Science Chapter 1 -Chemical Reactions and Equations
IMPORTANT NOTES
- The changes which take place in substances can be
broadly classified as physical changes and chemical changes.
- During a physical change,
only the state of the substance changes, but not its chemical composition.
Furthermore, a physical change is a temporary change, which can be
reversed by changing the physical experimental conditions. At the same time no
net energy is absorbed or given out.
- During a chemical change, the state as well as
the chemical composition of a substance changes. Furthermore, a chemical change
is a permanent change, which cannot be reversed by changing the physical
experimental conditions. At the same time, either energy is absorbed or given
out.
- Whenever, a chemical change occurs, the process which
takes place, is called a chemical reaction.
- During a chemical reaction one or more of the following
changes occur:
- Energy (generally in the form of heat or light) is
either absorbed or given out.
- New substances are formed.
- The state of the reacting substances changes.
- There may be a change in colour of the reacting
substances
- The temperature of the reacting substances changes.
- A gas may be evolved during the chemical reaction.
- The substances formed during a chemical reaction do not
change back to the original substance, when the physical experimental conditions
are altered.
- A chemical equation which represents a chemical reaction
briefly in words is called a word equation.
- The substance/substances which take part in a chemical
reaction are called reactants.
- The new substance/substances formed as a result of
chemical reactions, are called products.
- A plus sign is put in between reactants or
products, if their number is two or more.
-
An arrow ( ⟶ ) is put between reactants and products.
This sign is read as “to yield” or “to form”.
- The direction of the arrow
points in the direction in which the reaction proceeds.
- A chemical equation is a statement
that describes a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae.
- A chemical equation expressed in
symbols and formulae, such that the number of atoms of different elements
towards the side of the reactants is not equal to number of atoms of the same
elements towards the side of the products, is called a skeletal equation or
an unbalanced equation.
- An unbalanced equation is
unacceptable or is no equation, because, it goes against the law of
conservation of mass.
- A chemical equation in which the
numbers of atoms of each element are same on the side of reactants and products
is called a balanced chemical equation.
- A balanced chemical equation tells us:
- About the substances taking part in a chemical reaction
and the products formed.
- About the symbols and formulae of the reactants and
products.
- About the number of atoms or molecules of the reactants
and products involved in the chemical reaction.
- About the weights of the reactants and products involved
in the chemical reaction.
- A balanced chemical equation does not tell us:
- The physical state of the reactants and products.
- Whether the reaction will come to completion or not.
- About the speed of the chemical reaction.
- About the physical conditions which bring about the
chemical reaction.
- About changes, such as precipitation, change in colour,
evolution of heat, light, etc., during the chemical reaction.
- When one or more substances
(elements or compounds) undergo a chemical change, with the absorption or
release of energy (generally, heat energy) so as to form one or more products,
then the change which takes place, is called a chemical reaction.
- Chemical composition reaction: When
two elements or compounds react chemically to form a single new compound, the
chemical reaction which takes place is called a chemical composition reaction or
a chemical combination reaction.
A + B ⟶ AB
- Chemical decomposition reaction :
When a chemical compound decomposes on heating or absorbing some other kind of
energy, so as to form two or more new substances (elements or compounds), then
the chemical reaction which takes place is called a chemical decomposition
reaction or a chemical decombination reaction.
AB ⟶ A + B
Chemical decomposition reaction can be further classified into three types.
- Thermal decomposition reaction: When
a chemical compound decomposes on heating so as to form one or more
substances (elements or compounds), then the chemical reaction is
called a thermal decomposition reaction.
- Photo-decomposition reaction: When a
chemical compound decomposes on absorbing light energy, so as to form two or
more different substances, then the reaction which takes place is called a
photo- decomposition reaction.
- Electrochemical reaction: When a
chemical compound in an aqueous or fused state decomposes into two different
substances on the passage of electric current then the reaction is called an
electrochemical reaction.
- Chemical displacement reaction:
When a more active element displaces a less active element from its aqueous
ionic solution, the reaction which takes place is called a chemical displacement
reaction.
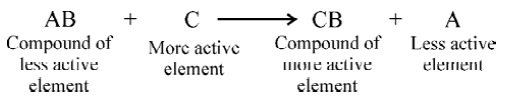
- Metals arranged in tabular form in
the order of their decreasing chemical activity are called metal activity
series.
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Sn > Pb > [H] > Cu > Hg > Ag > Au.
