Chapter 6 Triangles
Class 10th Maths NCERT Exemplar Solution
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1
Choose the correct answer from the given four options:
Question 1.
In the figure, if ∠BAC = 90° and AD ⊥ BC. Then,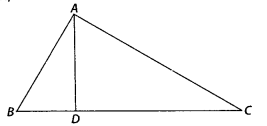
(A) BD . CD = BC2
(B) AB . AC =
BC2
(C) BD . CD = AD2
(D) AB . AC =
AD2
Solution:
(C)
In ∆ABC,
∠B + ∠BAC + ∠C = 180°
⇒ ∠B
+ 90° + ∠C = 180°
⇒ ∠B = 90° – ∠C
Similarly, In ∆ADC, ∠D AC = 90° – ∠C
In ∆ADB and ∆ADC,
∠D = ∠D = 90°
∠DBA = ∠D AC [each equal to (90° – ∠C)
∴ ∆ADB ~ ∆CDA
[by AA similarity criterion]
∴ \(\frac{B D}{A D}=\frac{A
D}{C D}\)
⇒ BD . CD = AD2
Question 2.
The lengths of the diagonals of a rhombus are 16 cm and 12 cm.
Then, the length of the side of the rhombus is
(A) 9 cm
(B) 10 cm
(C) 8
cm
(D) 20 cm
Solution:
(B)
We know that the diagonals of a rhombus
are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
Given, AC = 16 cm and BD = 12
cm
∴ AO = 8 cm, BO = 6 cm and ∠AOB = 90°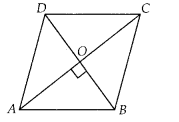
In right angled ∆AOB,
AB2 = AO2 +
OB2 [by Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ AB2 = 82 +
62 = 64 + 36 = 100
∴ AB = 10 cm
Question 3.
If ∆ABC ~ ∆EDFand ∆ABC is not similar to ∆DEF, then which of
the following is not true?
(A) BC . EF = AC . FD
(B) AB . EF = AC . DE
(C) BC . DE = AB . EF
(D) BC . DE = AB . FD
Solution:
(C)
Given,
∆ABC ~ ∆EDF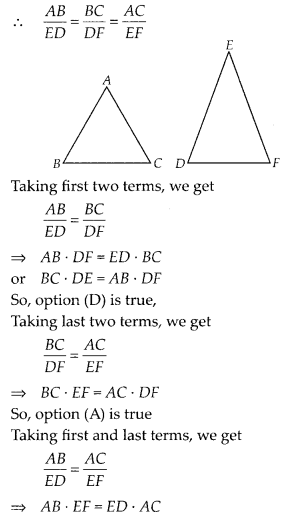
Hence, option (B) is true.
Question 4.
If in two triangles ABC and PQR, \(\frac{A B}{Q R}=\frac{B
C}{P R}=\frac{C A}{P Q}\) then
(A) ∆PQR ~ ∆CAB
(B) ∆PQR ~ ∆ABC
(C) ∆CBA
~ ∆PQR
(D) ∆BCA ~ ∆PQR
Solution:
(A)
Given, in triangles ABC and
PQR,
\(\frac{A B}{Q R}=\frac{B C}{P R}=\frac{C A}{P Q}\)
which shows that
sides of one triangle are proportional to the sides of the other triangle, then
their corresponding angles are also equal, so by SSS similarity, triangles are
similar i.e., ∆CAB ~ ∆PQR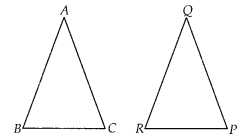
Question 5.
In the figure, two line segments AC and BD intersect each
other at the point P such that PA = 6 cm, PB = 3 cm, PC = 2.5 cm, PD = 5 cm,
∠APB = 50° and ∠CDP = 30°. Then, ∠ PBA is equal to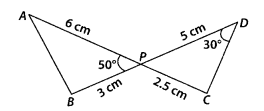
(A) 50°
(B) 30°
(C) 60°
(D) 100°
Solution:
(D): In ∆APB and ∆CPD, ∠APB = ∠CPD = 50°
[vertically opposite angles]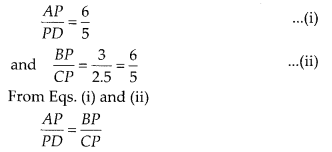
∴ ∆APB ~ ∆DPC [by SAS similarity criterion]
∴ ∠A = ∠D = 30° [corresponding
angles of similar triangles]
In ∆APB, ∠A + ∠B + ∠APB = 180° [sum of angles of
a triangle = 180°]
⇒ 30° + ∠B + 50° = 180°
∴ ∠B = 180° – (50° + 30°) =
100°
i.e., ∠PBA = 100°
Question 6.
If in two triangles DEF and PQR, ∠D = ∠Q and ∠R = ∠E, then
which of the following is not true?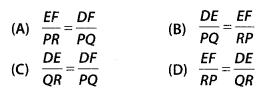
Solution:
(B)
Given, in ∆DEF and ∆PQR, ∠D = ∠Q, ∠R =
∠E
∴ ∆DEF ~ ∆QRP [by
AAA similarity criterion]
⇒ ∠F = ∠P
[corresponding angles of similar
triangles]
∴\(\frac{D F}{Q P}=\frac{E D}{R Q}=\frac{F E}{P R}\)
Question 7.
In ∆ABC and ∆DEF, ∠B = ∠E, ∠F = ∠C and AB = 3 DE. Then, the
two triangles are
(A) congruent but not similar
(B) similar but not
congruent
(C) neither congruent nor similar
(D) congruent as well as
similar
Solution:
(B)
In ∆ABC and ∆DEF, ∠B = ∠E,
∠F = ∠C and AB =
3DE
We know that, if in two triangles corresponding two angles
are same, then they are similar by AA similarity criterion.
Since, AB ≠
DE
Therefore ∆ABC and ∆DEF are not congruent.
Question 8.
It is given that ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR with \(\frac{B C}{Q
R}=\frac{1}{3}\) then \(\frac { { ar }(\Delta PRQ) }{ { ar }(\Delta BCA) } \)
equal to
(A) 9
(B) 3
(C) \(\frac{1}{3}\)
(D) \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Solution:
(A)
Given, ∆ABC ~ ∆QR and \(\frac{B C}{Q R}=\frac{1}{3}\)
We
know that, the ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to square of
the ratio of their corresponding sides.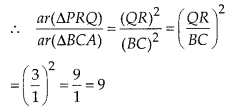
Question 9.
