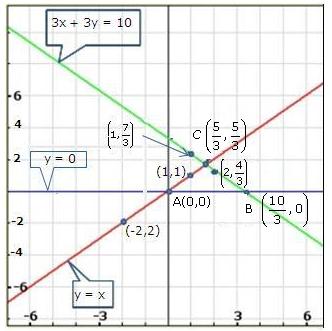

Solution 20

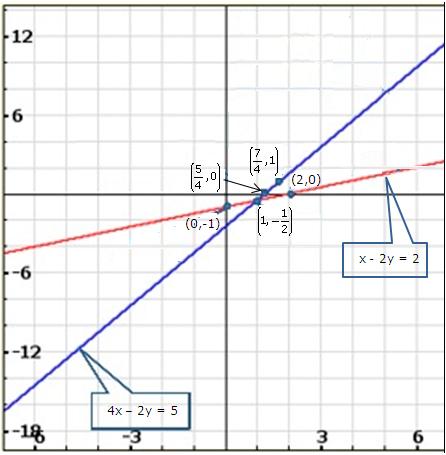

Solution 21(i)

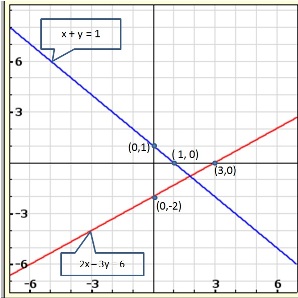

Solution 21(ii)
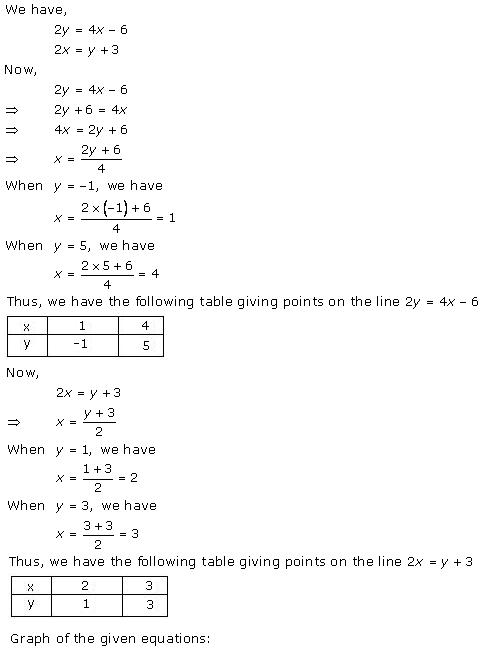
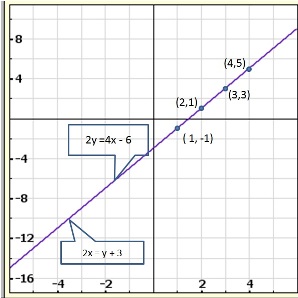
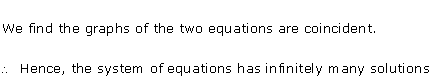
Solution 22(i)

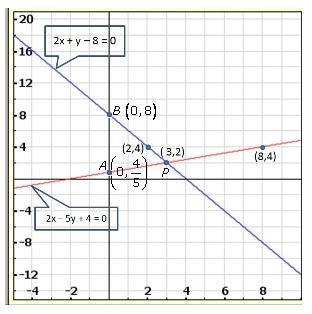

Solution 22(ii)

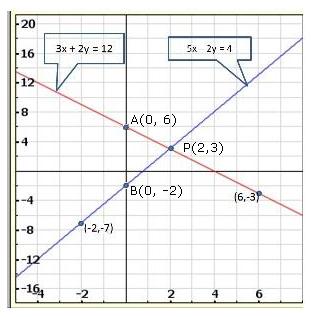

Solution 22(iii)

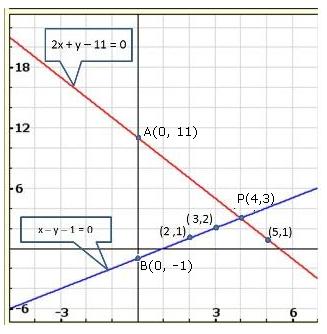

Solution 22(iv)
Solution 22(v)

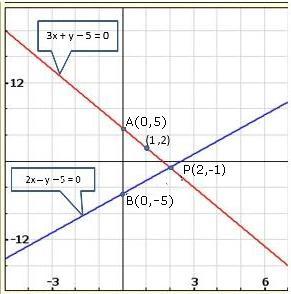

Solution 22(vi)

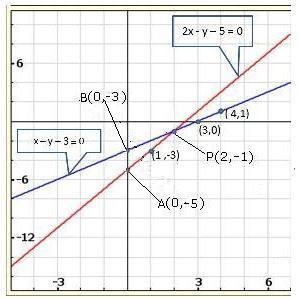

Solution 23(i)
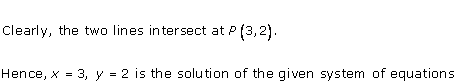
Solution 23(ii)
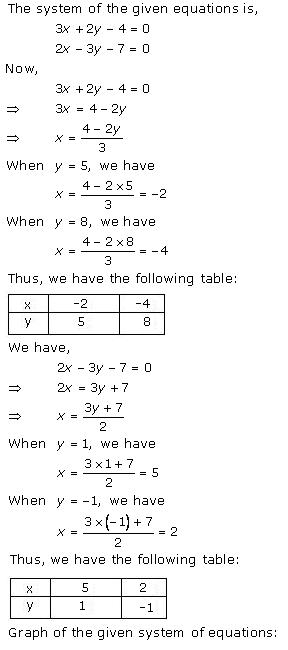
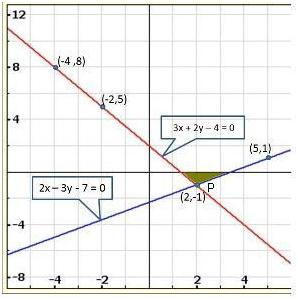
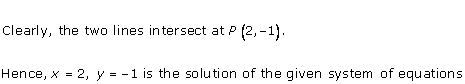
Solution 23(iii)
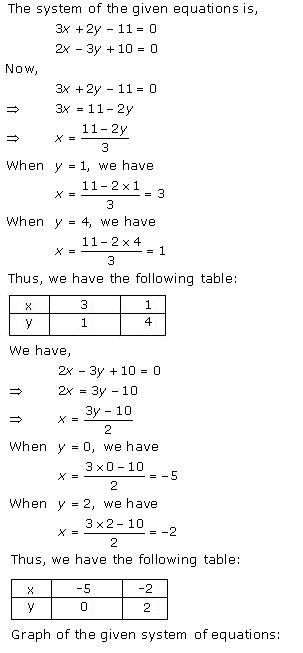

Solution 24
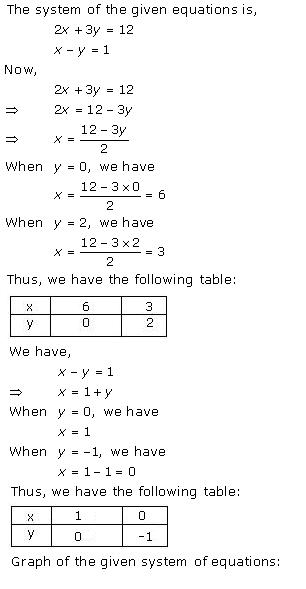

Solution 25
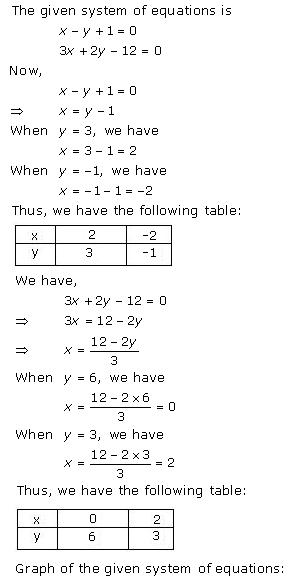


Solution 26
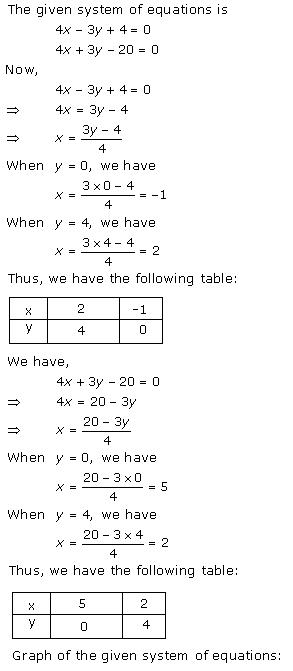
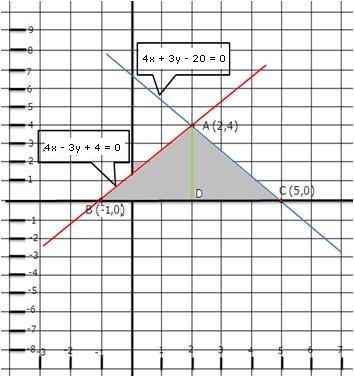


