Science Chapter 6 - Life Processes
IMPORTANT NOTES
- Every living organism has a need of nutrition as it is
through nutrition that one obtains energy.
- The process of intake and utilisation of nutrients (i.e.
substances that either release energy or help in the manufacture of
biomolecules) is known as nutrition.
- Green plants are autotrophs as they synthesise their own
food using sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide and water.
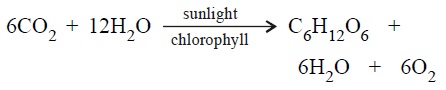
- Photosynthetic equation
- Chlorophyll is a light receiver which can trap solar
energy within its molecule.
- The site of chlorophyll activity is the special plant
cell organelles called chloroplasts.
- In humans the alimentary canal is basically a long tube
extending from the mouth to the anus. When we eat something we like, our mouth
‘waters’. This watery fluid is called saliva secreted by the salivary
glands.
- The gastric glands present in the stomach wall of human,
release hydrochloric acid, pepsin and mucus.
- Tooth decay or dental carries causes gradual softening
of enamel and dentine. Brushing the teeth after eating removes the dental
plaque.
- Factors that affect photosynthesis are
(i) Light,
(ii) Temperature,
(iii) Water, and
(iv) Carbon dioxide.
- Animal nutrition shows a very wide range. Unicellular
organisms like Amoeba obtain food by the process of phagocytosis. The
human digestive system climaxes the evolutionary development of the digestive
system with numerous glands, digestive juices and organs working together. The
various steps of nutrition are ingestion, digestion, absorption and
assimilation.
- The energy-rich molecule in which energy is first
captured is adenosine triphosphate or ATP.
- Breathing is a physical process which involves
inhalation and exhalation.
- Respiration is a biochemical process which includes
breathing and oxidation of food.
- Respiration in the presence of oxygen is known as
aerobic respiration.
- Respiration that occurs in absence of oxygen is known as
anaerobic respiration.
- During aerobic respiration, food (glucose) is completely
broken down into carbon dioxide and oxygen and energy is released in the form of
ATP.
- Aerobic respiration occurs in higher organisms including
human being.
- Anaerobic respiration occurs in certain bacteria, yeast
and also in our muscles.
- The muscles of vertebrate animals can continue working
for a minute or two without oxygen.
- Micro-organisms such as yeast and certain bacteria
obtain their energy by anaerobic respiration which is termed fermentation.
- Common type of fermentation is alcoholic fermentation
which is performed by yeast.
- Direct respiration is seen in unicellular organisms like
Amoeba, Paramecium, bacteria and Chlamydomonas.
- Diffusion is defined as the movement of a substance from
a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
- Rate of respiration in plants is much slower than in
animals.
- In higher plants, the exchange of gases occurs through
stomata and lenticels.
- Organs of respiration in animals are skin, trachea,
gills, lungs, etc.
- Thin-walled air sacs called alveoli are present in
lungs.
- The blood contains a pigment, haemoglobin, which helps
in the transport of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
- In human beings, four basic processes are involved in
respiration—breathing, gaseous transport, tissue respiration and
cellular respiration.
- In the thoracic cavity, the lungs are bound by a convex
muscular and elastic sheet called diaphragm.
- Diffusion is a major method by which transportation of
material occurs in single celled organisms like bacteria.
- Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of
higher concentration to that of lower concentration resulting in their uniform
distribution.
- The entire surface of the root is not associated with
absorption of water and nutrients.
- Only 1% to 2% of the total water absorbed by the roots,
is used up in photosynthesis and metabolic activities.
- The main process involved in the upward conduction of
water and minerals is called transpiration.
- Through transpiration pull, movement of water and
minerals take place.
- The transportation of food from the leaves to other
plant parts is termed translocation.
- In case of plants, xylem is made of tracheids and
vessels. Both are thick walled with perforations in their cell wall.
- Water and mineral salts are absorbed by root hair and
are transported in the plant by xylem vessels which are long interconnected
tubes.
- Transpirational pull works as a suction force for the
upward movement of the sap.
- Long distance transportation of food material from the
leaves to the other parts of the plant is known as ‘translocation’.
- Phloem is the living tissue that translocates prepared
food in aqueous solution. Phloem is made of living cells called ‘sieve tubes’.