It is given that ∆ABC ~ ∆DFE, ∠A =30°, ∠C = 50°, AB = 5 cm, AC
= 8 cm and DF= 7.5 cm. Then, the following is true:
(A) DE= 12 cm, ∠F=
50°
(B) DE= 12 cm, ∠F= 100°
(C) EF= 12 cm, ∠D = 100°
(D) EF= 12 cm, ∠D
= 30°
Solution:
(B)
Given, ∆ABC ~ ∆DFE, then ∠A = ∠D = 30°, ∠C = ∠E =
50°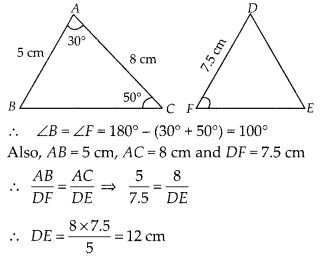
Hence, DE = 12 cm, ∠F = 100°
Question 10.
If in ∆ABC and ∆DEF, \(\frac{A B}{D E}=\frac{B C}{F D}\),
then they will be similar, when
(A) ∠B = ∠E
(B) ∠A = ∠D
(C) ∠B = ∠D
(D) ∠A = ∠F
Solution:
(C)
Given, in ∆ABC and ∆EDF,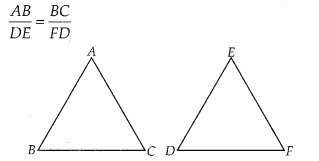
So, ∆ABC ~ ∆EDF if ∠B = ∠D [By SAS similarity criterion]
Question 11.
If ∆ABC ~ ∆QRP, \(\frac { { ar }(\Delta ABC) }{ ar(\Delta
PQR) } =\frac { 9 }{ 4 } \), AB= 18 cm and BC = 15 cm, then PR is equal to
(A) 10 cm
(B) 12 cm
(C) \(\frac{20}{3}\) cm
(D) 8 cm
Solution:
(A)
Given, ∆ABC ~ ∆QRP, AB = 18 cm and BC = 15 cm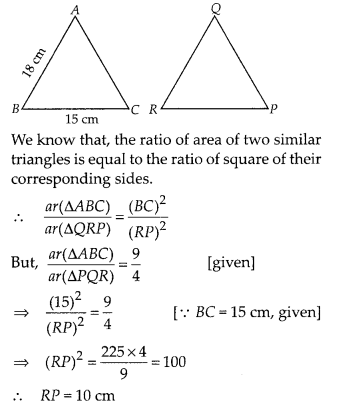
Question 12.
If S is a point on side PQ of a ∆PQR such that PS = QS = RS,
then
(A) PR – QR = RS2
(B) QS2 + RS2 =
QR2
(C) PR2 + QR2 = PQ2
(D)
PS2 + RS2 = PR2
Solution:
(C)
Given,
in ∆PQR,
PS = QS = RS …………. (i)
In ∆PSR, PS = RS [from Eq(i)]
⇒ ∠1 = ∠2
………… (ii)
[Angles opposite to equal sides are equal]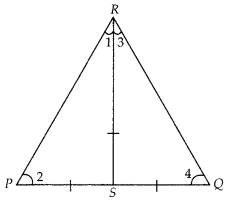
Similarly, in ∆RSQ, RS = SQ
⇒ ∠3 = ∠4 …………. (iii)
[angles opposite to equal sides are equal]
Now, in ∆PQR, sum of angles =
180°
⇒ ∠P + ∠Q + ∠P = 180°
⇒ ∠2 + ∠4 + ∠1 + ∠3 = 180°
⇒ ∠1 + ∠3 + ∠1 +
∠3 = 180°
⇒ 2(∠1 + ∠3) = 180°
⇒ ∠l + ∠3 = \(\frac{180^{\circ}}{2}\) =
90°
∴ ∠R = 90°
In ∆PQR, by Pythagoras theorem,
PR2 +
QR2 = PQ2
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise – 6.2
Question 1.
Is the triangle with sides 25 cm, 5 cm and 24 cm a right
triangle? Give reasons for your answer.
Solution:
False
Let a = 25 cm,
b = 5 cm and c = 24 cm
Now, b2 + c2 = (5)2 +
(24)2
= 25 + 576 = 601 ≠ (25)2
Hence, given sides do
not make a right triangle because it does not satisfy the property of Pythagoras
theorem.
Question 2.
It is given that ∆DEF ~ ∆RPQ. Is it true to say that ∠D = ∠R
and ∠F = ∠P? Why?
Solution:
False
We know that, if two triangles are
similar, then their corresponding angles are equal.
∴ ∠D = ∠R, ∠E = ∠P and ∠F
= Q
Question 3.
A and B are respectively the points on the sides PQ and PR of
A PQR such that PQ = 12.5 cm, PA = 5 cm, BR = 6 cm and PB = 4 cm. Is 4B||Q/??
Give reasons for your answer.
Solution:
True
Given, PQ = 12.5 cm, PA =
5 cm, BR = 6 cm and PB = 4 cm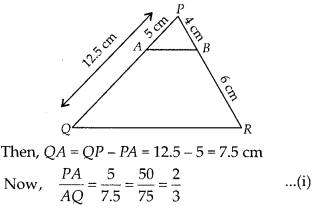
and \(\frac{P B}{B R}=\frac{4}{6}=\frac{2}{3}\)
From Eqs. (i) and (ii),
\(\frac{P A}{A Q}=\frac{P B}{B R}\)
By converse of basic proportionality
theorem, AB || QR
Question 4.
In the figure, BD and CE intersect each other at the point P.
Is A∆PBC ~ ∆PDE?Why?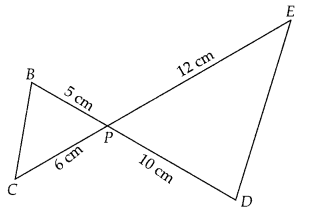
Solution:
True
In ∆PBC and ∆PDE,
∠BPC = ∠EPD [vertically opposite
angles]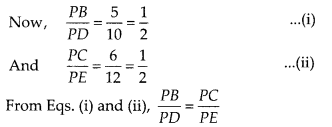
Since, one angle of ∆PBC is equal to one angle of ∆PDE and the sides including
these angles are proportional, so both triangles are similar.
Hence, ∆PBC ~
∆PDE, by SAS similarity criterion.
Question 5.
In ∆PQR and ∆MST, ∠P = 55°, ∠Q = 25°, ∠M = 100° and ∠S = 25°.
Is ∆QPR ~ ∆TSM? Why?
Solution:
False
We know that, the sum of three
angles of a triangle is 180°.