Solution 27
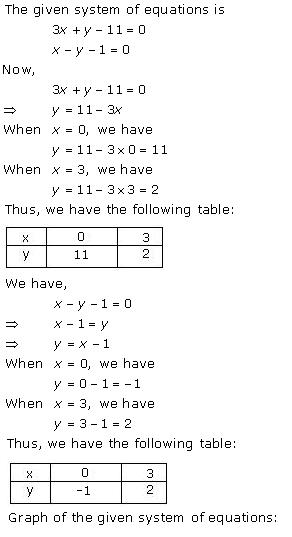
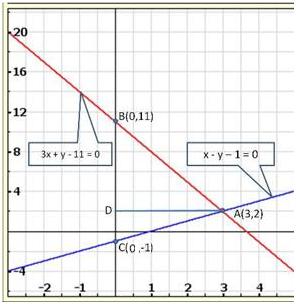


Solution 28(i)
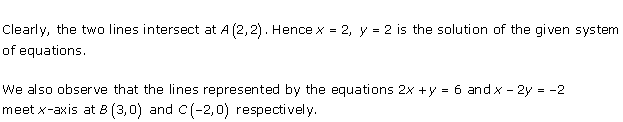
Solution 28(ii)
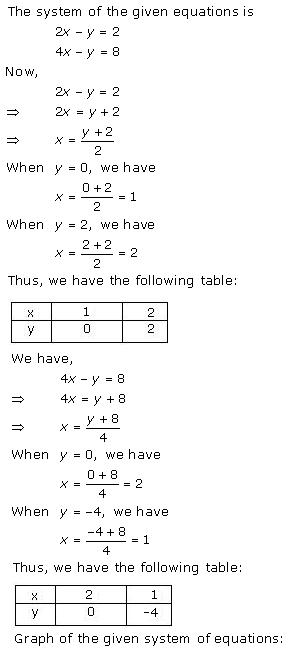
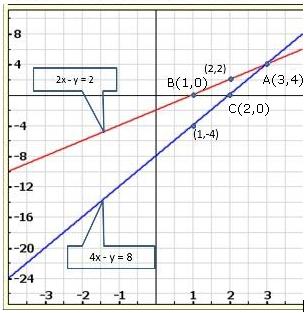
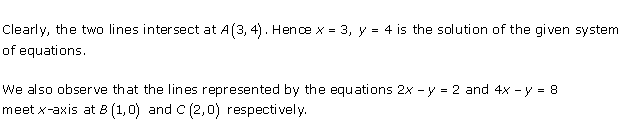
Solution 28(iii)
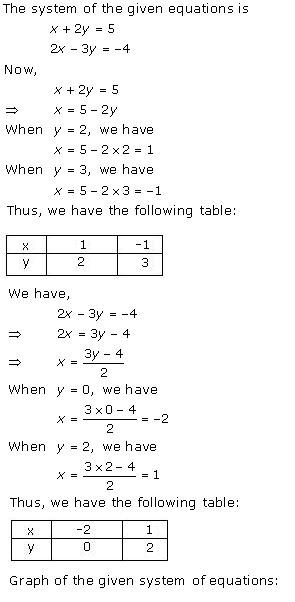
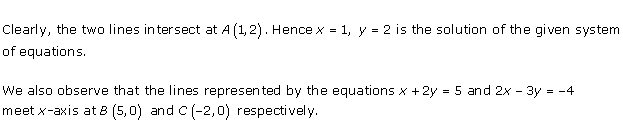
Solution 28(iv)
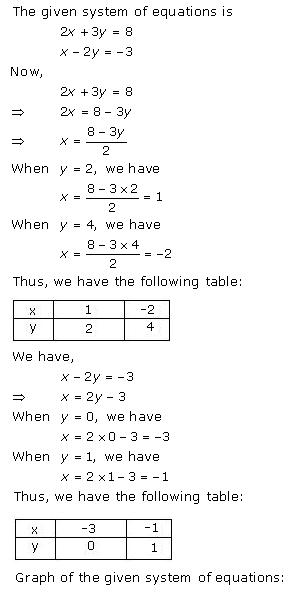
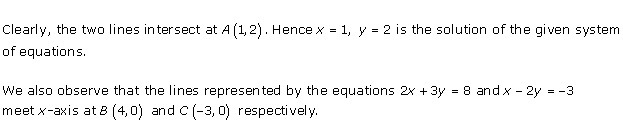
Solution 29
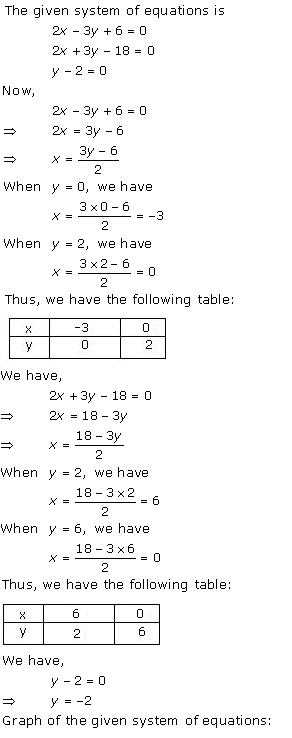
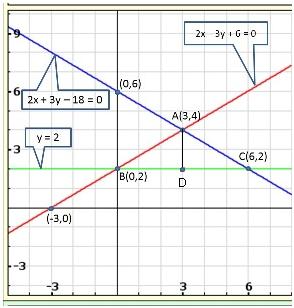
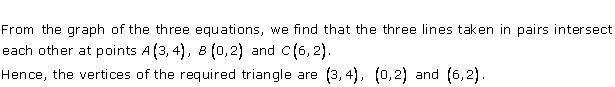

Solution 30
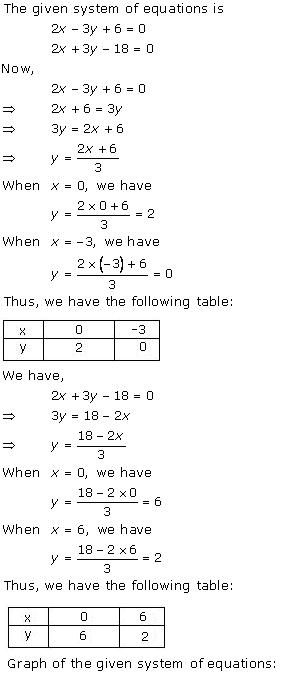
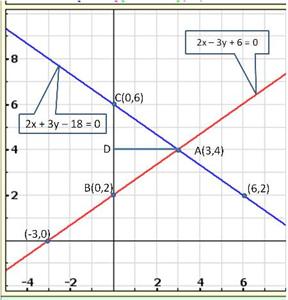
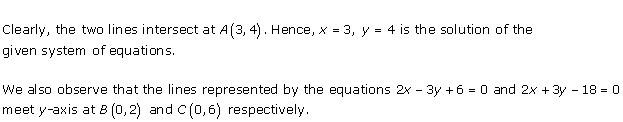
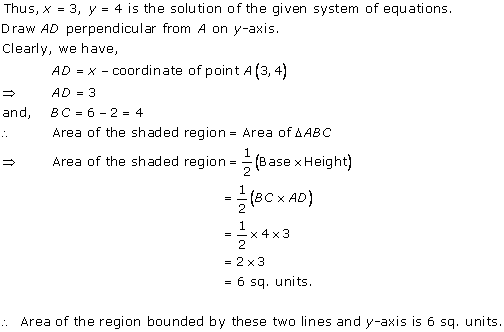
Solution 31
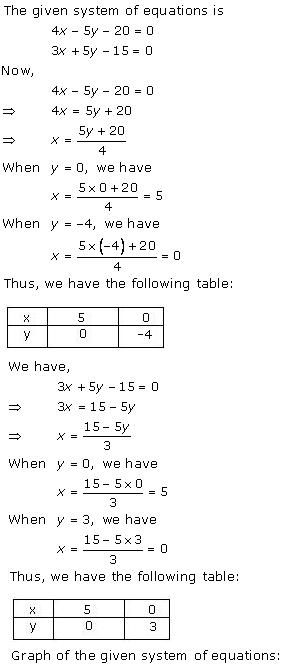
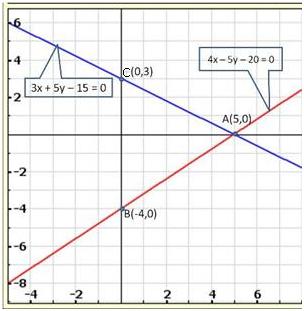