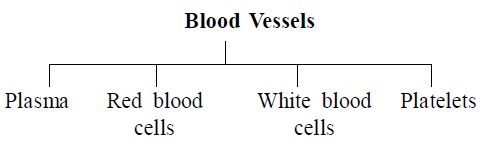
- In human beings the main transporter is the blood which
flows in blood vessels and is pumped by the heart.
- Lymph: Lymph is also known as
tissue fluid. It is another type of fluid involved in transportation. It is
colourless and contains less protein. Some amount of plasma, proteins and
blood-cells escape into intercellular spaces in the tissues in the form of
lymph. It drains into lymphatic capillaries from the intercellular spaces. It
drains excess fluid from the extra cellular space back into the blood. Lymph
carries digested as well as absorbed fat from the intestine.
- The pathway indicating the flow of
blood within the human heart. The right half of the heart always has
deoxygenated blood while the left half has only oxygenated blood.
- As the blood flows, a part of it
gets filtered out of the capillary walls. This forms the lymph.
- Lymph — carries digested fats.
- — returns proteins and other fluids for circulation.
- — lymphocytes contribute towards immunity.
- Lymph — carries digested fats.
- The waste products in animals
include carbon dioxide, nitrogenous compounds like ammonia, urea and uric acid,
bile pigments from the breakdown of haemoglobin, excess salts and vitamins.
- The most poisonous of all waste
by-products of metabolism is ammonia.
- The kidneys extract urea from the
blood and excrete it from the body as part of a liquid called urine.
- Excretion of waste products is very
simple and much less in plants as compared to animals.
- Excretory system of human, mainly
consists of a pair of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, etc.
- Excretory organs in animals are
lungs, skin, kidneys and liver.
- Dialysis is a process of separating
small molecules from larger ones using a semipermeable membrane.
- Bowman’s capsule is a cup shaped
body enclosing glomerulus part of a nephron.
- Glomerulus is a network of finely
divided blood capillaries enclosed in Bowman’s capsule.
- Structural and functional unit of
kidney is nephron.
- An artificial kidney machine works on the principle of dialysis.
- The parts of a nephron are
(a) a tuft of capillaries called ‘glomerulus’,
(b) Bowman’s capsule,
(c) extended tubular system and a collecting duct.
- Carbon dioxide produced during
respiration is carried by
(i)
haemoglobin in the blood and,
(ii)
water in which it gets dissolved.
- The kidneys perform two major
functions—
(i)
help to remove toxic wastes like urea from the blood and
thereby clean the blood,
(ii) control water balance and levels of mineral salts in the body.
- The filtration of blood for the
removal of wastes can be done by an artificial kidney, in cases of renal
failure. Such a system is called ‘Dialysis’.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. What is life process?
2. What are autotrophs?
3. What fulfills the carbon and energy requirements of
the autotrophic organism?
4. Which nutrient serves as the internal energy
reserve of the plant?
5. What are heterotrophic organisms?
6. What are the green dots present in a leaf?
7. When do desert plants take up carbon dioxide?
8. What are stomata?
9. When do guard cells swell?
10. Name some parasitic plants and animals.
11. What are the enzymes secreted by stomach?
12. What are villi?
13. What is respiration?
14. Plant respiration is slower than animal
respiration. Suggest one reason for it.
15. What are the two end products of anaerobic
respiration?
16. Why is nasal cavity warm and coated with mucous
inside?
17. What is the rate of breathing in human beings
under normal conditions?
18. Where can you see anaerobic respiration?
19. How long can the muscles of vertebrates work in
absence of oxygen?
20. What are the products of anaerobic fermentation?
21. How does diaphragm help in inspiration?
22. Why is blood called a ‘liquid connective tissue’?
23. Name the two major chambers of the human heart.
24. What is the other term for extracellular fluid?
25. Why does the face of a person become red in sunlight?
26. What is the main function of lymph nodes?
27. Name any two excretory organs in human.
28. Where is urine carried through the ureters?
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. Give one reason why multicellular organisms require
special organs for exchange of gases between their body and their environment?
2. What is ‘translocation’ in plants?
3. Where does digestion of fat take place in our
body?
4. Why are green plants called ‘producers’?
5. What is the mode of nutrition in human beings?
6. A young green plant receives sunlight from one
direction only. What will happen to its shoots and roots?
7. What will happen to a plant if its xylem is
removed?
8. How do autotrophs obtain CO2 and N2 to make their
food?