In ∆PQR, ∠P +∠Q +∠R = 180°
⇒ 55° + 25 ° + ∠R
= 180°
⇒∠R = 180° – (55° + 25 °)
= 180° – 80° = 100°
In ∆TSM, ∠T + ∠S +
∠M = 180°
⇒ ∠T + ∠25° + 100° = 180°
⇒ ∠T = 180° – (25° + 100°) = 180° –
125° = 55°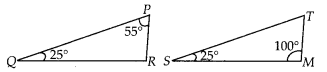
In ∆PQR and ∆TSM,
∠P = ∠T, ∠Q = ∠S and ∠R = ∠M
∴ ∠PQR = ∠TSM
[since,
all corresponding angles are equal]
Hence, ∆QPR is not similar to ∆TSM, since
correct correspondence is P ↔ T, Q ↔ S and R ↔ M.
Question 6.
Is the following statement true? Why? “Two quadrilaterals are
similar, if their corresponding angles are equal”.
Solution:
False
Two
quadrilaterals are similar if their corresponding angles are equal and
corresponding sides must also be proportional.
Question 7.
Two sides and the perimeter of one triangle are respectively
three times the corresponding sides and the perimeter of the other triangle. Are
the two triangles similar? Why?
Solution:
True
Here, the corresponding
two sides and the perimeters of two triangles are proportional, then the third
side of both triangles will also in proportion.
Question 8.
If in two right triangles, one of the acute angles of one
triangle is equal to an acute angle of the other triangle, can you say that the
two triangles will be similar? Why?
Solution:
True
Let two right angled
triangles be ∆ABC and ∆PQR
In which, ∠A = ∠P = 90° and ∠B = ∠Q = acute angle (Given)
Then, by AA similarity criterion, ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR
Question 9.
The ratio of the corresponding altitudes of two similar
triangles is \(\frac{3}{5}\).Is it correct to say that ratio of their areas is
\(\frac{6}{5}\) ? Why?
Solution:
False
Ratio of corresponding altitudes
of two triangles having areas A1 and A2 respectively is
\(\frac{3}{5}\).
By the property of area of two similar triangles,
\(\Rightarrow\left(\frac{A_{1}}{A_{2}}\right)=\left(\frac{3}{5}\right)^{2}
\Rightarrow \frac{9}{25} \neq \frac{6}{5}\)
So, the given statement is not
correct.
Question 10.
D is a point on side QR of ∆PQR such that PD ⊥ QR. Will it be
correct to say that ∆PQD ~ A∆RPD? Why?
Solution:
False
In ∆PQD and
∆RPD,
PD = PD [common side]
∠PDQ = ∠PDR [each 90°]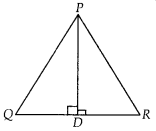
Here, no other sides or angles are equal, so we can say that
∆PQD is not similar to ∆RPD. But if ∠P = 90°, then ∠DPQ = ∠PRD
[each equal to
90° – ∠Q and by ASA similarity criterion, ∆PQD ~ ∆RPD]
Question 11.
In the figure, if ∠D = ∠C, then is it true that ∆ADE ~ ∆ACB?
Why?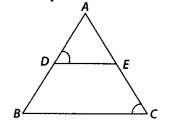
Solution:
True
In ∆ADE and ∆ACB,
∠A = ∠A [common
angle]
∠D = ∠C [given]
∴ ∆ADE ~ ∆ACB [by AA similarity criterion]
Question 12.
Is it true to say that if in two triangles, an angle of one
triangle is equal to an angle of another triangle and two sides of one triangle
are proportional to the two sides of the other triangle, then the triangles are
similar? Give reasons for your answer.
Solution:
False
Because,
according to SAS similarity criterion, if one angle of a triangle is equal to an
angle of the other triangle and the sides including these angles are
proportional, then the two triangles are similar.
Here, one angle and two
sides of two triangles are equal but these sides not including equal angle, so
given statement is not correct.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise – 6.3
Question 1.
In a ∆PQR, PR2 – PQ2 = QR2
and M is a point on side PR such that QM⊥ PR. Prove that QM2 = PM ×
MR.
Solution:
Given, In ∆PQR,
PR2 – PQ2 =
QR2 and QM ⊥ PR
To prove : QM2 = PM × MR
Proof :
Since, PR2 – PQ2 = QR2
⇒ PR2 =
PQ2 + QR2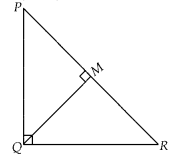
So, ∆PQR is right angled triangle right angle at Q.
In
∆QMR and ∆PMQ, ∠M = ∠M [each 90°]
∠MQR = ∠QPM [each equal to 90° – ∠R]
∴
∆QMR ~ ∆PMQ [by AA similarity criterion]
Now, using property of area of
similar triangles, we get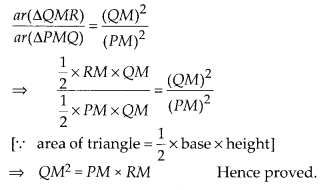
Question 2.
Find the value of x for which DE || AB is given figure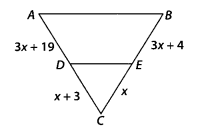
Solution:
Given, DE || AB
∴ \(\frac{C D}{A D}=\frac{C
E}{B E}\) [by basic proportionality theorem]
\(\frac{x+3}{3 x+19}=\frac{x}{3
x+4}\)
⇒ (x + 3)(3x + 4) = x (3x + 19)
⇒ 3x2 + 4x + 9x + 12 =
3x2 + 19x
⇒ 19x – 13x = 12
⇒ 6x = 12
∴ x = \(\frac{12}{6}\)
= 2
Hence, the required value of x is 2.
Question 3.
In the figure, if ∠1 = ∠2and ∆NSQ ≅ ∆MTR, then prove that ∆PTS
~ ∆PRQ.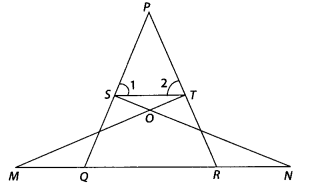
Solution:
Given ∆NSQ ≅ ∆MTR and ∠1 = ∠2
To prove : ∆PTS ~ ∆PRQ
Proof :
Since, ∆NSQ ≅ ∆MTR
So, SQ = TR ………….. (i)
Also, ∠1 = ∠2 ⇒ PT = PS …………
(ii)
[since, sides opposite to equal angles are also equal]
From Eqs.(i)
and (ii), \(\frac{P S}{S Q}=\frac{P T}{T R}\)
⇒ ST || QR
[by converse of basic proportionality theorem]
∴ ∠1 =
∠PQR [Corresponding angles]
and ∠2 =
∠PRQ
In ∆PTS and ∆PRQ,
∠P = ∠P [common angles]
∠1 = ∠PQR
∠2 =
∠PRQ
∴ ∆PTS ~ ∆PRQ [by AAA
similarity criterion]
Question 4.