Solution 32
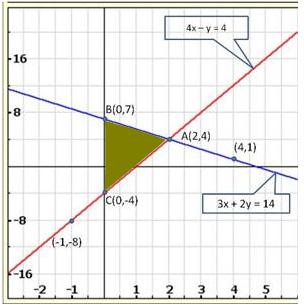
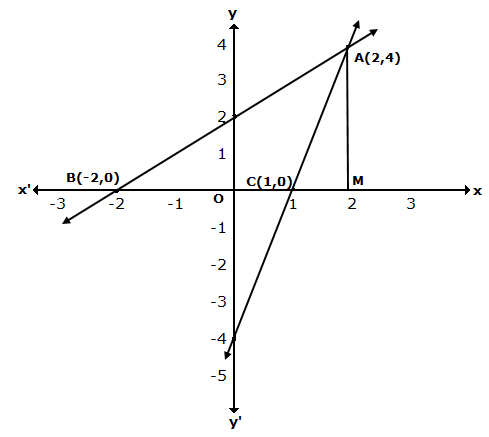
Three
solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| y | -5 | 0 | 5 |
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| y | -3 | 0 | 3 |
The graphical representation of the two lines will be as follows:
It can be observed that the required triangle is ![]() ABC.
ABC.
The
coordinates of its vertices are A (1, 0), B (0, -3), C (0, -5).
Concept
insight: In order to find the coordinates of the vertices of the
triangle so formed, find the points where the two lines intersects the y-axis
and also where the two lines intersect each other. Here, note that the
coordinates of the intersection of lines with y-axis is taken and not with
x-axis, this is because the question says to find the triangle formed by the two
lines and the y-axis.
Solution 33
(i) Let the
number of girls and boys in the class be x and y respectively.
According to
the given conditions, we have:
x + y = 10
x - y = 4
x + y =
10 ![]() x = 10 - y
x = 10 - y
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as
follows:
| x | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| y | 6 | 5 | 4 |
x - y = 4  x = 4 + y
x = 4 + y
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as
follows:
| x | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| y | 1 | 0 | -1 |
The graphical representation is as follows:
From the graph, it can be observed that the two lines intersect each other
at the point (7, 3).
So, x = 7 and y = 3.
Thus, the number of girls
and boys in the class are 7 and 3 respectively.
(ii)
Let the cost of one pencil and one pen be Rs x and Rs y
respectively.
According to the given conditions, we have:
5x + 7y =
50
7x + 5y = 46
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
| x | 3 | 10 | -4 |
| y | 5 | 0 | 10 |
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
| x | 8 | 3 | -2 |
| y | -2 | 5 | 12 |
The graphical representation is as follows:
From the graph, it can be observed that the two lines intersect each
other at the point (3, 5).
So, x = 3 and y = 5.
Therefore, the cost of
one pencil and one pen are Rs 3 and Rs 5 respectively.
(iii)
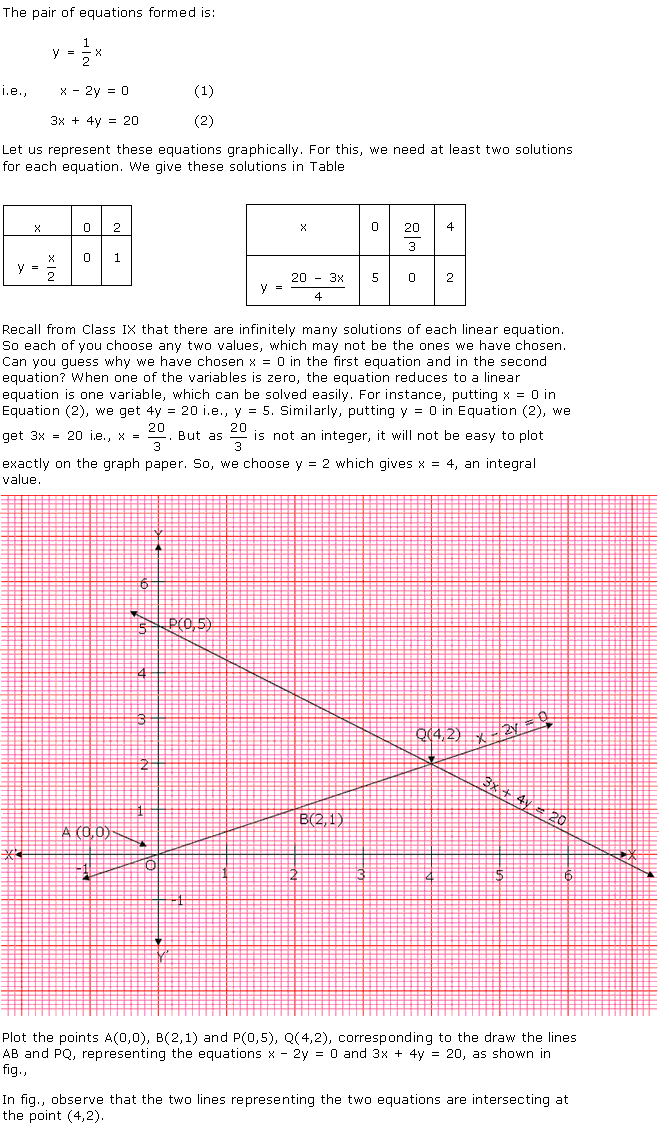
Let us denote the number of pants by x and the number of skirts by y. Then
the equations formed are:
y = 2x - 2 ...(1)
and y = 4x - 4
...(2)
Let us draw the graphs of Equations (1) and (2) by finding two
solutions for each of the equations.
They are given in Table
| x | 2 | 0 |
| y = 2x - 2 | 2 | -2 |
| x | 0 | 1 |
| y = 4x - 4 | -4 | 0 |
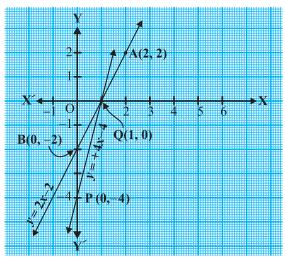
Plot the points and draw the lines passing through them to represent
the equations, as shown in fig.,
The two lines intersect at the point
(1,0). So, x = 1, y = 0 is the required solution of the pair of linear
equations, i.e., the number of pants she purchased is 1 and she did not buy any
skirt.
Concept insight: Read the question carefully and
examine what are the unknowns. Represent the given conditions with the help of
equations by taking the unknowns quantities as variables. Also carefully state
the variables as whole solution is based on it. On the graph paper, mark the
points accurately and neatly using a sharp pencil. Also, take at least three
points satisfying the two equations in order to obtain the correct straight line
of the equation. Since joining any two points gives a straight line and if one
of the points is computed incorrect will give a wrong line and taking third
point will give a correct line. The point where the two straight lines will
intersect will give the values of the two variables, i.e., the solution of the
two linear equations. State the solution point.
Solution 34(i)
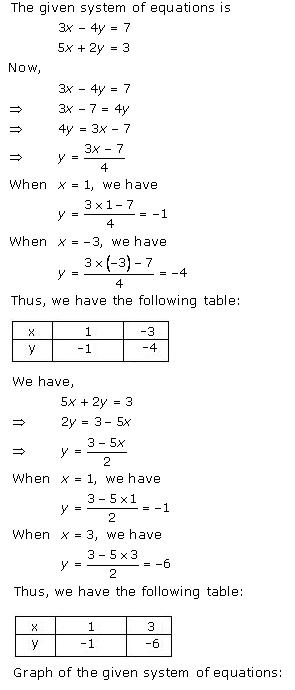
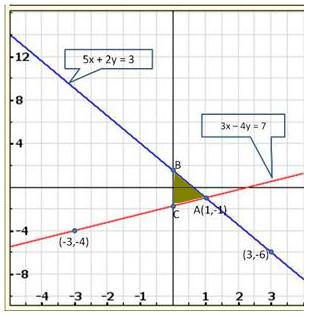