The above list constitutes the metal activity series in which potassium is
the most active metal and gold is the least active metal.
- Chemical double displacement reaction :
A chemical reaction in which two ionic compounds in their aqueous
solutions, react by exchanging their ions/radicals, to form two new compounds is
called a chemical double displacement reaction.
A+B– + C+D– A+D–
+ C+B–.
Chemical double displacement reaction can be further classified into two
kinds.
- Precipitation reaction: When aqueous
solutions of two ionic compounds react by exchanging their ions/radicals, to
form two or more compounds, such that one of the products formed is an insoluble
salt, and hence, forms a precipitate, the double displacement reaction is said
to be a precipitation reaction.
- Neutralization reaction: When an
aqueous solution of an acid reacts with a base (alkali) by exchanging their
ions/ radicals to form salt and water as the only products, the reaction which
takes place is called a neutralisation reaction.
- Exothermic reactions: A chemical
reaction which proceeds with the release (evolution) of heat energy is called an
exothermic reaction.
- Endothermic reaction: A chemical
reaction which proceeds with the absorption of heat energy is called an
endothermic reaction.
- Oxidation reaction: When a
substance gains oxygen or loses hydrogen, the reaction taking place is called an
oxidation reaction.
- Reduction reaction: When a substance
gains hydrogen or loses oxygen, the reaction taking place is called as reduction
reaction.
- Corrosion of metals: Formation of
layers of undesired compounds, such as metallic oxides or hydroxides on the
surface of metals is called a corrosion of metals.
- Rusting: Slow conversion of iron
into hydrated ferric oxide, in the presence of moisture and air is called
rusting.
- Rust: The flaky, non-sticky brown
powder formed on the surface of iron, when iron is exposed to moist air, is
called rust.
- Conditions for rusting: Iron should
be exposed to :
(i) Water, (ii) air, at the same time.
- Rancidity: The oxidation of food
materials, so that they become stale and start smelling is called rancidity.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. State your observations when a clean magnesium
strip is held in a Bunsen flame for some time.
2. Name the products formed when zinc granules are
treated with dilute sulphuric acid.
3. What do you observe when a matchstick flame is
brought near a tube containing hydrogen gas?
4. Write a balanced equation for chemical combination
reaction in which a metal reacts with non-metal.
5. Write a balanced chemical equation for a
photodecomposition reaction.
6. Write a balanced chemical equation for chemical
combination reaction in which two compounds react.
7. When copper metal corrodes, a green deposit is
formed on its surface. What is the chemical name and chemical formula of this
green deposit?
8. What kind of chemical reaction takes place when
electric current is passed through fused lead bromide? Support your answer by a
chemical equation.
9. Write a balanced chemical equation for the chemical
decomposition of copper carbonate.
10. Write a balanced equation for chemical composition
reaction in which two non-metals react.
11. Why is aluminum called a self-protecting metal?
12. What kind of reaction takes place between dilute
sulphuric acid and potassium hydroxide? Write fully balanced equation.
13. Write a chemical equation and state the kind of
chemical reaction which takes place when ethane gas (C2H6)
reacts with oxygen.
14.
CuO(s) + H2(g) ⟶
heat Cu(s) + H2O In the
above reaction which reactant is oxidized and which reactant is reduced?
15. What kind of reaction takes place when sodium
chloride solution is mixed with silver nitrate solution?
16. Why does copper reacts with silver nitrate
solution?
17. Write a balanced equation for chemical combination
reaction in which a compound reacts with an element.
18. What kind of reaction takes place when aluminium
metal is placed in zinc sulphate solution? Support your answer by a chemical
equation.
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. What change in colour is observed when white silver
chloride is left exposed to sunlight? What type of chemical reaction is this?
2. Distinguish between an exothermic and an
endothermic reaction. Amongst the following reactions, identify the exothermic
reaction and the endothermic reaction.
(i) Heating coal in air to form carbon
dioxide.
(ii) Heating limestone in a lime kiln to
form quicklime.
3. Give an example of exothermic reaction.
4. What is meant by skeletal equation?
5. Why are bags of chips flushed with nitrogen gas?
6. What is thermite reaction?
7. What is the brown coloured gas evolved when lead
nitrate crystals are heated in a dry test tube?
8. A compound is formed due to recrystallisation of
sodium carbonate. Identify the compound and write its chemical formula.
9. Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
10.
N2 + 3H2 ⟶2NH3, name the
type of reaction.
11. Give an example of double displacement reaction
(only reaction with complete balanced equation).