9. Which pancreatic enzyme is effective in digesting
proteins?
10. Which enzyme present in saliva breaks down starch?
11. Name the two ways in which glucose is oxidized to
provide energy in various organisms.
12. What process in plants is called transpiration?
13. Name the tissue which transports soluble products
of photosynthesis in a plant.
14. Name the tissue which transports water and mineral
in a plant.
15. State the term for transport of food from leaves
to other parts of the plant.
16. What is meant by ‘translocation’ with respect to
transport in plants?
17. Why is nutrition necessary for an organism?
18. Name the two stages in photosynthesis.
19. Name the respiratory organs of:
(i) Mosquito,
(ii) Earthworm,
(iii) Fish.
20. Name the term for transport of food from leaves to
other parts of plants.
21. Name the organelle in which photosynthesis occurs.
22. What is breathing?
23. Name the type of blood vessels which carry blood
from organs to the heart.
24. Name the mode of nutrition in amoeba.
25. Write the mode of nutrition in fungi.
26. Name the pigment present in plants which can
absorb solar energy.
27. Name the respiratory organs of animals like fish
that live in water.
28. Name two kinds of cells (elements) of xylem.
29. Name the largest artery in the human body.
30. What makes the red blood corpuscles (cells) red?
31. A farmer floods his field every day thinking that
watering in this manner will result a better yield of his wheat crop. What will
be the result of this action of the farmer?
32. Name the excretory unit of a kidney.
33. Which organelle in a cell is associated with the
production of energy by aerobic respiration?
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. What is the exact function of chlorophyll?
2. Autotrophs synthesise food for the entire living
world. Justify this statement in one sentence only inter-connecting autotrophs
and heterotrophs.
3. Write down the balanced photosynthetic equation.
4. In case of water deficiency, why is the rate of
photosynthesis lowered?
5. Mention two functions of the large intestine.
6. Give the role of guard cells in stomata.
7. What are the raw materials used in photosynthesis
by the plants other than CO2 and sunlight.
8. What is holozoic nutrition? Give an example.
9. How many pairs of salivary glands are there in
humans? Where do they open?
10. Which enzyme initiates the digestion of proteins?
Name the other enzyme produced by the same gland?
11. How is the absorptive surface of the small
intestine enhanced?
12. Nutrition is the intake of nutrients. Which two
properties should a substance have in order to be called a nutrient?
13. Are saprophytes a kind of parasites? If no, why?
14. Name any four parasites.
15. What is the role of (a) tongue and (b) teeth, in
digestion?
16. Name the first digestive organ that is associated
with the breakdown of proteins in humans. What are its releases?
17. How do roots respire?
18. What is diffusion?
19. Mention two characteristics that are possessed by
almost all the respiratory organs.
20. Do active tissues have rapid respiration? Explain
why.
21. Define transpiration.
22. Why is transpiration considered a necessity for
better ascent of sap?
23. Name the unit of phloem. How is it different from
xylem? Name a substance that is synthesised at the shoot and the root tip and
therefore, needs to be translocated.
24. How is lymph formed?
25. Mention the role of the valves in maintaining
blood flow in the heart.
26. What is the purpose of making urine in our body?
27. When does an artificial kidney be used?
28. Which is the major nitrogenous waste product in a
human being? How is it removed from the body?
29. What is dialysis?
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. How do guard cells regulate opening and closing of
stomatal pores?
2. Why and how does water enter continuously into the
root xylem?
3. Mention the components of the transport system in
highly organized plants. State the functions of these components.
4. What is the function of the trachea? Why do its
walls not collapse even when there is less air in it?
5. Name any two digestive enzymes secreted in the
human digestive system and write their functions.
6. Stomata of desert plants remain closed during day
time. How do they take up carbon dioxide and perform photosynthesis?
7. (a) What will happen to the guard cells and
stomatal pore when water flows to guard cells?
(b) How do plants transmit informations from cell to
cell?
8. Which is the internal energy reserve in plants? Do
the animals have the same energy reserve?
9. Two green plants are kept separately in oxygen free
containers, one in the dark and the other in continuous light. Which one will
live longer? Give reasons.
10. “All plants give out oxygen during day and carbon
dioxide during night”. Do you agree with this statement? Give reason.
11. Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba.
12. How are the alveoli designed to maximize the
exchange of gases?
13. How are the fats digested in our bodies where does
this process take place?