Diagonals of a trapezium PQRS intersect each other at the
point O, PQ || RS and PQ = 3 RS. Find the ratio of the areas of ∆POQ and
∆ROS.
Solution:
Given PQRS is a trapezium in which PQ || RS and PQ =
3RS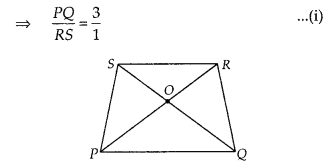
In ∆POQ and ∆ROS,
∠SOR = ∠QOP [vertically opposite
angles]
∠SRP = ∠RPQ [alternate angles]
∴ ∆POQ ~
∆ROS [by AA similarity criterion]
By property of
area of similar triangles,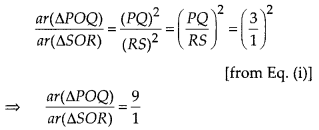
Hence, the required ratio is 9 : 1
Question 5.
In the figure if AB || DC and AC and PQ intersect each other
at the point O, prove that OA . CQ = OC . AP.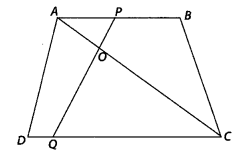
Solution:
Given AC an PQ intersect each other at point O
and AB || DC
To prove : OA . CQ = OC . AP
Proof: In ∆AOP and ∆COQ,
∠AOP
= ∠COQ [vertically opposite angles]
∠APO = ∠CQO
[since AB || DC and PQ is
transversal, so alternate angles]
∴ ∆AOP ~ ∆COQ
[by AA similarity criterion]
Then, \(\frac{O A}{O C}=\frac{A P}{C
Q}\)
[since, corresponding sides are proportional]
⇒ OA . CQ = OC . AP
Hence proved.
Question 6.
Find the altitude of an equilateral triangle of side 8 cm.
Solution:
Let ABC be an equilateral triangle of side 8 cm i.e., AB = BC = CA
= 8 cm
Draw altitude AD which is perpendicular to BC. Then, D is the
mid-point of BC.
∴ BD = CD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) BC = \(\frac{8}{2}\) = 4 cm
Now, AB2 = AD2 + BD2 [by Pythagoras
theorem]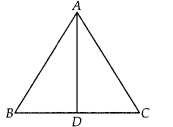
⇒ (8)2 = AD2 + (4)2
⇒ 64
= AD2 + 16
⇒ AD2 = 64 – 16 = 48
⇒ AD = \(\sqrt{48}\)
= \(4 \sqrt{3}\) cm
Hence, altitude of an equilateral triangle is \(4
\sqrt{3}\) cm
Question 7.
If ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF, AB = 4 cm, DE = 6 cm, EF = 9 cm and FD = 12
cm, find the perimeter of ∆ABC.
Solution:
Given AB = 4 cm, DE = 6 cm and
EF = 9 cm and FD = 12 cm
Also, ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF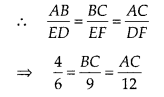
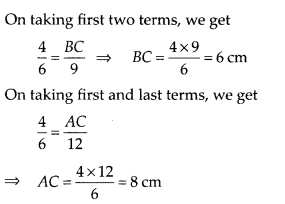
Now, perimeter of ∆ABC = AB + BC + AC = 4 + 6 + 8 = 18 cm
Question 8.
In the figure, if DE || BC, find the ratio of ar(∆ADE) and
ar(∆ECB).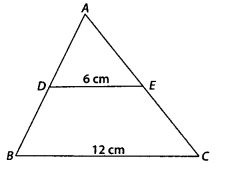
Solution:
Given, DE || BC, DE = 6 cm and BC = 12 cm
In
∆ABC and ∆ADE,
∠ABC = ∠ADE [corresponding
angle]
and ∠A = ∠A [common side]
∴ ∆ABC ~
∆ADE [by AA similarity criterion]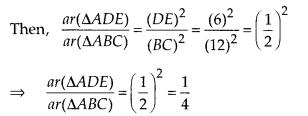
Let ar(∆ADE) = k, then ar(∆ABC) = 4k
Now, ar(∆ECB) = ar(ABC) – ar(ADE) = 4k –
k = 3k
∴ Required ratio = ar(ADE): ar(DECB)
= k : 3k = 1 : 3
Question 9.
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and P, Q are points on
AD and BC, respectively such that PQ || DC. If PD = 18 cm, BQ = 35 cm and QC =
15 cm, find AD.
Solution:
Given, a trapezium ABCD in which AB || DC. P and
Q are points on AD and BC, respectively such that PQ || DC. Thus, 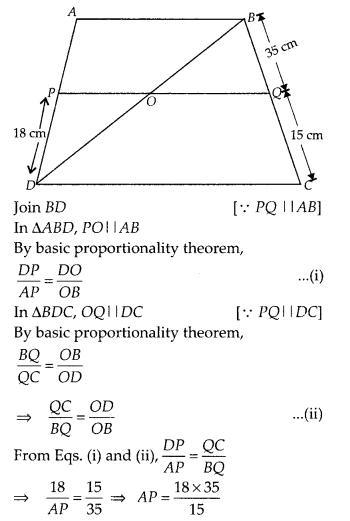
⇒ AP = 42 cm.
Now; AD = AP + PD = 42 + 18 = 60
∴ AD = 60 cm
Question 10.
Corresponding sides of two similar triangles are in the ratio
of 2 : 3. If the area of the smaller triangle is 48 cm2, find the
area of the larger triangle.
Solution:
Given, ratio of corresponding sides
of two similar triangles is 2 : 3 or \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Area of smaller triangle
= 48 cm2
By the property of area of two similar triangles,
Ratio of area of both triangles = (Ratio of their corresponding
sides)2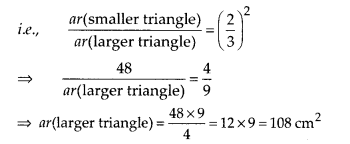
Question 11.