12. Why are decomposition reaction called the opposite
of combination reaction? Write equations for these reactions.
13. Write a balanced chemical equation to represent
the following reaction. Carbon monoxide reacts with hydrogen gas at 340 atm. to
form methyl alcohol.
14.
Complete and balance the reaction: Fe2O3+
Al ⟶
15. Which one is a chemical change–fermentation of
fruit juice or diluting fruit juice?
16. Which one is chemical change–Electrolysis of water
or sodium chloride exposed in sunlight?
17. Which one is a chemical change–Rusting of iron or
melting of iron?
18. Which one is a chemical change–Melting of iron or
corrosion of iron?
19. Balance the chemical equations:
Pb(NO3)(s) heat⟶ PbO(s)
+ NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
20. Balance the chemical equations:
MnO2
+ HCl(aq) ⟶
MnCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + Cl2(g)
21. Define Rancidity.
22. Name a reducing agent that may be used to obtain
manganese from manganese dioxide.
23. On what basis is a chemical equation balanced?
24.
Balance the given chemical equations: Al(s) +
CuCl2(aq)⟶
AlCl3(aq) + Cu(s)
25.
Balance the given chemical equation: FeSO4(s)
heat ⟶Fe2O3(s) + SO2(g)
+ SO3(g)
26. What happens chemically when quicklime is added to
water?
27. Identify the type of reaction in the following
example:
Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq)⟶
BaSO4(s) +2NaCl(aq)
28. Identify the type of reaction in the following
example
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq)⟶
FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
29. Identify the type of reaction in the following
example:
2H2(g) + O2(g)⟶
2H2O(l)
30. Classify the following reactions into slow and
fast reactions.
(i) Reaction
between an acid and a base
(ii) Rusting of
iron
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. (i) State two uses of chemical decomposition
reaction in industry.
(ii) What kind of chemical reaction takes place during
the digestion of food?
2. Correct the formulae and balance the following
equation
K(s) + H2(l)⟶
KOH(aq) + H2(g)
3. Write fully balanced chemical equation and state
the physical condition and physical state of the reactants in the following
reaction. Aluminum metal dissolves in aqueous copper sulphate solution with the
formation of aluminium sulphate and copper.
(i) What do you understand by the following
terms used in a chemical equation?
(a) Reactants
(b)
products?
(ii) What does symbol (
) represent in a chemical equation?
4. Grapes hanging on the plant do not ferment but
after being plucked from the plant can be fermented. Under what conditions do
these grapes ferment? Is it a chemical or a physical change?
5. A substance X, which is an oxide of a group 2
element, is used intensively in the cement industry. This element is present in
bones also. On treatment with water it forms a solution which turns red litmus
blue. Identify X and also write the chemical reactions involved.
6. Which among the following are physical and chemical
changes? [HOTS]
(a) Evaporation of petrol.
(b) Burning of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)
(c) Heating of an iron rod to red hot.
(d) Curdling of milk.
(e) Sublimation of solid ammonium chloride.
7. Zinc and aluminium are very high in metal activity
series, yet they resist corrosion to a great extent. Explain.
8. Why are halides (chloride, bromide, and iodide) of
silver kept in dark brown or black bottles?
9. Why do fire flies glow at night?
10. Give one example in case of following displacement
reactions:
(i) When a more active metal displaces a less
active metal from its aqueous salt solution.
(ii) When an active metal displaces hydrogen from
dilute acid.
11.
(i) Fe(s) + ZnSO4(aq)⟶
FeSO4(aq) + Zn(s)
(ii) Mg(s) + ZnSO4(aq)⟶
MgSO4(aq) + Zn(s).
Which amongst the above reaction will not
proceed and why?
12. Brightly polished iron nails are placed in copper
nitrate solution. Describe all that you will observe after one hour.
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. When the powder of a common metal is heated in an
open china dish, its colour turns black. However, when hydrogen is passed over
the hot black substance so formed, it regains its original colour. Based on the
above information answer the following questions:
(i) What type of chemical reaction takes place in each
of the two given steps?
(ii) Name the metal initially taken in the powder form.
Write balanced chemical equations for both reactions.
2. "Oxidation and reduction processes occur
simultaneously." Justify this statement with the help of an example.
3. "Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to
give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate"
(i) Translate the above statement
into a chemical equation.
(ii) State two types in which
this reaction can be classified.
4. "A solution of potassium chloride when mixed with
silver nitrate solution, an insoluble white substance is formed".