14. What is the role of saliva in the digestion of
food?
15. What are the common features of the respiratory
organs in aquatic and terrestrial animals?
16. Explain the significance of peristaltic movement
that occurs all along the gut during digestion.
17. Explain parasitic mode of nutrition with two
examples.
18. What do the following transport?
(i) xylem (ii) pulmonary artery (iii) pulmonary vein (iv) phloem.
19. How are water and minerals absorbed by the plant?
20. How is the process of transpiration useful to
plant?
21. Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with
vaseline. Will this plant remain healthy for long? Give reasons for your answer.
22. Major amount of water is selectively reabsorbed by
the tubular part of nephron. On what factor does the amount of water reabsorbed
depend on?
23. Which is the largest digestive gland present in
human body? What are the names and function of its secretion?
24. Write one function each of the following
components of the transport system in a human being.
(a) Blood vessels (b) Blood platelets
(c) Lymph (d) Heart
25. (a) Name two different ways in which glucose
oxidised to provide energy in various organisms.
(b) Write any two differences between the
two ways of oxidation of glucose in organisms.
26. State two vital functions of the human kidney.
Name the procedure used in the working of artificial kidney.
27. Point out differences between an artery and a
vein.
28. Describe the mechanism of blood clotting.
29. Write any two points of differences between
respiration in plants and respiration in animals.
30. Amylase is secreted by two different glands. Name
them. What is the action of amylase on food?
31. What is the role of HCl in protein digestion?
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. How do the plants obtain carbon dioxide?
2. Briefly explain the role of water in controlling the photosynthetic rate.
3. What is the exact role of light in photosynthesis?
4. Where does digestion begin in humans? Which enzyme
works there? What is the digestive juice? What is the end product? What is the
substrate? Where is the digestive juice produced?
5. What are the events occur during the process of
photosynthesis?
6. How do the following organisms get their food?
(a)
Amoeba (b)
Paramecium (c) Human being
7. What are villi? Where are they present? What is
their function?
8. Explain the process by which inhalation occurs
during breathing in human beings.
9. Enumerate the three basic properties associated
with a surface functioning as a respiratory surface.
10. Write the chemical equations for aerobic
respiration and anaerobic respiration.
11. Where exactly does the oxidation of glucose take
place? In which form is energy released? Name one organ in humans where
anaerobic respiration takes place. Which kind of respiration is shown by red
muscles?
12. Give three reasons to justify that energy is
required during sleep.
13. What are the internal factors of photosynthesis?
How do they affect photosynthesis?
14. What are the end products of photosynthesis? What
are the uses of these end products?
15. Describe the structure of the human heart very
briefly. 16. Write the functions of blood vessels.
17. What is the need of special tissues or organs for
transportation of substances in plants and animals?
18. Describe transport of the following materials in
plants: (i) water, (ii) minerals, (iii) food
19. What is blood? Describe its composition.
20. (i) Name the blood vessel that brings oxygenated
blood to the human heart.
(ii) Which chamber of human heart receives
oxygenated blood?
(iii) Explain how oxygenated blood from
this chamber is sent to all parts of the body.
21. Briefly describe the mechanism of urine formation.
22. How does excretion take place in a plant?
23. List various functions of food.
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. Explain the process of breakdown of glucose in a
cell (i) in the presence of oxygen (ii) in the absence of oxygen.
2. What are the final products produced after
digestion of carbohydrate, protein and fats.
3. State the role of the following in the human
respiratory system
(i) Nasal cavity, (ii) Diaphragm,
(iii) Alveoli
4. How does blood circulate between lungs and heart in
human beings? Give two functions of lymph.
5. What is lymph? Write its important functions.
6. What are stomata? Draw a labelled diagram of
stomata. Write two functions of stomata.
7. (a) Name the process by which autotrophs prepare
their own food.
(b) List the three events which occur during this
process.
(c) State two sources from which plants obtain nitrogen
for the synthesis of proteins and other compounds.
8. (a) State two differences between autotrophic
nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition.
(b) Give one example each of these nutritions.
9. Why is blood clotting useful? In a flow chart
illustrate the four major events involved in blood clotting.
10. Give reason for the following:
(i) Glottis is covered by epiglottis,
(ii) Lung alveoli are covered with blood
capillaries,
(iii) The wall of trachea is supported by
cartilage rings.
