Science Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination
IMPORTANT NOTES
- Stimulus is defined as any change in
the external or internal environment of an organism which brings about a
response from it.
- The working together of the various organs in a
systematic manner is called coordination.
- Chemical coordination in both plants and animals is
responsible for growth and development.
- The plant movement which is dependent on growth, is
called tropic movement or tropism.
- The type of movement which is independent of growth is
called nastic movement.
- The plants use electro-chemical means to convey the
information from cell to cell.
- In plants, there is no specialised tissue for the
conduction of information, unlike animals.
- Movement of a plant or its parts due to light is called
phototropism.
- Movement of a plant or its parts due to water is called
hydrotropism.
- Movement of a plant or its parts due to gravity is
called geotropism.
- Certain chemical substances in plants necessary for
growth are plant hormones also called phytohormones.
- Some of the hormones stimulate plant growth while others
act as growth inhibitors. For this reason, plant hormones are often referred to
as growth regulators.
- Five main groups of growth regulators are auxin,
gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene and abscisic acid.
- auxin stimulates cell elongation and growth.
- gibberellin stimulates growth and flowering.
- cytokinin stimulates cell division and chlorophyll
retention.
- abscisic acid is a growth inhibitor and brings about
fall in leaves and fruits.
- The coordinated activity of an organism depends on the
continuous input of information for the internal and external environment.
- Animals possess a number of sense organs to perceive
different sensations.
- The functional junction between nerves is called
synapse.
- In animal, the nervous system controls and coordinates
various functions in the body.
- NERVES
- Sensory Nerves (carry messages from the sense organs to
the brain)
- Motor nerves (carry messages from the brain to the
effector organs like muscles/ glands)
- Mixed Nerves (function as both sensory and motor nerves)
- Brain is the ultimate coordinator of the body. The three
parts of the brain are:
- Fore-brain mainly consists of
cerebrum, the largest and the specialised portion of the brain. It is further
divided into four parts:
- Fore-brain mainly consists of
cerebrum, the largest and the specialised portion of the brain. It is further
divided into four parts:
1.
frontal lobe controlling muscular activities.
2.
parietal lobe controlling touch, smell, etc.
3.
temporal lobe controlling hearing.
4.
occipital lobe controlling vision.
- Mid-brain controls a few motor
activities.
- The hind-brain is in turn made of
1.
cerebellum, deals with coordination of postures.
2.
pons varolii, controlling respiration and its regulation.
3.
medulla oblongata regulates reflexes like swallowing, coughing, etc.
- The brain being an extremely delicate organ is well
protected by the cranium or the brain box, three coverings called ‘meninges’ and
a fluid in between the meninges called the cerebrospinal fluid.
- The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron,
whose structure can be detailed as follows :
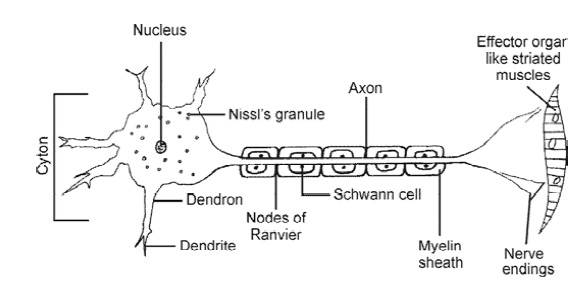
- Reflex actions are unconscious or involuntary responses
of the effector organs to a stimulus, which is monitored through the spinal
cord. The route thus taken by the impulse (i.e., from the receptor organs to the
spinal cord) and the response thereof (i.e., from the spinal cord to the
effector organs) is known as the reflex arc. Sneezing, coughing, withdrawal of
the hand upon touching a hot object are examples of reflex action.
- Hormones are chemical substances secreted in trace
amounts by endocrine glands and are the means of information transmission.
- The hormones in animals show following characteristic
features:
- They are synthesised by endocrine glands.
- They are produced at a place other than the site of
action. They travel through blood to other parts where they cause changes.
- They are secreted directly into the blood stream.
- They act on specific tissues or organs. The tissues or
organs that respond to the hormones are called as target organs. For
example, the target organs for the hormone adrenaline includes the heart.
- They are secreted in response to changes in the external
or the internal environment of the body and are also called chemical
messengers.
- They may stimulate or inhibit the activity of the target
organ, thus regulating its activity.
- They are effective in minute quantities, often in
trace amounts which are difficult to detect at times.
- Excess or deficiency of a
hormone may lead to serious consequences.