(i) Translate the above statement into a chemical
equation.
(ii) State two types in which this reaction can be
classified.
5. Write the chemical name and formula of common salt.
State how sodium hydroxide is prepared using this salt.
6. Why do we store silver chloride in dark coloured
bottle? Explain in brief.
7. What is meant by thermal decomposition reaction?
Explain with an example.
8. An aluminium can is used to store ferrous sulphate
solution. It is observed that in few days holes appeared in the can. Explain the
observation and write chemical equation to support your answer.
9. (i) Define photochemical reaction.
(ii) Write the balanced equation for the following
reaction and identify the type of reaction.
Potassium bromide + Barium Iodide
Potassium iodide + Barium bromide
10. Write balanced equations for the reaction of:
(i) Iron with steam
(ii) Calcium with water.
11. What would you observe when zinc is added to a
solution of iron (II) sulphate? Name the type of reaction and write th chemical
equation.
12. Write the balanced chemical equation for the
following reaction and write the name of the reaction:
Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate
Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride.
13. A metal A, which is used in thermite process, when
heated with oxygen gives an oxide B, which is amphoteric in nature. Identify A
and B. Write down the reactions of oxide B with HCl and NaOH.
14. Write one equation each for decomposition
reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
15. A metal is treated with dil. H2SO4, the gas
evolved is collected by the method shown in the figure. Answer the following:
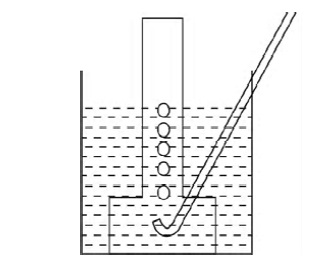
(i)
Name the gas.
(ii)
Name the method of collection of the gas.
(iii)
Is the gas soluble or insoluble in water?
(iv)
Is the gas lighter or heavier than air?
16. Crystals of a substance changed their colour on
heating in a closed vessel but regained it after sometime, when they were
allowed to cool down.
(a) Name one
such substance.
(b) Explain
the phenomenon involved.
17. A white solid when dropped in water produces a
hissing sound. What the solid may be? Give the chemical reaction for above. Name
the product formed.
18. Write observation with reaction for the following:
granulated zinc reacts with dil. sulphuric acid.
19. What happens when an iron nail is put inside
copper sulphate solution? Write reaction with observation.
20. What do you see when pentahydrated copper sulphate
crystals are heated? Give reaction too.
21. Give an example each for thermal decomposition and
photochemical decomposition reactions. Write relevant balanced chemical
equations also.
22. Write the balanced chemical equation for the
chemical reaction between manganese dioxide and aluminium powder. What happens
if manganese powder is heated with aluminium oxide?
23. With the help of suitable example, explain
oxidation and reduction in terms of gain or loss of oxygen.
24. Define double displacement reaction with the help
of an example.
25. Respiration is considered as exothermic reaction.
Explain why?
26. What are exothermic and endothermic reactions?
Explain with the help of one example each.
27. A shiny brown coloured element X on heating in air
becomes black in colour. Name the element X and the black coloured compound
formed. Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
28. Arrange iron, copper and zinc in increasing order
of reactivity on the basis of following reactions. Give reasons.
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq)⟶
FeSO4 + Cu(s)
Zn(s) + FeSO4(aq)⟶ZnSO4(aq) + Fe(s)
29. What is corrosion? Give two methods to protect
iron articles from corrosion.
30. What is an oxidation reaction? Give an example of
oxidation reaction. Is oxidation an exothermic or an endothermic reaction?
31. (a) What is the colour of ferrous sulphate
crystals? How does this colour change after heating?
(b) Name the products formed on strongly
heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this
change?
32. Define a combination reaction. Give one example of
a combination reaction which is also exothermic.
33. (i) What is observed when a solution of potassium
iodide is added to a solution of lead nitrate taken in a test tube?
(ii) What type of reaction is this?
(iii) Write a balanced chemical equation to
represent the above reaction.
34. Crystals of copper sulphate are heated in a test
tube for some time. What is the colour of copper sulphate crystals?
(i) Before heating, and
(b) after heating?
35. What is a redox reaction? When a magnesium ribbon
burns in air with a dazzling flame and forms a white ash, is magnesium oxidised
or reduced? Why?
36. When magnesium ribbon burns in air or oxygen, a
product is formed. State the type of chemical reaction and name the product
formed in the reaction. Write balanced chemical equation of this reaction.