11. Write the functions of the following in the
digestive process:
(i) Bile (ii) Bicarbonate
secreted by the duodenal wall (iii) Pancreatic amylase.
12. Draw a diagram of human alimentary canal showing
duodenum, small intestine, liver and pancreas.
13. Explain the role of the following in the process
of digestion in the human body
(i) Saliva (ii) Gastric Juices (iii)
Trypsin
14. How do each of the following factors affect the
productivity in the process of photosynthesis?
(a) Temperature (b) Water (c) Carbon
dioxide
15. How do plants obtain their food? What are the two
phases of photosynthesis? Draw a labeled diagram of Calvin-Benson cycle.
16. What happens to glucose which enters nephron along
with filtrate during excretion in human beings? State two vital functions of
kidney.
17. (a) Describe the mechanism of breathing in human
beings.
(b) (i) Under normal conditions, what is
the rate of breathing per minute?
(ii)
Why does the rate of breathing increase by 20-25 times during vigorous exercise?
18. What is the function of epiglottis in man? Draw a
labelled diagram showing the human respiratory system?
19. Explain the process by which inhalation occurs
during breathing in human beings
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. Give a detailed summary of the types of nutrition
seen in the living world, describing each type.
2. What are the two basic raw materials for
photosynthesis other than light? How are they taken up by the plants?
3. Give a brief of the process of photosynthesis.
4. Enumerate all the activities related to digestion
in the mouth and oesophagus in human.
5. Enumerate all the events of digestion in the human
stomach and small intestine.
6. (a) Draw a diagram of a ‘palisade cell’.
(b) Label—vacuole, chloroplast, cell wall and
cytoplasm on the diagram drawn. (c) Name the two stages of photosynthesis.
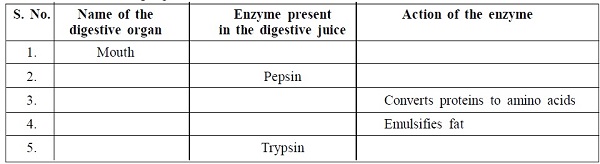
7. Complete the undermentioned table:
8.
What is the significance of photosynthesis?
9. Make a comparison between photosynthesis and
respiration.
10. Explain the process of gaseous exchange in human
beings.
11. Write in details about the processes involved in
respiration in human being.
12. (a) Draw the respiratory system of human beings.
(b) Label the following on the
diagram drawn: Larynx, Trachea, Primary Bronchus, Lungs.
(c) What happens to the carbon
dioxide which collects in human tissues?
13. Write a note on lymphatic system in human beings
stating two major functions of lymph.
14. State differences between artery, vein and
capillary.
15. Give stepwise details of the working of human
kidneys leading to the formation of urine.
16. How does excretion take place in a plant?
17. How does an artificial kidney or dialysis machine
work?
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. List three events that occur during the process of
photosynthesis. State in brief the role of stomata in this process.
Describe an experiment to show that sunlight is
essential for photosynthesis.
2. (a) Why is nutrition a necessity for an organism?
State three reasons.
(b) What is likely to happen if green plants disappear
from earth?
(c) “All plants give out oxygen during day and carbon
dioxide during night”. Justify this statement.
3. (a) Draw a neat diagram of alimentary canal and
label the following parts.
(i) The largest gland.
(ii) the gland that secretes digestive enzymes as
well as hormones.
(iii) The part where digested food is absorbed.
(b) What are Villi? Mention their functions.
4. (a) Draw the cross section of the leaf and label
the following parts.
(i) Upper epidermis (ii) chloroplast
(b) Define photosynthesis.
(c) List three events which occur during this process.
(d) Write down the chemical equation involved in
photosynthesis. (e) How is unused energy stored in plants?
5. (a) Draw the human excretory system and label:
(i) kidney (ii) aorta
(iii) ureter (iv) urinary bladder
(b) What is the purpose of sending blood to the kidneys
for filtration?
6. (a) Draw a diagram of human alimentary canal and
label on it:
(i) gall bladder (ii) liver (iii) pancreas (iv)
small intestine
(b) What is emulsification of fats? Why is it
necessary?
7. (a) Draw a sectional view of the human heart and
label :
(i) Pulmonary artery (ii) aorta (iii)
septum (iv) ventricles
(b) Arteries have thick elastic walls while veins have
valves, explain.