Solution 34(ii)
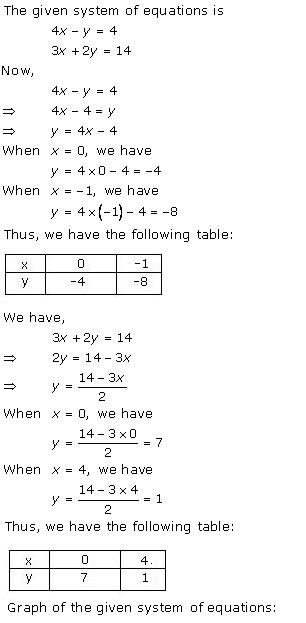

Solution 35
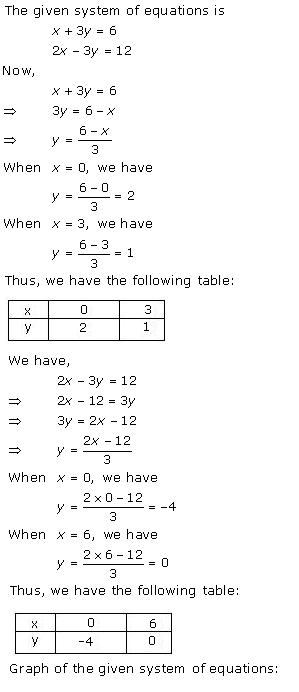

Solution 36
(i) For the
two lines a1x + b1x + c1 = 0 and a2x
+ b2x + c2 = 0, to be intersecting, we must have
So, the other linear equation can be 5x + 6y - 16 = 0 ![]()
(ii)
For the two lines a1x + b1x + c1 = 0 and
a2x + b2x + c2 = 0, to be parallel, we must
have
So, the other linear equation can be 6x + 9y + 24 = 0,
(iii) For the two lines a1x + b1x +
c1 = 0 and a2x + b2x + c2 = 0 to be
coincident, we must have
So, the other linear equation can be 8x + 12y - 32 = 0,
Concept insight: In order to answer such type of
problems, just remember the conditions for two lines to be intersecting,
parallel, and coincident. This problem will have multiple answers as their can
be many equations satisfying the required conditions.
Solution 37(i)
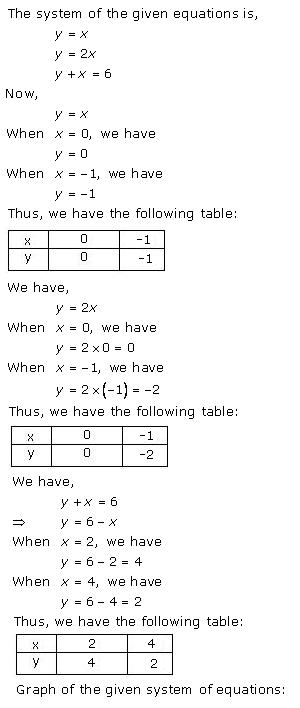
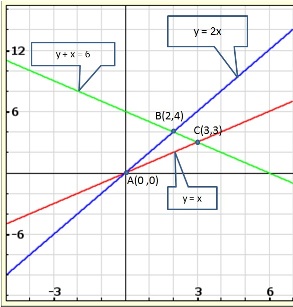

Solution 37(ii)
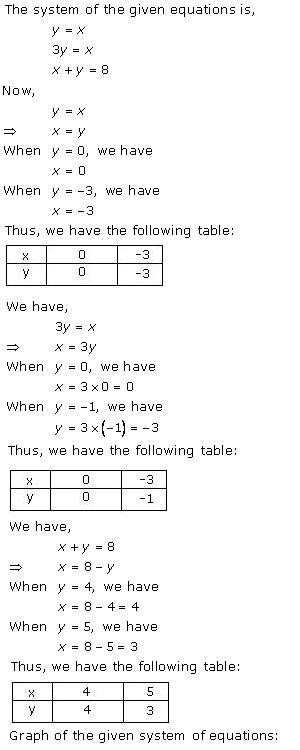
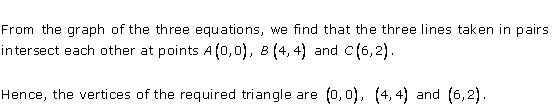
Solution 38
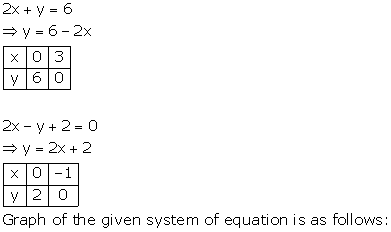
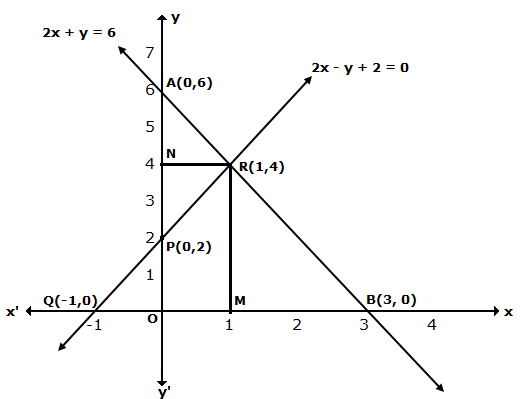
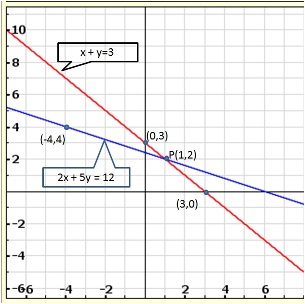
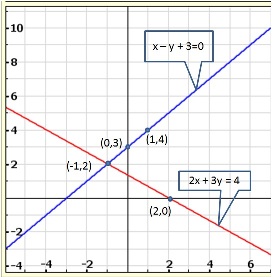
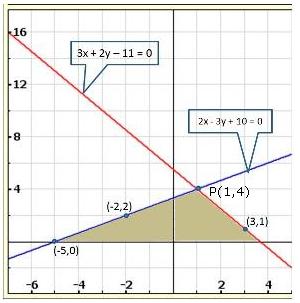
The lines AB and CD intersect at point R(1, 4). Hence, the solution of the given pair of linear equations is x = 1, y = 4.
From R, draw RM ⊥ X-axis and RN ⊥ Y-axis.
Then, from graph, we have
RM = 4 units, RN = 1 unit, AP = 4 units, BQ = 4 units

Solution 39
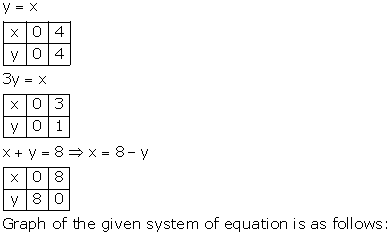
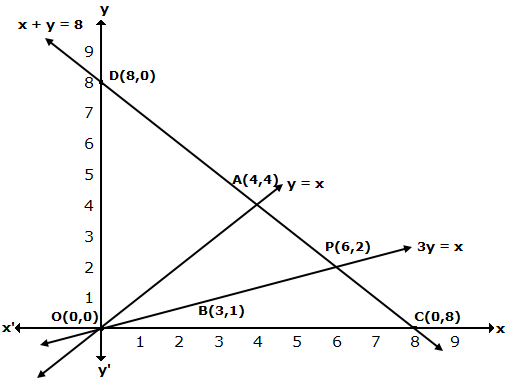
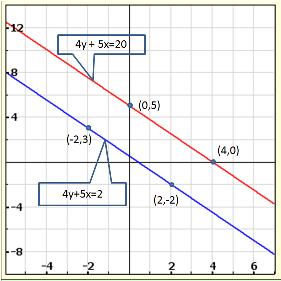
From the graph, the vertices of the triangle AOP formed by the given lines are A(4, 4), O(0, 0) and P(6, 2).
Solution 40
The graph of x = 3 is a straight line parallel to Y-axis at a distance of 3 units to the right of Y-axis.
The graph of x = 5 is a straight line parallel to Y-axis at a distance of 5 units to the right of Y-axis.
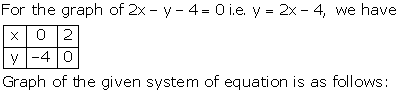

Solution 41
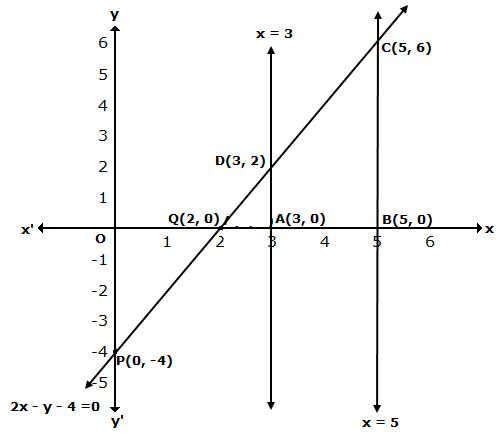
The graph of x = -2 is a straight line parallel to Y-axis at a distance of 2 units to the left of Y-axis.
The graph of y = 3 is a straight line parallel to X-axis at a distance of 3 units above X-axis.
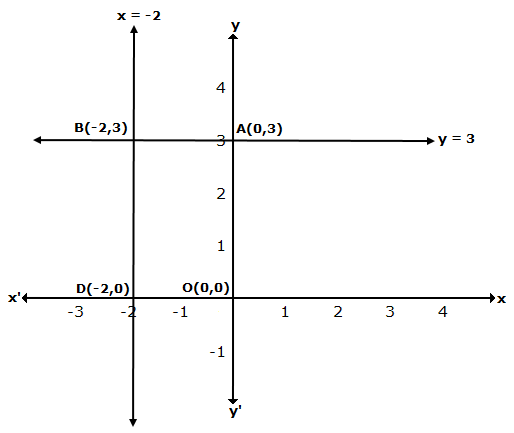

Solution 42
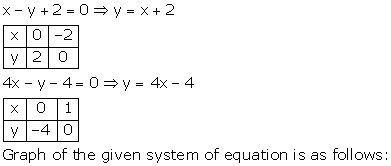
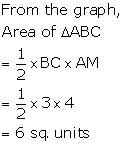
Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.3
Solution 1