In a ∆PQR, N is a point on PR, such that QN ⊥ PR. If PN . NR
= QN2, prove that ∠PQR = 90°
Solution:
Given, ∆PQR, N is a
point on PR, such that QN ⊥ PR and PN . NR = QN2
To prove : ∠PQR =
90°
Proof: We have, PN . NR = QNc
⇒ PN . NR = QN . QN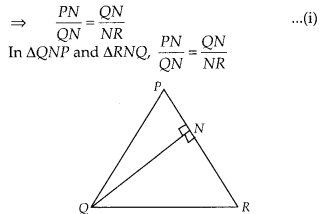
and ∠PNQ = ∠RNQ [each equal to 90° ]
∴ ∆QNP ~ ∆RNQ
[by SAS similarity criterion]
Then, ∆QNP and ∆RNQ are equiangulars.
i.e.,
∠PQN = ∠QRN
⇒ ∠RQN-∠QPN
On adding both sides, we get
∠PQN + ∠RQN = ∠QRN
+ ∠QPN
⇒ ∠PQR = ∠QRN + ∠QPN …………… (ii)
We know that, sum of angles of a
triangle is 180°
In ∆PQR, ∠PQR + ∠QPR + ∠QRP = 180°
⇒ ∠PQR + ∠QPN + ∠QRN =
180°
[ ∵∠QPR = ∠QPN and ∠QRP = ∠QRN]
⇒ ∠PQR + ∠PQR = 180° [using Eq.
(ii)]
⇒ 2∠PQR = 180°
⇒ ∠PQR = \(\frac{180^{\circ}}{2}\) = 90°
∴ ∠PQR =
90° Hence proved.
Question 12.
Areas of two similar triangles are 36 cm2 and 100
cm2 . If the length of a side of the larger triangle is 20 cm, find
the length of the corresponding side of the smaller triangle.
Solution:
Given, area of smaller triangle = 36 cm2
and area of larger
triangle= 100 cm2
Also, length of a side of the larger triangle =
20 cm
Let length of the corresponding side of the smaller triangle = x cm
By property of area of similar triangles,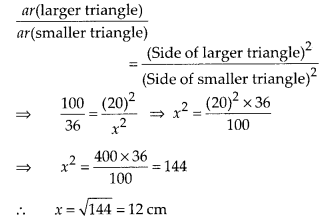
Question 13.
In the figure, if ∠ACB = ∠CDA, AC = 8 cm and AD = 3 cm, find
BD.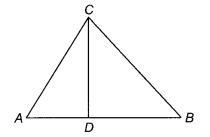
Solution:
Given, AC = 8 cm, AD = 3 cm
and ∠ACB =
∠CDA
In ∆ACD and ∆ABC,
∠A = ∠A [Common
angle]
∠ADC = ∠ACB [Given]
∴ ∆ADC ~ ∆ACB
[By AA similarity criterion]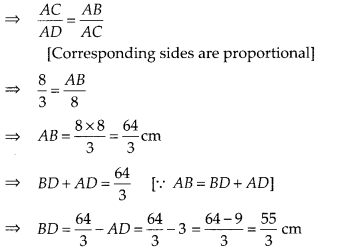
Question 14.
A 15 metres high tower casts a shadow 24 metres long at a
certain time and at the same time, a telephone pole casts a shadow 16 metres
long. Find the height of the telephone pole.
Solution:
Let BC = 15 m be
the tower and its shadow AB is 24 m. At that time ∠CAB = θ. Again, let EF = h be
a telephone pole and its shadow DE = 16 m. At the same time ∠EDF = θ. Here, ∆ABC
and ∆DEF both are right angled triangles.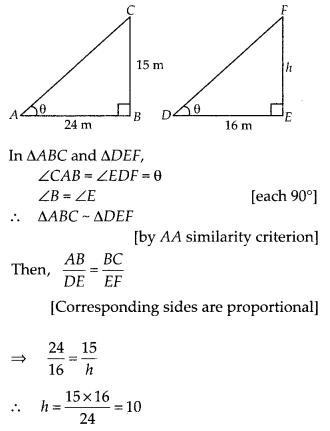
Hence, the height of the point on the wall where the top of the ladder reaches
is 8 m.
Question 15.
Foot of a 10 m long ladder leaning against a vertical wall is
6 m away from the base of the wall. Find the height of the point on the wall
where the top of the ladder reaches.
Solution:
Let AB be a vertical wall
and AC = 10 m is a ladder. The top of the ladder reached to A and distance of
ladder from the base of the wall BC is 6 m.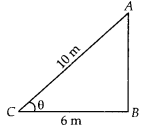
In right angled ∆ABC
AC2 = AB2 +
BC2 [by Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (10)2 = AB2 +
(6)2
⇒ 100 = AB2 + 36
⇒ AB2 = 100 – 36 =
64
∴ AB = \(\sqrt{64}\) = 8 m
Hence the height of the point on th wall
where the top of the ladder reaches is 8 m.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise – 6.4
Question 1.
In the given figure, if ∠A = ∠C, AB = 6 cm, BP = 15 cm, AP =
12 cm and CP = 4 cm, then find the lengths of PD and CD.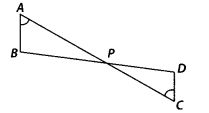
Solution:
Given ∠A = ∠C, AB = 6 cm, BP = 15 cm,
AP = 12
cm and CP = 4 cm
In ∆APB and ∆CPD,
∠A = ∠C [given]
∠APB = ∠CPD
[vertically opposite angles]
∴ ∆APB ~ ∆CPD [by AA similarity
criterion]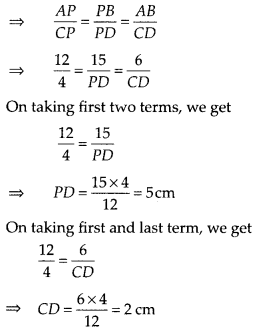
Hence, length of PD is 5 cm and length of CD is 2 cm.
Question 2.
It is given that ∆ABC ~ ∆EDF such that AB = 5 cm, AC = 7 cm,
DF = 15 cm and DE = 12 cm. Find the lengths of the remaining sides of the
triangles.
Solution:
Given, ∆ABC ~ ∆EDF, so the corresponding sides of
∆ABC and ∆EDF are in the same ratio
i.e., \(\frac{A B}{E D}=\frac{A C}{E
F}=\frac{B C}{D F}\) ………………. (i)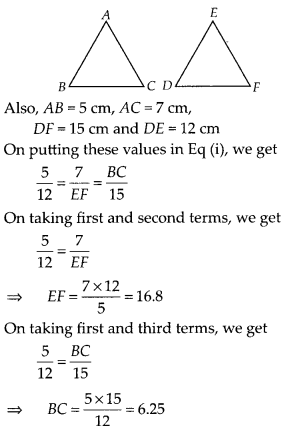
Hence, lengths of the remaining sides of the triangles are EF = 16.8 cm and BC =
6.25 cm.