8. (a) Draw the human excretory system and label:
(i) left kidney (ii) urethra
(iii) urinary bladder (iv) vena cava
(b) What is the main toxic waste that a kidney filters
from the blood?
(c) Name any two substances which are selectively
reabsorbed from the tubules of a nephron.
9. (a) Draw a neat labelled diagram of human
alimentary canal. Label the following.
(i) Buccal cavity (ii) Liver
(iii) Pancreas (iv) Stomach
(v) Gall bladder (vi) Large intestine
(b) On which type of food does salivary amylase act at buccal cavity and
write the name of the initial product due to the action of amylase.
10. (a) Draw a neat labelled diagram of human
respiratory system and label the following parts.
(i) Bronchiolus
(ii) Rings of cartilage
(iii) Pharynx (iv) Trachea
(v) Larynx (vi) Diaphragm
(b) What are the factors needed for maintaining the
direction of diffusion in plants?
11. (a) Draw the diagram of human respiratory system
and label the following parts.
(i) Pharynx (ii) Trachea
(iii) Diaphragm (iv) Rings of cartilage
(b) How are lungs designed in human beings to maximise
the area for exchange of gases?
12. (a) Draw the sectional view of the human heart and
label the following parts :
(i) Left atrium (ii)
Pulmonary arteries
(iii) Right ventricle (iv) Aorta
(b) Why are the valves needed in the heart?
(c) Leakage of blood from vessels reduces the
efficiency of pumping system. How is the leakage prevented?
13. What is the advantage of having four chambered
heart? Support your answer with a diagram of the section of a human heart.
14. Draw the diagram of alimentary canal of man and
label the following parts: Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Intestine. Where do
carbohydrates, proteins and fats get digested in human beings?
15. Draw a neat diagram of internal structure of human
heart and label the parts which do the following functions :
(a) Chamber where oxygenated blood from lungs is
collected.
(b) Largest blood vessel in our body.
(c) Muscular wall separating right and left
chambers.
(d) Blood vessel that carry blood from heart to
the lungs.
16. How do the guard cells regulate opening and
closing of stomatal pores? Explain with the help of diagram. Also, indicate what
happens to the rate of photosynthesis if stomata get blocked due to dust.
17. (a) Draw a diagram showing human respiratory
system and label on it the following. Larynx, Trachea, Lungs, Bronchi
(b) Why do walls of the trachea not collapse when there
is less air in it?
18. Describe an experiment to prove that CO2 is
necessary for photosynthesis.
19. (a) Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba
with suitable diagram.
(b) During one cycle how many times blood
goes to heart of fish and why?
20. (a) What are the events occurring during
photosynthesis?
(b) Name the respiratory pigment present in
our body? Where is it present?
(c) Why are valves present in heart and
veins?
21. (a) What are the events occurring during
photosynthesis?
(b) What is the term used for transport of
food from leaves to other parts of plants?
(c) What is the main product formed during
anaerobic respiration in our muscles?
22. (a) Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba
with suitable diagram.
(b) What are capillaries? What is their
function?
23. (a) Draw the diagram of human heart and label the
following:
(i) Part which receives deoxygenated blood from
vena cava.
(ii) Part which send deoxygenated blood to
lung through pulmonary artery.
(iii) Part which receives oxygenated blood
from lungs.
(iv) Part which sends oxygenated blood to
all parts of the body through aorta.
(b) What does the blood consist?
(c) Write two functions of blood.
24. (a) Draw diagram to show the nutrition in
Amoeba and label the part used for this purpose. Mention any other purpose
done by this part other than nutrition.
(b) Name the glands associated with digestion of starch
in human digestive tract and mention their role.
(c) How is required pH maintained in the stomach and
small intestine?
25. (a) Draw a neat diagram of excretory system of
human beings and label the following.
(ii) Kidney
(ii) Ureter
(iii) Urinary
Bladder (iv) Urethra
(b) How is urine produced?
(c) Name two excretory products other than O2 and CO2
in plants.
26. (a) Draw diagram of human alimentary canal and
label the following.
(i) Part in which starch
digestion starts.
(ii) Part in which bile is
stored.
(iii) Part in which nutrients are absorbed.
(iv) Part in which water is absorbed.
(b) Mention the role of hydrochloric acid in the
stomach.
(c) What function is served by the
following.
(i) Gastric sphincter (ii) Anal sphincter
27. (a) Draw diagram of respiratory system and label
the following.
(i) Part through
which air is taken in.