Solution 2

Solution 3
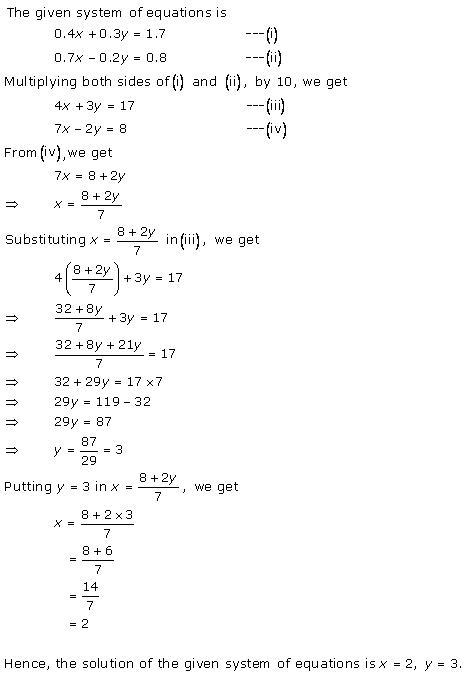
Solution 4
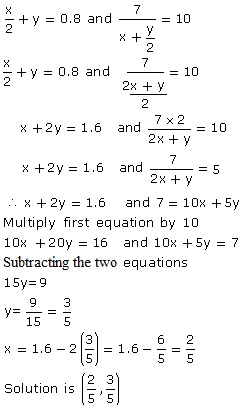
Solution 5

Solution 6

Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9
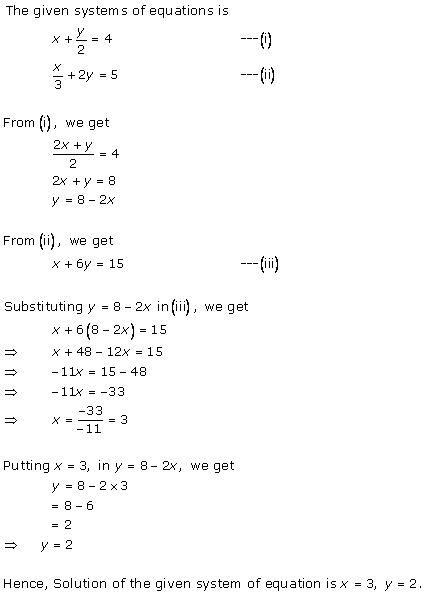
Solution 10

Solution 11

Solution 12
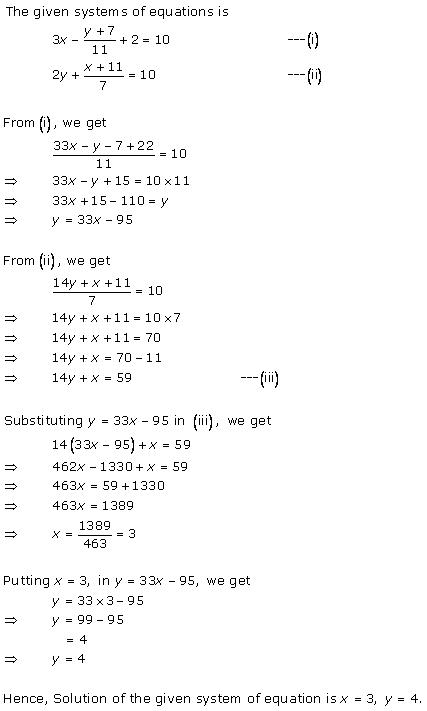
Solution 13

Solution 14

Solution 15
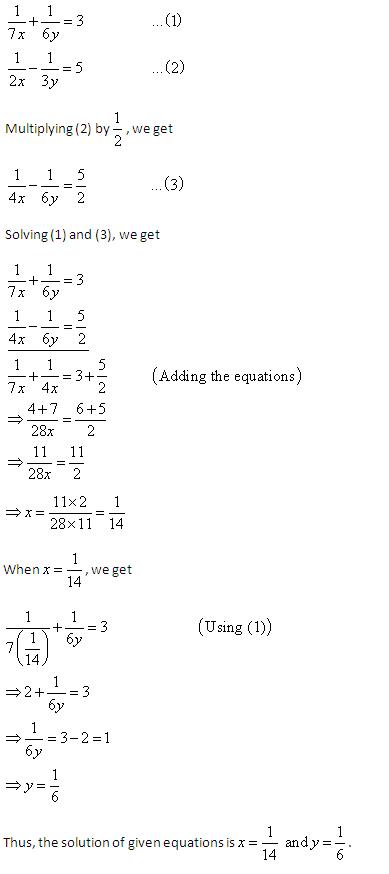
Solution 16

Solution 17

Solution 18

Solution 19

Solution 20

Solution 21
Solution 22

Solution 23

Solution 24

Solution 25

Solution 26

Solution 27
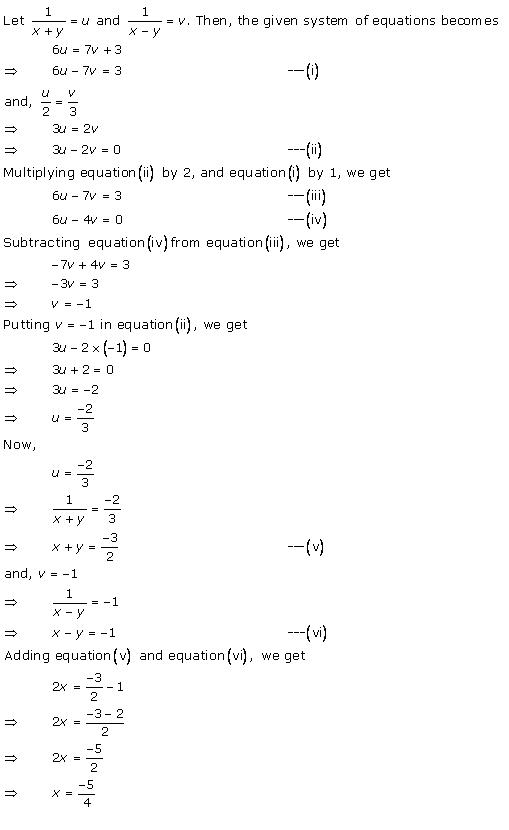

Solution 28

Solution 29

Solution 30

Solution 31

Solution 32


Solution 33

Solution 34

Solution 35

Solution 36

Solution 37

Solution 38

Solution 39
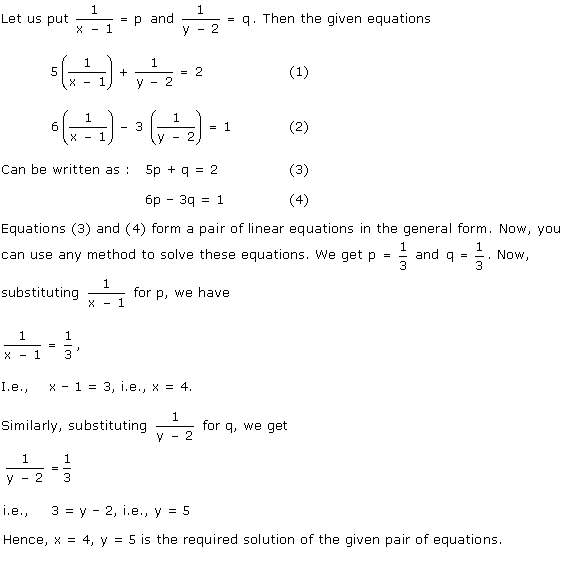
Solution 40
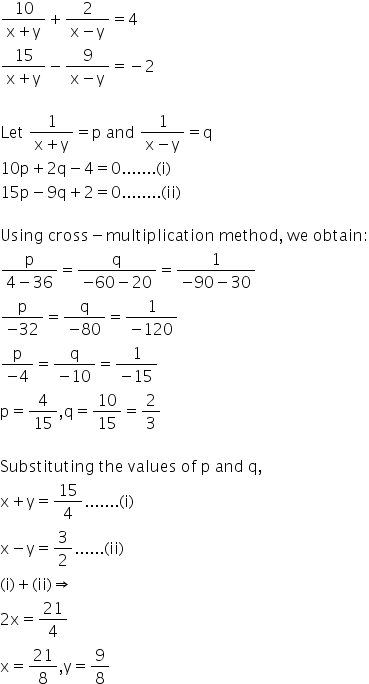
Solution 41