Question 3.
Prove that if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a
triangle to intersect the other two sides, then the two sides are divided in the
same ratio.
Solution:
Let a ∆ABC in which a line DE parallel to BC
intersects AB at D and AC at E.
To prove : DE divides the two sides in the
same ratio.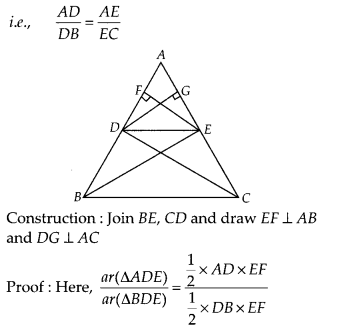
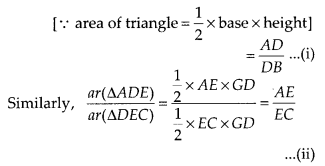
Now, since, ∆BDE and ∆DEC lie between the same parallel lines DE and BC and on
the same base DE
So, ar(∆BDE) = ar(∆DEC) ………….. (iii)
From Eqs. (i), (ii)
and (iii),
\(\frac{A D}{D B}=\frac{A E}{E C}\)
Hence proved
Question 4.
In the figure, if PQRS is a parallelogram and AB || PS, then
prove that OC || SR.
Solution:
Given PQRS is a parallelogram, so PQ || SR and
PS || QR. Also AB || PS.
To prove : OC || SR
Proof : In ∆OPS and ∆OAB, PS
|| AB
∠POS = ∠AOB [common angle]
∠OSP = ∠OBA
[corresponding angles]
∴ ∆OPS ~ ∆OAB
[by AA similarity criterion]
Then, \(\frac{P S}{A B}=\frac{O
S}{O B}\) ………… (i)
In ∆CQE and ∆CAB, QR || PS || AB
∠QCR = ∠ACB [common
angle]
∠CRQ = ∠CBA [corresponding angles]
∴ ∆CQR ~ ∆CAB
On subtracting 1 from both sides, we get OB CB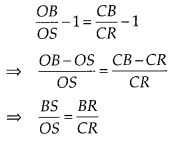
By converse of basic proportionality theorem, SR || OC.
Hence proved
Question 5.
A 5 m long ladder is placed leaning towards a vertical wall
such that it reaches the wall at a point 4 m high. If the foot of the ladder is
moved 1.6 m towards the wall, then find the distance by which the top of the
ladder would slide upwards on the wall.
Solution:
Let AC be the ladder of
length 5 m and BC = 4 m be the height of the wall, which ladder is placed. If
the foot of the ladder is moved 1.6 m towards the wall i.e, AD = 1.6 m, then the
ladder is slide upward i.e., CE = x m.
In right angled ∆ABC,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2 [by
Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (5)2 = (AB)2 +
(4)2
⇒ AB2 = 25 – 16 = 9
⇒ AB = 3m
Now, DB = AB –
AD = 3 – 1.6 = 1.4 m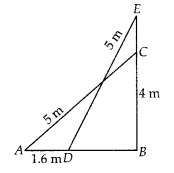
In right angled ∆EBD,
ED2 = EB2 + BD2
[by Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (5)2 =
(EB)2 + (1.4)2 [ ∵ BD = 1.4 m]
⇒ 25 = (EB)2
+ 1.96
⇒ (EB)2 = 25 – 1.96 = 23.04
⇒ EB = \(\sqrt{23.04}\) =
4.8
Now, EC = EB – BC = 4.8 – 4 = 0.8
Hence, the top of the ladder would
slide upwards on the wall at distance is 0.8 m.
Question 6.
For going to a city B from city A, there is a route via city C
such that AC ⊥ CB, AC = 2x km and CB = 2 (x + 7) km. It is proposed to construct
a 26 km highway which directly connects the two cities A and B. Find how much
distance will be saved in reaching city B from city A after the construction of
the highway.
Solution:
Given, AC ⊥ CB, AC = 2xkm,CB = 2(x + 7)km and AB =
26 km
On drawing the figure, we get the right angle ∆ACB right angled at
C.
Now, In ∆ACB, by Pythagoras theorem,
AB2 = AC2 +
BC2
⇒ (26)2 = (2x)2 + {2(x +
7)}2
⇒ 676 = 4x2 + 4(x2 + 49 + 11x)
⇒ 676
= 4x2 + 4x2 + 196 + 56x
⇒ 676 = 8x2 + 56x +
196
⇒ 8x2 + 56x – 480 = 0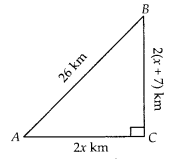
On dividing by 8, we get x2 + 7x – 60 = 0
⇒
x2 + 12x-5x-60 = 0
⇒ x(x + 12) – 5(x + 12) = 0
⇒ (x + 12)(x –
5) = 0
∴ x = -12, x = 5
Since, distance cannot be negative.
∴ x = 5 [∵
x ≠ 12]
Now, AC = 2x = 10 km and BC = 2(x + 7) = 2(5 + 7) = 24 km
The
distance covered to reach city B from city A via city C = AC + BC = 10 + 24 = 34
km
Distance covered to reach city B from city A after the construction of the
highway is
BA = 26 km
Hence, the required saved distance is 34 – 26
i.e., 8 km
Question 7.
A flag pole 18 m high casts a shadow 9.6 m long. Find the
distance of the top of the pole from the far end of the shadow.
Solution:
Let BC = 18 m be the flag pole and its shadow be AB = 9.6 m. The distance of the
top of the pole, C from the far end i.e., A of the shadow is AC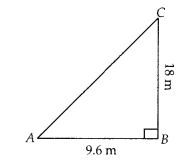
In right angled ∆ABC
AC2 = AB2 +
BC2 [by Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ AC2 = (9.6)2 +
(18)2
⇒ AC2 = 92.16 + 324
⇒ AC2 =
416.16
∴ AC = \(\sqrt{416.16}\) = 20.4 m
Hence, the required distance is
20.4 m.
Question 8.
A street light bulb is fixed on a pole 6 m above the level of
the street. If a woman of height 1.5 m casts a shadow of 3m, find how far she is
away from the base of the pole.