- The chemical messengers of our body are the hormones
produced by the endocrine system. Hormones are carried by the blood to their
target organs where they bring about appropriate actions.
- The master endocrine gland of the body is the pituitary
gland also known as the hypophysis. Hypophysis is in turn under the control of
hypothalamus—a part of the brain located at the base of cerebrum.
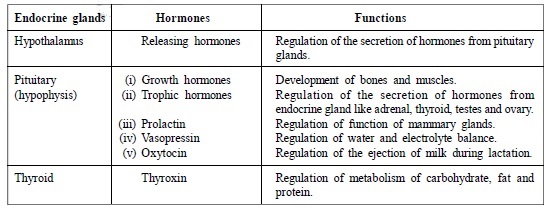
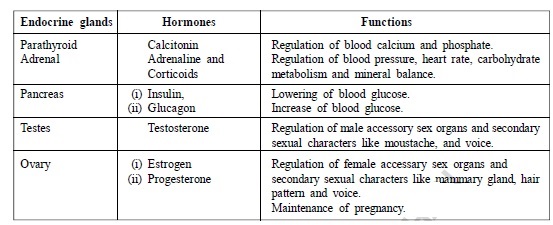
- Endocrine glands, their hormones and functions
I. VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. What is a ganglion?
2. Define nerve impulse.
3. Define synapse.
4. How does an impulse travel through a neuron, what
exactly is happening?
5. Name the coverings in brain and the fluid present
in between.
6. What is the function of medulla oblongata?
7. What is the function of cyton in a neuron?
8. Name the neuron which carry impulses from the
spinal cord to the effector.
9. Which part of the brain is the seat of
consciousness, thinking and stimulates interpretation?
10. What are the environmental triggers that can
change the direction of growth in plants?
11. Why does response occur?
12. What is the main characteristic of “touch me not”
plant?
13. How are the plant responses reflected?
14. What is tropic movement?
15. What are the two main kinds of coordination
present in living organisms?
16. What is nastic movement?
17. Name one chemical substance of plant which
promotes ripening of fruits.
18. Write the full form of ABA.
19. Which gland is known as master gland?
20. What is known as “fight or flight” hormone?
21. Deficiency of which hormone causes goitre?
22. What causes gigantism?
23. Write down two functions of testis.
24. Name two ovarian hormones.
25. Name the hormone that regulates protein metabolism
and body growth.
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. Mention one example of chemotropism.
2. Mention the function of hind brain in humans.
3. Name and explain the function of the hormone
secreted by the pituitary gland in humans.
4. State the main function of abscisic acid in plants.
5. Name the plant hormone responsible for the
promotion of cell division.
6. Which hormone is injected to a diabetic patient and
why?
7. Name the hormone secreted by an endocrine gland
during emergency? Name the gland which secretes this hormone.
8. What will happen if intake of iodine in our diet is
low?
9. What do we call the movement of shoot towards
light?
10. Name the plant hormone responsible for elongation
of cells.
11. Which part of the brain controls posture and
balance of the body?
12. Define ‘chemotropism’.
13. Which of the following actions on touch is an
example of chemical control? Movement on touch a sensitive plant. Movement in
human leg.
14. A young green plant receives sunlight from one
direction only. What will happen to stem and roots?
15. Name two tissues that provide control and
coordination in multicellular animals.
16. In our bodies what is the function of thyroxine
hormone?
17. Name the endocrine gland that secretes insulin in
our bodies.
18. Name the main hormone secreted by thyroid gland
and state its one function.
19. Name the plant hormone that retards growth of the
plant.
20. What is the function of hormone secreted by the
endocrine gland, pituitary?
21. Name the hormone the secretion of which is
responsible for dramatic change in appearance in girls when they approach 10-12
years of age.
22. Which endocrine gland secretes the growth hormone?
23. What is neuron?
24. What is phytohormone?
25. List two functions performed by ovaries in a human
female.
26. Name the structural and functional unit of human
nervous system.
27. Name the part of the hindbrain which takes part in
the regulation of respiration.
28. Write the function of the hormone “thyroxin” in
our bodies.
29. Which hormone helps in lowering the level of blood
glucose in human beings?
30. Which hormone is responsible for the development
of moustache and beard in men?
31. Which type of glands in human body secrete
hormones? State any one location for them.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. What exactly is spinal cord and how is it
protected?
2. Represent the reflex arc with the help of a flow
chart.
3. What is a cerebrospinal fluid? What is its
function?