Solution 42
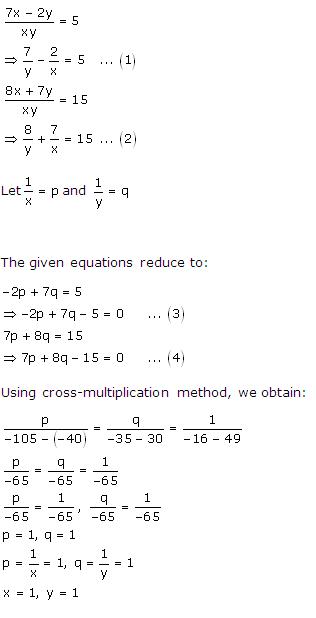
Solution 43

Solution 44

Solution 45

Solution 46

Solution 47

Solution 48

Solution 49

Solution 50
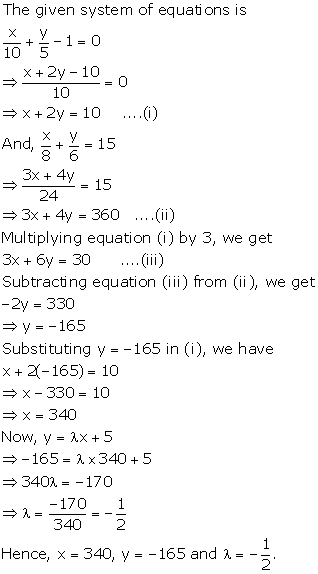
Solution 51
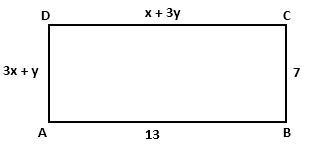

Solution 52

Solution 53

Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.4
Solution 1

Solution 2

Solution 3

Solution 4

Solution 5

Solution 6

Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9


Solution 10

Solution 11


Solution 12

Solution 13
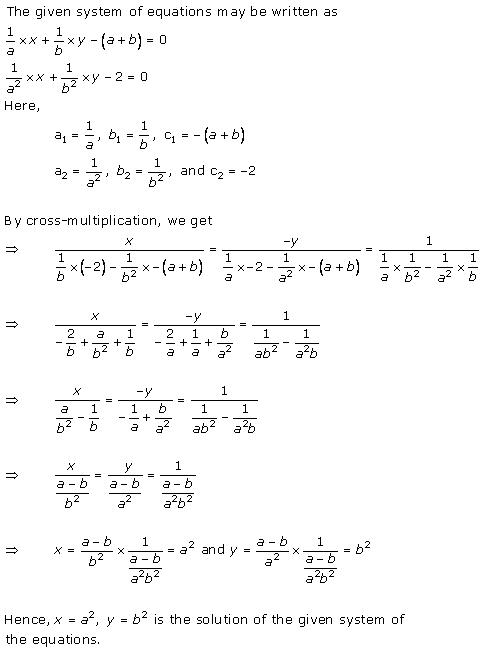
Solution 14
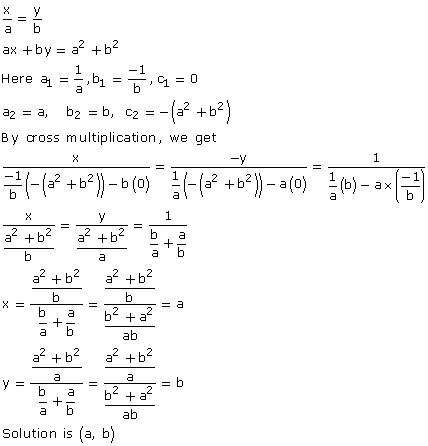
Solution 15

Solution 16

Solution 17

Solution 18

Solution 19

Solution 20


Solution 21

Solution 22

Solution 23

Solution 24


Solution 25

Solution 26


Solution 27

Solution 28

Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.5
Solution 1

Solution 2

Solution 3

Solution 4

Solution 5

Solution 6
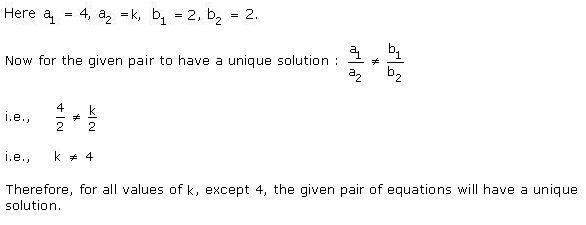
Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9

Solution 10

Solution 11

Solution 12

Solution 13

Solution 14

Solution 15

Solution 16

Solution 17

Solution 18

Solution 19

Solution 20
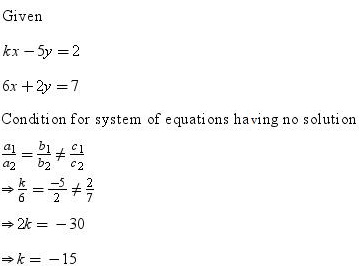
Solution 21

Solution 22

Solution 23

Solution 24

Solution 25
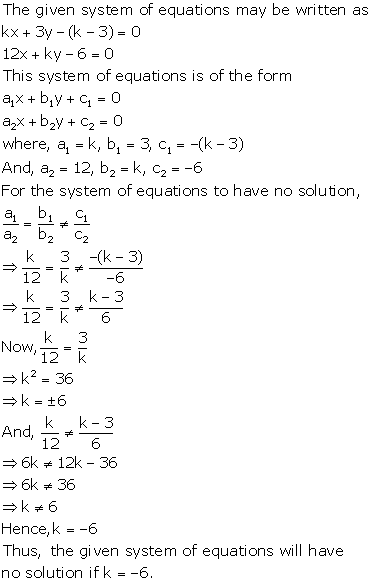
Solution 26

Solution 27

Solution 28

Solution 29
The given system of equations will have infinite number of solutions if
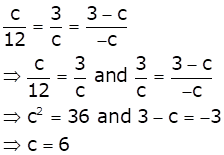
Solution 30


Solution 31

Solution 32

Solution 33

Solution 34

Solution 35

Solution 36 (i)

Solution 36 (ii)

Solution 36 (iii)

Solution 36 (iv)

Solution 36 (v)
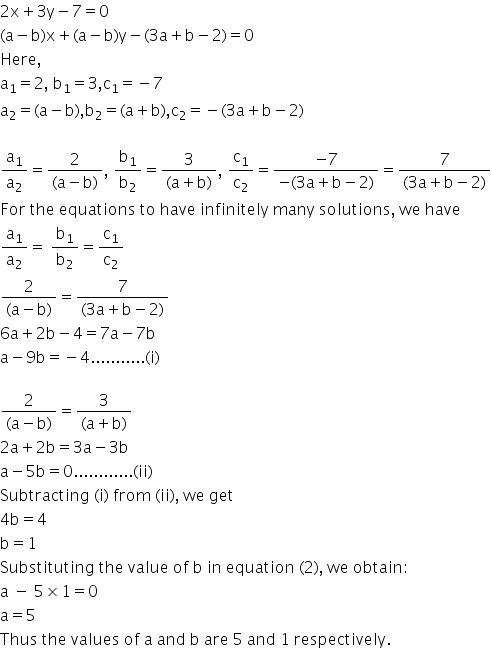
Solution 36 (vi)

Solution 36 (vii)

Solution 36(viii)

Solution 36(ix)
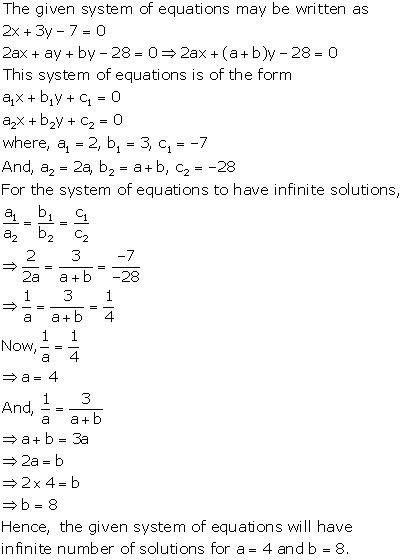
Solution 37(i)
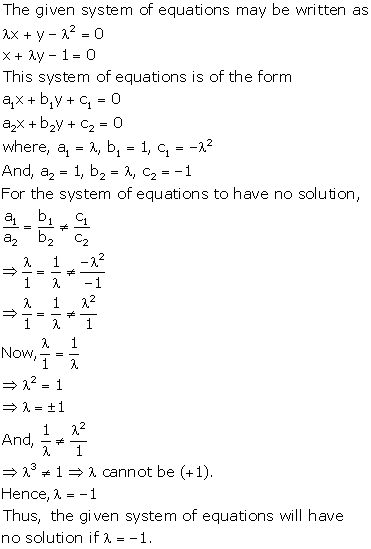
Solution 37(ii)
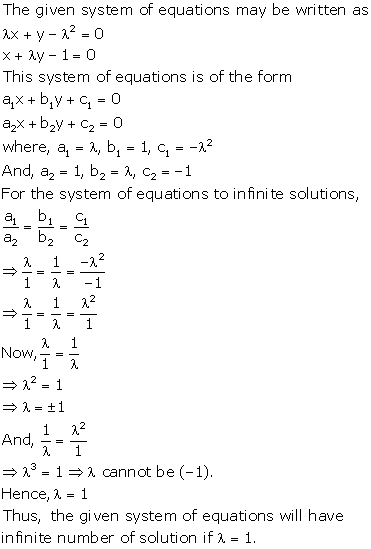
Solution 37(iii)

Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.6
Solution 1

Solution 2

Solution 3

Solution 4

Solution 5

Solution 6

Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9

Solution 10

Solution 11

Solution 12

Solution 13

Solution 14

Solution 15

Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.7
Solution 1

Solution 2

Solution 3

Solution 4

Solution 5

Solution 6

Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9

Solution 10

Solution 11

Solution 12

Solution 13
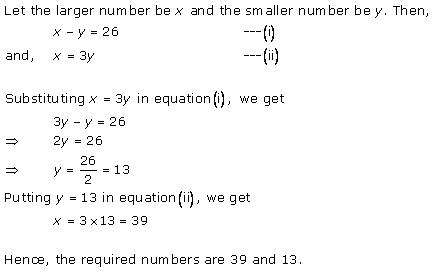
Solution 14

Solution 15

Solution 16

Solution 17

Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.8
Solution 1

Solution 2

Solution 3

Solution 4

Solution 5

Solution 6

Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9
Let the fraction be ![]()
According to the given conditions, we have
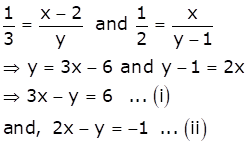
Subtracting (ii) from (i), we get x = 7
Substituting the value of x in (ii), we get
y = 15
Solution 9Old

Solution 10

Solution 11
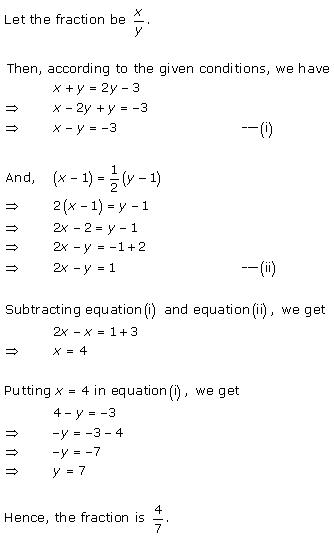
Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.9
Solution 1

Solution 2

Solution 3
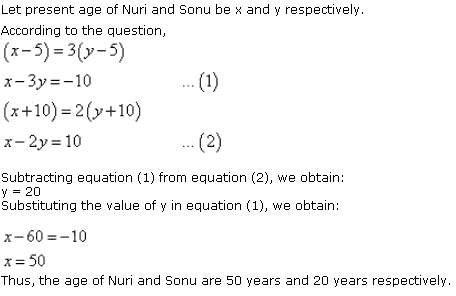
Solution 4

Solution 5

Solution 6

Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9
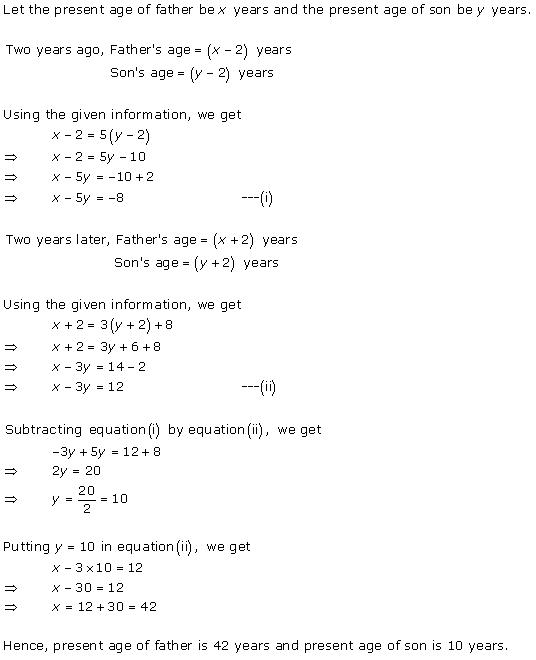
Solution 10

Solution 11
The
difference between the ages of Ani and Biju is given as 3 years. So, either Biju
is 3 years older than Ani or Ani is 3 years older than Biju.
Let the age of Ani and Biju be x
years and y years respectively.
Age of
Dharam = 2 × x = 2x years
x - y = 3 ... (1)
Age of Biju = 19 - 3 = 16 years
Case II: Biju is older than Ani by 3 years
y - x = 3 ... (3)
4x - y = 60
... (4)
Adding (3) and (4), we obtain:
3x
= 63
x = 21
Age
of Ani = 21 years
Age of Biju = 21 + 3
= 24 years
Concept
Insight: In this problem, ages of Ani and Biju are the unknown
quantities. So, we represent them by variables x and y. Now, note that here it
is given that the ages of Ani and Biju differ by 3 years. So, it is not
mentioned that which one is older. So, the most important point in this question
is to consider both cases Ani is older than Biju and Biju is older
than Ani. For second condition the relation on the ages of Dharam and
Cathy can be implemented . Pair of linear equations can be solved using a
suitable algebraic method.
Solution 12

Solution 13
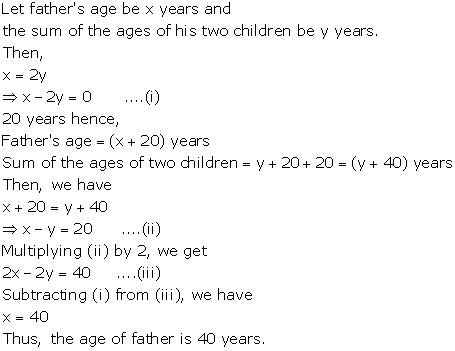
Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.10
Solution 1

Solution 2

Solution 3


Solution 4
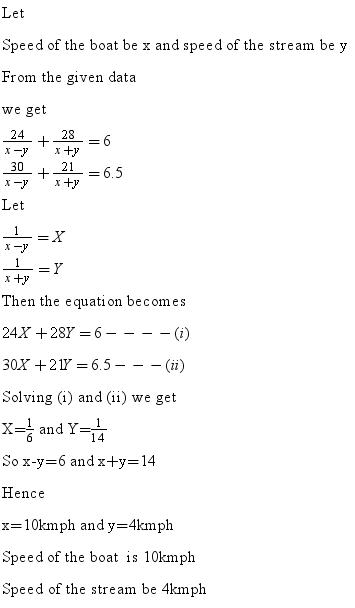
Solution 5

Solution 6

Solution 7

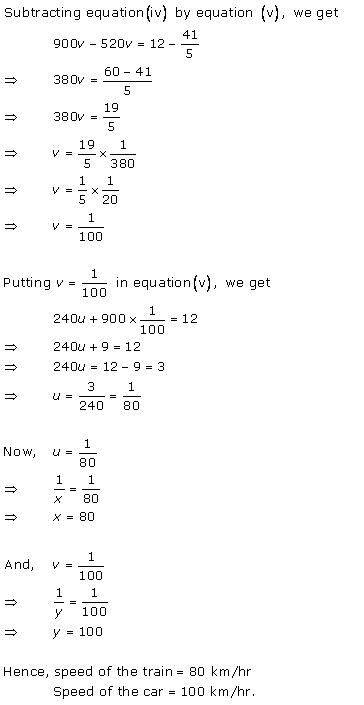
Solution 8


Solution 9


Solution 10


Solution 11


Solution 12

Solution 13
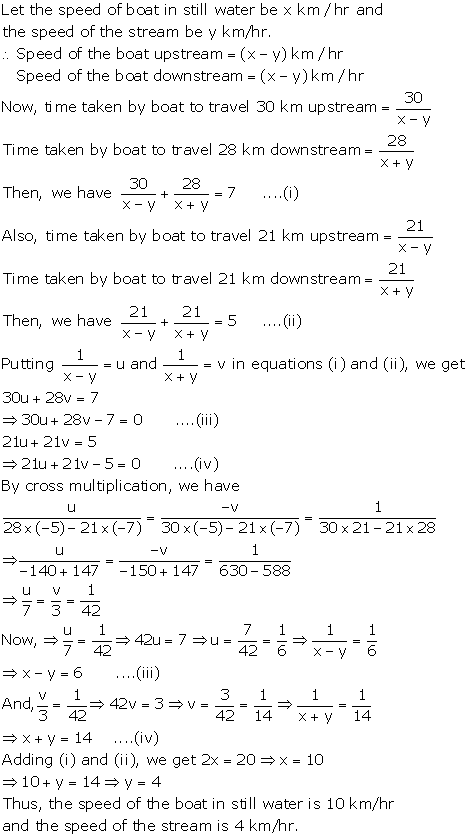
Solution 14


Solution 15
According to the question,
By using equation (1), we obtain:
3x - 10t = 30 ... (3)
Adding equations (2) and (3), we obtain:
x = 50
Substituting the value of x in equation (2), we obtain:
(-2) x (50) + 10t = 20
-100 + 10t = 20
10t = 120
t = 12
From equation (1), we obtain:
d = xt = 50 x 12 = 600
Thus, the distance covered by the train is 600 km.
Concept insight: To solve this problem, it is very important to remember the relation
by three different
variables. By using the given conditions, a pair of equations will be obtained. Mind one thing that the equations obtained will not be linear. But they can be reduced to linear form by using the fact that
be solved easily by elimination method.
Solution 16