Solution:
Let A be the position of the
street bulb fixed on a pole AB = 6 m and CD = 1.5 m be the height of a woman and
her shadow be ED = 3 m. Let distance between pole and woman be x m.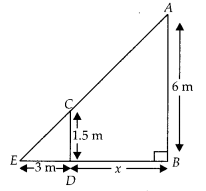
Here, woman and pole both are standing vertically
So, CD
|| AB
In ∆CDE and ∆ABE,
∠E = ∠E [common angle]
∠ABE = ∠CDE [each equal
to 90°]
∴ ∆CDE ~ ∆ABE [by AA similarity criterion]
Then \(\frac{E D}{E
B}=\frac{C D}{A B} \Rightarrow \frac{3}{3+x}=\frac{1.5}{6}\)
⇒ 3 × 6 = 1.5(3
+ x)
⇒ 18 = 1.5 × 3 + 1.5x
⇒ 1.5x = 18 – 4.5
∴ x = \(\frac{13.5}{1.5}\)
= 9 m
Hence, she is at the distance of 9 m from the base of the pole.
Question 9.
In the figure, ABC is a triangle right angled at B and BD ⊥
AC. If AD = 4 cm, and CD = 5 cm, find BD and AB.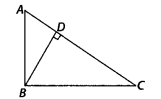
Solution:
Given, ∆ABC in which ∠B = 90° and BD ⊥ AC
Also, AD = 4 cm and CD = 5 cm
In ∆DBA and ∆DCB,
∠ADB = ∠CDB [each equal to
90°]
and ∠BAD = ∠DBC [each equal to 90° – ∠C] ;.
∴ ∆DBA ~ ∆DCB [by AA
similarity criterion]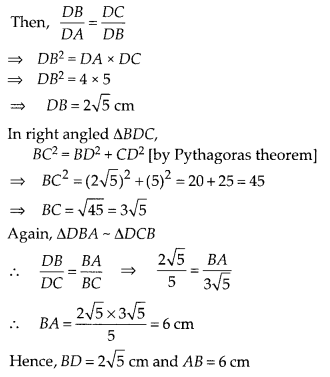
Question 10.
In the figure, PQR is a right triangle right angled at Q and
QS ⊥ PR. If PQ = 6 cm and PS = 4 cm, find QS, RS and QR.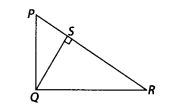
Solution:
Given, ∆PQR in which ∠Q = 90°, QS ⊥ PR and PQ =
6 cm, PS = 4 cm
In ∆SQP and ∆SRQ,
∠PSQ = ∠RSQ [each equal to 90°]
∠SPQ
= ∠SQR [each equal to 90° – ∠R]
∴ ∆SQP ~ ∆SRQ [By AA similarity
criterion]
Then, \(\frac{S Q}{P S}=\frac{S R}{S Q}\)
⇒ SQ2 = PS
× SR ………….. (i)
In right angled ∆PSQ,
PQ2 = PS2 +
QS2 [by Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (6)2 = (4)2.+
QS2
⇒ 36 = 16 + QS2
⇒ QS2 = 36 – 16 =
20
∴ QS.= \(\sqrt{20}=2 \sqrt{5}\) cm
On putting the value of QS in Eq(i),
we get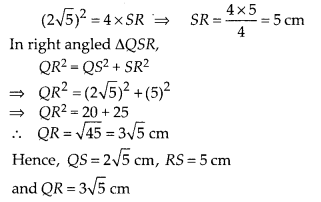
Question 11.
In ∆PQR, PD ⊥ QR such that D lies on QR . If PQ = a, PR = b,
QD = c and DR = d, prove that [a + b)(a – b) = (c + d)(c – d).
Solution:
Given: In ∆PQR, PD ⊥ QR, PQ = a, PR = b,
QD = c and DR = d
To prove : (a +
b)(a -b) = (c + d)(c – d)
Proof : In right angled ∆PDQ,
PQ2 =
PD2 + QD2 [by Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ a2 =
PD2 + c2
⇒ PD2 = a2 –
c2 …………. (i)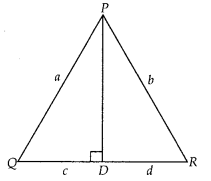
In right angled ∆PDR,
PR2 = PD2 +
DR2 [by Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ b2 = PD2 +
d2
⇒ PD2 = b2 – d2 …………..
(ii)
From Eqs. (i) and (ii)
a2 – c2 = b2
– d2
⇒ a2 – b2 = c2 –
d2
⇒ (a – b)(a + b) = (c – d)(c + d)
Hence proved.
Question 12.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, ∠A + ∠D = 90°. Prove that
AC2 + BD2 = AD2 + BC2 [Hint: Produce
AB and DC to meet at E]
Solution:
Given : Quadrilateral ABCD, in which ∠A
+ ∠D = 90°
To prove : AC2 + BD2 = AD2 +
BC2
Construct: Produce AB and CD to meet at E
Also join AC and
BD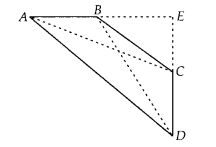
Proof: In ∆AED, ∠A + ∠D = 90° [given]
∴ ∠E = 180° – (∠A +
∠D) = 90°
[ ∵ sum of angles of a triangle = 180°]
Then, by Pythagoras
theorem,
AD2 = AE2 + DE2
In ∆BEC, by
Pythagoras theorem,
BC2 = BE2 + EC2
On
adding both equations, we get
AD2 + BC2 =
AE2 + DE2 + BE2 + CE2 ………… (i)
In
∆AEC, by Pythagoras theorem,
AC2 = AE2 +
CE2
and in ∆BED, by Pythagoras theorem,
BD2 =
BE2 + DE2
On adding both equations, we get
AC2 + BD2 = AE2 + CE2 +
BE2 + DE2 ………… (ii)
From Eqs. (i) and (ii)
AC2 + BD2 = AD2 + BC2
Hence
proved.
Question 13.
In the given figure, l || m and line segments AB, CD and EF
are concurrent at point P. Prove that \(\frac{A E}{B F}=\frac{A C}{B D}=\frac{C
E}{F D}\)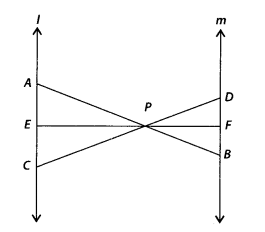
Solution:
Given l || m and line segments AB, CD and EF are
concurrent at point P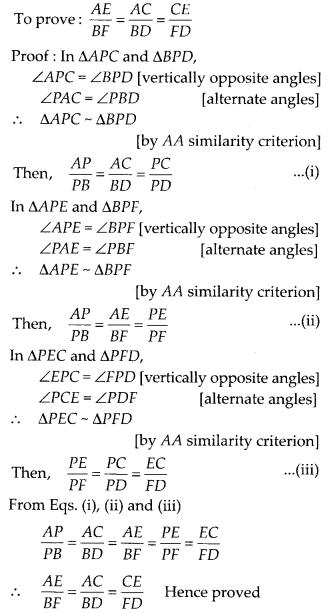
Question 14.