37. State any two observations in an activity which
may suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. Give examples to support
your answer.
38. Observe the two test tubes A and B in the diagram
given below and answer the following questions:
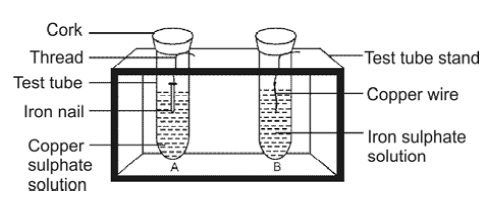
(a) In which test tube will the reaction
takes place?
(b) Write a balanced equation of the
reaction.
(c) Name the type of reaction.
39. Solid calcium oxide was taken in a container and
water was slowly added to it.
(i) State the two observations made in the
experiment.
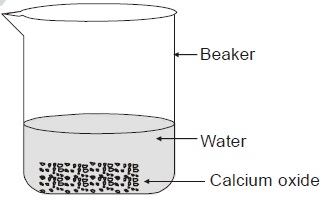
(ii) Write the name and chemical formula of the
product formed.
40. What is an oxidation reaction? Identify in the
following reaction:
ZnO + C ⟶
Zn + CO
(i) The substance oxidised and (ii)
The substance reduced
41. Give an example of a decomposition reaction.
Describe an activity to illustrate such a reaction by heating.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. What conclusions can be drawn from the chemical
reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric acid?
2. (i) What do you understand by chemical double
displacement reaction?
(ii) By giving one chemical equation write:
(a) Precipitation reaction
(b) Neutralisation reaction
3. State the reactions, if any of the following metals
react with lead nitrate solution. In case the reaction takes place, support it
by a chemical equation.
(a) Silver, (ii)
zinc,
(iii) copper, and (iv) iron.
4. What is galvanised iron? How is galvanised iron
protected from rust?
5. How will you show that iron is more reactive than
copper?
6. On adding a drop of barium chloride solution to an
aqueous solution of sodium sulphate, a white precipitate is obtained.
(a) Write a balanced chemical equation of the
reaction involved.
(b) What other name can be given to this
precipitation reaction?
(c) On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to the
reaction mixture the white precipitate disappears. Why?
7. Identify the reducing agent in the following
reactions.
(a) 4NH3 + 5O2⟶
4NO + 6H2O
(b) Fe2O3 + 3CO ⟶ 2Fe + 3CO2
8. What happens when a piece of:
(a) Zinc metal is added to copper sulphate
solution?
(b) aluminium metal is added to dilute
hydrochloric acid?
(c) Silver metal is added to copper sulphate
solution?
Also, write balanced chemical equation if the reaction
occurs.
9. Which among the following changes are exothermic or
endothermic in nature?
(a) Decomposition of ferrous sulphate.
(b) Dissolution of sodium hydroxide in water
(c) Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. Name the products formed in each case when:
(a) Hydrochloric acid reacts with caustic soda.
(b) Granulated zinc reacts with caustic soda.
(c) Carbon dioxide is passed into lime water.
2. Design an activity to show decomposition reaction
in which light is used to decompose a reactant. Write chemical equation of the
reaction and state its one use.
3. Draw a labeled schematic diagram to show the
electrolysis of water. Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test
tubes in this activity double of the amount collected in the other?
4. Give three differences between displacement and
double displacement reaction.
5. A, B and C are three elements which undergo
chemical reactions according to the following equations.
A2O3
+ 2B⟶ B2O3
+ 2A
3CSO4
+ 2B⟶ B2(SO4)
+ 3C
3CO + 2A ⟶
A2O3 + 3C
Answer the following questions with reasons:
(a) Which element is the most reactive?
(b) Which element is the least reactive?
(c) What is the type of reactions listed above?
6. In the electrolysis of water;
(i) Name the gas collected at the cathode and
anode.
(ii) Why is the volume of gas collected at
one electrode double the other?
(iii) Why are a few drops of dil H2SO4
added to the water?
7. Describe an activity to show that rusting of iron
requires air and water.
8. Write the balanced equation involved, when:
(i) chlorine is passed over dry slaked lime.
(ii) sodium bicarbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric
acid
(iii) sodium bicarbonate is heated.
9. Account for the following:
(a) Aluminium is more reactive than iron, but its
corrosion is less than iron.
(b) Hydrogen gas is not evolved when zinc metal reacts
with dil. HNO3.