4. What is the difference between auxin and axon?
5. What is the significance of reflex action?
6. Define ‘nerve impulse’. Which structure in a neuron
helps to conduct a nerve impulse?
(i) towards the cell body?
(ii) away from the cell body?
7. With which part of the nervous system do you
associate the following actions?
(a) sensation of smell (b)
swallowing
(c) hearing ability
(d) muscular activities
8. What do you mean by meninges? What is their
function?
9. Discuss phototropism.
10. Define stimulus.
11. What is coordination?
12. Name the four plant hormones.
13. Suggest a proof that even unicellular organisms
like amoeba respond to stimuli. Justify by giving two example that even plants
respond to stimuli.
14. Name the plant hormones responsible for the
following:
(a) elongation of cells
(b) growth of stem
(c) promotion of cell division
(d) falling of senescent leaves.
15. Name the stimulus in:
(a) Phototropism (b) Chemotropism
(c) Hydrotropism (d) Geotropism
16. Why are endocrine glands also referred to as
ductless glands?
17. Which two endocrine glands perform dual functions?
18. How do you support the statement that ‘pancreas’
is the overall controller of the blood glucose level?
19. Name the hormone associated with—
(a) maintenance of
pregnancy
(b) regulation of
male sex characters
20. Why is pituitary gland called the ‘master
endocrine gland’?
21. Why is iodised salt necessary for our body?
22. Justify that the pancreas and the gonads perform
dual functions.
23. List the functions of testosterone and estrogen.
24. Name the hormones secreted by following endocrine
glands:
(a) Thyroid
(b) Pancreas
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. Name the two main organs of our central nervous
system. Which one of them plays a major role in sending command to muscles to
act without involving thinking process? Name the phenomenon involved.
2. State the role of the brain in reflex action.
3. How does our body maintain blood sugar level?
4. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
5. Label the parts of a neuron in Figure.
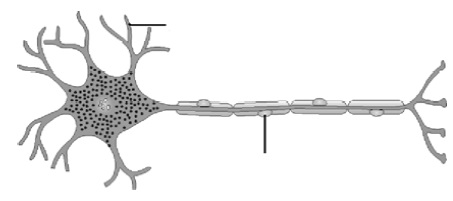
6. What are the end products formed during
fermentation in yeast. Under what condition a similar process takes place in our
body that leads to muscle cramps?
7. Differentiate between tropic and nastic movements
in plants. Give one example of each.
8. Draw the diagram of a nerve cell and label the
following on it:
(a)
Nucleus
(b) Dendrites
9. Write the name and the functions of any two parts
of the hind brain.
10. What are ‘nastic’ and ‘curvature’ movements? Give
one example of each.
11. What are plant hormones? Write two functions of
auxin.
12. Name the hormones secreted by testis and ovary.
Write one function each of these hormones.
13. (a) Distinguish between voluntary and involuntary
actions of our body.
(b) Choose involuntary actions amongst the
following: Reading, beating of heart, salivation in the mouth on viewing a tasty
food, talking.
14. Name the three major regions of human brain.Which
part of brain maintains posture equilibrium of the body?
15. Explain the cause of shoots of the plant bending
towards light.
16. What is autonomic nervous system? Name the
subsystem in which it is subdivided.
17. Name the two hormones secreted by pancreas. Write
one function of each hormone named.
18. Name the hormone responsible for regulation of:
(i) metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and
proteins.
(ii) balance of calcium and phosphate.
(iii) blood pressure.
(iv) water and electrolyte balance.
19. Name the main function of ‘pituitary gland’. Write
the effect of excessive and undersecretion of pituitary gland.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. Justify that brain is a highly protected organ.
Name the most controlled part by each division.
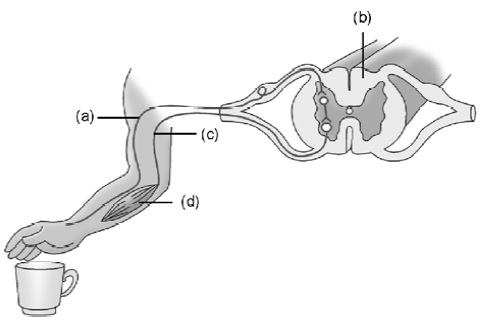
2. Label the parts (a), (b), (c) and (d) and show the
direction of flow of electrical signals in figure.
3. Which part of brain is associated with the
following?