In the figure, PA, QB, RC and SD are all perpendiculars to a
line l,AB = 6 cm, BC = 9 cm, CD = 12 cm and SP = 36 cm. Find PQ,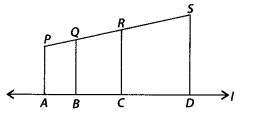
Solution:
Given, AB = 6 cm, BC = 9 cm, CD = 12 cm and SP =
36 cm
Also, PA, QB, RC and SD are all perpendiculars to line l
∴ PA || QB
|| RC || SD By Basic proportionality theorem,
PQ : QR : RS = AB : BC : CD = 6
: 9 : 12
Let PQ = 6x, QR = 9x and RS = 12x
Since, length of PS = 36 cm
∴ PQ + QR + RS = 36
⇒ 6x + 9x + 12x = 36
⇒ 27x = 36
∴ x =
\(\frac{36}{27}=\frac{4}{3}\)
Now, PQ = 6x = 6 × \(\frac{4}{3}\) = 8 cm
QR
= 9x = 9 × \(\frac{4}{3}\)= 12 cm
and RS = 12x = 12 × \(\frac{4}{3}\) = 16
cm
Question 15.
O is the point of intersection of the diagonals AC and BD of
a trapezium ABCD with AB || DC. Through 0, a line segment PQ is drawn parallel
to AB meeting AD in P and BC in Q. Prove that PO = QO.
Solution:
Given
ABCD is a trapezium. Diagonals AC and BD are intersect at O.
PQ || AB ||
DC
To prove : PO = QO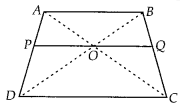
Proof : In ∆ABD and ∆POD, PO || AB [∵ PQ || AB]
∠D = ∠D
[common angle]
∠ABD = ∠POD [corresponding angles]
∴ ∆ABD ~ ∆POD[by AA
similarity criterion]
Then, \(\frac{O P}{A B}=\frac{P D}{A D}\) …………… (i)
In ∆ABC and ∆OQC, OQ || AB
∠C = ∠C [common angle]
∠B AC = ∠QOC
[corresponding angles]
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆OQC [by AA similarity criterion]
Question 16.
In the figure, line segment DF intersect the side AC of a
∆ABC at the point E such that E is the mid-point of CA and ∠AEF = ∠AFE. Prove
that \(\frac{B D}{C D}=\frac{B F}{C E}\)
[Hint:Take point G on AB such that
CG || DF]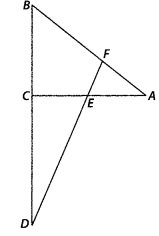
Solution:
Given ∆ABC, E is the mid-point of CA and ∠AEF =
∠AFE
To prove : \(\frac{B D}{C D}=\frac{B F}{C E}\)
Construction : Take a
point G on AB such that CG || DF
Proof : Since, E is the mid-point of
CA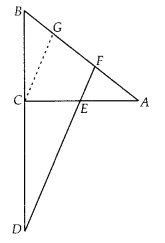
∴ CE = AE
In ∆ACG, CG || EF and E is mid-point of CA
So, CE = GF …………… (ii) [by mid-point theorem]
Now, in ∆BCG and ∆BDF, CG ||
DF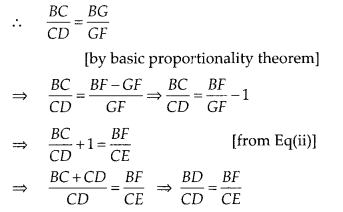
Question 17.
Prove that the area of the semicircle drawn on the hypotenuse
of a right angled triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the semicircles
drawn on the other two sides of the triangle.
Solution:
Let ABC be a right
triangle, right angled at B and AB = y, BC = x
Three semi-circles are drawn
on the sides AB,
BC and AC, respectively with diameters AB,
BC and AC,
respectively
Again, let area of circles with diameters AB,
BC and AC are
respectively A1, A2 and A3
To prove :
A3 = A1 + A2
Proof : In ∆ABC, by Pythagoras
theorem,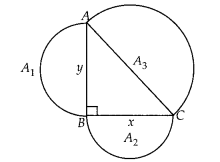
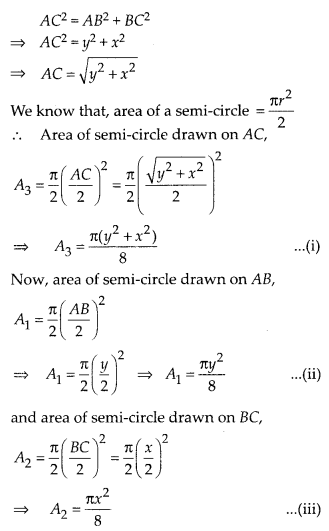
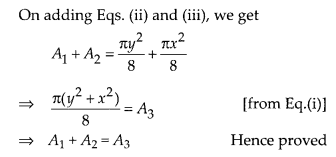
Question 18.
Prove that the area of the equilateral triangle drawn on the
hypotenuse of a right angled triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the
equilateral triangles drawn on the other two sides of the triangle.
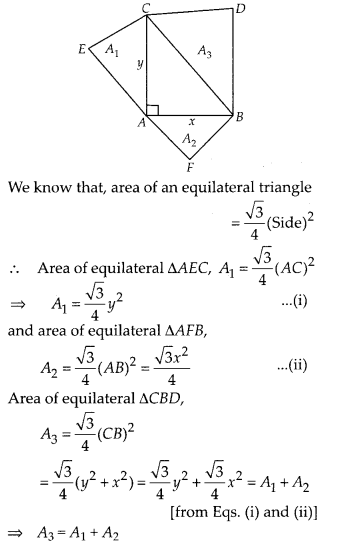
Solution:
Lett a right triangle BAC in which ∠A is right angle and AC = y, AB
= x
Three equilateral triangles ∆AEC, ∆AFB and ∆CBD are drawn on the three
sides of ∆ABC.
Again, let area of triangles made on AC, AB and BC are
A1, A2 and A3, respectively.
To prove :
A3 = A1 + A2
Proof : In ∆CAB, by Pythagoras
theorem,
BC2 = AC2 + AB2
⇒ BC2
= y2 + x2
⇒ BC = \(\sqrt{y^{2}+x^{2}}\)