Solution 17


Solution 18


Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 3.11
Solution 1

Solution 2

Solution 3

Solution 4

Solution 5

Solution 6
We know that the sum of the measures of opposite angles in a cyclic
quadrilateral is 180°. ![]() A
+
A
+ ![]() C
= 180
C
= 180
4y + 20 - 4x = 180
-4x + 4y = 160
x - y = -40
... (1)
Also, ![]() B
+
B
+ ![]() D
= 180
D
= 180
3y - 5 - 7x + 5 = 180
-7x + 3y = 180
... (2)
Multiplying equation (1) by 3, we obtain:
3x - 3y = -120 ... (3)
Adding
equations (2) and (3), we obtain:
-4x = 60
x = -15
Substituting the
value of x in equation (1), we obtain:
-15 - y = -40
y = -15 + 40 = 25
![]() A
= 4y + 20 = 4(25) + 20 = 120o
A
= 4y + 20 = 4(25) + 20 = 120o![]() B
= 3y - 5 = 3(25) - 5 = 70o
B
= 3y - 5 = 3(25) - 5 = 70o![]() C
= -4x = -4(-15) = 60o
C
= -4x = -4(-15) = 60o![]() D
= -7x + 5 = -7(-15) + 5 = 110o
D
= -7x + 5 = -7(-15) + 5 = 110o
Concept insight:
The most important idea to solve this problem is by using the fact that
the sum of the measures of opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral is
180o. By using this relation, two linear equations can be obtained
which can be solved easily by eliminating a suitable variable.
Solution 7


Solution 8
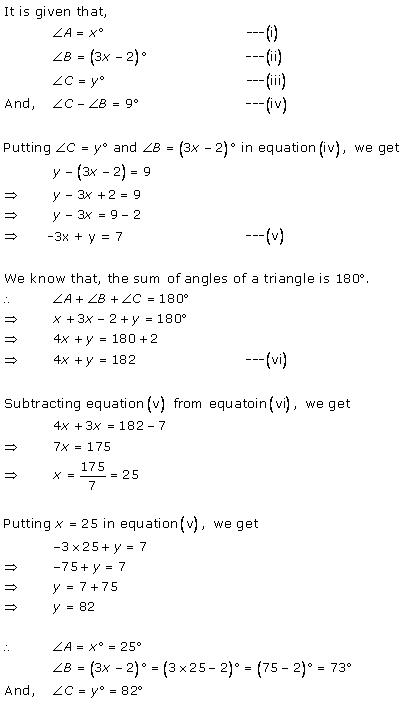
Solution 9

Solution 10

Solution 11

Solution 12

Solution 13

Solution 14

Solution 15

Solution 16

Solution 17

Solution 18

Solution 19

Solution 20

Solution 21

Solution 22
Let the money
with the first person and second person be Rs x and Rs y
respectively.
According to the question,
x + 100 = 2(y - 100)
x +
100 = 2y - 200
x - 2y = -300 ...
(1)
6(x - 10) = (y + 10)
6x - 60 = y + 10
6x - y = 70
... (2)
Multiplying equation
(2) by 2, we obtain:
12x - 2y = 140 ...
(3)
Subtracting equation (1) from equation (3), we obtain:
11x = 140 +
300
11x = 440
x = 40
Putting the value of x in equation (1), we
obtain:
40 - 2y = -300
40 + 300 = 2y
2y = 340
y = 170
Thus,
the two friends had Rs 40 and Rs 170 with them.
Concept insight:
This problem talks about the amount of capital with two friends. So, we
will represent them by variables x and y respectively. Now, using the given
conditions, a pair of linear equations can be formed which can then be solved
easily using elimination method.
Solution 23

Solution 24

Solution 25

Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.114
Solution 1

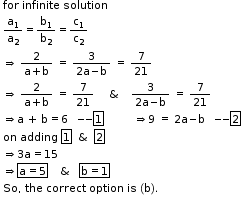
So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 2
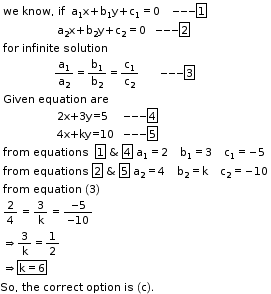
Solution 3
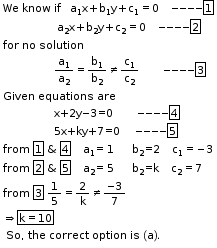
Solution 4
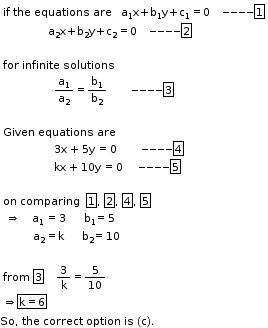
Solution 5
Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.115
Solution 6
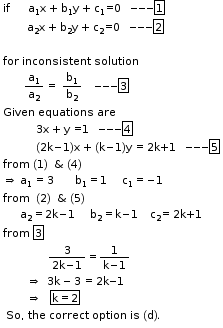
Solution 7

So, the correct option is (a).
Solution 8
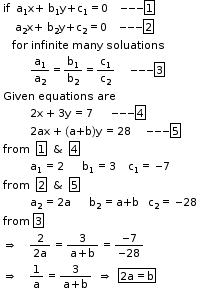
So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 9
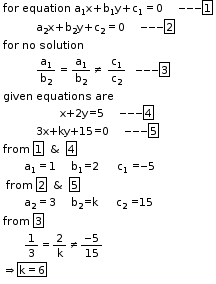
So, the correct option is (a).
Solution 10

So, the correct option is (c).
Solution 11
Consistent solution means either linear equations have unique solutions or infinite solutions.
⇒ In case of unique solution; lines are intersecting
⇒ If solutions are infinite, lines are coincident.
So, lines are either intersecting or coincident
So, the correct option is (d).
Solution 12
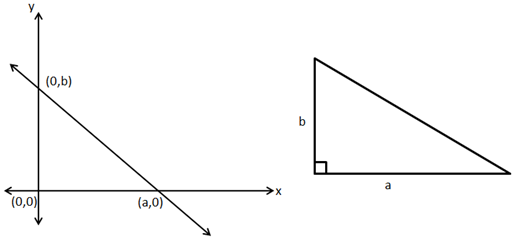
So, the correct option is (c).
Solution 13
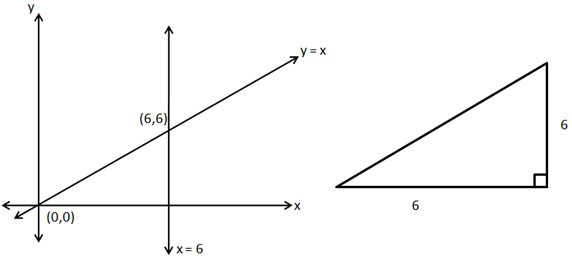
![]()
So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 14
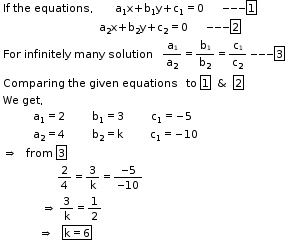
So, the correct option is (d).
Solution 15
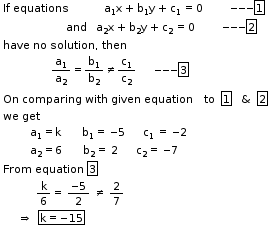
So, the correct option is (d).
Solution 16
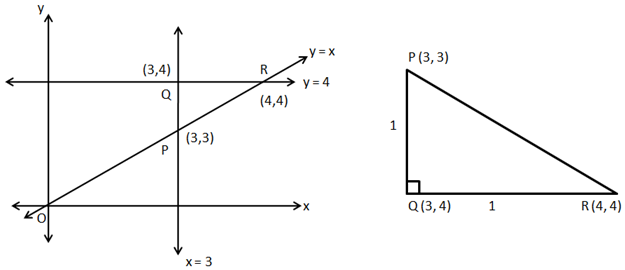
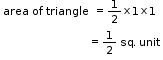
So, the correct option is (a).
Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.116
Solution 17
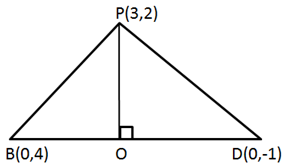

So, the correct option is (b).
Solution 18

Solution 19
Since x = a and y = b is the solution of given system of equations x - y = 2 and x + y = 4, we have
a - b = 2 ….(i)
a + b = 4 ….(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), we have
2a = 6 ⇒ a = 3
⇒ b = 4 - 3 = 1
Hence, correct option is (a).
Solution 20

Solution 21