(i) Stimulus interpretation
(ii) Movement of tongue
(iii) Walking
(iv) Muscular movement
(v) Respiratory activities
(vi) Hunger
4. What is the need for protection of brain? How is
brain protected?
5. How does control and coordination take place in
plants?
6. Write down the functions of gibberellins,
cytokinins and abscisic acid (one of each).
7. Name the functions of some phytohormones
8. What do you know about phototropism in plants?
9. Name the movement associated with the following:
(i) Roots of a plant move downward in the soil.
(ii) Plant parts move towards light.
(iii) Growth of pollen tube towards the ovule.
(iv) Movement of shoot against gravity.
(v) Bending of roots of the plants towards water.
(vi) Plant part moves away from light.
10. Give any two differences between hormones and
enzymes. Describe the endocrine role of pancreas.
11. Name the source gland and give one main action of
the following hormones.
(i) Prolactin
(ii) Calcitonin
(iii) Insulin
12. Where are vasopressin and oxytocin produced in
human body? Give their functions.
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. Name the hormone secreted by thyroid gland. Write
its function. Why it important is for us tohave iodised salt in our diet?
2. How does feed-back mechanism regulate the hormone
secretion?
3. Explain how the human body responds when adrenaline
is secreted into blood.
4. Why does the shoot of the plant bend towards light
when it is kept inside cardboard box with a small hole?
5. (a) If the cerebellum is not functioning properly,
what are the activities of our body affected?
(b) How do muscle cells move?
6. If you are happened to touch a hot object, what
would be your response? How will it happen? Show it with the help of diagram.
7. If you keep the potted plant horizontally for 2- 3
days, what type of movements would be shown by the shoot and root after 2 or 3
days. Why?
8. Name various plant hormones. Give one function of
each.
9. Label the parts (a), (b), (c) and (d) and show the
direction of flow of electrical signals in the figure given.
10. Ram has met with an accident after that he lost
the capacity to:
(i) walk in straight line
(ii) smell anything
(iii) does not feel full after eating?
Which part of brain is damaged in each case?
11. Compare the nervous and hormonal systemsfor
control and co-ordination in human beings.
12. (a) Give an example of plant hormone that promotes
growth.
(b) Name a plant hormone that promotes cell
division.
(c) Give an example of plant hormone that
inhibits growth.
13. In a neuron:
(i) Where do information received?
(ii) Through what information travels as an impulse?
(iii) Where does the impulse get converted into chemical
signal for outward transmission?
14. (a) Which hormone is secreted when growing plants
detect light?
(b) Why do plants appear to bend towards
light?
15. (a) How is movement of leaves of touch-menot
plant and movement of plant towards light different?
(b) Give a suitable example of chemotropism.
16. With the help of a diagram explain reflex arc and
reflex action.
17. List the names of hormones secreted by the
following endocrine glands and mention their functions.
(i) Thyroid gland
(ii) Pituitary gland
(iii) Adrenal gland
18. (i) Differentiate between sensory neurons and
motor neurons.
(ii) How is brain protected in our body?
(iii) Name the part of the brain
responsible for precision of voluntary actions and maintaining body posture and
balance of the body.
19. What is tropism? Design an experiment to
demonstrate hydrotropism with the help of diagram.
20. Draw diagram of human brain and label any four
parts. Write one function each of any two parts.
21. What is the function of receptors in human body?
What are the types of receptors found in humans? What problems are likely to
occur if receptor do not work properly?
22. Draw a labelled diagram of a Neuron. Explain its
functions.
23. What is endocrine gland? Name any two endocrine
glands present in a human body and write hormones secreted by them.
24. Name the hormone synthesised at the shoot tips.
How does it help the plant to response to light?
25. Tendril encircles or coils around the object in
contact with it. Elaborate.
26. Name the hormone secreted by ovary, testes and
adrenal glands. Write a function of each hormone.
27. What is tropism? Describe the types of tropism.
Mention two differences between tropism and nastic movement.
28. Draw a labelled diagram of the largest cell in the
human body. Mention its main functions.
29. A compound of iodine is compulsorily added to
common salt in small quantity.
(a) Why is it important for us to have iodised
salt in our diet.
(b) Name the disease caused by its deficiency.
(c) Write our symptoms of the disease.
30. What is reflex action? Describe the steps involved
in reflex action.
31. What is ‘hydrotropism’? Describe an experiment to
demonstrate ‘hydrotropism’?
32. What is ‘phototropism’? How does it occur in
plants? Describe an activity to demonstrate phototropism.