(ii) Part which protects
the lungs.
(iii) Part which
carry the air into the lungs.
(b) What are alveoli? Mention
their role in respiration.
(c) Differentiate between
aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
28. (a) Draw a schematic representation of movement of
water in plants during transpiration, and explain.
(b) Explain transport of food and other substances in plants.
(c) Diffusion will not be sufficient to provide raw materials
in leaves and energy in roots in plants. Therefore a proper system of
transpiration is essential. Explain.
29. (a) Draw a labeled diagram of stomata. Write two
functions of stomata.
(b) What are the raw materials used during
photosynthesis. Write chemical equation for photosynthesis.
30. Draw a labelled diagram of human heart. Draw a
table to show the functions of any two chambers of human heart.
31. Draw neat diagram of digestive system. Label it’s
all parts. How the main components of the food are digested in the small
intestine? Explain.
32. Draw a neat diagram of excretory system in humans
and label the following.
(i) Kidney
(ii) Left renal artery
(iii) Left renal vein
(iv) Vena cava
(v) Urinary bladder
(vi) Ureter
33. (a) What is meant by breathing? What happens to
the rate of breathing during vigorous exercise and why?
(b) Define translocation with respect to
transport in plants. Why is it essential for plants? Where in plants are the
following synthesized:
(i) Sugar
(ii) Hormone
34. (a) Draw a sectional view of the human heart and
label on it aorta, pulmonary arteries, vena cava, left ventricle.
(b) Why is double circulation of
blood necessary in human beings?
35. (a) Draw a schematic representation of transport
and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during transportation of blood in
human beings and label on it.
(b) What is the advantage of separate channels in
mammals and birds for oxygenated and deoxygenated blood?
36. (a) Draw a diagram of excretory system in human
beings and label on it: aorta, vena cava, urinary bladder, urethra
(b) List two vital functions of the kidney.
37. (a) Draw the structure of a nephron and label the
following on it. Glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, Renal artery, Collecting duct.
(b) What happens to glucose that enters the nephron along with filtrate?
38. (a) Draw a diagram depicting human alimentary
canal and label on it, gall bladder, liver and pancreas.
(b) State the roles of liver and pancreas.
(c) Name the organ which performs the following
functions in humans.
(i) Absorption of digested food. (ii) Absorption of water.
39. How is ‘respiration’ different from ‘breathing’?
Explain the process of ‘aerobic’ respiration and ‘anaerobic’ respiration.
40. (a) Draw a diagram of human alimentary canal and
label on it: oesophagus, gall bladder, liver and pancreas.
(b) Explain the statement, ‘Bile does not
contain any enzyme but it is essential for digestion’
41. (a) Draw a sectional view of the humans heart and
label on it aorta, right ventricle and pulmonary veins.
(b) State the functions of the following
components of transport system.
(i) Blood
(ii) Lymph
42. (a) Draw a diagram of human alimentary canal.
(b) Label Oesophagus, Liver, Pancreas and Gall
bladder on the diagram drawn.
(c) What is the function of the enzyme
‘pepsin’ in the digestion process?
43. (a) Draw a diagram of the human urinary system and
label in it:
(i) kidney (ii) ureter
(iii) urinary bladder (iv) urethra
(b) Name the two major components of normal
human urine.
44. Define the terms ‘nutrition’ and ‘nutrients’. List
two differences between ‘Holozoic nutrition’ and ‘Saprophytic nutrition’. Give
two examples of each of these two types of nutrition.
45. Explain the process of ‘photosynthesis’ in plants.
List four facts which influence this process and
describe how each of them affects the rate
of photosynthesis process.
46. (i) Name the blood vessel that brings deoxygenated
blood to the human heart.
(ii) Which chamber of human heart receives
deoxygenated blood?
(iii) Describe how deoxygenated blood from this
chamber is sent to lungs for oxygenation.
47. (i) State two structural differences between an
artery and a vein.
(ii) Name a non-nucleated cell present in human blood
and state one function of this cell. (iii) Draw a labelled diagram of human
heart.
48. (i) Why is circulation of blood in man known as
double circulation?
(ii) Which blood cell in human blood carries
haemoglobin? What is its average life span? (iii) Draw a labelled diagram
of human heart.
49. Name the main organs of human digestive system in
the order in which they are involved in digestion of food. In what steps and
how does digestion of carbohydrates and proteins take place in our body?