(c) Carbon is not used for reducing aluminium
from aluminium oxide.
10. (a) What is thermite reaction? How it is used in
joining railway tracks and cracked parts of machines.
(b) How do we get stainless steel?
11. Salt A commonly used in bakery products on heating
gets converted into another salt B which itself is used for removal of hardness
of water and a gas C is evolved. The gas C when passed through lime water, turns
it milky. Identify A, B and C. Write balanced chemical equations for each step.
12. Write the balanced chemical equations for the
following reactions:
(a) Sodium carbonate on reaction with hydrochloric acid
in equal molar concentrations gives sodium chloride and sodium hydrogen
carbonate.
(b) Sodium hydrogen carbonate on reaction with hydrochloric
acid gives sodium chloride, water and liberates carbon dioxide.
13. Take a small amount of calcium oxide or quick lime
in a beaker and slowly add water to this:
(a) Is there any change in temperature?
(b) What type of reaction is taking place?
(c) Write chemical equation for above reaction.
14. (a) Define 'water of crystallisation'.
(b) Give two examples of substances having
water of crystallisation. Write their molecular formulae also.
15. Name the type of chemical reaction presented by
the following equations.
(i)
CaCO3(s) heat⟶
CaO(s) + CO2(g )
(ii) CaO(s) + H2O(l)⟶
Ca(OH)2 (aq)
(iii) Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq)⟶
ZnSO4 (aq) + H2(g)
16. Identify the substances that are oxidised and that
are reduced in the following reactions.
(a) ZnO + C ⟶
Zn + CO
(b) CuO + H2⟶
Cu + H2O
(c) MnO2 + 4HCl ⟶
MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
1. State the characteristics of a chemical reaction.
2. State the limitations of a balanced chemical
equation.
3. Give examples of articles made from iron which are
protected from rusting by:
(i) Red lead paint
(ii) Paint
(iii) Enamelling
(iv) Plastic coating
(v) Tinning
(vi)Electroplating
(vii)Galvanising
(viii)Tarring
(ix) Alloying
(x) Oiling and greasing
4. (i) On heating a blue coloured powder of copper
(II) nitrate in a boiling tube, copper oxide (black), oxygen gas and a brown gas
X is formed
(a) Write a balanced chemical equation of the
reaction.
(b) Identify the brown gas X evolved.
(c) Identify the type of reaction.
(d) What could be the pH range of the aqueous
solution of gas X?
(ii) Give the characteristic test for the following gas.
(a) CO2
(b) SO2
(c) O2
QUESTIONS FROM CBSE EXAMINATION PAPERS
1. (i) Account for the following.
(a) White silver chloride turn grey in sunlight.
(b) Brown coloured copper powder on heating in
air turns into black coloured substance.
(ii) What do you mean by?
(a) Displacement reaction
(b) reduction reaction
(c) combination reaction? Write balanced chemical equation.
2. (i) Solid calcium oxide was taken in a container
and water was added slowly to it:
(a) Write the observation
(b) write the chemical formula of the product
formed.
(ii) What happens when carbon dioxide gas is bubbled through lime
water?
(a) in small amount
(b) in excess
3. (a) What happens chemically when quick lime is
added to water?
(a) Balance the following chemical equatio MnO2
+ HCl⟶ MnCl2 + Cl + H2O
(c) What is decomposition reaction? Explain it
with suitable example.
(b) Identify the type of reaction in the equation given below.
Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq)⟶
BaSO4 (s) + NaCl(aq)
(c) You could have noted that when copper powder is heated in a china
dish, the surface of copper powder becomes coated with black colour substance.
(i) Why has this black coloured substance
formed?
(ii) What is the black substance?
(iii) Write the chemical equation of the reaction
take place.
5. A student dropped few pieces of marble in dilute
hydrochloric acid, contained in a test tube. The evolved gas was then passed
through lime water. What change would be observed in lime water? What will
happen if excess of gas is passed through lime water? Write balanced chemical
equations for all the changes observed
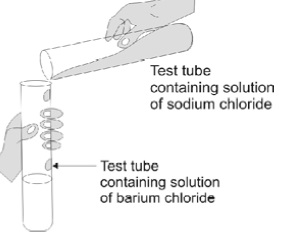
7. Observe the given figure and answer the following
questions.
(i) Write the complete balanced reaction for the
above.
(ii) Type of reaction involved.
(iii) Is there any precipitate formed?
(iv) If any precipitate formed, write the colour of the
precipitate.