33. What are ‘hormones’? State one function of each of
the following hormones:
(i) Thyroxin
(ii) Insulin
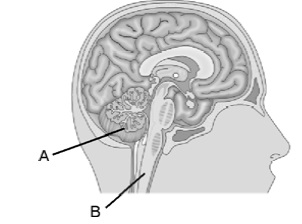
34. In the given diagram of human brain label A and B
and write their functions.
35. Define ‘hormones’. Name the hormone secreted by
thyroid. Write its function. Why is the use of iodised salt advised to us?
36. Describe the central nervous system in human
beings under the following heads:
(i) regions
included
(ii) three
functions of any one region
37. What are the male and female gonads in human
beings? State any two functions of each of them.
38. Which animal or plant hormone is associated with
the following?
(i) increased sugar level in blood
(ii) changes at puberty in boys
(iii) inhibits growth of plants
(iv) rapid development of fruit
(v) dwarfism
(vi) goitre
39. Draw a diagram showing endocrine glands in a male
body. Label the following glands on it:
(i) Pituitary
(ii) Thyroid
(iii) Adrenal
(iv) Testes
40. What is the difference between sensory and motor
neurons? Which parts of human brain are responsible for auditory reception and
sensation of smell?
41. Name the two major divisions of the autonomic
nervous system in man. In the human body, what is the effect of the following
systems. (i) Blood vessels (ii) Urinary bladder
42. Define nerve impulse. Which structure in a neuron
helps to conduct a nerve impulse:
(i) towards the cell body (ii) away from the cell
body
43. Draw a diagram of human brain and label the
following parts:
(i) Cerebrum
(ii) Meninges n
(iii) Medulla oblongata
(iv) Cerebellum
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. What are the three major components of the nervous
system in animals? How are nerves further classified? What are the three major
types of nervous system and how is one different from the other?
2. State six reflex actions of the body. Explain how
the reflex arc is the same in all of them.
3. Give the various parts of nervous system. What is
the function of nervous system?
4.
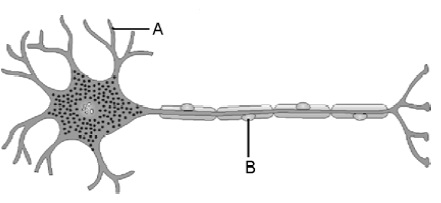
(i) Name the
parts labelled A and B in the neuron drawn above.
(ii) Which
part acquires the information in the neuron?
(iii) Through
which part does the information travel?
(iv) In what
form does this information travel?
(v) Where is
the impulse converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission?
5. Name the various plant hormones. Also give their
physiological effects on plant growth and development.
6. Can ‘adrenals’ be called the ‘stress managing
glands’ of the body? Justify your answer giving five points.
7. Suggest any five differences between endocrine and
exocrine gland.
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. (a) Name the hormone which is injected to a
diabetic patient.
(b) Why should we use iodised salt in our diet?
(c) If iodine is insufficient in one’s diet, what
might be the deficiency disease and its symptoms?
2. (a) What is reflex arc?
(b) What are the components of reflex arc?
(c) How do muscle cells move?
3. (a) Draw labelled diagram of human brain.
(b) What is the function of mid brain.
(c) Name the three different parts of hind brain and
give one function of each.
4. (a) Name two hormones secreted by pancreas. Write
one function of each hormone.
(b) How does our body respond when alternative is
secreted into the blood.
(c) Write an example to explain feedback mechanism for
regulation of hormonal secretion.
5. (a) Draw the structure of a neuron and label the
following on it. Nucleus, Dendrite, Cell body and Axon
(b) Name the part of neuron:
(i) where
information is acquired.
(ii) through which
information travels as an electrical impulse.
6. (a) What is (i) Phototropism and (ii) geotropism?
With labelled diagrams describe an activity to show that light and gravity
change the direction that plant parts grow in.
(b) Mention the role of each of the following plant hormones.
(i) Auxin (ii) Abscisic acid
7. (a) What is the reflex action? Give its two
examples. Illustrate the pathway followed by a message from the receptor in
reflex arc.
(b) Name the action of sympathetic and
parasympathetic nervous system on eye.
8. (a) What are ‘hormones’?
(b) List four characteristics of hormones.
(c) Name the hormones required for the following:
(i) Functioning of memory glands.
(ii) Regulation of calcium and phosphate in blood.
(iii) Lowering of blood glucose.
(iv) Development of moustache and beard in human male.